Equine diagnostic imaging
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Metacarpophalangeal joint is also known as the
Fetlock joint
What makes up the fetlock joint
Cannon, long pastern, and proximal sesamoid bones
Ligaments that make up the fetlock joint
collateral, palmar sesamoidean, short sesamoidean, and suspensory ligament
Tendons that make up the fetlock joint
common digital extensor and superficial and deep digital flexor tendons
A joint capsule surrounds the joint
Articular capsule
A boiled pad on the distal aspect of the <cIII that cushions the joint
Synovial pad
Signs the fetlock joint is in pain
lameness, swelling, heat, and pain
The proximal interphalangeal joint is also known as the
pastern joint
What does the pastern joint do
allows the horse to flex and extend it’s food
What time of joint is the pastern joint
hinge joint
What ligaments support the pastern joint
Collateral, abaxial, and axial ligaments
Osteoarthritis is known as
high ringbone
Common disorders with the pastern joint
osteoarthritis, fractures, luxation, and subluxation
Distal interphalangeal joint is also known as the
Coffin joint
The coffin bone allows for
flexion and extension of the foot
The coffin joint is made of the
distal and proximal phalanx
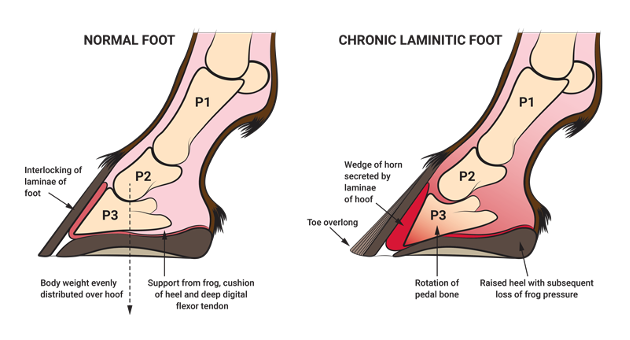
Lamenitis can cause the coffin bone to
rotate and damage the coffin joint
Small fluid-filled sac in horse’s feet that cushions the navicular bone
Navicular bursa
the Navicular nurse does what
lubricates the deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT)
The navicular bursa is located between
the navicular bone and deep digital flexor tendon
The medial and palmar nerves run between the
suspensory ligament and the deep digital flexor tendon
Main artery supply to the fetlock and digit
Median palmar artery
Radiographs in horses are used for
lameness, dental issues and sinus issues
4 positions for the coffin bone
LM, DP, DLPMO/DMPLO, and skyline
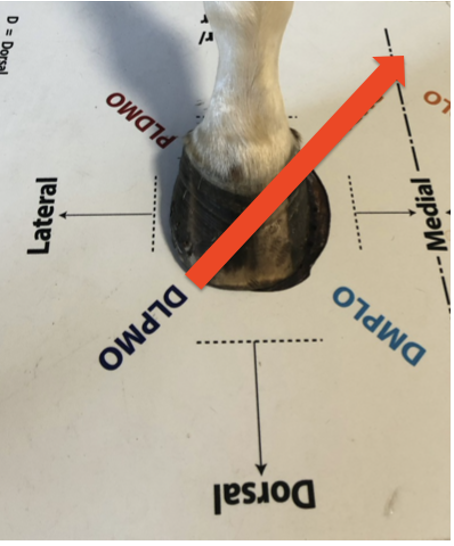
Positioning angles for the fetlock
LM, DP, and DLPMO/DMPLO
Nuclear scintigraphy is a
bone scan
Bone scan is used to elevate
lameness and poor performance
CT stands for
Computed tomography
MRI stands for
magnetic resonance imaging
What is the purpose of the white line of a hoof
joins the sole to the inner wall of the hoof, seals off the border
What is the purpose of the frog of a hoof
aids in shock absorption
Purpose of the sole of a hoof
offers a protective surface
Purpose of the bar of the hoof
controls the movement of the back of the hoof
Thin, waxy layer of tissue that covers the outer surface of a horse’s hoof wall
Periople
What can cause laminitis
inflammation, endocrine disease, and trauma