Microeconomics Chapter 3
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Perfectly Competitive Market
All Goods exactly the same
Buyers & sellers ao numerous that no one can affect market price— each is a “Price Taker”
Agents have NO Market Power
Quantity Demanded
The amount of good that buyers are willing and able to purchase
Law of Demand
the claim that quantity demanded of a good falls, when the price of the good rises, other things equal
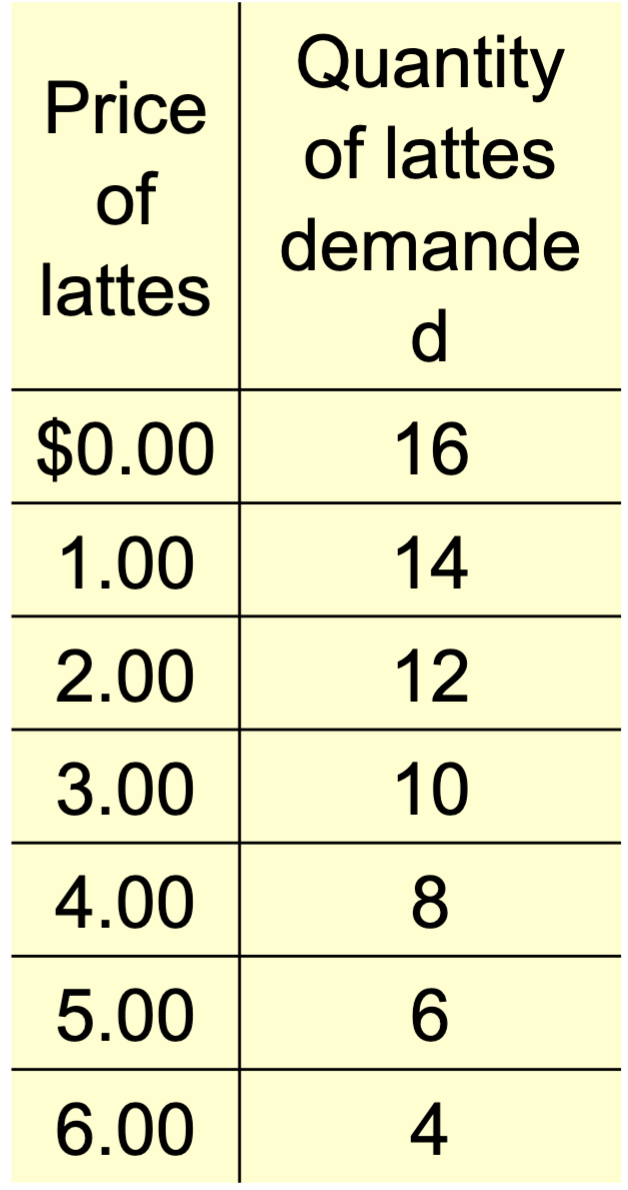
Demand Schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
Demand for a Normal Good
Is positively related to income
Increase in income cause increase in quantity demanded at each price , Shift D curves to the right
Demand for a inferior good
Is negatively related income
An increase in income shifts D curve for inferior goods to the left
Substitutes
Two goods are substitues if an increase in the price of one causes an increase in demand for the other.
Complements
Two goods are Complements if an increase in the price of one causes a fall in demand for the other
Quantity Supplied
The Quantity Supplied of any good is the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell
Law of Supply
the claim that quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises, other things equal
Supply Schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
Equilibrium Price
that price that equates quantity supplied and quantity demanded
Equilibrium Quantity
The Quantity Supplied and Quantity Demanded at the equilibrium price
Surplus (a.k.a. excess supply)
When Quantity Supplied is greater than Quantity Demanded.
Shortage (a.k.a. excess demand)
When Quantity Demanded is greater than Quantity Supplied
Change in Supply
A shift in the S curve occurs when a non-price determinant of supply changes (like technology or costs)
Change in Quantity Supplied
a movement along a fixed S (supply) curve occurs when P (price) changes
Change in Demand
a shift in the D (demand) curve occurs when a non-price determinant of demand changes (like income or # of buyers)
Change in Quantity Demanded
a movement along a fixed D curve occurs when P changes
Price Ceiling
a legal maximum on the price of a good or service
Example: Rent Control
Price Floor
a legal minimum on the price of a good or service