Halogenoalkanes
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Define methyl with respect to the classification of halogenoalkanes
The carbon to which the halogen-group is attached to has no R-groups
Define primary with respect to the classification of halogenoalkanes
The carbon to which the halogen-group is attached to has only 1 R-group
Define secondary with respect to the classification of halogenoalkanes
The carbon to which the halogen-group is attached to has two R-groups
Define teritiary with respect to the classification of halogenoalkanes
The carbon to which the halogen-group is attached to has three R-groups
What is a nucleophile
An electron pair donor
What is needed for an halogenoalkane to undergo a substitution reaction
A nucleophile
What is conditions are necessary for the nucleophilic substitution of a halogenoalkane with OH- ions (NaOH or KOH)
heated
Under reflux
In aqueous solution
Outline the mechanism for the reaction between bromoethane and NaOH(aq)


State the role of the hydroxide ion here
Nucleophile/electron donor
What is this: CN-
A cyanide ion
What are the conditions necessary for the nucleophilic substitution of CN- with a halogenoalkane (KCN)
heated
Under reflux
In ethanol/water mix
Outline the mechanism for the reaction between bomoethaen and KCN in ethanol/water solution
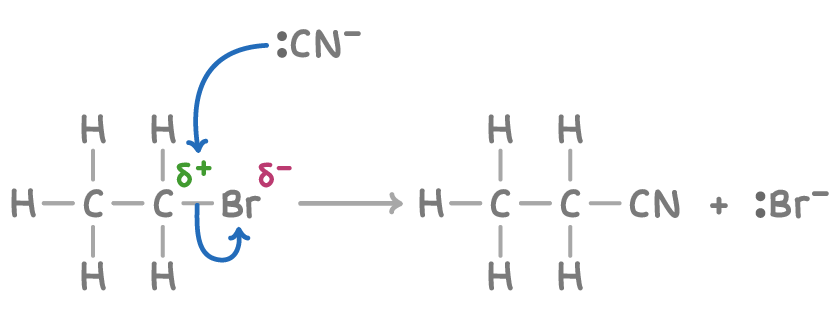
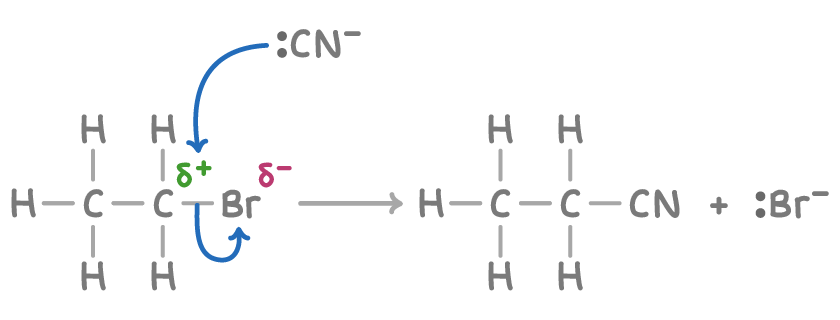
What is the IUPAC name for the product formed here
Propanenitrile
What are the conditions necessary for the nucleophilic substitution of NH3 with a halogenoalkane
Heat
In sealed tube
In ethanol
Why is ethanol used as a solvent during the nucleophilic substitution of ammonia
It minimised the chances of hydrolysis of the halogenoalkane to form an alcohol and increases miscibility
Ammonia is slightly soluble in ethanol
Outline the mechanism for the reaction between bromoethane and ammonia
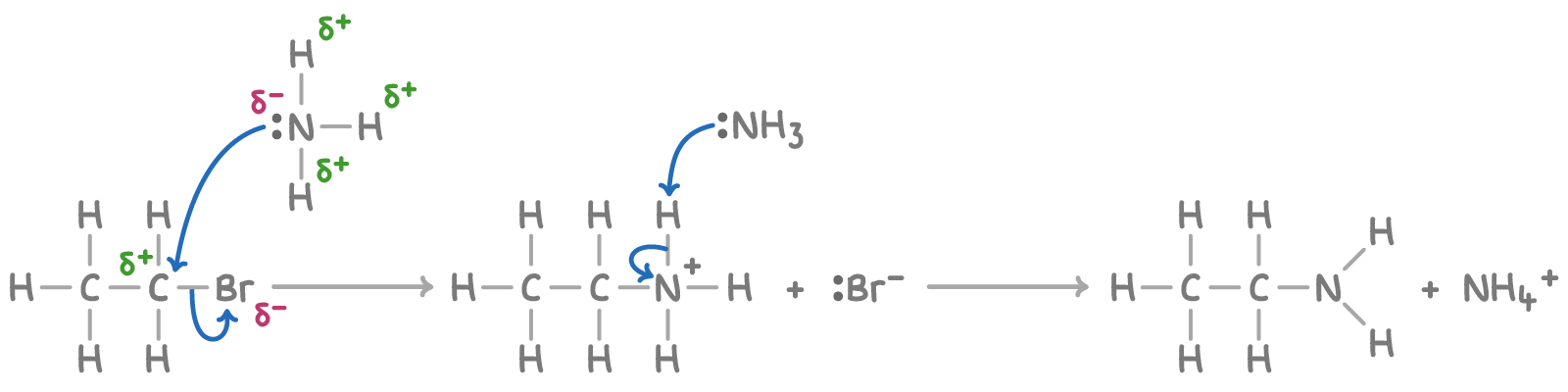
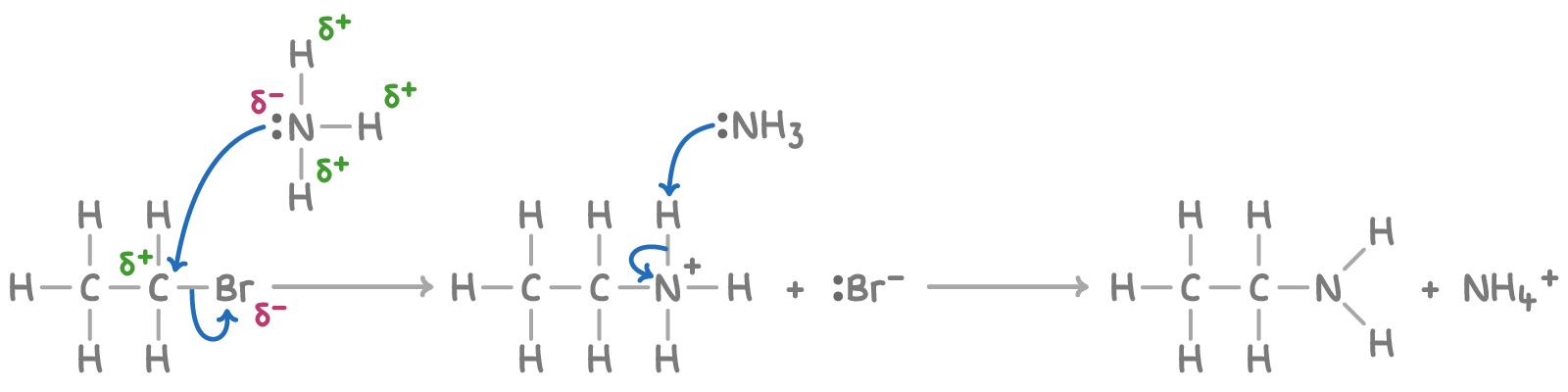
Give the IUPAC name for the organic product formed here
Ethanamine
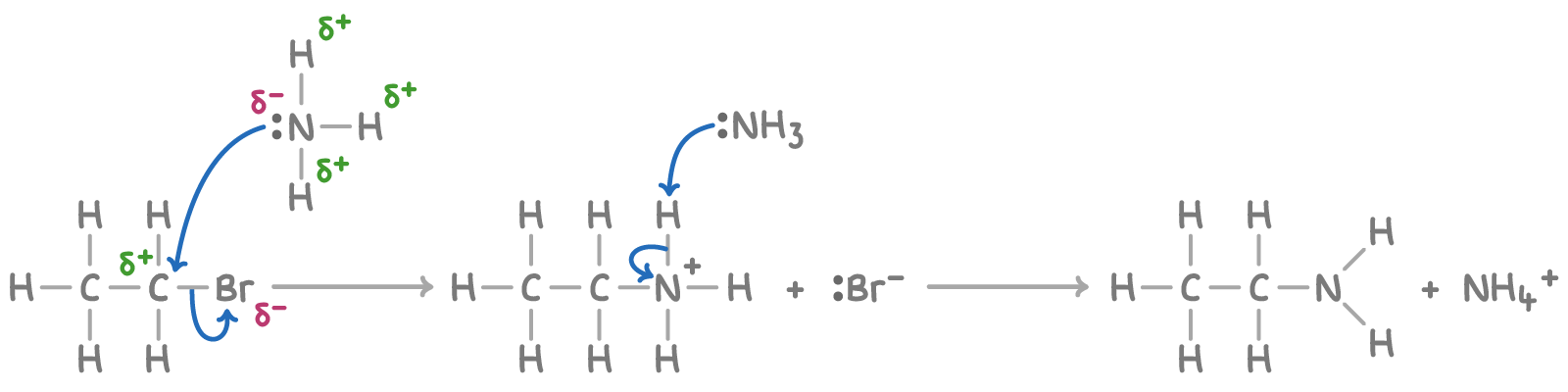
Explain why the amine produced here can lead to the production of (C2H5)2NH and (C2H5)3N
Amine produced still has a lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom so can still act as a nucleophile and can facilitate further substitution of halogenoalkanes to form secondary or tertiary amines
Describe and explain the test for halogenoalkanes
add ethanol and aqueous silver nitrate
Warm mixture gently
Water acts as a nucleophile and substitutes halogenoalkanes
Halide ions formed forms precipitate of silver halide in presence of Ag+(aq) ions
CH3X + H2O → HX + CH3OH
Why do we need to add ethanol in the test for halogenoalkanes
It acts as a solvent to dissolve both the halogenoalkane and water so they can mix fully and react together
Why is 1-iodobutane more reactive than 1-chlorobutane
C-I bonds are longer and have lower bond enthalpy so less energy required to break C-I bonds
What are the conditions necessary for the elimination reaction of halogenoalkanes
heated to a boil
Under reflux
With potassium hydroxide
In ethanol
With NaOH or KOH
What is given off in an elimination reaction of halogenoalkanes
Water, an alkene and a halide ion
Outline the mechanism for the elimination reaction between OH- ions and chloroethane
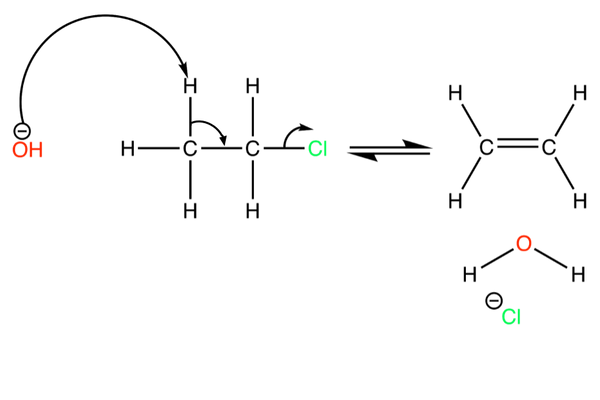
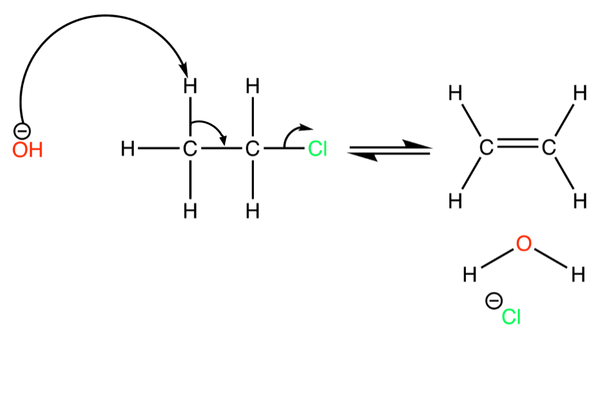


What is the OH- ion working as here
A base
What class of halogenoalkane is needed for nucleophilic substitution
Primary or secondary (Tertiary too stable?)
What class of halogenoalkane is needed for elimination
Secondary or tertiary
What temperatures are necessary for nucleophilic substitution
Relatively low
What temperatures are needed for elimination
Relatively higher
What solvent is used for substitution
Aqueous
What solvent is used for elimination
Ethanol