MCAT Biology - The Nervous System
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
tubocurarine
parlytic, blowdarts, used for anaesthesia, still could sense
neurons
specialized cells capable of transmitting electrical impulses and then translat, ing those electrical impulses into chemical signals
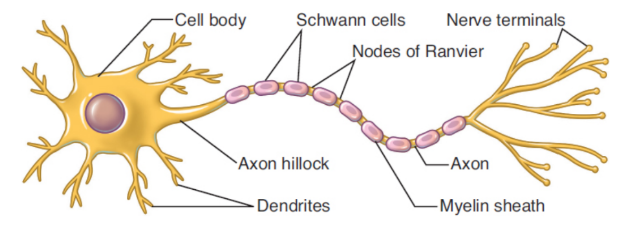
cell body/soma.
contains neuron’s nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes
dendrites
appendages which receive incoming messages from other cells
axon hillock
integrates the incoming signals
action potentials
transmission of electrical impulses down the axon; excitatory or inhibitory; all or nothing; cause the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
axon
long appendage that terminates in close proximity to a target structure (a muscle, a gland, or another neuron)
myelin
a fatty membrane that provides insulation to prevent signal loss or crossing of signals and increase the speed of conduction in the axon
myelin sheath
maintains the electrical signal within one neuron
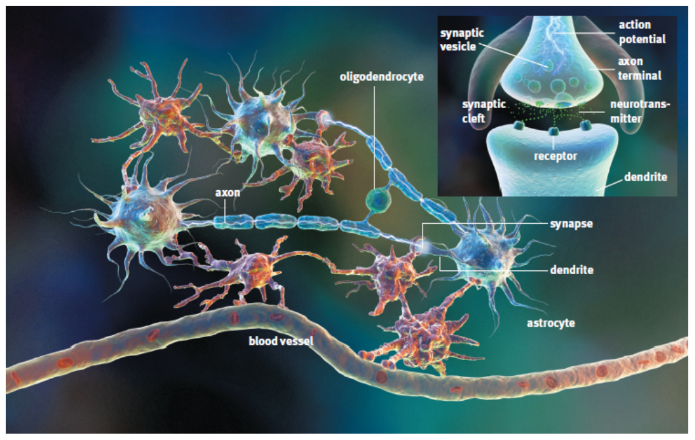
oligodendrocytes
produce mylein in CNS
Schwann cells
produce mylein in PNS
nodes of Ranvier
small breaks in the myelin sheath with exposed areas of axon membrane used for saltatory conduction
nerve terminal/synaptic bouton (knob)
nlarged and flattened structure at end of the axon to maximize transmission of the signal to the next neuron and ensure proper release of neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters
the chemicals that transmit information between neurons
demyelination
the body mounts an immune response against its own myelin, leading to the destruction of this insulating substance; slows down information transfer
multiple sclerosis (MS)
common demyelinating disorder; the myelin of the brain and spinal cord is selectively targeted; many different kinds of neurons are demyelinated → wide variety of symptoms including weakness, lack of balance, vision problems, and incontinence
synaptic cleft
space between the terminal portion of the axon rof the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendrites of the adjacent, post-synaptic neuron
synapse
the nerve terminal, synaptic cleft, and postsynaptic membrane together
nerve
Multiple neurons bundled together in the PNS; may be sensory, motor, or mixed, which refers to the type(s) of information they carry
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies of neurons of the same type
tracts
axons bundled together in the CNS; only carry one type of information.
nuclei
the cell bodies of neurons in the same tract
glial cells/neuroglia
cells in the nervous system that are not neurons but provide structure and support for them
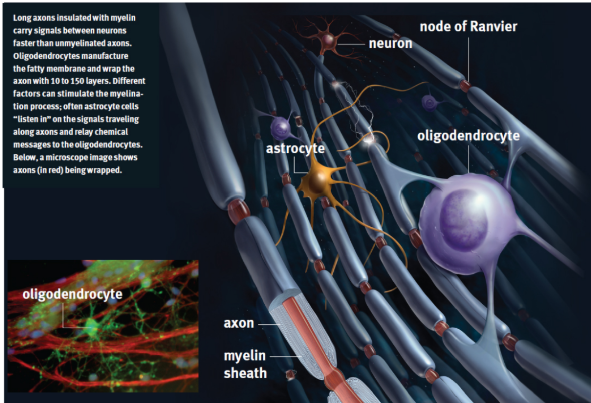
Astrocytes
nourish neurons and form the blood–brain barrier
Ependymal cells
line the ventricles of the brain and produce cerebrospinal fluid
blood–brain barrier
controls the transmission of solutes from the bloodstream into nervous tissue
cerebrospinal fluid
physically supports the brain and serves as a shock absorber
Microglia
phagocytic cells that ingest and break down waste products and pathogens in the central nervous system
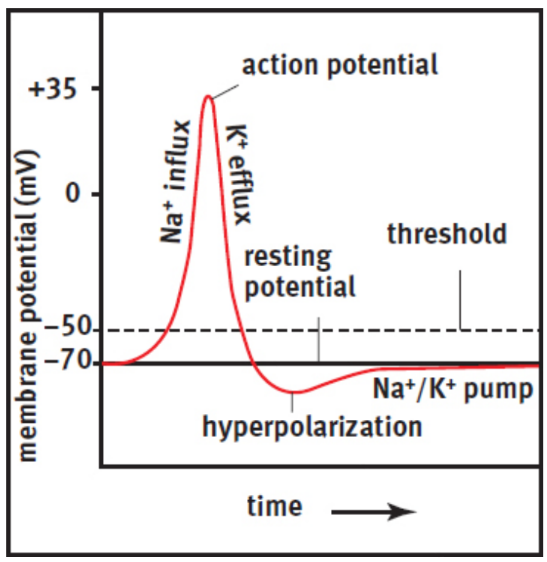
resting membrane potential
the net electric potential difference that exists across the cell membrane, created by movement of potassium and sodium ions across that membrane; maintained by membrane proteins
ex. neurons -70 mV
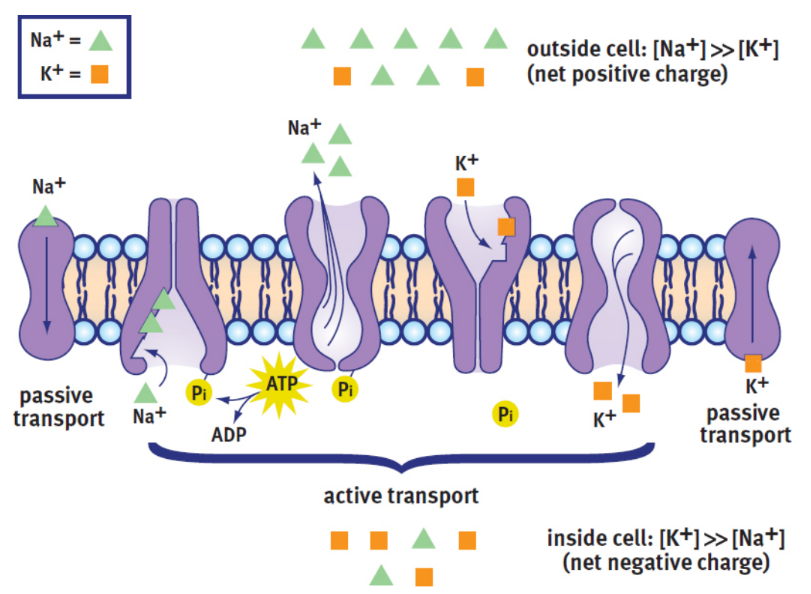
potassium leak channels
allow the slow leak of potassium out of the cell, where the concentration is lower
inside concentration: 140 mM
outside concentration: 4 mM
equilibrium potential of potassium
no more net movement of the ion, as the cell is in equilibrium with respect to potassium; around -90 mV; negative sign is because a positive ion (potassium) is leaving the cell
sodium leak channels
allow the slow leak of potassium into the cell, where the concentration is lower
inside concentration: 12 mM
outside concentration: 145 mM
equilibrium potential of sodium
no more net movement of the ion, as the cell is in equilibrium with respect to sodium; around 60 mV; positive because sodium is moving into the cell
Na+/K+ ATPase
pumps sodium and potassium back to where they started: potassium into the cell and sodium out of the cell, to maintain their respective gradients
more ATP is spent by this transport protein to maintain these gradients than for any other single purpose.
depolarization
Excitatory input; raising the membrane potential, Vm, from its resting potential; neuron more likely to fire an action potential
hyperpolarization
Inhibitory input; lowering the membrane potential from its resting potential; makes the neuron less likely to fire an action potential;
efflux of potassium ions, overshooting the membrane potential; makes neuron refractory to more action potentials
threshold value
membrane potential of -55mV to -40 mV, above which an action potential will be triggered
summation
additive effect of multiple signals, excitatory and inhibitory
temporal summation
multiple signals are integrated during a relatively short period of time
spatial summation
additive effects are based on the number and location of the incoming signals; a large number of inhibitory signals firing directly on the soma will cause more profound hyperpolarization of the axon hillock than the depolarization caused by a few excitatory signals firing on the dendrites of a neuron
electrochemical gradient
the interior of the cell is more negative than the exterior of the cell; there is a higher concentration of sodium outside the cell than inside; both favors the movement of positively charged sodium cations into the cell
inactivation
proteins chennales have a conformational stage other than open and closed; functionally same as closed
ex. sodium channels when Vm is from +35 mV to resting potential
repolarization
restoration of the negative membrane potential from potassium ions being driven out of the cell
absolute refractory period
no amount of stimulation can cause another action potential to occur
relative refractory period
there must be greater than normal stimulation to cause an action potential because the membrane is starting from a potential that is more negative than its resting value
impulse propagation
action potential travel down the axon; Action potentials are propagated down the axon when proximal sodium channels open and depolarize the membrane, inducing distal sodium channels to open as well; because of the refractory character of these channels, the action potential can move in only one direction.
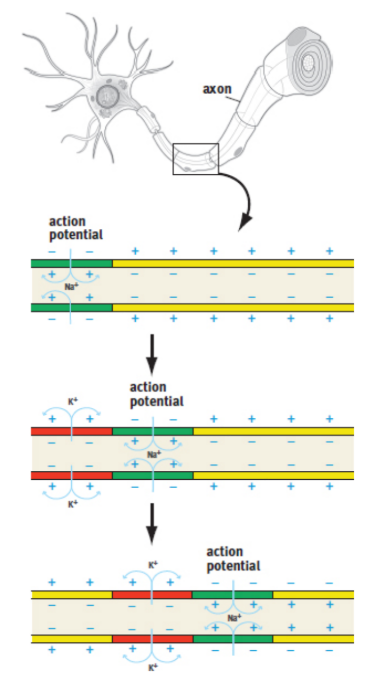
tetrodoxin (TTX)
pufferfish toxin, blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels, blocking neuronal transmission; causes death by preventing nerve signalling to diaphragm, leading to paralysis of the muscle and cessation of breathing
effector
the postsynaptic cell when it is not a neuron but a gland or muscle
chemical synapse
uses neurotransmitters to send messages from one cell to the next
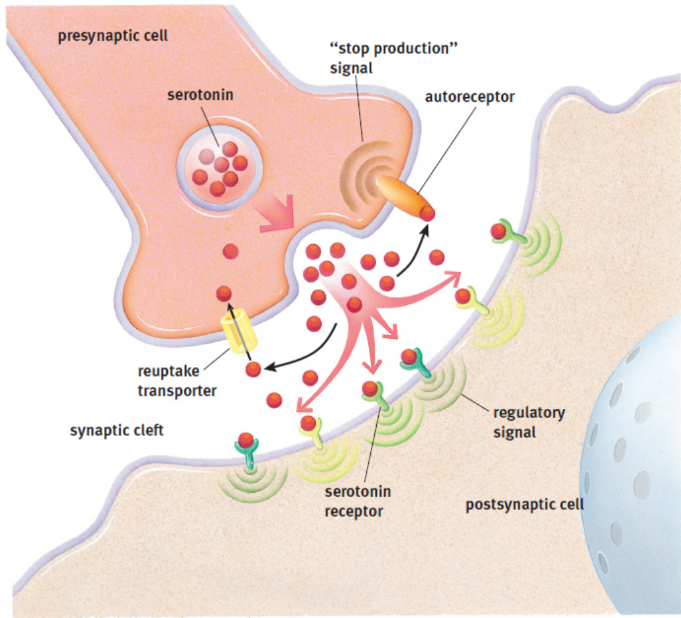
neurotransmitters
small messenger molecules in neurons; stored in membrane-bound vesicles in the nerve terminal; bind to receptors on postsynaptic membrane; must be removed to prevent constant signalling via enzymes, reuptake, diffusion
reuptake carriers
absorb neurotransmitters back into the presynaptic neurons
ex. serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE)
cocaine blocks reuptake
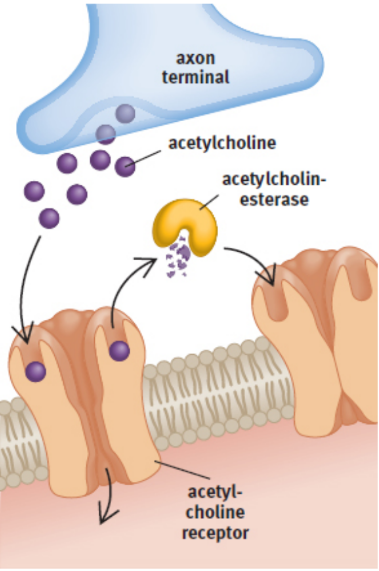
enzymatic breakdown of neurotransmitters
acetylcholine (ACh) by acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
drugs for Alzheimer’s, glaucoma, and myasthenia gravis can block the enzyme — also nerve gases
diffusion of neurotransmitters
Nitric oxide (NO)
homeostasis
dynamic equilibrium; keeps organisms alive
Sensory/afferent neurons
transmit sensory information from sensory receptors to the spinal cord and brain
Motor/efferent neurons
transmit motor information from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
Interneurons
found between other neurons; most numerous of the three types; located predominantly in the brain and spinal cord; often linked to reflexive behavior
central nervous system (CNS)
composed of the brain and spinal cord
white matter
part of brain consists of axons encased in myelin sheaths; deeper in brain; superficial in spine
grey matter
unmyelinated cell bodies and dendrites; superficial in brain; deep in spine
brainstem,
responsible for basic life functions such as breathing
spinal cord
four regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral
Almost all of the structures below the neck receive sensory and motor innervation
vertebral column
backbone; transmits nerves at the space between adjacent vertebrae.
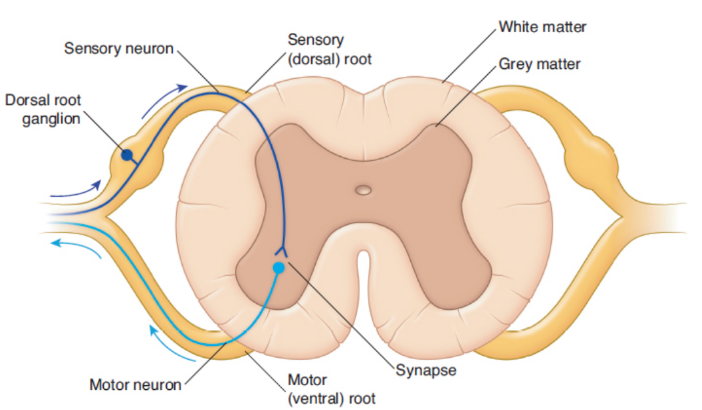
dorsal root ganglia
cell bodies of sensory neurons
spinal pathway
Sensory neurons bring information in from the periphery and enter on the dorsal (back) side
Motor neurons exit the spinal cord ventrally, or on the side closest to the front of the body
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
made up of nerve tissue and fibers outside the brain and spinal cord
ex. all 31 pairs of spinal nerves and 10 of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves (- olfactory and optic (CNS))
somatic nervous system
sensory and motor neurons distributed throughout the skin, joints, and muscles
a motor neuron goes directly from the spinal cord to the muscle without synapsing
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
regulates heartbeat, respiration, digestion, and glandular secretions and other involuntary muscles; regulates body temperature by activating sweating or piloerection
peripheral component contains two neurons - preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron
parasympathetic nervous system
conserve energy; resting and sleeping states; reduce heart rate and constrict the bronchi; manage digestion; manged by acetylcholine
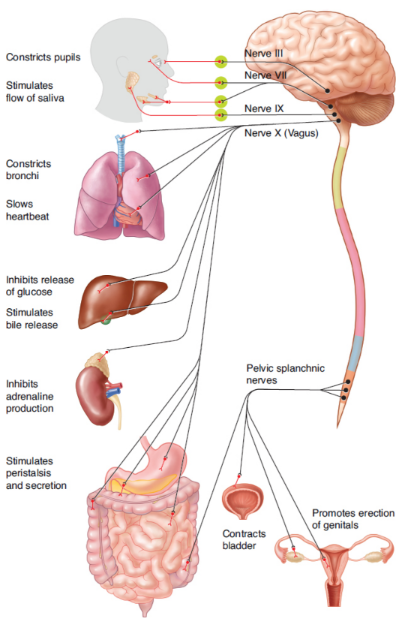
vagus nerve (cranial nerve X)
responsible for much of the parasympathetic innervation of the thoracic and
abdominal cavity.
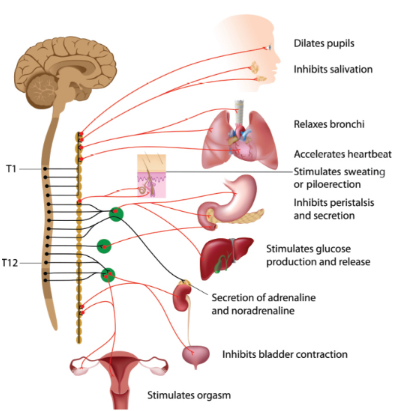
sympathetic nervous system
activated by stress; “fight-or-flight”; preganglionic use acetylcholine, postganglionic use norepinepherine
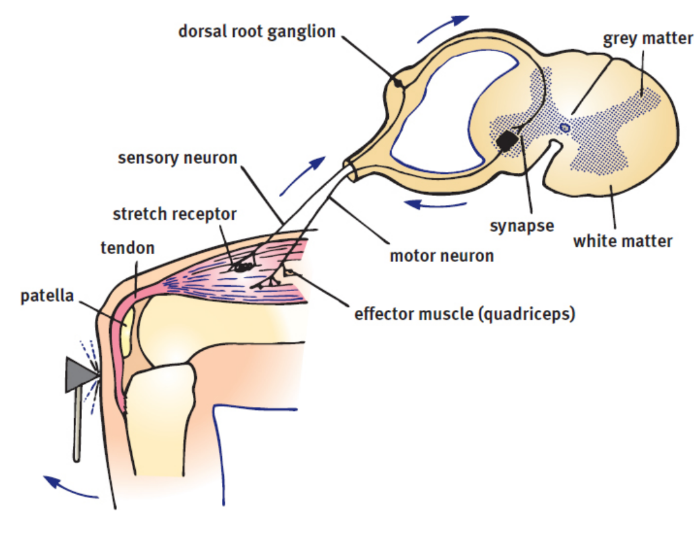
reflex arcs
control reflexive behavior; interneurons relay information to higher structure and can send signals to muscles immediately.
monosynaptic reflex arc
single synapse between the sensory neuron that receives the stimulus and the motor neuron that responds to it
ex. knee-jerk - pattelar tendon stretched → afferent neuron → spinal cord → efferent neuron → contraction of the quadriceps muscles → leg extension → less tension on patellar tendon
polysynaptic reflex arc
at least one interneuron between the sensory and motor neurons
ex. withdrawal - stepping off a nail and balancing weight on other leg