Biopsychology
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Biopsychology
The ways in which biological factors influence mental processes, emotions and behaviours.
What are the 2 major systems used to gain and respond to information from the environment
The nervous and endocrine system
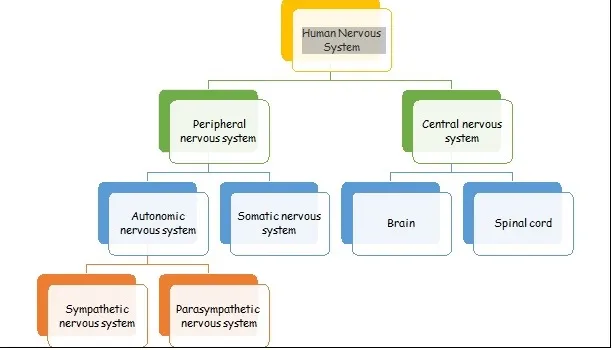
What diagram is this
The organisation of the human nervous system
What are the divisions/branches of the nervous system
The central and peripheral nervous system
What is the central nervous system (CNS)
It is the system that passes messages to and from the brain and connects nerves to the peripheral nervous system
What are the divisions of the central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord
The brain
The centre of conscious awareness, decision making and is involved in all psychological processes
What is the cerebral cortex
It is found in the brain and is what distinguishes our higher mental functions from those of animals
The spinal cord
It transports messages to and from the brain to the peripheral nervous system and is responsible for reflex actions.
What is the peripheral nervous system
The PNS transmits messages throughout the whole body from the brain and also relays messages back to the brain
What is the PNS made up of
31 spinal nerves, containing millions of sensory and motor pathways
What are the divisions of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Autonomic and somatic nervous system
What is the somatic nervous system (SNS)
It is a system that controls voluntary movements, and transmits and receives messages from the senses apart from sight
Why does the SNS not receive message from sight
Because the retina and optic nerve are connected directly to the brain
What are the two components that make up the somatic nervous system
The sensory pathway and motor pathway
What is the sensory (afferent) pathways
They bring sensory information towards the central nervous system
How does the sensory pathways work
The sensory receptors make up these pathways and trigger nerve impulses (action potentials) in sensory neurons
These neurons carry the sensory information into the spinal cord (CNS) via the spinal nerves (PNS)
In the spinal cord, they make synaptic connections on to the relay neurons that carry the information up to the spinal cord, to the brain where it is processed
What is the motor (efferent) pathways
They carry motor commands away from the central nervous system to the effectors
What are effectors and examples
Biological components that produce a response to a stimulus or signal, causing a physical or chemical change e.g. muscles, glands, cells, or molecules
How does the motor pathways work
The commands needed to move our muscles are formulated in the cerebral cortex of the forebrain
Then they travel down through the brain and spinal cord to the spinal nerves
The axons of motor neurons travel in spinal nerves out to the skeletal muscles of the body, allowing the brain to control bodily movement
What is the automatic nervous system (ANS)
It is a system that controls involuntary movements, and transmits and receives messages from the organs
How does the automatic nervous system work
It’s centres are located in the brain stem and the pathways run down through the spinal cord
These are then distributed throughout the body by the spinal nerves
What are other functions of the ANS
Plays a central role in states of bodily arousal
Responsible for vital functions such as heartbeat, digestions
It only has motor (efferent) pathways and operates automatically
What are the two branches of autonomic nervous system that helps it carry out its functions
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
What is sympathetic nervous system (SPNS)
It is involved in “the fight or flight response” and leads to bodily arousal like increased heart rate, blood pressure and a decrease in activity in the digestive system
What is Parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)
It is involved in “the rest and digest response” and leads to body relaxation like decreased heart rate, psychological calm, lower blood pressure and increase in digestive activity
What is a Neuron
Cells that make up the nervous system and are specialised for transmitting electrical impulses
What is the term for electrical impulses
Action potentials
Features of a neuron
Cell body, dendrites, axon, axon terminal, nucleus, myelin sheath and nodes of Ranvier
Cell body
It is a part of a neuron that contains the nucleus
Nucleus
Where most of the metabolic work of each
Dendrites
They receive action potentials from other neurons and direct these towards the cell body
Axon
It carries the action potentials away from the cell body towards other neurons
Myelin sheath
A fatty substance that covers the axon and increases the speed at which action potentials travel
nodes of Ranvier
Breaks of between 0.2 & 2mm in the myelin sheath that speeds transmission of action potentials as they “jump” from node to node
Axon terminal
Where the neuron will synapse with another neuron or an effector
The three types of neuron
Sensory, relay and motor
Sensory neuron
Carries signals from receptors to spinal cord and brain
Relay neuron
Carries messages from one part of the CNS to another
Motor neuron
Carries signals from the CNS to effectors
Locations of the 3 types of neurons
Sensory and motor is located in the PNS and relay is located in the CNS
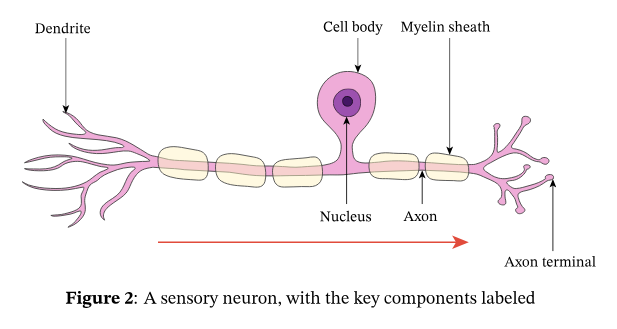
What neuron is this
Sensory neuron
How the sensory neuron works
They receive signals from receptors that detect external stimulation
These signals enters through the dendrites
Passes it to the cell body via the axon and onto the axon terminals where they connect to other neurons
Dendrites and axons of sensory neuron
They have long dendrites and short axons
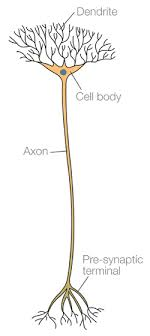
What neuron is this
Relay neuron
How the relay neuron works
They form connections between other neurons
How many relay neurons are in the body
more than 100 billion
Dendrites and axons of relay neuron
They have short dendrites and short axons
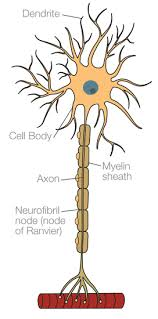
What neuron is this
Motor neuron
How the motor neuron works
Information enters motor neurons from the dendrites
It is then passed all the way along the axon terminals
If the motor neuron connects with a muscle the axon terminal will be called a motor end plate
Dendrites and axons of a motor neuron
They have short dendrites and long axons
Synaptic transmission
The process by which one neuron communicates with another
The process of Synaptic Transmission
The neurons connect but do not make direct contact as there is a small gap between them called synapse
Information is passed down the axon of the neuron as an action potential
Once the action potential reaches the end of the axon it needs to cross the gap between the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neuron which is the synaptic gap
In the axon terminal are synaptic vesicles which contains chemicals called neurotransmitters
When the action potentials reaches these synaptic vesicles, they release neurotransmitters that carry signals that diffuse across the synaptic gap
They bind to receptor sites on the post-synaptic cell that then becomes activated
Once the receptor sites have been activated, they either produce excitatory or inhibitory effects on the post-synaptic cell
Excitatory neurotransmitters
They are chemicals like glutamate which cause the neuron to become positively charged, making it more likely to fire
The term for when the neuron becomes positively charged or less negatively charged
Depolarisation
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
They are chemicals like GABA that cause the neuron to become negatively charged, making it less likely to fire
The term for when the neuron becomes negatively charged or less positively charged
Hyperpolarisation
Summation
The addition of positive and negative post-synaptic potentials
Explain the net effect
When the positive and negative potentials a cell receives are summed
Excitation
Occurs when receptor stimulation results in an increase in the positive charge of the postsynaptic neuron which increases the likelihood of the neuron firing
Inhibition
Occurs when receptor stimulation results in an increase in the negative charge of the postsynaptic neuron which decreases the likelihood of the neuron firing
Endocrine system
It secretes the hormones required to regulate many bodily functions into the bloodstream including growth and reproduction
What nervous system is the endocrine system part of?
It is not part of the nervous system but it interacts with the PNS
Glands that make up the endocrine system
Pituitary, pineal, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas and gonads
What does the pituitary gland secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes various hormones that controls reproduction, metabolism, growth and other vital functions
What does the pineal gland secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes hormone melatonin which regulates the body’s internal clock to control sleep-wake cycles
What does the thyroid gland secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) to regulate metabolism, body temperature, heart rate and growth
Releases calcitonin to help regulate calcium levels
What does the adrenal gland secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes hormones like adrenaline, noradrenaline etc to regulate a wide range of bodily functions including blood pressure, blood sugar, metabolism and stress response
What does the pancreas secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar
Releases somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide to help control absorption of nutrients and release of digestive hormones
What does the gonads secrete into the bloodstream and its function
Secretes steroid and protein hormones that are essential for developing and maintaining reproductive organs, regulating sexual characteristics and enabling reproduction
What is the endocrine system controlled by?
The hypothalamus
Location of the hypothalamus
In the midbrain and directly connected to the pituitary gland
Function of the hypothalamic hormones
Stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete its hormones
Why is the Pituitary gland classed as the ‘master gland’
Because the hormones secreted by this gland control the functioning of other endocrine glands
Direct effects of adrenaline on the body
Increases heart rate to increase blood flow to organs and increase movement of adrenaline around the body
Increases respiration and sweating to regulate temperature
Increases breathing rate to increase oxygen intake
Increases blood and oxygen to brain for rapid response planning
Increases blood to skeletal muscle for physical action
Diverts blood flow from the skin, kidney and digestive system to increase energy for other essential functions
Pupil dilation to increase light entry into the eye and enhance vision
General effects of adrenaline on the body
Prepares the body for action (fight or flight)
Increase blood supply
Increases oxygen intake
What happens when the threat has passed
The parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to its resting state
What Taylor et al. (2000) fight or flight research suggests females do
Women are more likely to protect their offspring and form alliances with other women - they adopt a ‘tend and befriend’ response, in dangerous situations