3.7 unorganic carboncompounds
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are inorganic compounds:
a COMPOUND
Atmosphere
where carbondioxide gass is made
How carbondioxide gass absorb long electromagnetic radiation
CO2-molecule can absorb heatradiation -> the energy increases the rotation and vibration of the molecule. +
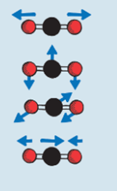
Ocean -
how carbonic acid is made
Creation of carbonic acid
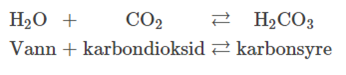
Carbon acid when dissolved in water
disociates the H+ -ions in steps. (The reactions can og both ways) +
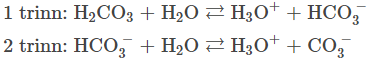
The prosses when the carbonic acid turns into HCO3- and water
(hydrogencarbonation) The prosses when the carbonic acid truns into CO32-
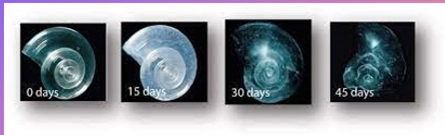
Example of shellfish that struggle with acidification
pteropod, tiny sea creature (size of a pea), major food source. When put in sea water reflecting the pH and carbonate levels for the year 2100 -> their shell nearly disapears. +