I S 300 Midterm: Key Terms
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
CIO
Chief information officer
CSO
Chief security officer
CKO
Chief knowledge officer
CDO
Chief data officer
Views of IT over time
Connection view: IT as tool (eg. landline phone)
Immersion view: IT as environment (eg. classroom projector)
Fusion view: IT as fabric (eg. wearable tech)
Web 1.0 vs 2.0 vs. Web 3.0
Web 1.0: Information consumer
Web 2.0: Information producer
Web 3.0 (moving into): Consume, produce, & own info w/ blockchain (allows for compensation)
Information technology (IT)
Use of computers & software to convert, store, protect, process, transmit, & retrieve info
Information system (IS)
System that collects & processes data (info) and provides it to managers at all levels for decision making, planning, program implementation & control.
Broader than IT – also includes study/business discipline of managing IT in a business context
IS based on 6 factors
Technical
Management science
CS
Operations research
Behavioral
Psychology
Economics
Sociology
3 dimensions of IS
Organization
IT
Management
How does IS fit into business?
Connects hardware, datamangement, & telecom w/ business strategic objectives & processes
Strategic business objectives of IT
Operational excellence (eg. UPS fleet logistics)
New products, services, & business models (eg. Uber disrupting taxi industry)
Customer & supplier intimacy (eg. Zara fast fashion model)
Improved decision making (eg. Verizon customer service & IT support)
Competitive advantage (eg. Walmart’s scale)
Survival (eg. Blockbuster vs. online streaming)
More tech [= / ≠ ] more productive
Not always equal - depends on complementary assets
Complementary assets
Assets that amplify tech’s utility
Organizational assets
Appropriate business model
Efficient business processes
Managerial assets
Incentives for management innovation
Teamwork & collaborative work environments
Social assets
Internet & telecom infrastructure
Tech standards
Business processes
Flow of material, info, & knowledge
Logically related set of tasks that define how specific business tasks are performed
May be tied to functional area or be cross-functional
Business = collection of business processes
Types of business processes & example tech used
Sales & marketing (up until sale)
Finance & accounting
Manufacturing & production (everything after sale - including fulfillment & tracking order status)
eg. package tracking system
eg. self check-in system at airport (side job is sales of add-ons)
HR
POS System
Point-of-sale system (eg. self-checkout)
Order fulfillment process
Sales: Generate order & submit order (→ accounting)
Accounting: Check & approve credit (→ manufacturing & production) → Generate invoice
Manufacturing & production: Assemble & ship product
Organizational structure & IS system used
Senior mgmt: ESS (Executive support system)
Middle mgmt: MIS & DSS (Decision support system)
Operational mgmt: TPS (Transaction processing system)
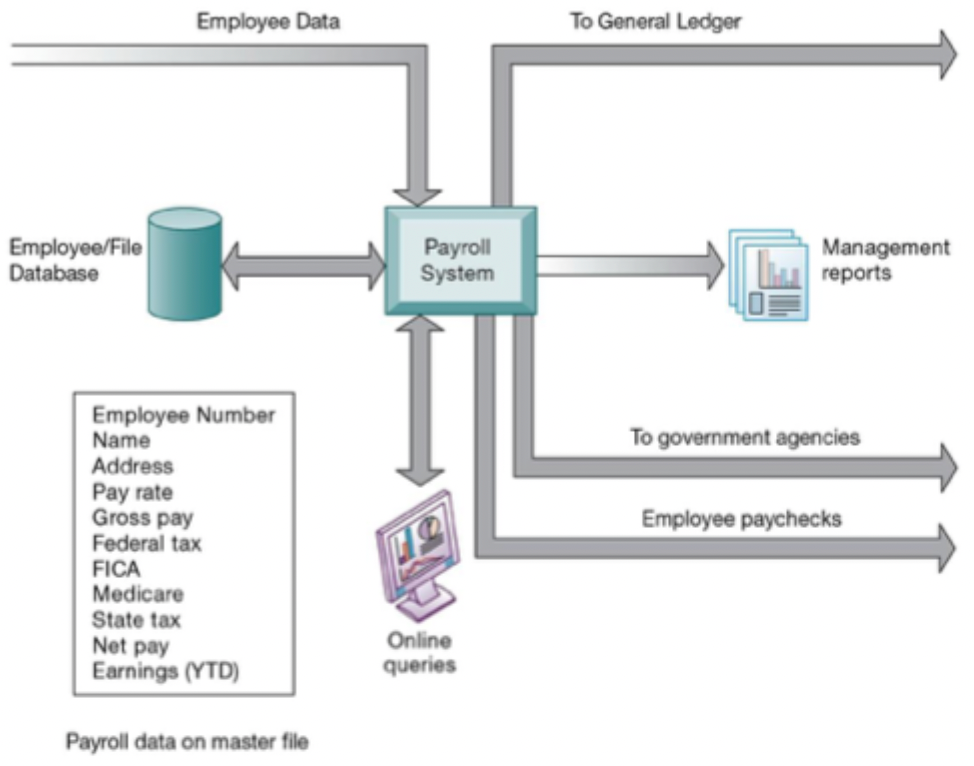
TPS
Transaction processing system
Collects data & connects it to existing info in database
Eg. Payroll, order processing, material resoruce planning system, general ledger
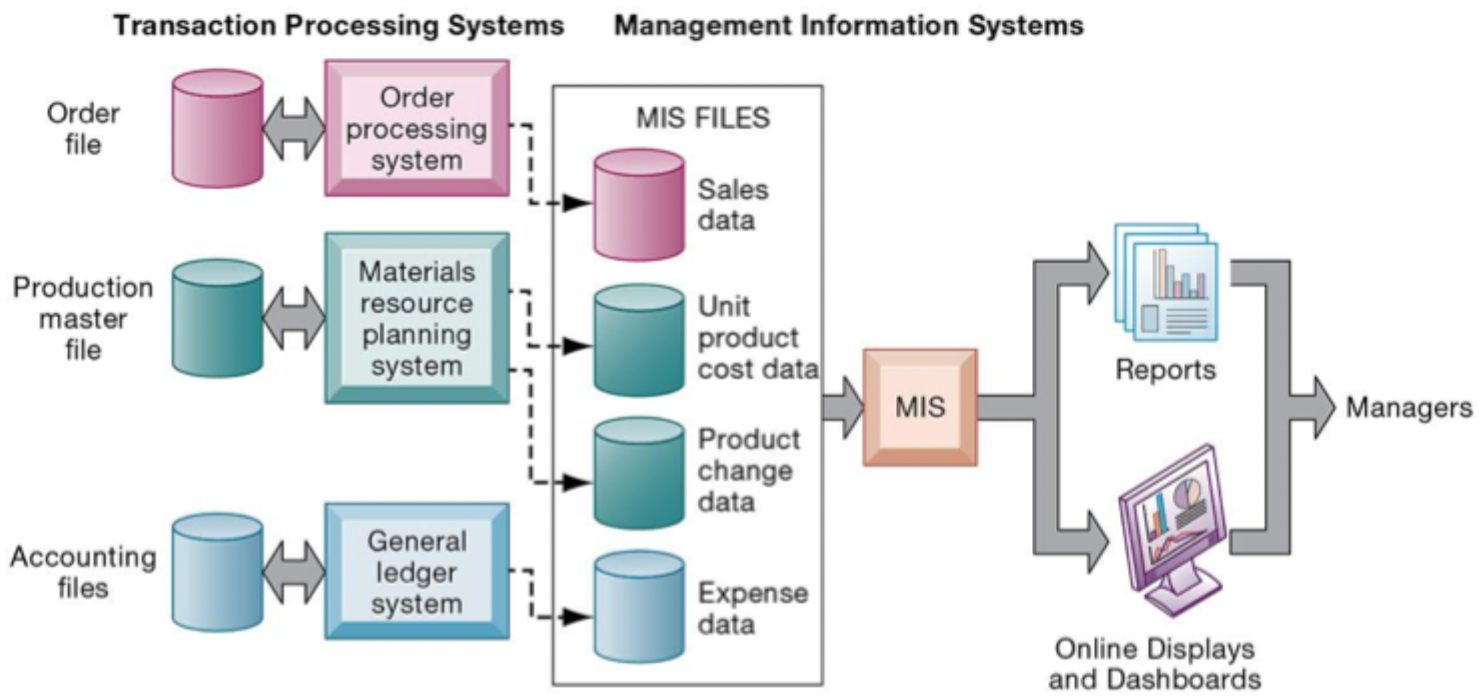
MIS
Management information system (descriptive)
Compile, organize, process, analyze, & generate reports from data
Used by middle management
Relationship between MIS & TPS
Multiple TPS systems feed into MIS files to generate reports
eg. Sales + production + accounting info → Report on planned & actual sales by product & region
DSS
Decision support system (prescriptive)
Eg. voyage-estimating system
Used by middle management
ESS
Organizational dashboard
Used by senior management
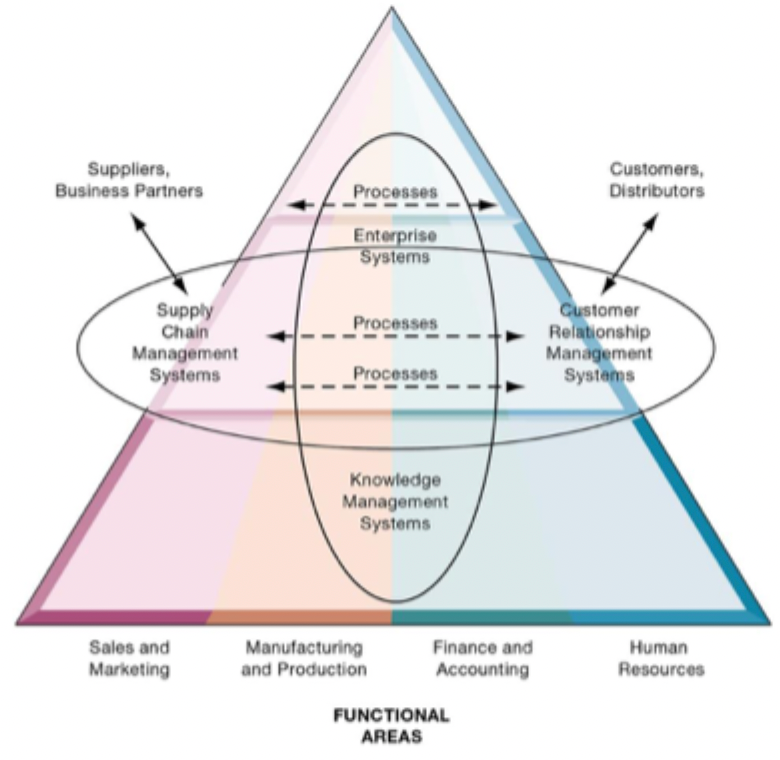
EAA
Enterprise application architecture
Combine different information systems into one super system
ERP Systems
Enterprise resource planning
Integrate data from key business processes into one system
Speed up communication of info throughout firm
Greater flexibility in responding to customer requests & greater accuracy in order fulfillment
Let managers see overall view of operations
SCM Systems
Supply chain management systems
Manage supplier relations, logistics, & order/production/inventory info
Goal: move correct amt of product as quickly & cheaply as possible
Automate flow of info across org boundaries
CRM System
Customer relationship mgmt
Coordinate business processes related to sales, mktg, & customer service
Goals:
Optimize sales & revenue
Improve customer satisfaction & retention
Identify & retain most profitable customers
KM System
Knowledge management system
Manage processes for capturing & applying knowledge & expertise
Links firm to external sources of knowledge
Collaboration requirements
Collaboration capability (org structure & culture)
Collaboration technology
E-business vs e-commerce vs m-commerce
E-business: Managing enterprise through tech (eg. hire ppl online)
E-commerce: Buying & selling online
M-commerce: Buying & selling on mobile device
4 screens
TV
Computer/laptop
Phone
Car dash
Reach
Range of customers a company can reach
Defined by how far customers are willing to travel for your good
Types of e-commerce
B2C (eg. Amazon)
B2B (eg. Alibaba)
C2C (eg. eBay)
How is e-commerce different?
Ubiquity: Shop anywhere & anytime
Global reach: Reach customers everywhere
Universal standards: Seamless communication between different systems, lower entry/search cost
Information richness: Multiple channels & more depth + scope
Interactivity: eg. AR
Information density: Reduced info cost & asymmetry
Personalization/customization: Tracking tech
Social aspect: User-generated content (eg. reviews)
E-commerce business models
E-tailer: Sell physical products directly to customers or businesses
Transaction broker: Process online B2C transactions
eg. Expedia
Market creator: Digital environment for C2C transactions
Content provider: Provide digital content
eg. Magazines, newspapers
Community provider: Meeting place for people to communicate & find info
eg. Reddit
Portal: Initial point of entry to web (categorize/classify webpages)
eg. Yahoo, MSN
Service provider: Applications (eg. photo & video sharing, online data storage)
Disintermediation
Getting rid of middle man (manufacturer → customer, no distributor or retailer)
Digital vs traditional markets
Info asymmetry: lower (for digital)
Search costs: lower
Transaction costs: low-none
Delayed gratification: Higher for physical goods, lower for digital goods
Menu costs: Lower
Dynamic pricing: Low cost & instant
Price discrimination: Low cost & instant
Market segmentation: Low cost, more precise
Switching costs: Depends on product characteristics
Network effects: Stronger
Disintermediation: More possible/likely
SDLC
Software design life cycle
Concept
Prototyping
Development
Testing
Deployment
Release
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language
WYSIWYG
What you see is what you get
Web development model
Box-based layout
Boxes & elements form tree
Boxes & elements can be stylized
parent’s style gets inherited unless overridden
Styles can be combined into classes
E-commerce revenue models
Advertising
Sales
Subscription
Free/freemium
Transaction fee
Affiliate
CPM
Cost per mille (thousand) impressions
Ad revenue/cost = (views / 1000) x CPM x Commission rate
Marketing channel w/ highest & lowest CPM
Highest: Direct mail
Lowest: Social media
Crowdsourcing
Obtaining info or input into task/project by enlisting services of large # of ppl (usually via internet)
eg. Yelp reviews, Wikipedia, YouTube
Information goods
Info-based (eg. movie, music album, good)
Properties:
0 marginal cost/unit
High cost of production
~0 copying cost
Low distribution & inventory cost
Variable mktg cost
Variable pricing
Main areas of growth in m-commerce
Mass market retailing (eg. Amazon, eBay)
Digital content sales (eg. music, TV)
In-app sales to mobile devices
M-commerce gives businesses
More detailed customer info (eg. location)
Location-based services
Geosocial services (where friends are)
Geo-advertising (what shops are nearby)
Geo-info services (price of house you are passing)
Example m-commerce services (not location)
Financial account mgmt apps
Mobile advertising (in Google, Facebook, games, etc.)
Games & entertainment
Mobile app payment systems
NFC (Near field communication)
eg. Apple Pay
QR Code-based payment systems
eg. Starbucks
P2P (Peer-to-peer) payment systems
eg. Venmo, Zelle
Characteristics of entering digital market
Extremely easy: Low barrier for entry, lots of opportunities
Handling competition: Need clear definition of business model w/ target market
Relationship-based (eg. Starbucks) vs transaction-based (eg. Walmart)
Front-end (client-facing) vs back-end (internal); DIY vs outsourcing
Need to choose right tech to achieve business objectives
Parts of e-commerce presence map
Websites
Email
Social media
Offline media
Parts of e-commerce presence timeline
Planning
Website development
Social media plan
Social media implementation
Mobile plan
Major types of AI
Expert systems
ML
Neural networks & deep learning networks
Genetic algorithms
Natural language processing
Computer vision
Robotics
Intelligent agents
Expert system
Decision flow chart/tree based on knowledge of experts
Machine learning
Given data & outputs, computer generates model to apply to new situations
vs. Traditional programming: Computer gets data & program to generate output
Machine learning is focused on
Recognizing patterns in very large sets of data
Types of (machine) learning
Supervised learning (eg. neural network)
System given examples of desired inputs & outputs identified by humans in advance
Unsupervised learning (eg. recommendations)
Humans don’t provide examples of desired outputs
Neural networks
Find patterns & relationships in large amounts of data too complicated for humans to analyze
Supervised learning
Limitations of neural networks & ML
Require very large datasets
Patterns may not “make sense”
Can't explain how system arrived at solution
Most useful for classifying into binary categories - not always possible in real world
No sense of ethics
Genetic algorithms
Find optimal solution by examining large # of possible solutions
Used in optimization
Natural language processing
Process voice or text command using natural human language
Computer vision system
Emulate human visual system to view & extract info from real-world images
eg. Self-driving cars can recognize signs & road markers
Robotics
Design, construct, & operate movable machines & support computer systems to substitute for humans
Intelligent agents
Work w/o direct human intervention to carry out repetitive, predictable tasks
Benefits of outsourcing
Cost saving
Improve process speed
Better quality
Increase ability to focus on core business
Leavitt diamond
Interdependent:
Information tech use
Business processes
Org form
Requisite ppl skills
Enterprise systems architecture
Consolidate all info in centralized database
ERP benefits
Quality & efficiency
Cost saving
Decision support & knowledge management
Enterprise agility
Challenges of enterprise systems
Difficult to build & costly to implement
Complex technology & investments required
Centralized org coordination & decision making
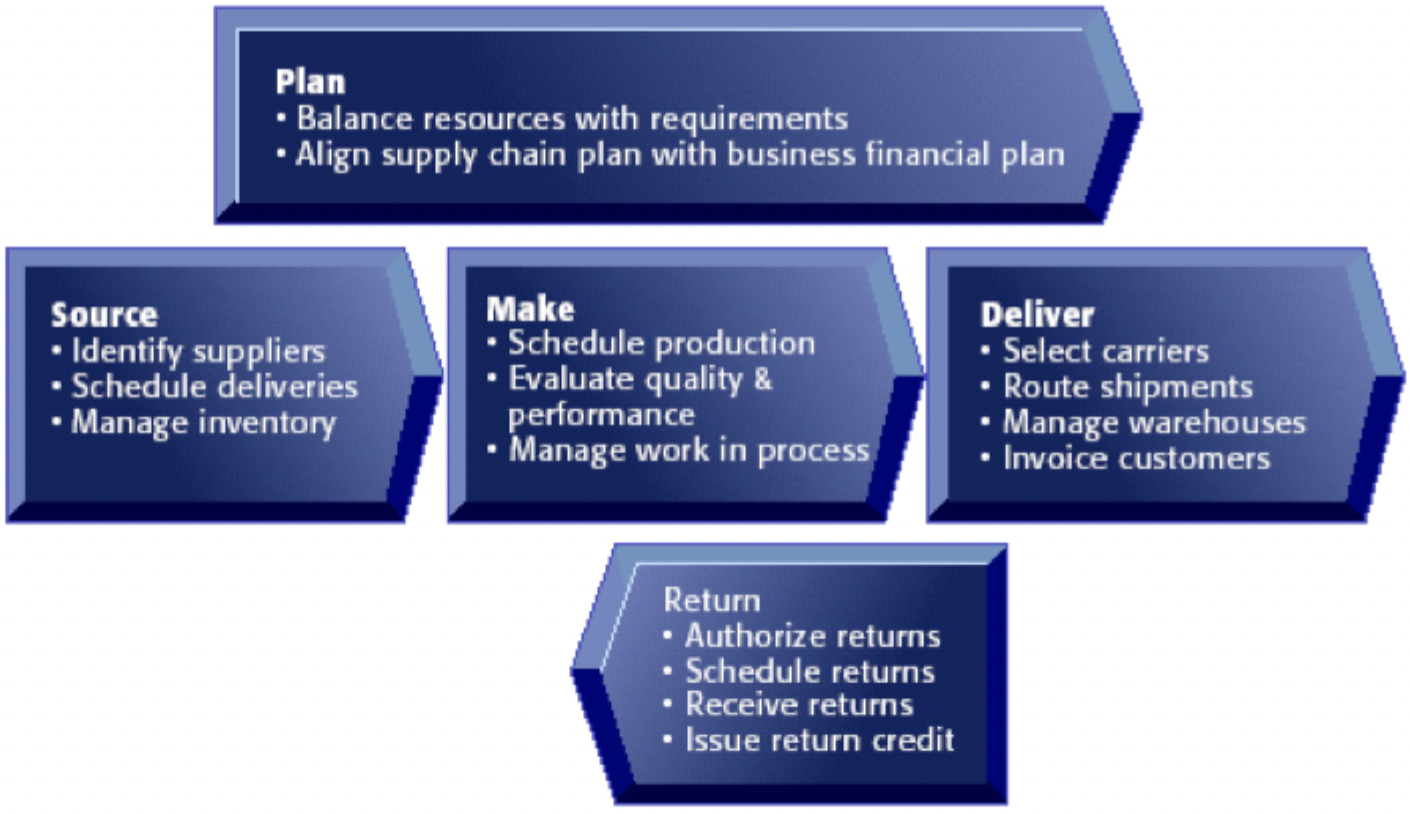
Key SCM processes
Plan
Source
Make
Deliver
Return
Push vs pull-based supply chain model
Push: Produce based on sales forecasts
Pull: Produce after receiving order (eg. fresh pizza)
Touch points
Method of interaction w/ customer (eg. telephone, email, social media - increasingly popular)
Data hierarchy
Database → file → record → field → byte → bit
Problems with traditional record keeping
Files maintained separately by diff departments
Data redundancy & inconsistency
Program-data dependence
Poor security
Lack of flexibility, data sharing, & availability
Relational database
Separate entity groups connected by relationships
Normalization
Break table or relation into set of tables so each only has one theme

Equivalent terms in data management
Table = relation = file
Row = record = tuple
Column = field = attribute
Database entity
Object/thing about which info is stored
Characteristics of relation
Row contains data about an entity
Column contains data about attributes of entity
Cells hold single value
All entries in column are of the same kind
Each column has unique name
Order of columns & rows is unimportant
No two rows can have identical sets of values
Primary vs foreign key
Primary key: identifies each record in relation
Foreign key: primary key from another relation used to represent relationship
Referential integrity
Every value of foreign key must match a value of an existing primary key
Monte Carlo simulation
Generate random values for uncertain inputs in model multiple times & compute output to understand output distribution
Types of decision models
Descriptive: Describe relationship & provide info for evaluation
Prescriptive (optimization models): Determine best course of action
What-if analysis
Evaluate how specific combinations of model inputs affect outputs
aka sensitivity analysis