N/V and Anticholinergics- Khan
1/33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Which enzyme is responsible for ACh biosynthesis?
Choline acetyltransferase
Which enzyme is responsible for ACh metabolism?
Acetylcholinesterase
Which enzyme is used as a drug target?
acetylcholinesterase
What are the 2 receptors of cholinergic nervous system?
muscarinic
nicotinic
Where are the muscarinic receptors located? What location is the only place with sympathetic neurons?
brain
any organs with parasympathetic neurons
sweat glands w/ SYMPATHETIC neurons that released ACh
List the steps associated transduction with M1-M3 receptors:
Ach binds to M receptor
M receptor activates Gq
Gq activates PLC
PLC cuts PIP2 into DAG and IP3
DAG and IP3 activate PKC
Which muscarinic receptors are present in the salivary gland and GI organs?
M3
What are the important muscarinic functions? Which function is mediated by sympathetic neurons?
GI—> gastric acid secretion, increase tone and mobility of GI smooth muscle
salivation
Sweating—> sympathetic
bladder contraction
eye—> miosis, focusing, decrease eye pressure
others: bradycardia, bronchial secretions, bronchoconstriction
What are the names of the muscarinic agonists? What are each used for?
pilocarpine- glaucoma, miotic agent, dry mouth
cevimeline- dry mouth (Xerostomia, Sjogrens)
What are the structural requirements for muscarinic agonists?
NEED + charged N
NEED alkyl groups on N should not exceed size of methyl
Should have O
Should have 2C bridge between N and O
List the names of the muscarinic antagonists? What are they used for in the GI system?
atropine
hyoscyamine
dicyclomine
Used for GI spasms
What isomer is responsible for the effect of atropine?
L-isomer aka hyoscyamine
What are the important biological effects of muscarinic antagonists?
GI—> INHIBIT gastric acid secretion, DECREASE tone and mobility of GI smooth muscle, prolong gastric emptying
INHIBIT salivation
INHIBIT sweating—> sympathetic
bladder relaxation
eye—> mydriasis, distance focus, increase eye pressure
others: tachycardia, reduce bronchial secretions, bronchodilation
Which muscarinic antagonist has a contraindication? What is it?
Atropine- glaucoma
What are some drugs with anticholinergic side effects?

What are the symptoms of nausea?
unpleasant feeling
tachycardia
salivation
increase respiration rate
sweating
Which drugs are known to cause emesis?
chemotherapy drugs
opioids
bromocriptine
apomorphine
Where is the emetic center located in the brain? Where is the BBB located?
emetic center is located in the medulla.
BBB is located between periphery and CNS
What are the 2 broad categories of antiemetic drugs? What drugs classes belong to each?
category: motion sickness
H1 antihistamines
antimuscarinic/ muscarinic receptor antagonist
category: chemo-induced n/v
5-HT3 receptor antagonists
substance P antagonists
corticosteroids
antipsychotic
dopamine antagonist
cannabinoids
benzodiazepine
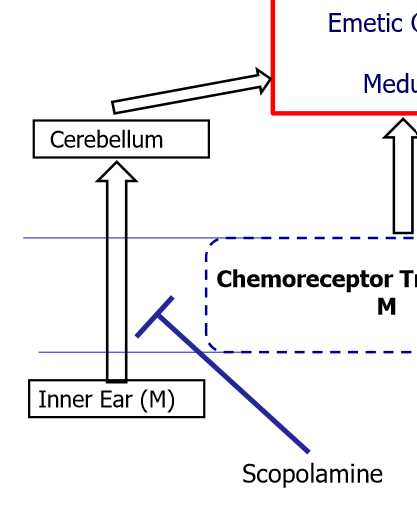
Answer the following about Scopolamine:
what is it used to prevent?
site of action?
MOA?
used to prevent motion sickness
acts in BBB between inner ear and cerebellum
muscarinic receptor antagonist
Answer the following about antihistamines:
list the generic names
site of action
Meclizine, Diphenhydramine, Dimenhydrinate
acts on h1 receptors in STN and inner ear
All serotonin receptors are ___________ except for 5HT3.
GCPRs
How is the 5HT3 receptor different from other receptor subtypes?
It is a Na+/K+ Ion channel receptor
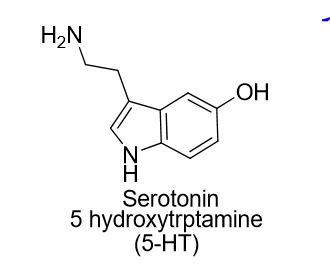
What is the enzyme involved in the rate limiting step of converting Tryptophan to Serotonin?
Tryptophan hydroxylase
Answer the following about 5HT3 antagonists:
list the brand/generics
MOA
what peripheral and central cellular sites do they act on?
What does the structure of serotonin look like?
Ondansetron (Zofran), Granisetron (Kytril), Palonosetron (Aloxi)
Block 5HT3 receptors
Peripheral- Block small intestine 5HT3 to vagal and spinal afferent
Central- CTZ and STN
What are the functions of substance P and NK receptor?
pain transmission
hypotension
n/v
Answer the following about Substance P Antagonists (NK antagonists):
list the agents generic ONLY
brand name of aprepitant
MOA
Drug Interactions with dexamethasone
Aprepitant, Fosaprepitant, Netupitant, Rolapitant
EMEND
NK1 receptor antagonists
FOR ALL BUT ROLAPITANT—→ interacts with dexamethasone, must decrease dose of DEXA
Answer the following about Dexamethasone:
MOA
antiemetic effect in cancer
activates Glucocorticoid receptor (nuclear receptor)
in cancer, suppresses peritumoral inflammation and PG production
Answer the following about Olanzapine:
class
what is it used for?
atypical antipsychotic
used for chemotherapy induced n/v
Answer the following about Lorazepam:
what component is decreased by Lorazepam?
site of action
side effect
reduces anticipatory component of nausea and vomiting (like fear)
cerebral cortex?
sedative, anti-anxiety, amnesia
What brain structure receives the anticipatory component of n and v?
higher centers of the brain/ medulla?
What is the main MOA of prochlorperazine and promethazine?
Block D2 receptors at the CTZ
What is the site of action of dopamine antagonists?
CTZ
Answer the following about Cannabinoids:
list brand/generic
MOA
ADRs
Dronabinol (Marinol), Nabilone (Cesamet)
Stimulate CB1 receptors around the emetic center
Euphoria, Dysphoria, Somnolence, Increased appetite