Social influence - conformity and obedience
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is conformity?
when a person changes their behaviour or opinions as a result of real or imagined pressure
three types of conformity
compliance, identification, internalisation
what is compliance?
conforming publicly but continuing privately to disagree - shallowest form of conformity
what is identification?
moderate form of conformity where we act the same as the group because we want to be accepted, change of belief often temporary
what is internalisation?
deep form on conformity where a person conforms publicly and privately as they have accepted the views of the group - permanent
two process theory
Deutsch and Gerad 1955 - two reasons people conform, to be liked and to be right, NSI and ISI work together
Normative social influence
the need to be liked, go along with the norms of the majority
Informational social influence
the need to be right, go along with the group as you believe they have more information
Asch’s procedure and findings
male Americans, shown a series of lines asked what lines were the same length, confederates told to give incorrect answer on 12/18 trials, on 12 critical trials 36.8% of responses where incorrect - support for NSI
variations to Asch’s study
Group size - little conformity when 1 confed, 13% when 2 confeds, when majority of 3 confederates jumped to 31.8% when majority increased further little change in conformity
Unanimity - when one confed that gave correct answer conformity dropped to 5%
Difficulty of the task - when line lengths were more similar, conformity increased - ISI
evaluation of Asch
Artificial situation, beta bias and cultural bias, research support Lucas et al
Lucas et al
asked ppt to answer easy and hard maths questions, ppts given answers from 3 confeds, conformed more when questions harder - ISI, but those more confident less likely to conform
social roles
the parts people play as members of social groups, gives us expectations of behaviour, identification
procedure of SPE
meant to be 2 weeks only lasted 6 days, ppts screened to be mentally stabke, randomly assigned roles, guards given sunglasses and military uniforms, prisoners in uniforms and referred to as numbers, Z. told guards they had complete control
findings of SPE
prisoners rebelled on 2 day
guards punished rebels harshly
one ppt showed extreme signs of distress so had to leave after telling over ppts they were not allowed to leave
guards extremely aggressive one made a decision to be as intimidating as possible
strengths of Asch’s study
Lab - controlled environment, internal validity
Real life applications - people to write answers down instead of saying them out loud
Conclusions of SPE
good person in evil situation can become evil
power corrupts
evil is caused by situational factors not dispositional
strengths of SPE
Same conformity present in Abu Ghraib military prison notorious for abuse - external validity so the findings can be used to prevent abuses in the future
Good control of variables - emotionally stable and randomly assigned so rules out
Internal validity - ppts felt like it was a real prison
weaknesses of SPE
when a sample who have not heard of the study where shown its method, majority guessed the aim
PPts acted how they thought Z. wanted them to - some guards admitted to acting like stereotypes from films
Only minority of guards acted in brutal manner
Ethical concerns
Milgram’s procedure
40 males, thought randomly assigned but always ‘teacher’
punishments were electric shocks, 15V - 450V
ppts heard pre-recorded answers from learner including sounds of pain and screaming as the voltage got higher
what were the prompts Milgram used?
Please continue
please go on
the experiment requires that you continue
it is absolutely essential that you continue
you have no other choice you must go on
Milgram’s findings
100% went to 300V, 65% went to 450V
dissented verbally but continued to obey
signs of distress
three people had seizures
Key variations of Milgram
experimenter absent - 22%
run down office - 45%
disobedient confeds - 10%
confed gave shocks - 95%
Ethical issues in Milgram’s experiment
Deception, lack of protection from harm, right to withdraw not clear BUT debrief and counselling offered
Obedience alibi
Mandel 1998 - blaming situational factors give people an alibi for bad behaviour
Internal validity in Milgram’s experiment
Milgram said 70% ppt thought shocks real
Perry 2013 - listened to tapes of Milgram’s ppts and reported many expressed doubts about the shocks
social identity theory Milgram
obedience lies in group identification
obedience fell as ppts identified less with science more with the learner
When prompts appealed to science obedience was higher
cross cultural replications of Milgram
Miranda et al - replicated findings - 90% obedience rates in Spanish students
BUT - also a western culture
Research support for Milgram
Hofling et al - nurses told by unknown doctor to deliver unknown drug on phone - 21/22 obeyed BUT unrealistic
Rank and Jacobson - told to give lethal dose of valium over phone by known doctor allowed to discuss with others - 2/18 obeyed - mundane realism
Bickman et al - field experiment - more obeyed when asked to perform an action by someone in a security guards uniform
2 situational explanations for why people obey
agentic state and legitimate authority
what is the agentic state?
when we perceive someone as above us in the social hierarchy we are likely to act as an agent for them, following orders
what is agentic shift?
when you ordered by an authority figure you go from an autonomous state to agentic state
what is a binding factor?
mindset that reduces moral strain e.g blaming the victim or authority figure, minimising impact on victim
neurological evidence for agentic state
Research on brain activity while ppts inflict pain, found that obeying orders reduces empathy and guilt related brain activity for the inflicted pain, may explain why people are able to commit immoral acts under coercion
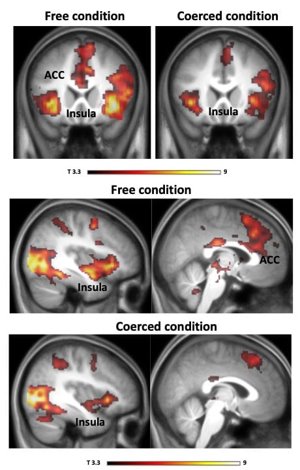
observational evidence to support the agentic state
Blass and Schmitt - lab based observation and survey method
Showed ppts clips of Milgram’s experiment, asked to assign responsibilities, majority attributed responsibilities to researcher not ppt
strengths of brain imaging evidence
quantifiable data, direct evidence for how obedience affects us biologically, objective
legitimacy of authority
authority is legitimate when it is agreed by society in a hierarchy
destructive authority
powerful leaders can use legitimate powers for destructive purposes
challenge for situational factors of obedience
WWI German reserve battalion obeyed orders to shoot civilians despite being told they could be reassigned, can’t have shifted to agentic state
Evaluation of situational explanations for obedience
real world application - military ranking system, Lai massacre
external validity - countries with different hierarchy systems and would then have lower obedience levels e.g. Australia
Hoffling et al - nurses did not show anxiety suggesting they were acting on their own accord
what is a dispositional explanation?
behavioural explanations
features of the authoritarian personality
from strict parenting, conformist, dogmatic, especially obedient to authority
Adorno’s F-scale
2000 middle class white Americans, those with high score identified with strong people, strong positive correlation between authoritarianism and prejudice
explanations for authoritarian personality
strict discipline parenting style - high standards, severe criticism
creates resentment in the child, child cant show feelings so displaces on who appears to be weaker
problems with f-scale
leading question
social desirability bias
closed questions
acquiescence bias - tendency to agree
clear what they are trying to figure out
Christie and Jahoda 1954 - political biased interpretation of a right wing authoritarianism personality, left and right wing can both have the personality
positive of authoritarian personality
no obedience alibi - individual held accountable
Milgram and Elms 1966 method
follow up study with ppts who took part in Milgram’s shock experiment, 20 obedient and 20 defiant ppts, completed MMPI scale and F-scale, asked about their relationships with their parents
Milgram and Elms 1966 findings
higher levels of authoritarianism among those classed as obedience, obedient ppts reported being less close to fathers in childhood, saw authority figure as more admirable than learner
BUT - fully obedient ppts reported having a very good relationship with their parents