dialysis and renal dosing
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
brady, renal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
renal drug excretion is the major route for which types of drugs
polar drugs
water soluble drugs
drugs with low molecular weight
drugs that are biotransformed slowly
drugs are excreted though the kidney into the urine by…
glomerular filtration
active tubular secretion
tubular reabsorption
glomerular filtration is a ___ process
passive
glomerular filtration depends on ___ and ____
GFR(CLGFR) and the fraction of the drug not bound to plasma proteins
fu stands for
fraction of drug not bound to plasma protein
equation for glomerular filtration
CLGFR=GFR x fu
active tubular secretion is carrier mediated that requires ___
energy
how many tubular secretion pathways are there in the kidneys
2
examples of weak acids that go through active tubular secretion pathways
probenecid
penicillin
examples of weak bases that go through active tubular secretion pathways
cimetidine and creatinine
tubular reabsorption is a ___ process
passive
tubular reabsorption depends on
degree of lipophilicity
degree of ionization (pka and pH)
urine flow rate
increased urine flow rate due to diuretics will lead to an ____ in the time for drug reabsorption
decrease
what are the indexes of renal function
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
creatinine clearance (CrCl)
drugs are usually filtered though the glomerulus in a nonselective process if they are in _____ form
free, non-protein bound
units of renal function are expressed in
volume per time
what is the best overall index of renal function in health and disease
glomerular filtration rate
glomerular filtration can be directly measured but…
collection is often unreliable
GFR is estimated based on…
substances that are filtered in the glomerulus
GFR can be estimated based on the substances that are filtered in the glomerulus but they must be ____ and must have ____
freeely filtered
minimal secretion/reabsorption in the renal tubules
what is most commonly used to estimate GFR
creatinine clearance
what is the basis for most renal dosing recs on package inserts
creatinine clearance
creatinine is a metabolic product of ____
muscle
the rate of creatinine formation determined by ____
muscle mass or lean body weight
creatinine is distributed in ____
total body water
creatinine is not bound to ____
plasma proteins
creatinine is freely filtered at the ____
glomerulus
options for measuring creatinine
24 hour urine collection, the serum creatinine sample is taken at midpoint of the urine collection period
serum creatinine

what is this equation used for? (note this equation is given on the test, need to know how and why to use)
used to estimate of renal function from timed urine collection
what are the equation options for estimating renal function at steady state SCr concentrations
crockcroft gault equation
MDRD equation
CKDEPI
crockcroft gault estimates ___ and is the most commonly used for medication adjustments
creatinine clearance
MDRD equation can estimate ___
GFR
CKD-EPI equation estimates ___ and is more accurate than ___ equation
GFR;
MDRD
which equation should be used for estimation of renal function in pts with non steady state SCr concentrations
jelliffe equation
which equation should be used to estimate renal function in pts who are obese
salazar and corcoran equation
male IBW formula (not given)

female IBW formula (not given)

when to use the actual body weight
ABW<IBW
when to use adjusted body weight
when ABW is > 120% of IBW
adjusted body weight formula (not given)
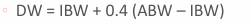
if you were to use the jelliffe equation you would first need to estimate…
creatinine production
after estimating the creatinine production using the jelliffe equation, you then need to…
correct Cr production for renal function and adjust the estimated CrCl value based on if the function is getting better or worse
what are the 3 approaches to dose modification for pts with renal insufficiency
Decrease the drug dose and retain the usual dosage interval
Retain the usual dose and increase the dosage interval
Simultaneously decrease the dosage and prolong the dosage interval
dose modification for pts with renal insuff depends on…
route of administration, the dosage forms available, and the pharmacodynamic response to the drug
factors to consider when adjusting doses for renal insuff pts
crcl is a starting point
toxicities
clinical conditions
which meds commonly need renal adjustments
most antibiotics
some diabetes meds
lovenox (enoxaparin)
crestor (rosuvastatin)
brand name of enoxparin
lovenox
brand name of rosuvastatin
crestor
meperidines metabolite (normeperidine) is____ and can lead to ____
neurotoxic; seizures
NSAIDs ___ diuretic response and ____ risk of hyperkalemia if taken with K+ sparing diuretics, ACEis, or ARBs
decrease; increase
chlorpropamide has an _____ half life when taken by pts with renal insuff
increased
metformin renal dosing is based on ____
GFR
pts with renal insuff have ____ clearance of exogenously admin insulin
decreased
AMGs and vanco need renal adjustments bc…
they tend to accumulate and can lead to nephrotoxicity
cimetidine, triamterene, and trimethoprim all ____ of Cr so they lead to a rise in SCr
inhibit tubular secretion
cimetidine, triamterene, and trimethoprim all inhibit tubular secretion of Cr so they lead to…
a rise in SCr
HD depends on
Membrane composition and surface area
Blood and dialysate flow rate
Duration of dialysis treatment
Number of times dialyzer has been use
flow of blood through the dialyzer (QD) varies from ____
100-400 mL/min
increased blood flow rates occurring in HD will lead to
deliver greater amounts of drug to the dialysis membrane
what 4 things determine the dialyzability of a drug
Molecular weight
Water/lipid solubility
Plasma protein binding
Volume of distribution
which sized molecules are more easily removed
small ones (<500 Da)
to be dialyzied a drug has to be ____ in the dialysate solution
soluble
Water ____molecules will tend to remain in the blood compartment rather than diffusing into the dialysate
insoluble
what is the most important determinant of a drug’s dialysance
plasma protein binding
Only _____ (bound or unbound) drug molecules can pass through the pores in the semipermeable dialysis membrane
unbound
Small volumes of distribution (< 1 L/kg) usually demonstrate _____ dialysis clearance rates
high
examples of drugs with small volumes of distribution
AMGs and theophylline
Large volumes of distribution (> 2 L/kg) are generally, _____ for removal by dialysis
NOT available
examples of drugs with large volumes of distribution
digoxin and tricyclic antidepressants
fick principle
arterial-venous difference
dialysance directly measures the efficiency of…
extraction
what is ultrafiltration
Net loss of blood as it passes through the unit
if ultrafiltration leads to the venous blood sample being…
concentrated, artificially elevated
if ultrafiltration occurs it leads to the dialysance being
underestimated
measurements of dialysance can be wrong up to
30% off of what it should be
which parameter is used to predict the time required to remove a given fraction of drug from the body
half life
T or F: Whatever affects half-life of a drug during a dialysis period will influence how effectively dialysis removes a given fraction of drug from the body
T
T or F: Shortest half-life gives largest fraction removed
T
what determines half life
clearance, Volume of distrib