MCAT Organic Chemistry - Carboxylic Acids
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
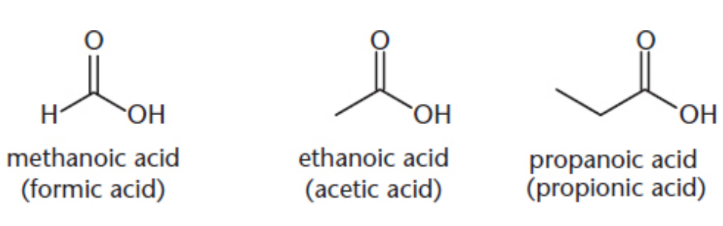
carboxylic acid
contains both a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group, bonded to the same carbon; always terminal groups
IUPAC: parent root + -ioc acid or cycloalkane + carboxylic acid
common names: formic (methanoic) acid, acetic (ethanoic) acid, proionic (propanoic) acid
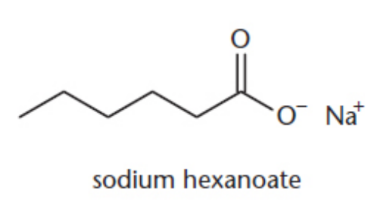
carboxylic salts
carboxylic acid anions
IUPAC: parent root + -oate
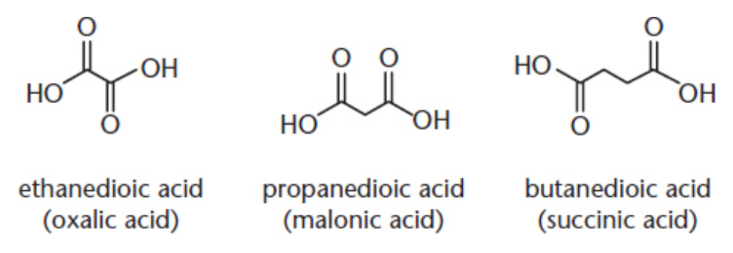
dicarboxylic acids
have a carboxylic acid group on each end of the molecule
IUPAC: parent alkane + -dioc acid
common names: oxalic (ethanedioic) acid, malonic, succinic, glutaric, adipic, pimelic
dimers
pairs of molecules connected by two hydrogen bonds
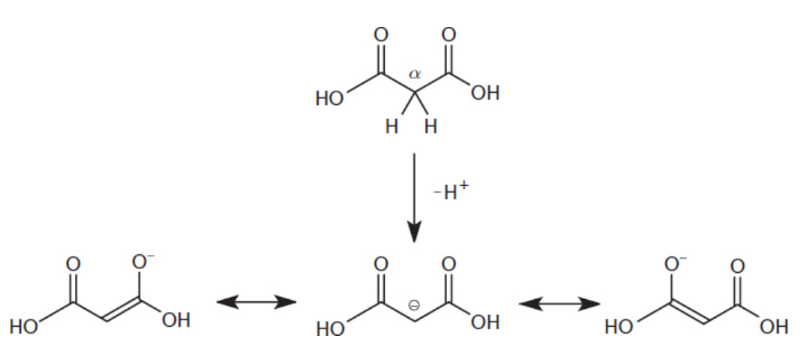
β-dicarboxylic acids
dicarboxylic acids in which each carboxylic acid is positioned on the β-carbon of the other; notable for the high acidity of the α-hydrogens located on the carbon between the two carboxyl groups (pKa ≈ 9−14).
Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
prepared via oxidation of aldehydes and primary alcohols
oxidants: dichromate salt (Na2Cr2O7 or K2Cr2O7), chromium trioxide (CrO3), or potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
similar to nucleophilic addition to an aldehyde or ketone; after opening the carbonyl via nucleophilic attack and forming a tetrahedral intermediate, the carbonyl can reform, thereby kicking off the leaving group; favored by a good leaving group.
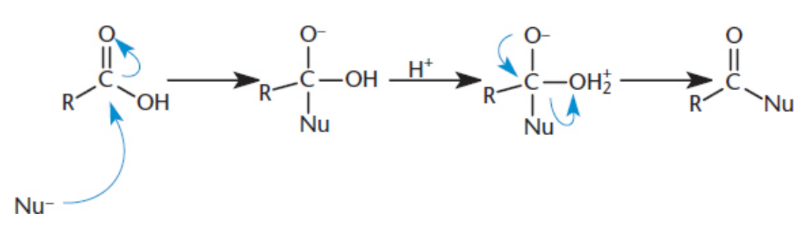
Acyl derivatives
all molecules with a carboxylic acid-derived carbonyl, including carboxylic acids, amides, esters, anhydrides, and others.
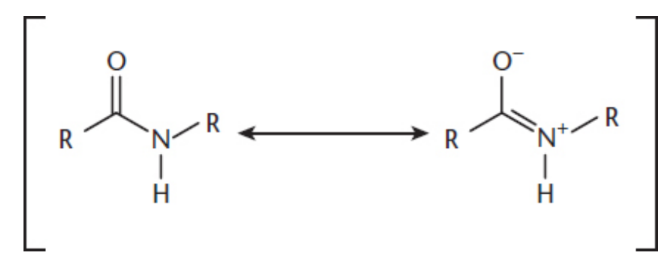
Amides
a derivative of a carboxylic acid (R−C(=O)−OH) with the hydroxyl group (−OH) replaced by an amino group (−NR′R″); exist in a resonance state where delocalization of electrons occurs between the oxygen and nitrogen atoms
IUPAC: parent carboxylic acid - -oic acid + amide
alkyl groups on the nitrogen are placed at the beginning of the name with the prefix N−
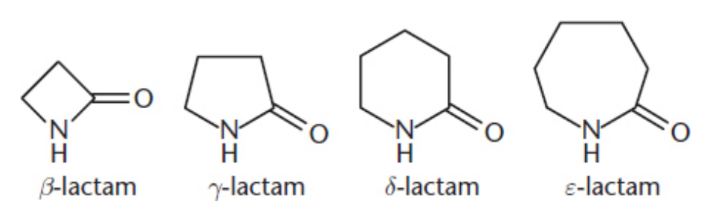
lactams
cyclic amides
IUPAC: parent carboxylic acid - -oic acid + -lactam / named by indicating the specific carbon that is bonded during cyclization
Esters
hybrid between a carboxylic acid and an ether (ROR′),
IUPAC: non-carbonyl containing chain + parent carboxylic acid root + -oate
Esterification
condensation reaction using carboxylic acid to make ester with water as a side product;
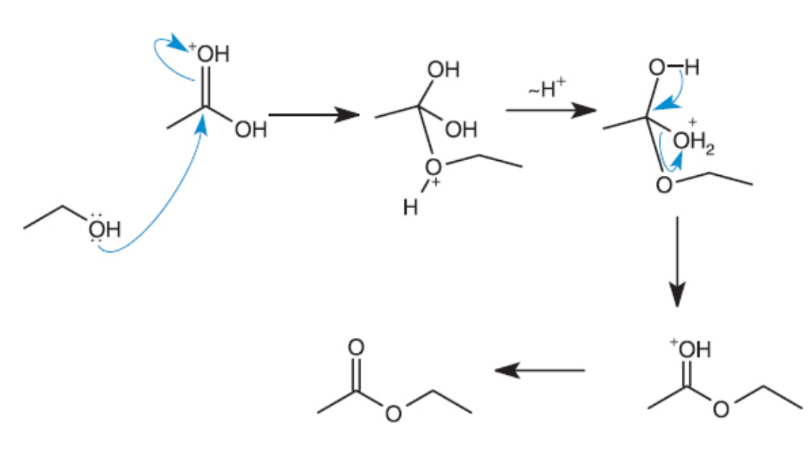
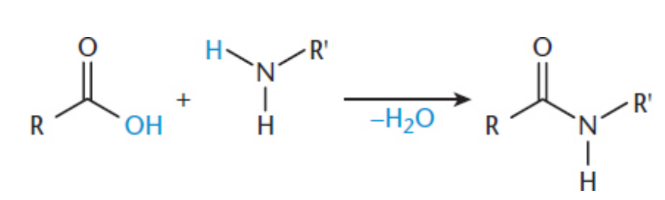
amide synthesis
amide formed from carboxylic acid via nucleophlic substitution of carboxylic acid under acidic or basic conditions
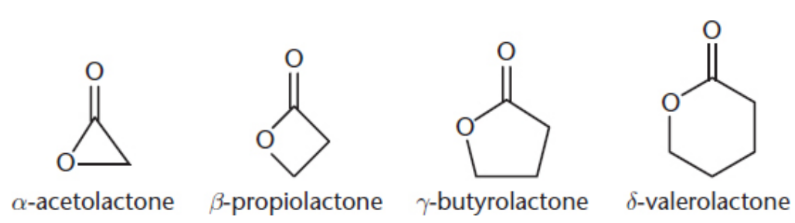
lactones
cyclic esters
IUPAC: parent carboxylic acid - -oic acid + -lactone / named by indicating the specific carbon that is bonded during cyclization
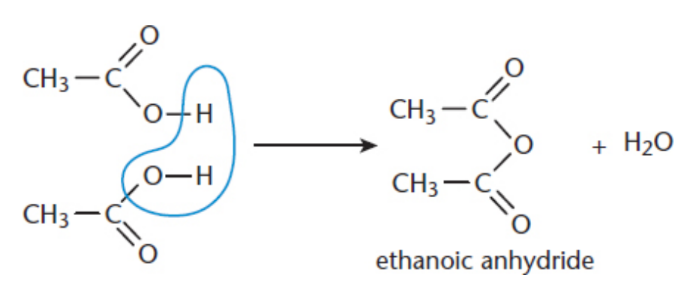
Anhydrides
combination of two carboxylic acids at the hydroxyl site
IUPAC: parent carboxylic acid - acid + anhydride
anhydride synthesis
Carboxylic Acid Condensation; nucleophilic acyl substitution
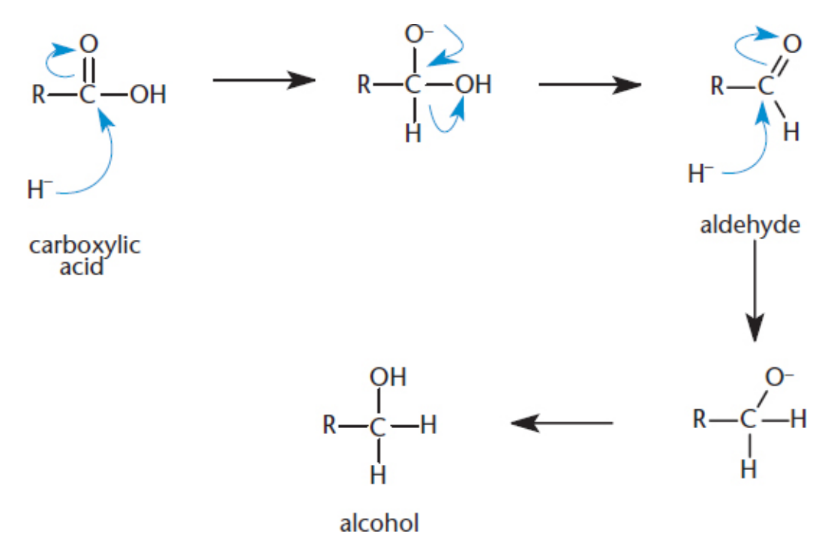
Reduction
Carboxylic acids can be reduced to primary alcohols by the use of lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) but NOT NaBH4
Decarboxylation
complete loss of the carboxyl group as carbon dioxide
1,3-Dicarboxylic acids and other β-keto acids spontaneously decarboxylate when heated
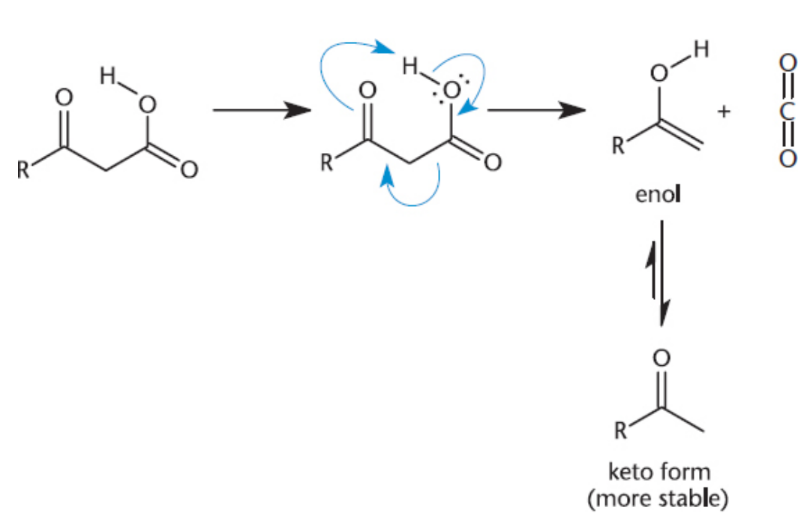
saponification
carboxylic acids react with sodium or potassium hydroxide and a salt is formed;
soap
mixing fatty acids with lye (sodium or potassium hydroxide) resulting in the formation of a salt; solvate nonpolar organic compounds in aqueous solutions because they contain both a nonpolar tail and a polar carboxylate head
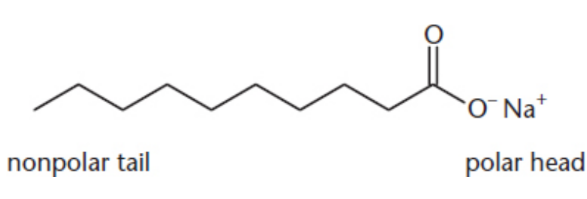
micelles
spherical structures of soap; polar heads face outward, where they can be solvated by water, and the nonpolar hydrocarbon chains are oriented toward the inside of the sphere, protected from the solvent
