Knee & Patella
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Knee Technicolor Factors
(AP, Obliques, Lateral)
SID: 40”
Collimation Field Size: 10 × 12
IR Alignment: Portrait
Grid:
Grid or Bucky: > 10 cm
Nongrid: < 10 cm
kVp: 65-80
Knee Technical Factors
(Tunnel)
SID: 40”
Collimation Field Size: 8 × 10
IR Alignment: Portrait
Grid: Yes
kVp: 70-80
Patella Technical Factors
SID: 48” - 72”
Collimation Field Size: 8 x 10
IR Alignment: Portrait or Landscape
Grid: No
kVp: 70-80
Patient Position for Settegast Method (Sunrise)
Have patient seated on XR table
Flex knee to 90°
Have patient hold cassette against distal femur
CR and Tube Angle for Settegast Method
CR: Tangential to patellofemoral joint space
Tube angle: 15° - 20° from lower leg
AP Knee Patient Positioning
Place patient supine
Rotate leg internally 3°- 5° for true AP knee
Tube angle: None for average build
AP Knee CR Position
½ inch distal to apex of patella
AP Oblique Internal Rotation Knee Patient Positioning
Patient supine
Rotate leg internally 45°
Tube angle: None for average patients
CR for AP Oblique Internal Knee
Midpoint of knee at level ½ inch distal to apex of the patella
CR for AP Oblique Knee Lateral (External) Rotation
Midpoint of knee at level ½ inch distal to apex of patella
Tube angle for Lateral Knee
5-7° cephalad
Short patients w/ wide pelvis: 7-10° cephalad
Tall patients w/ narrow pelvis: 5° cephalad
Lateral Knee Patient Positioning
Patient in lateral recumbent with affected side down
Flex knee 20-30°
To prevent over-rotation, place opposite limb behind affected limb for support
AP Oblique External Rotation Knee Patient Positioning
Patient supine
Rotate leg externally 45°
CR for Lateral Knee
1” distal to medial epicondyle of femur
What is the common name for the Béclère Method?
Tunnel View
What is another name for the Settegast Method?
Sunrise View
Béclère Method (Tunnel) CR
½ inch distal to apex of patella
Béclère Method (Tunnel) Tube Angle
40-45° cephalad (perpendicular to lower leg)
Béclère Method Patient Positioning
Patient supine
Flex knee 40-45°
Adjust IR to center IR to mid knee joint area
CR for Settegast Method
Tangential to patellofemoral joint space
Tube angle for Settegast Method
15-20° from lower leg
Settegast Method Patient Positioning
Seated:
Patient seated on XR table
Flex the knee 90°
Have patient hold cassette against distal femur
In a lateral knee image, what are characteristics of an under rotated knee?
Knee is too far away from IR
Fibulas head is too far anterior
In a lateral knee image, what are characteristics of an over rotated knee?
Knee is too far toward IR
Fibulas head too far posterior
In a lateral knee image, what are characteristics of an image with no tube angle?
Medial and lateral femoral condyles are not superimposed.
A medial (internal) oblique knee projection shows what in profile?
Lateral condyle in profile w/o superimposition.
Opens up tibiofibular joint
A lateral (external) oblique knee projection shows what in profile?
Medial condyle in profile w/o superimposition
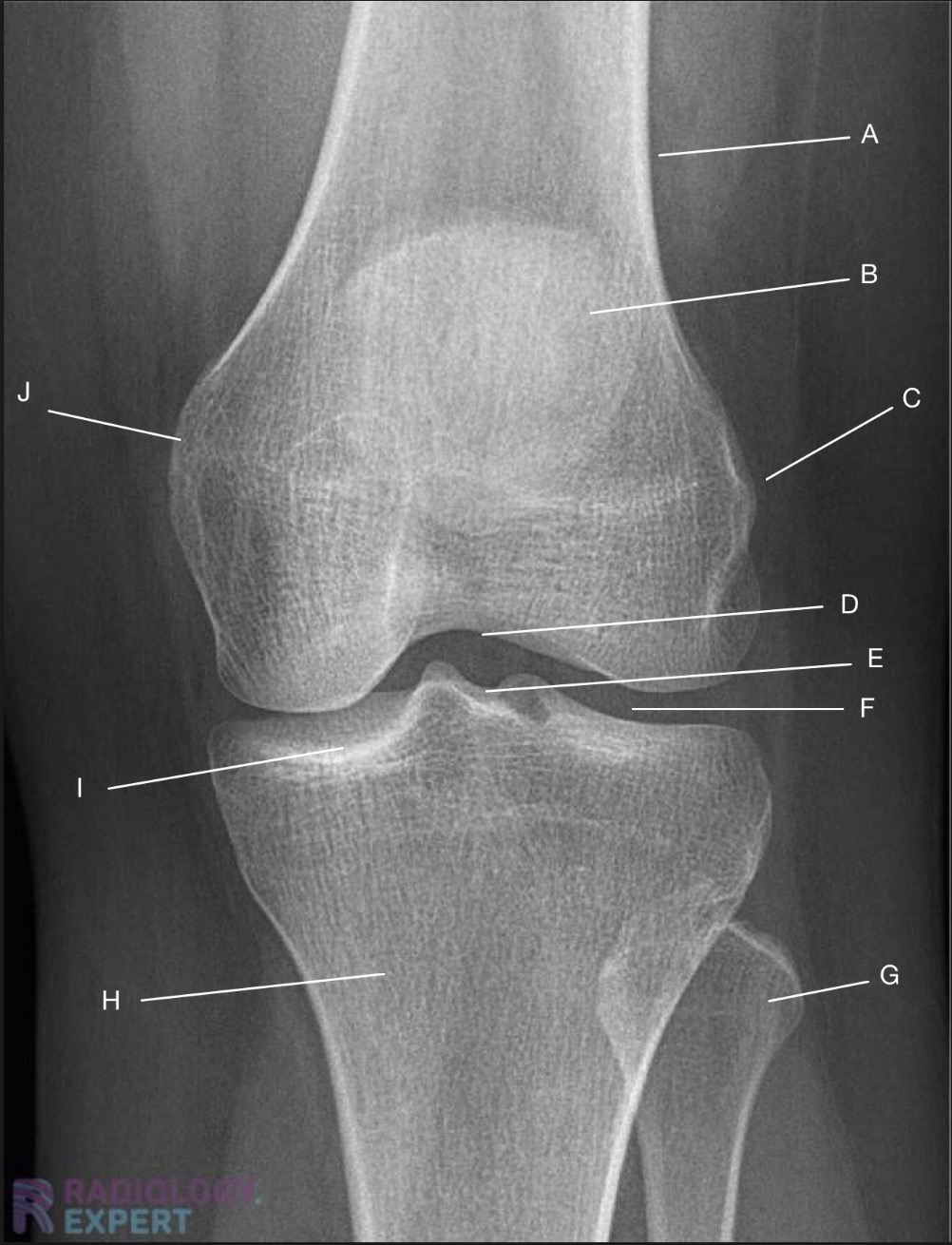
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
AP Knee
No
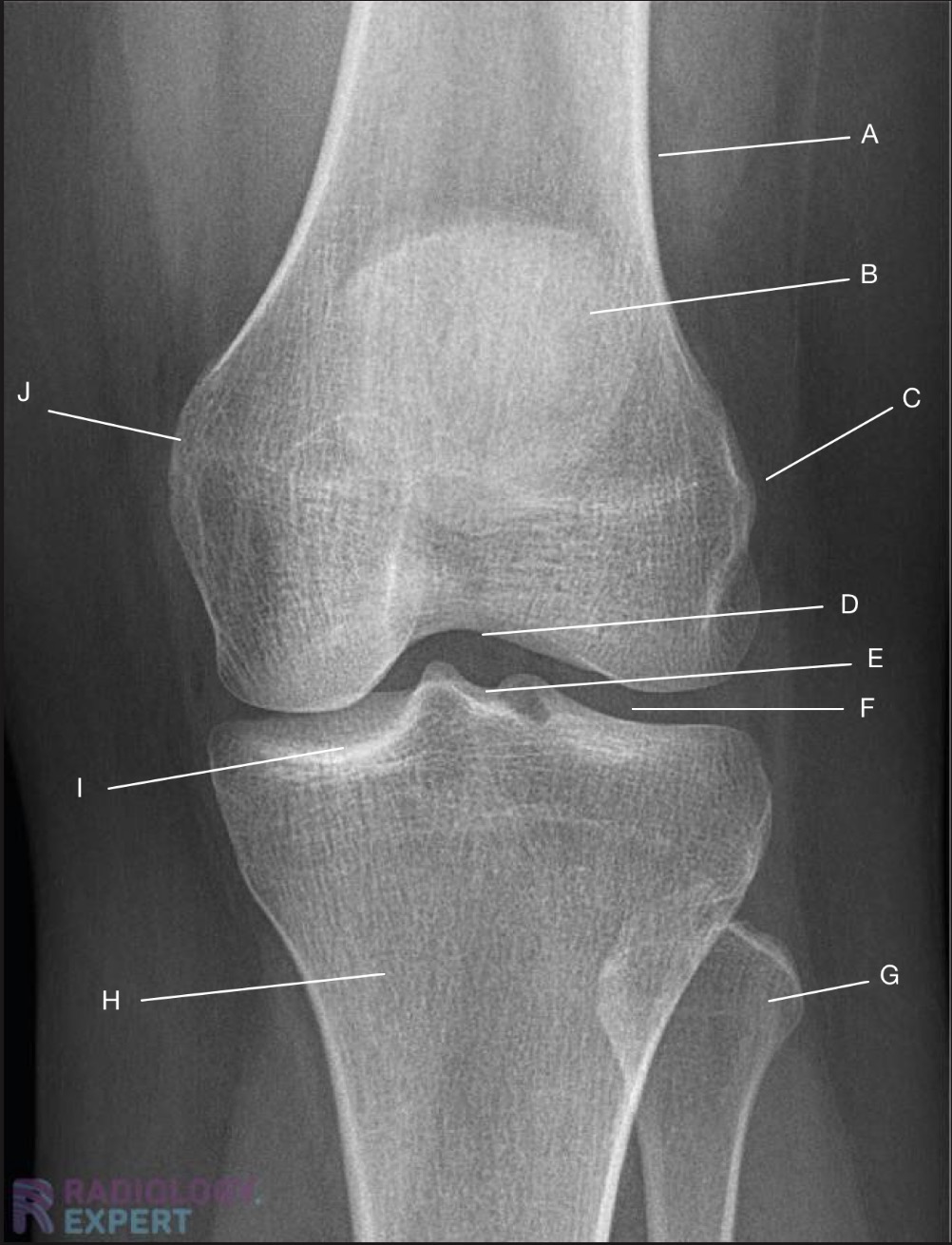
Label the image
A) Femur
B) Patella
C) Lateral femoral epicondyle
D) Intercondylar fossa
E) Intercondylar eminence
F) Femorotibial joint
G) Fibula
H) Tibia
I) Tibial condylar margin
J) Medial femoral epicondyle
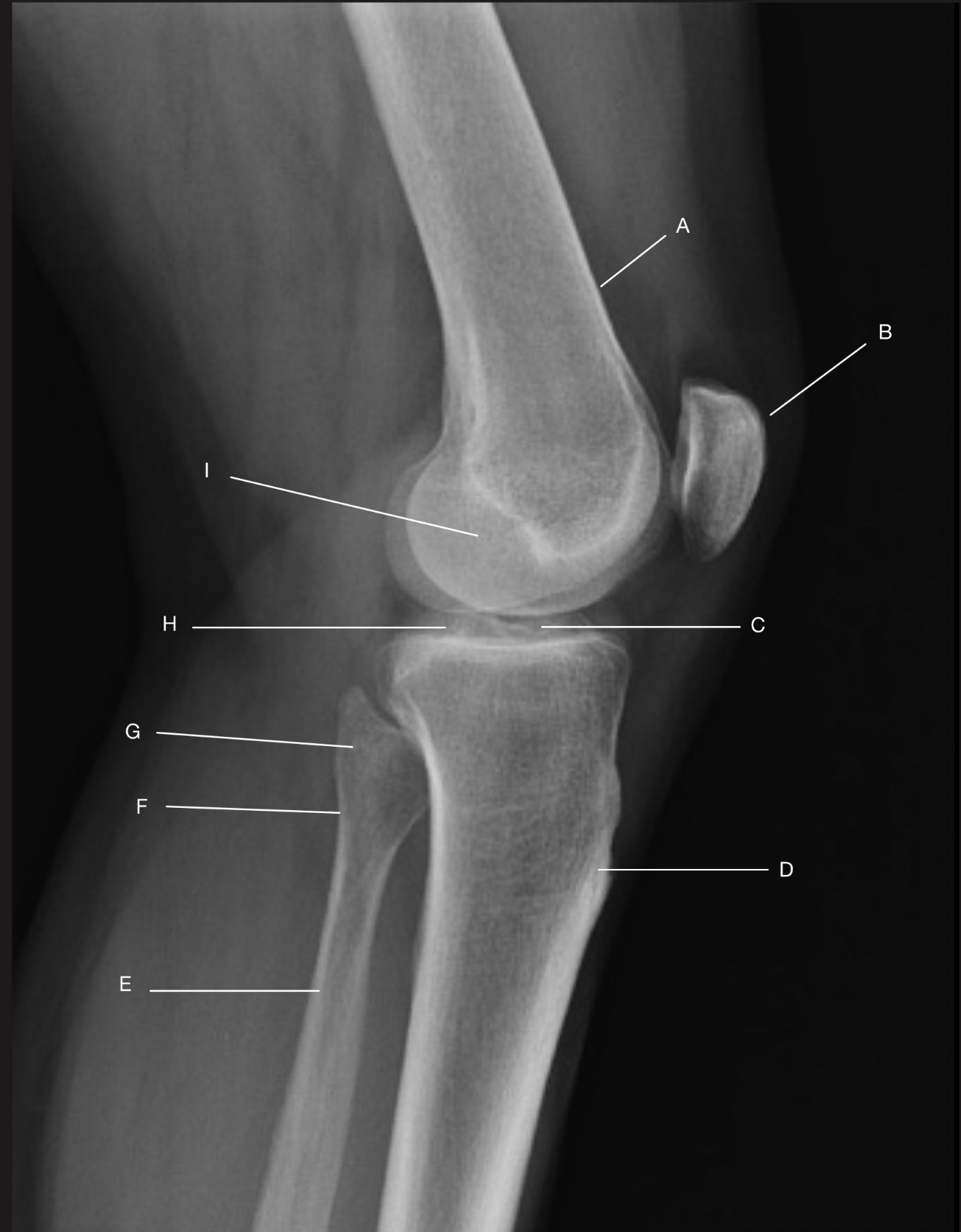
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
Lateral Knee
Yes. Patient is not in true lateral.
Fibular head and tibia are not superimposed.
Femoral condyles not superimposed
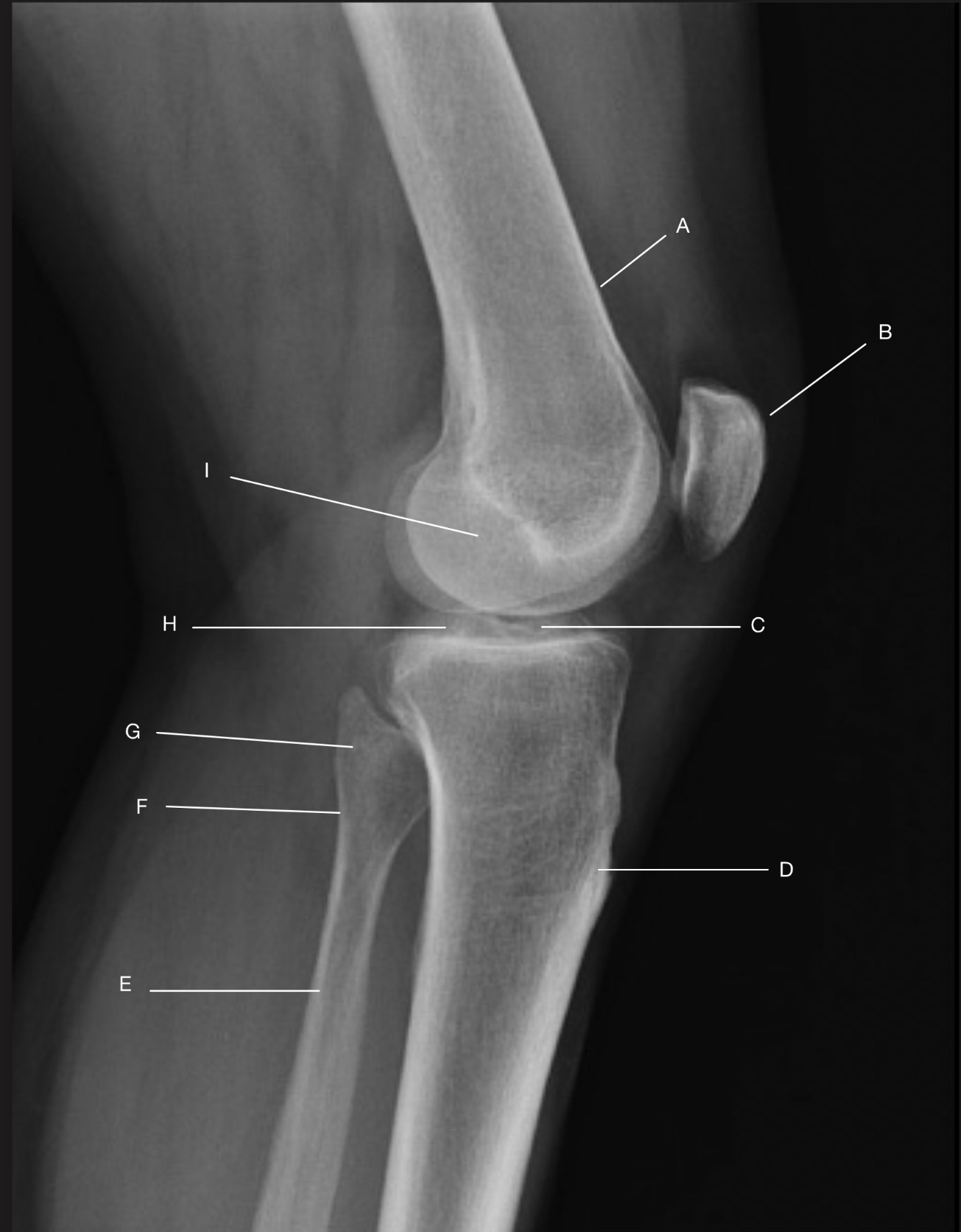
Label the image
A) Femur
B) Patella
C) Intercondylar eminence
D) Tibia
E) Fibular shaft
F) Fibular neck
G) Fibular head
H) Femorotibial joint
I) Femoral condyles
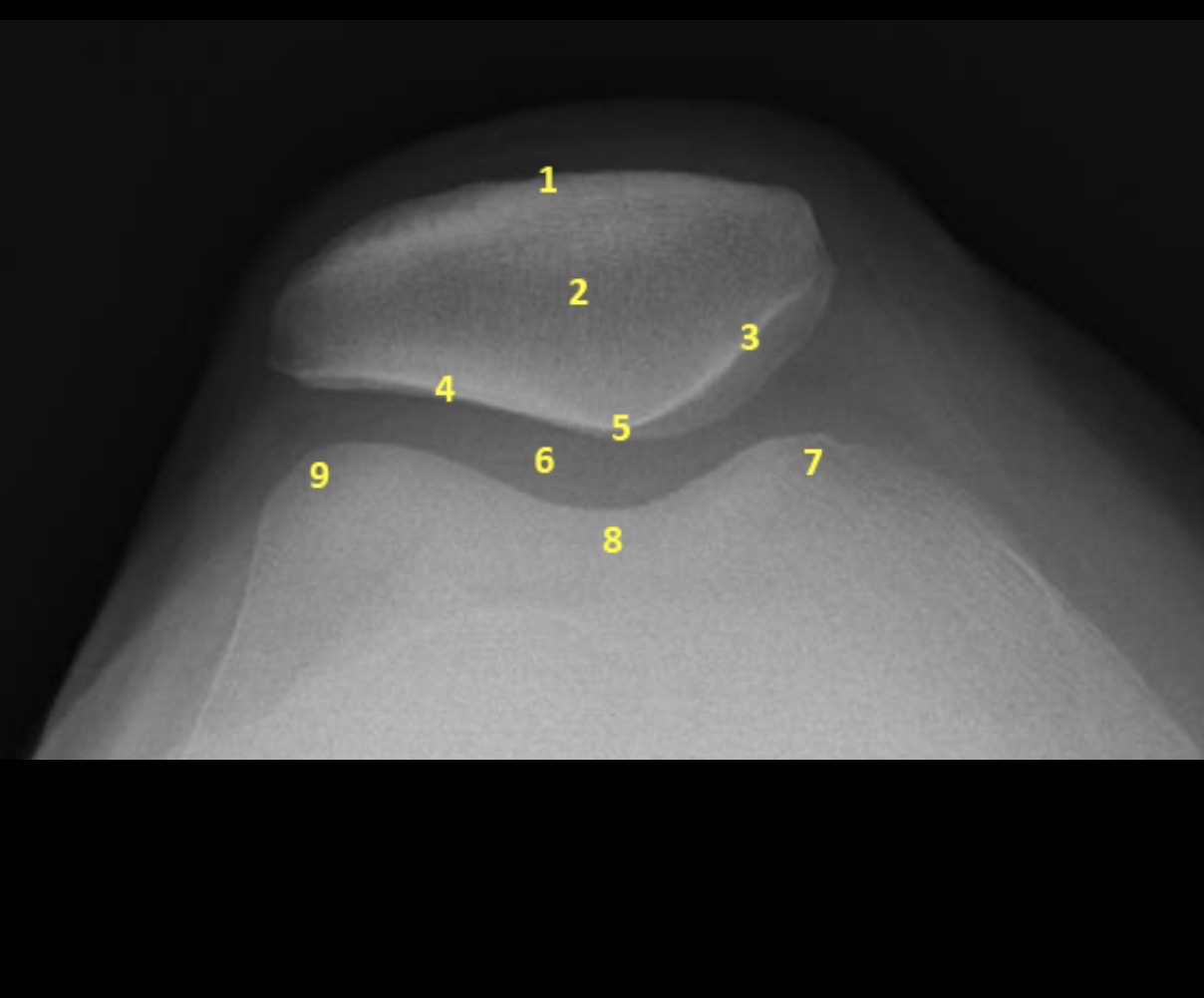
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
Settegast Method or Sunrise View
No.
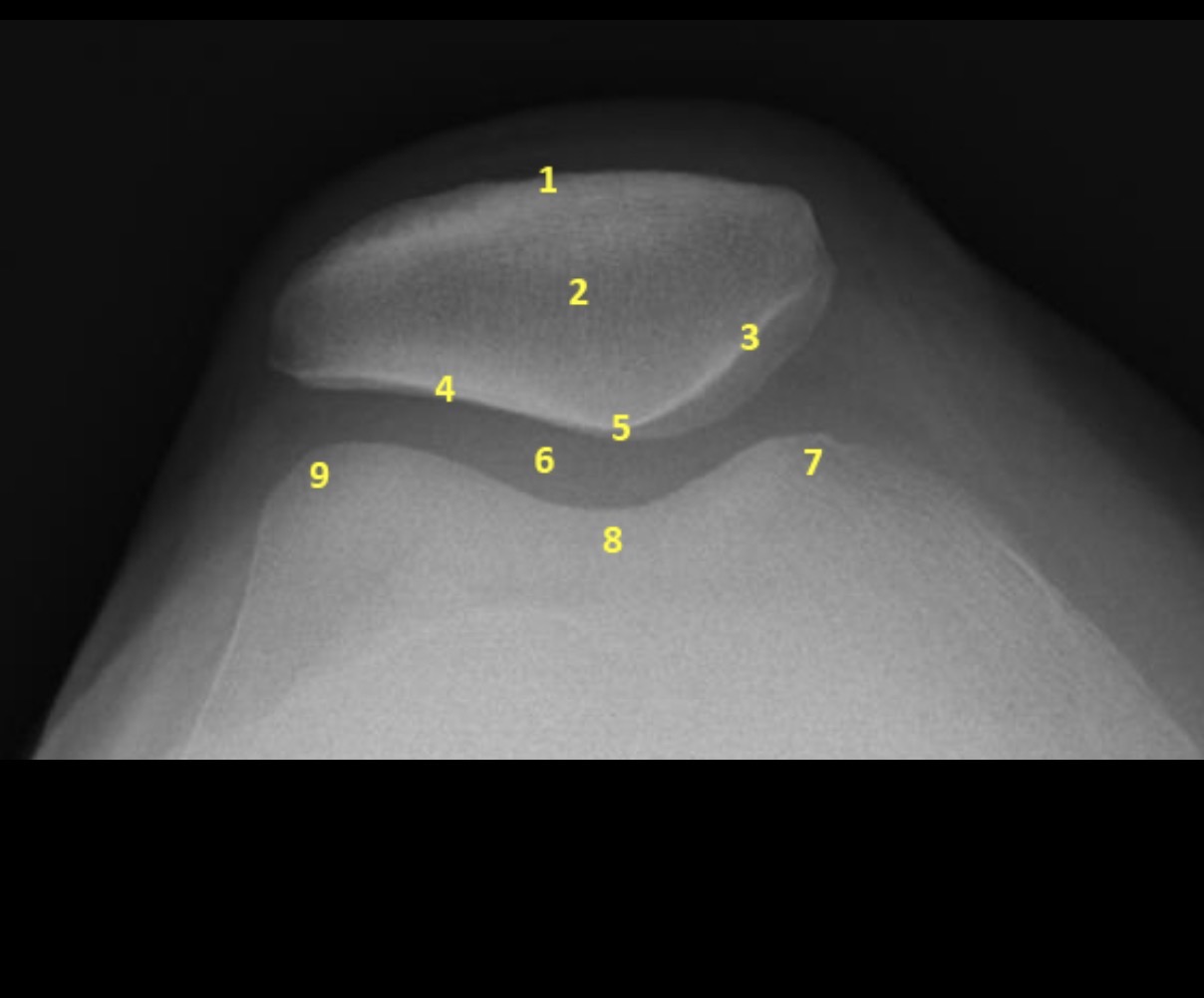
Label the image.
External cortical surface of patella (not needed for practical)
Patella
Medial facet of patella
Lateral facet of patella
Median patellar ridge
Femoropatellar joint
Medial trochlear ridge
Trochlear groove
Lateral trochlear ridge
What causes superimposition of the femur on a Tunnel View?
Knee is over flexed
Tube not perpendicular to the tunnel
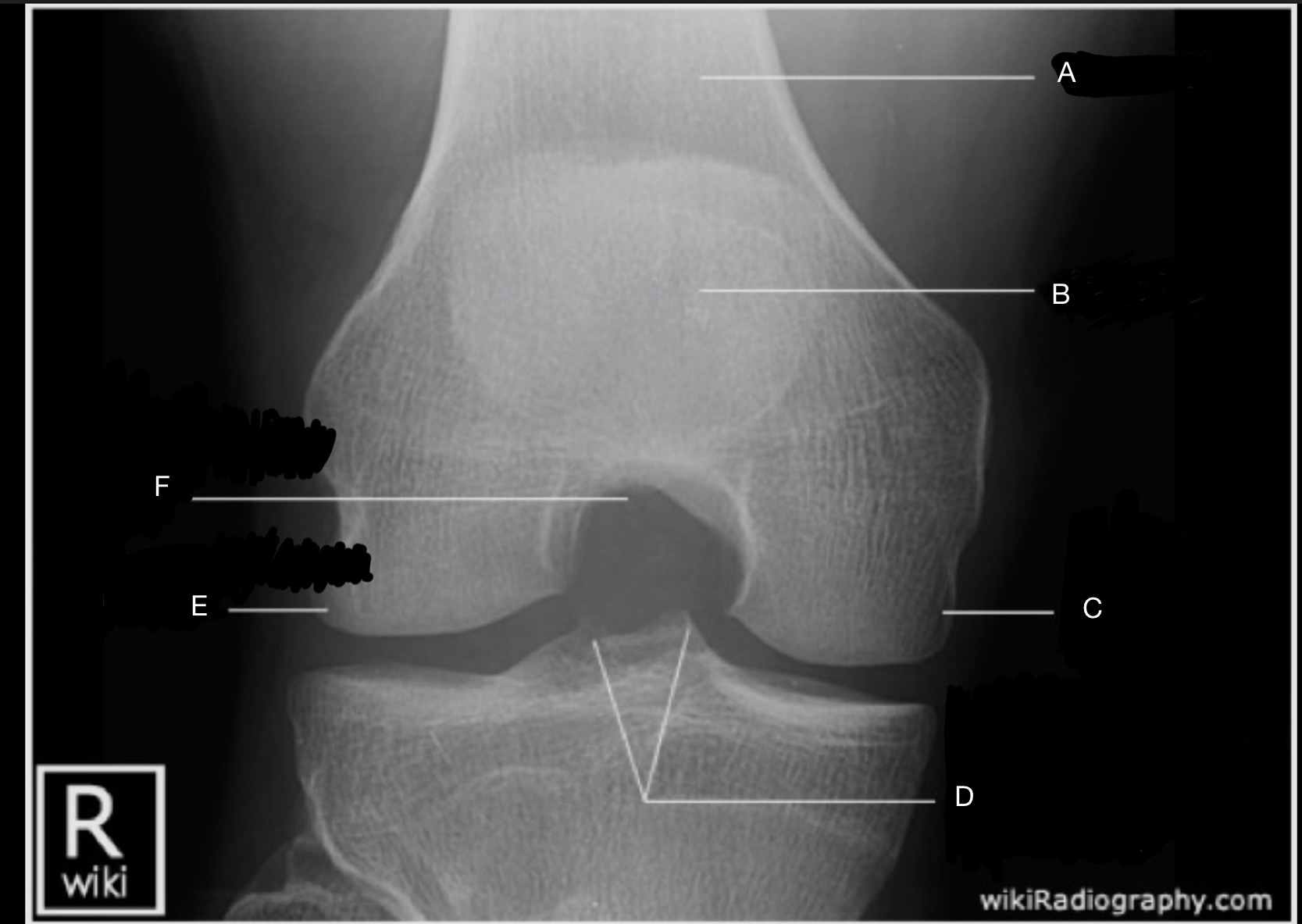
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
Béclère Method or Tunnel View
No.
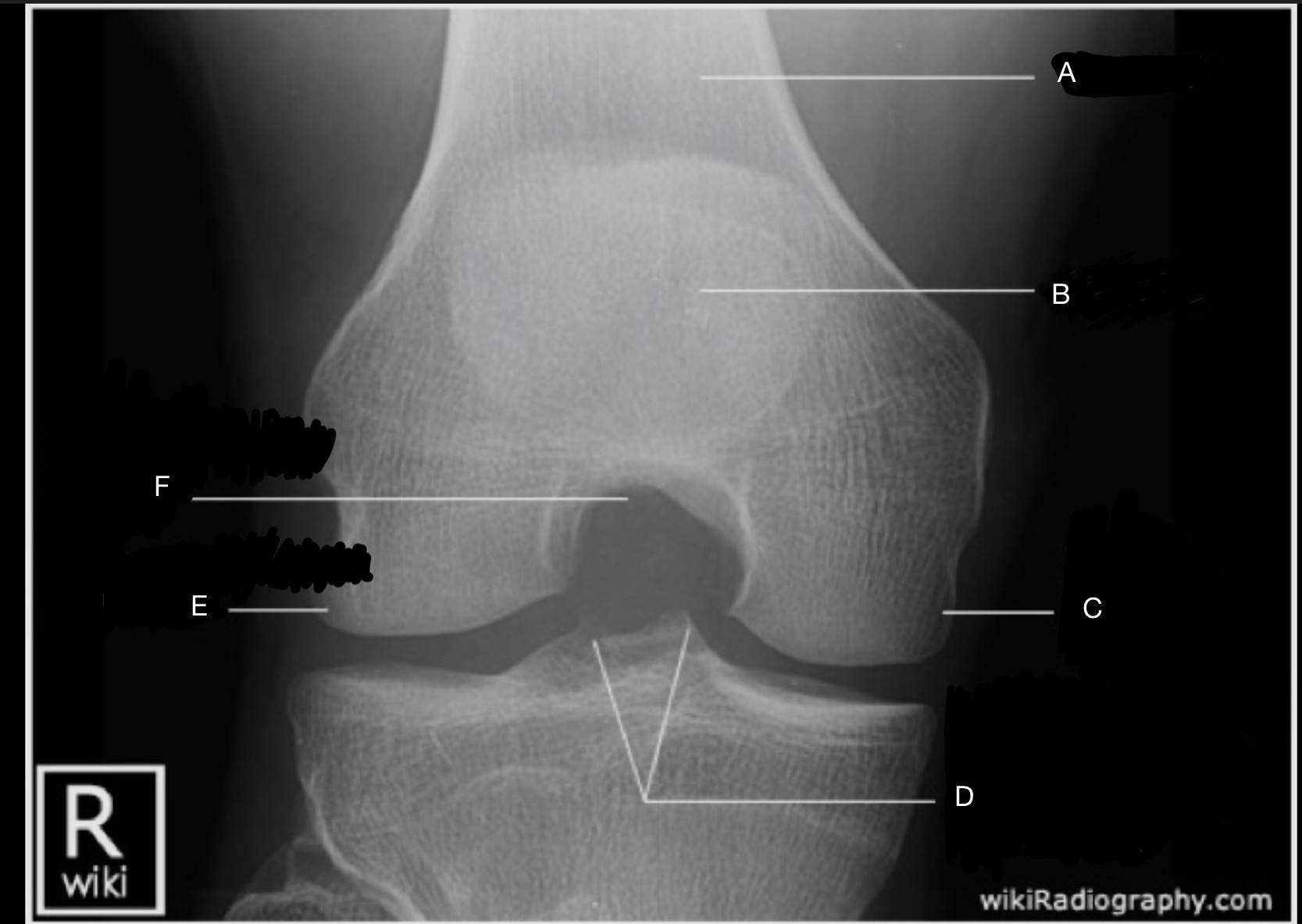
Label the image.
A) Femur
B) Patella
C) Medial femoral condyle
D) Medial & Lateral Tubercles of Intercondylar Eminence
E) Lateral femoral condyle
F) Intercondylar fossa
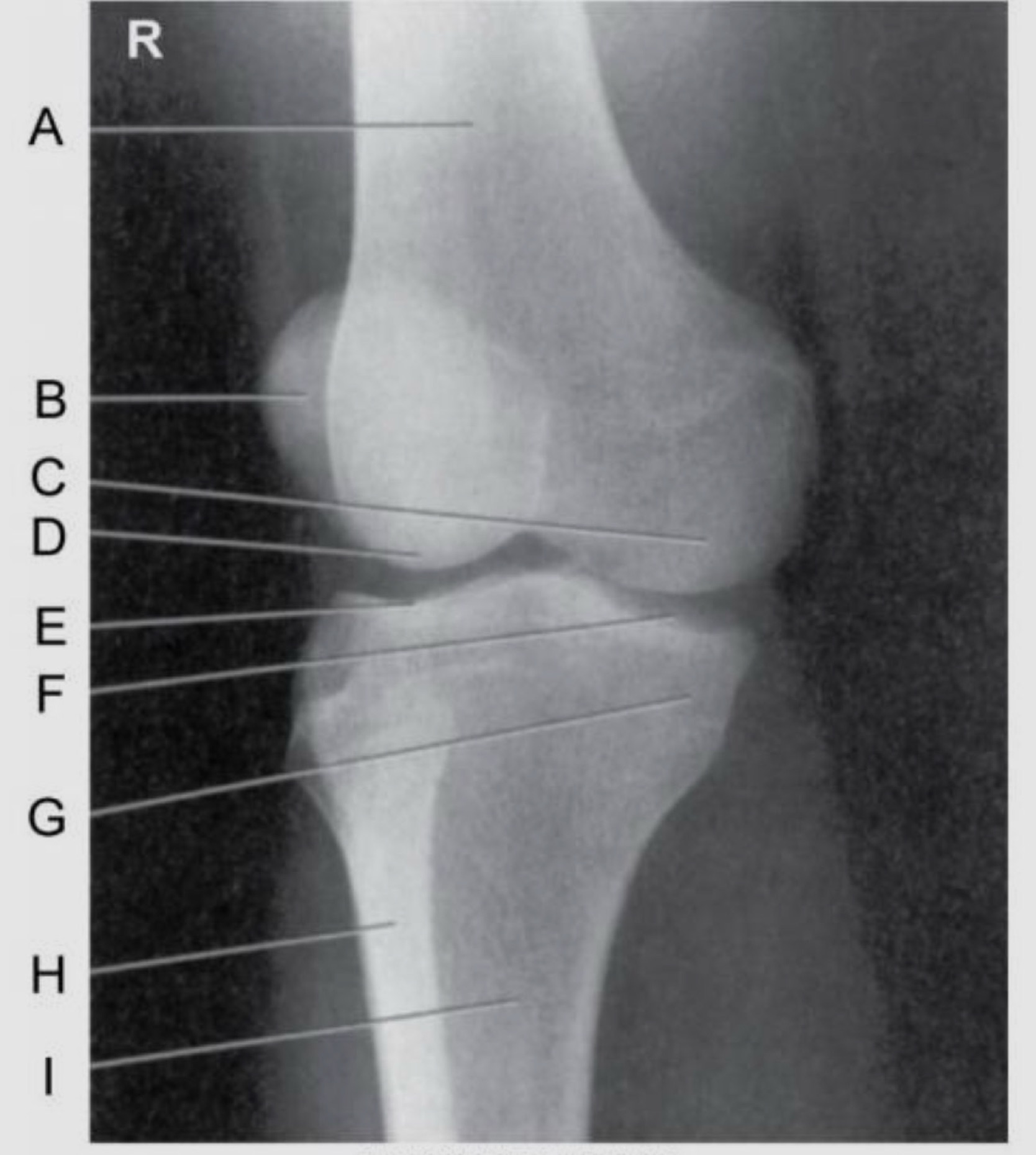
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
AP Lateral (external) Oblique
No.
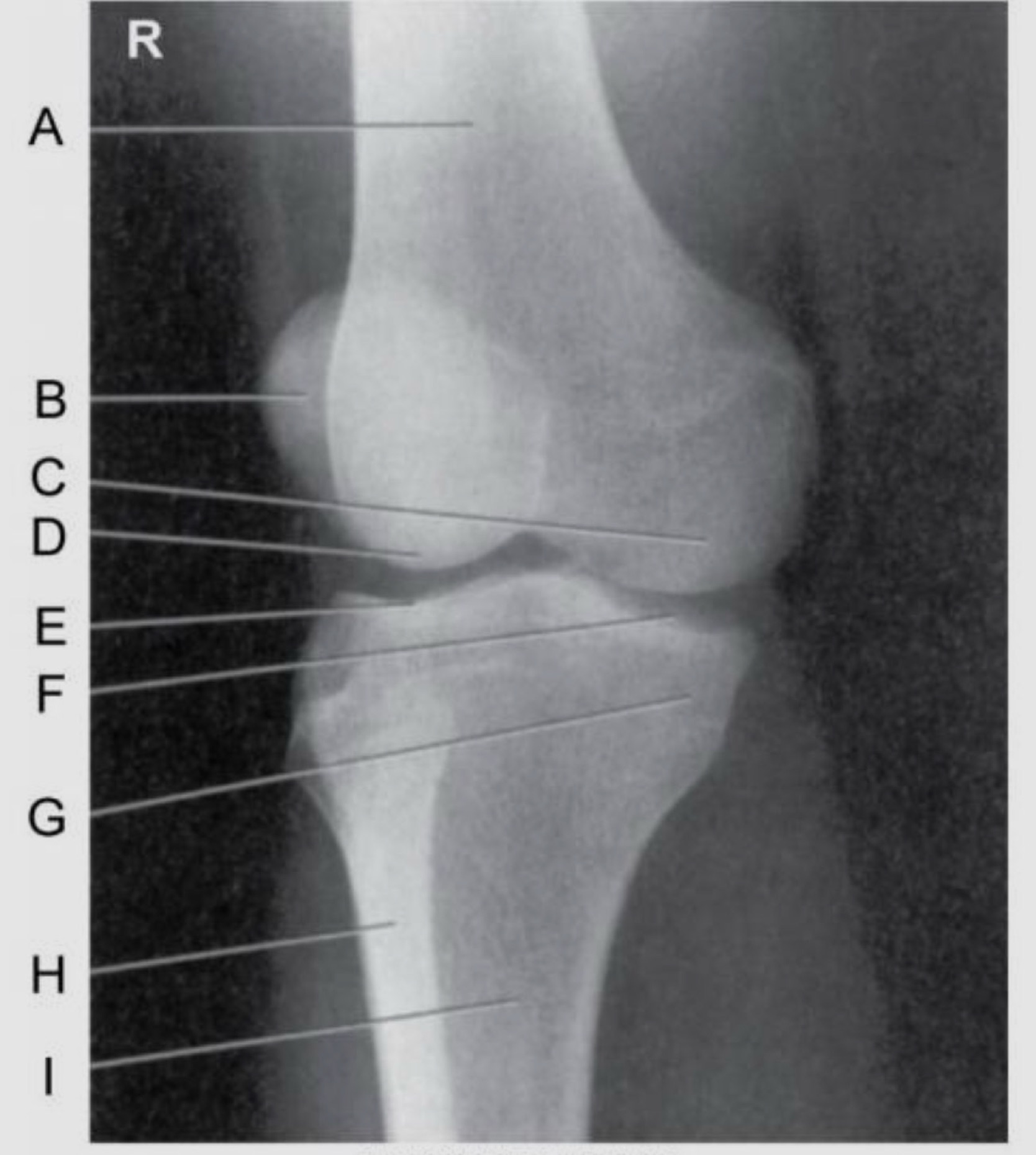
Label the image.
A) Femur
B) Patella
C) Medial femoral condyle
D) Lateral femoral condyle
E) Lateral tibial plateau
F) Medial tibial plateau
G) Medial tibial condyle
H) Fibula
I) Tibia
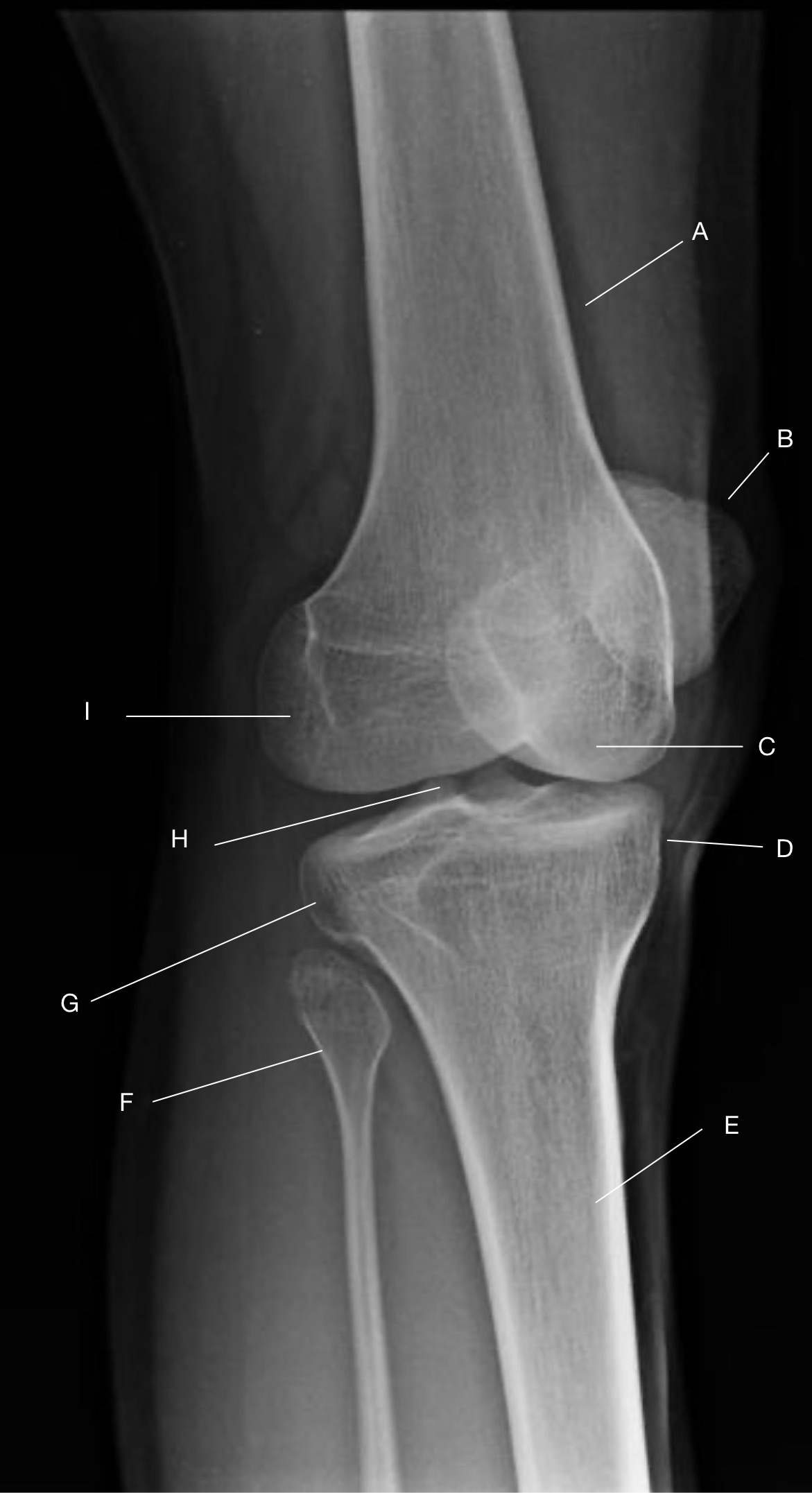
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
AP Internal (Medial) Oblique
No.
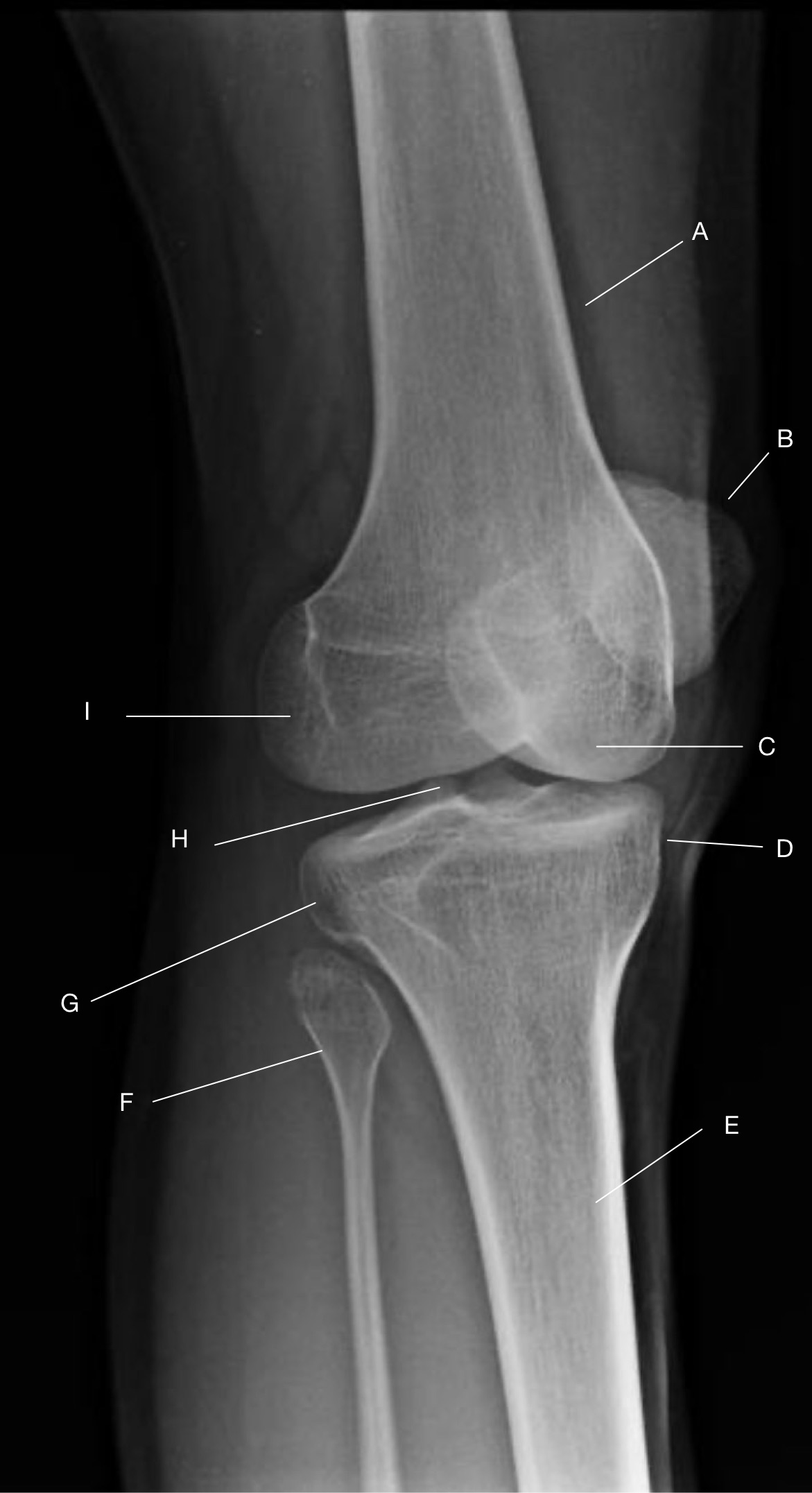
Label the image.
A) Femur
B) Patella
C) Medial femoral condyle
D) Medial tibial condyle
E) Tibia
F) Fibula
G) Lateral tibial condyle
H) Intercondylar eminence(s)
I) Lateral femoral condyle
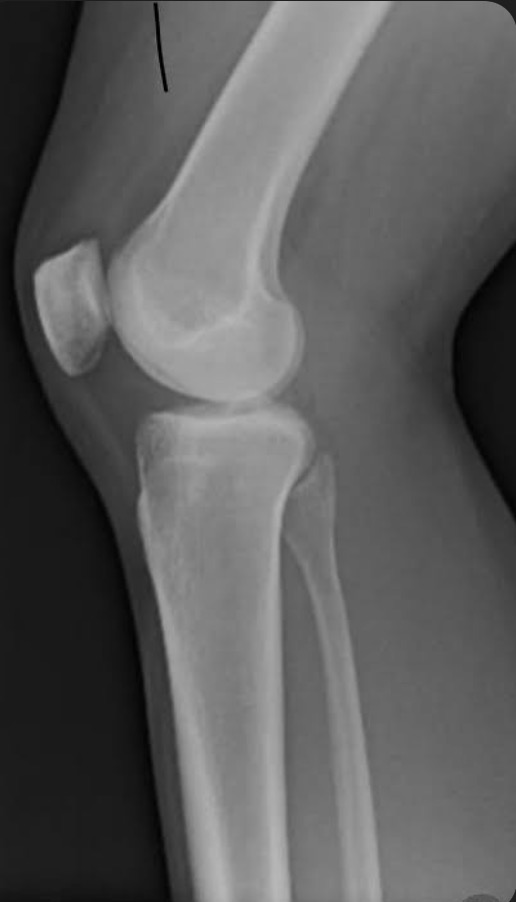
Name the projection.
Should it be repeated, if so why?
Lateral Knee.
No.
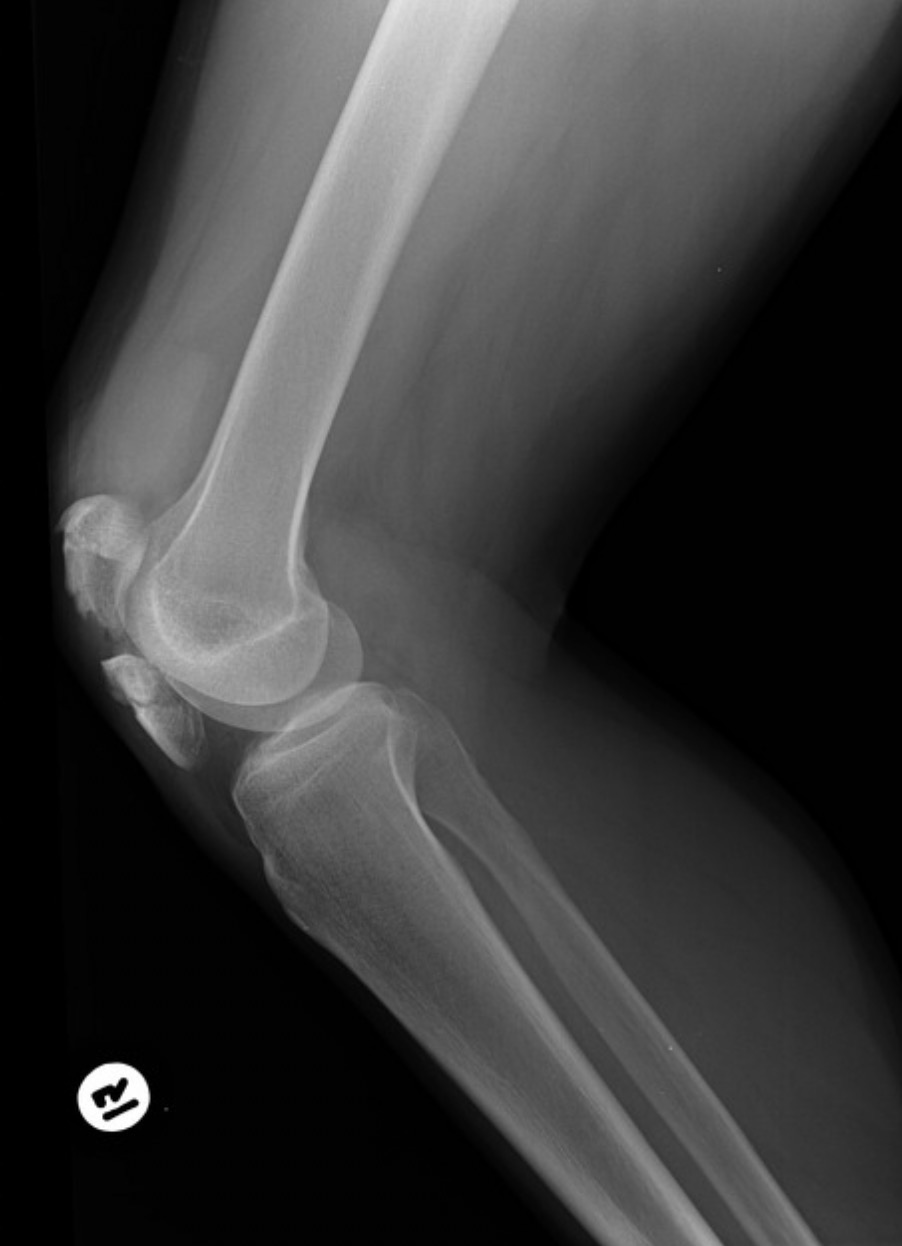
Ignoring pathology and other factors - Is the tube angled appropriately in this image?
No. The femoral condyles are not superimposed, indicating no tube angle.
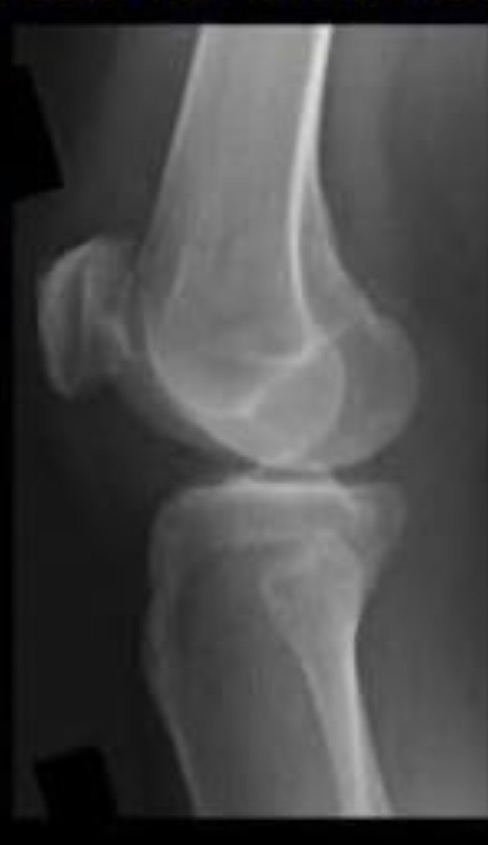
Is the patient in true lateral with proper tube angle? Explain.
True lateral: No. Patient is under rotated. Fibular head too anterior.
Tube angle: No. Femoral condyles not superimposed.
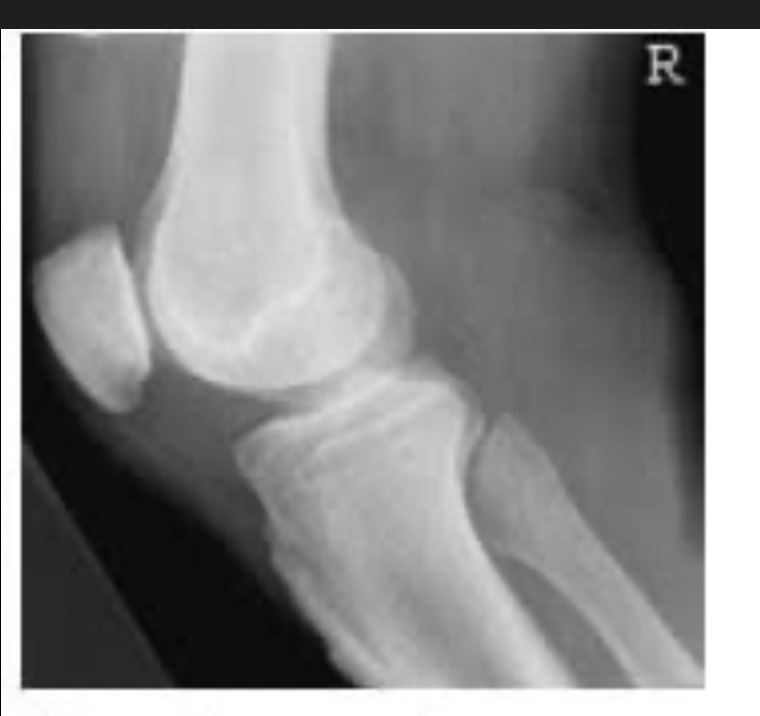
Is the patient in true lateral with proper tube angle? Explain.
True lateral: No. Patient is over rotated. Fibular head too posterior.
Tube angle: No. Femoral condyles not superimposed.