review
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
depressant effects: prescribed for pain relief. morphine, oxycodone
opioids
regulates the body's calcium balance
thyroid
similar to waking brain activity but blocked in the brainstem, characterized by rich, hallucinatory, story-like dreaming
NREM-3
sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified unlike nightmares night terrors occur during NREM-3 sleep, within 2 or 3 hours of falling asleep and are unlikely to be remembered. Usually dissipates into young adulthood.
night terrors
vivid, emotional and often bizarre. 8 in 10 reported containing a negative event
REM dreams
produces testosterone
testes
chemical substance used purposefully to alter perception, mood, or consciousness
hallucinogens
secreted in the ovaries, regulates the menstrual cycle
progesterone
stimulates bone & muscle growth
HGH
distort perceptions and evoke hallucinations. LSD, marijuana
psychoactive drugs
slow brain waves, when bedwetting most common
NREM-2
Examination of a deceased individual's body
autopsy
computed tomography. A combined computer and X ray image showing slices of the skull from multiple angles including the soft tissues of the brain
CT scan
regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24 hr cycle
circadian rhythm
located above the kidneys, produces adrenaline and corticosteroids
adrenal glands
no larger than a pea, controls the function of other glands
pituitary
produces progesterone & estrogen
ovaries
the idea that REM sleep triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories which are then woven into a narrative
neural activation/activation synthesis
electroencephalogram, electrodes placed in specific locations around the skull detect changes in electrical activity and display them visually
EEG
activated by light sensitive proteins in the retina, triggers pineal gland to reduce melatonin
superchiasmatic nucleus
secreted in the ovaries, responsible for secondary female sex characteristics
estrogen
similar to waking alpha and beta brain woves, lasting 10 minutes, hypnagogic experiences and sudden movements
NREM-1
secreted by the pineal gland and regulated the sleep wake cycle
melatonin
Removal or damage of regions of the brain and studying corresponding behaviour changes under controlled conditions
lesion studies
formulated by Schachter and Singer's adrenaline studies - all emotions are the product of awareness of physiological state and cognitive labelling of the environment
2-factor theory of emotion
regular brain stimulation from REM sleep may help develop and preserve neural pathways
physiological function
Travel in the blood, indirectly affect behavior/alter probability of a behavior and have long term/duration effects
hormones
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and momentary awakenings. Repeated hundreds of times per night. Results in lowered REM sleep. Affects overweight males most. Treated with external breathing aids (CPAP)
sleep apnea
the tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation (from awakenings)
REM rebound
marked by sleep spindles, lasting 20 minutes
NREM-2
Positron emission tomography - injection of radioactive sugars shows parts of the brain consuming then and undergoing metabolic use
PET scan
drugs that reduce neural activity. Sleeping pills, alcohol
depressants
secreted in the pituitary gland, released during birth and physical stimulation during breast feeding. Involved in formation of social bonds and stress reduction
oxytocin
depression linked to the beginning and the end of winter
SAD
chemical substance that excites neural activity. Caffeine, cocaine
stimulants
the idea that dream content reflects the dreamers level of cognitive development - their knowledge and understanding
cognitive development
Magnetic resonance imagery, observation of radio waves in a body and soft tissues in a strong magnetic field
MRI
secreted in the adrenal glands, changes the body's metabolism of sugars into fats and response to stress
cortisol
stimulates milk production in females
prolactin
Dreams helps sort out the day's events and consolidate memory. Dreams can contain unexperienced events
information processing
dreams preserve sleep and provide a "psychic safety valve" expressing otherwise unacceptable feelings or thoughts
wish fulfilment
sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person's mind
dreams
sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. Usually lasting less than 5 minutes. Lapsing directly into REM sleep. Affects estimated 1 in 2000 individuals. Genetic origin and treated with medications
narcolepsy
secreted in the adrenal glands, responsible for the fight or flight response
adrenaline
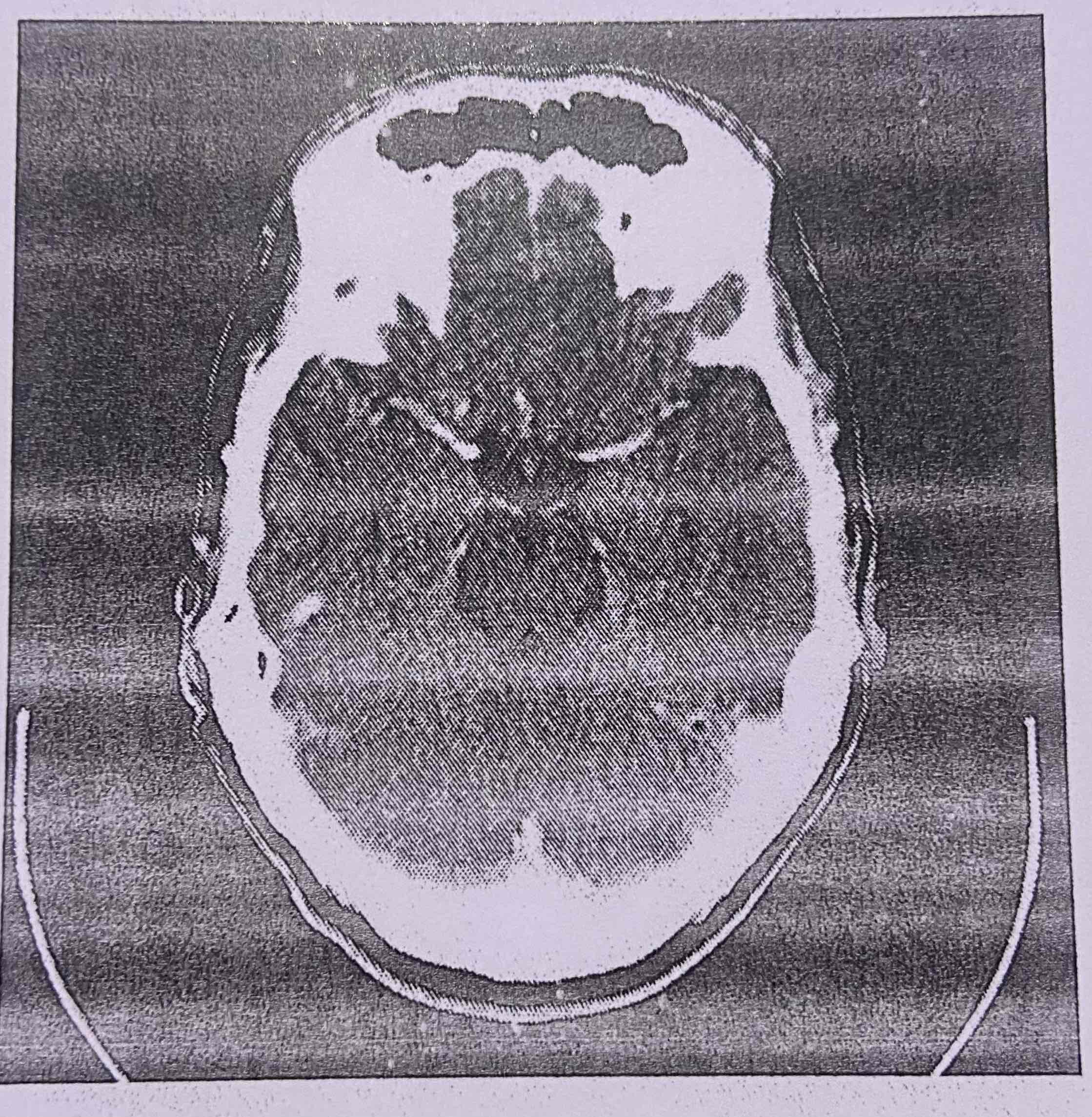
CT scan
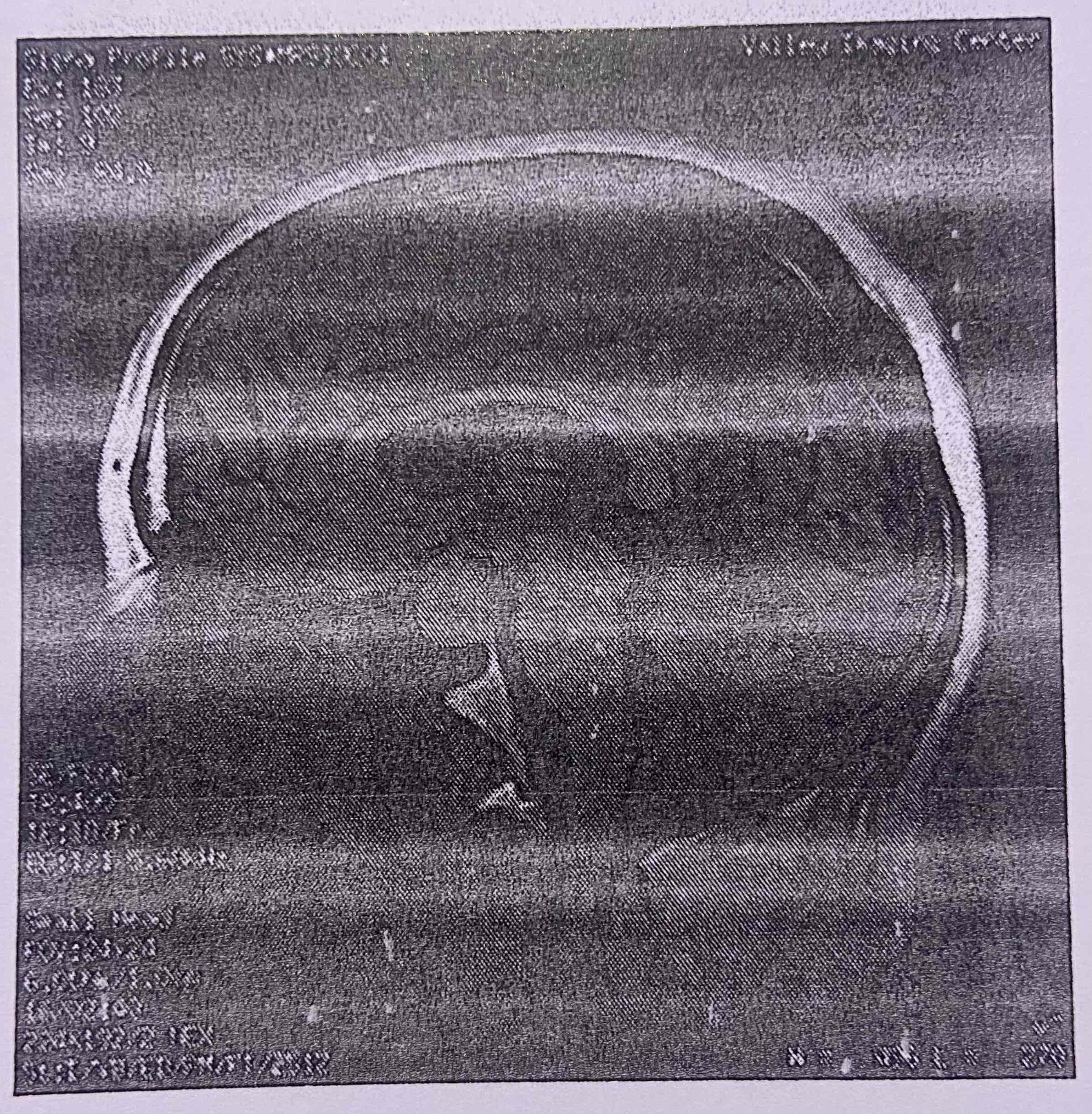
MRI