Muscle Anatomy and Movements: Key Terms and Definitions
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
Epimysium
Covers the entire muscle
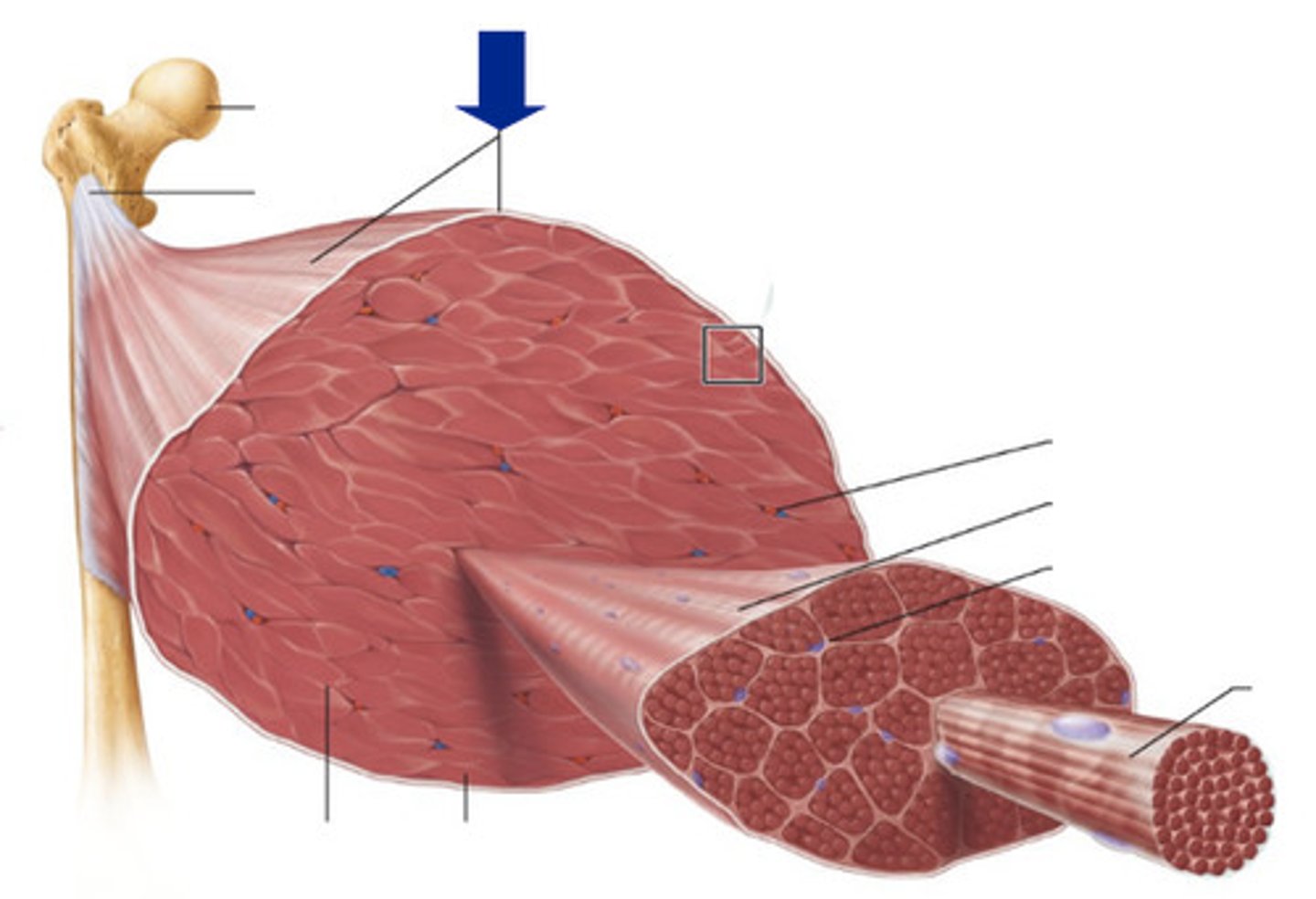
Fascicles
A group of muscle cells surrounded by Perimysium

Perimysium
Covering of fascicles
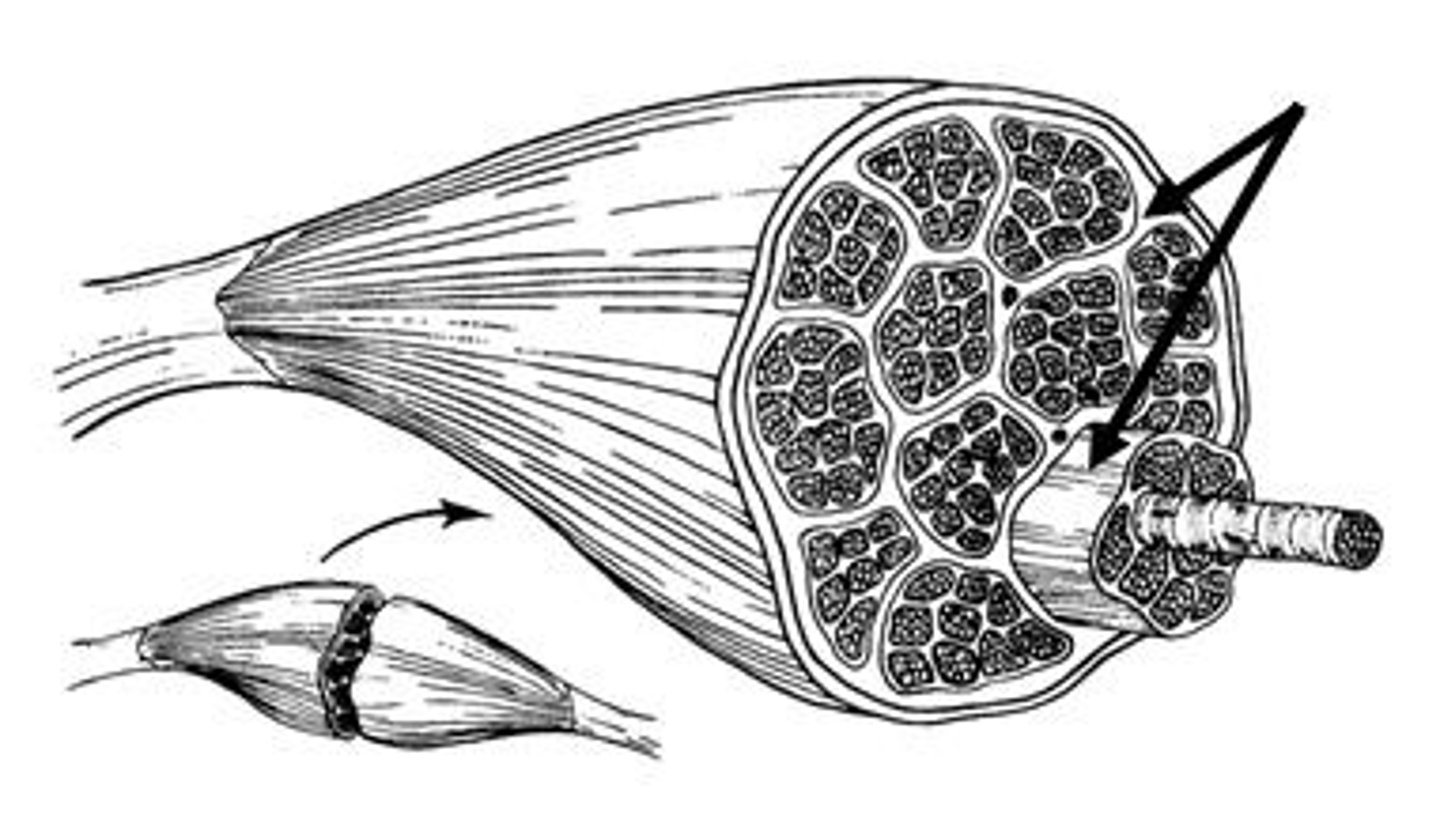
Muscle fiber
A single muscle cell
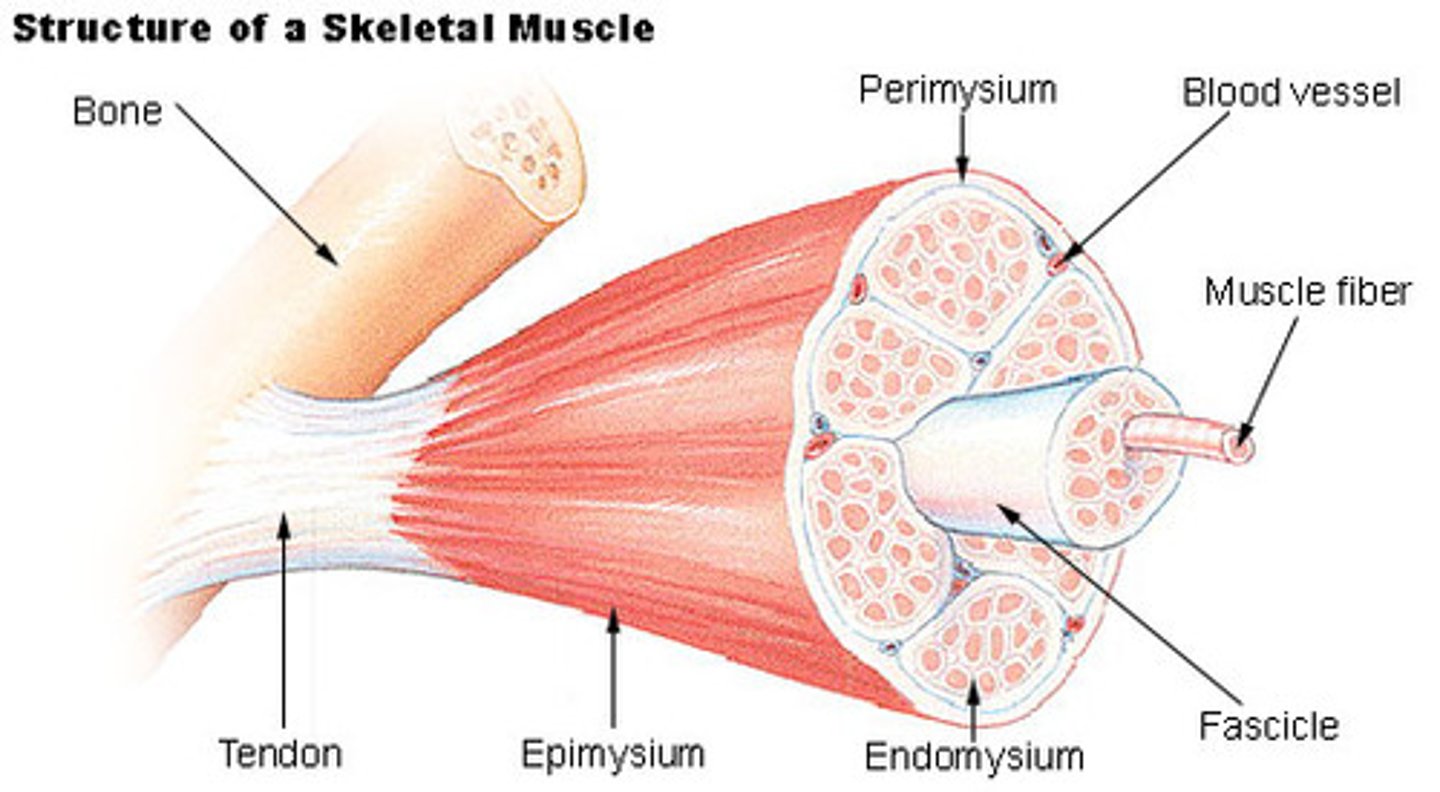
Endomysium
covering of a single muscle cell
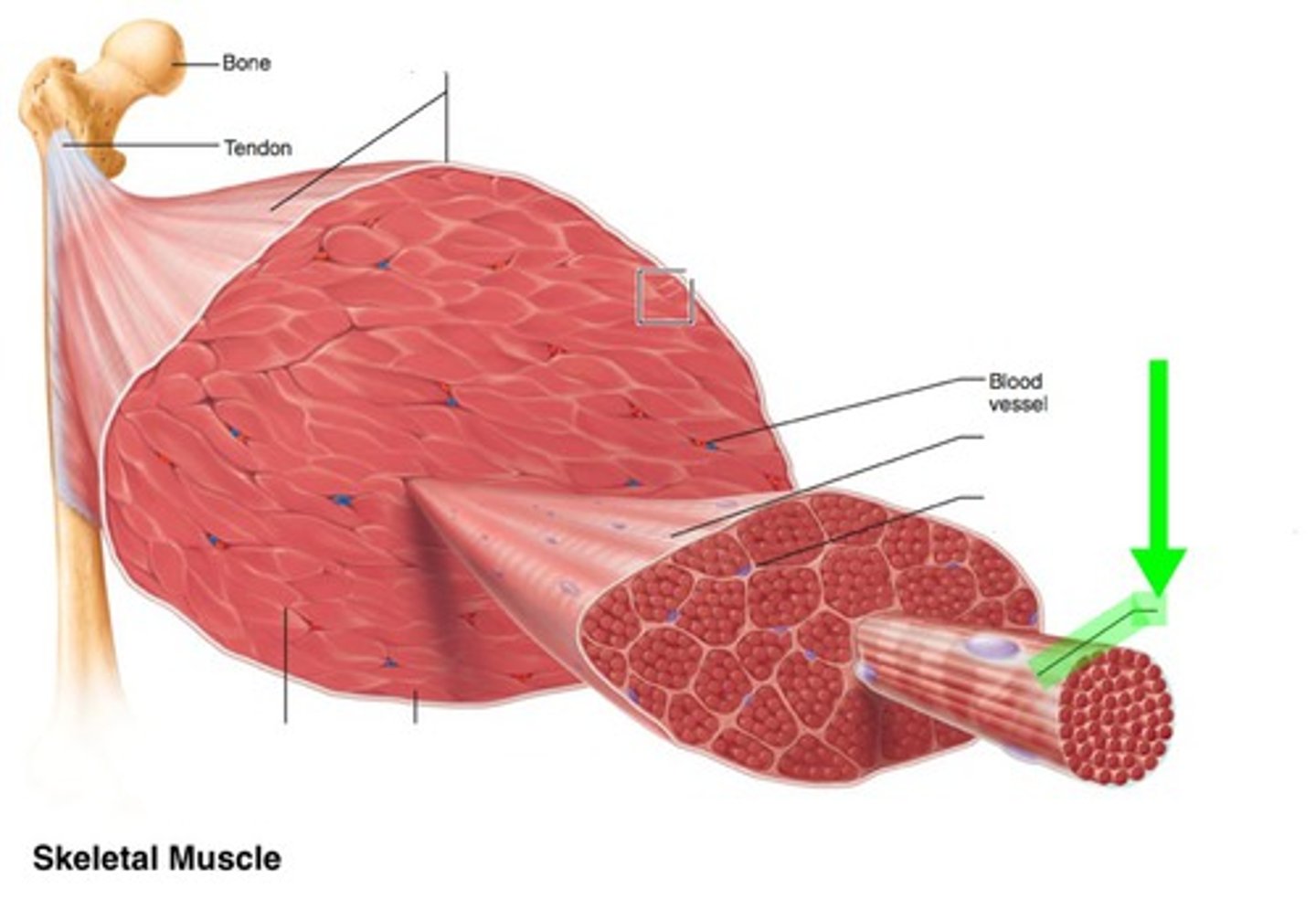
tendon
Attaches muscle to bone
Aponeurosis
A fibrous or membranous sheet connecting a muscle to the part it moves
Origin
Attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a movable bone or the end opposite the origin
action
what the muscle does
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
extention
increases joint angle
Hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
Rotation
CIRCULAR MOVEMENT AROUND AN AXIS
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
plantar flexion
bends the foot downward at the ankle
Agonists
A contraction that generates movement
Antagonists
relaxation required for movement
Synergists
Contract with the agonist to aid movement
Fixators
Synergists that stabilize joints
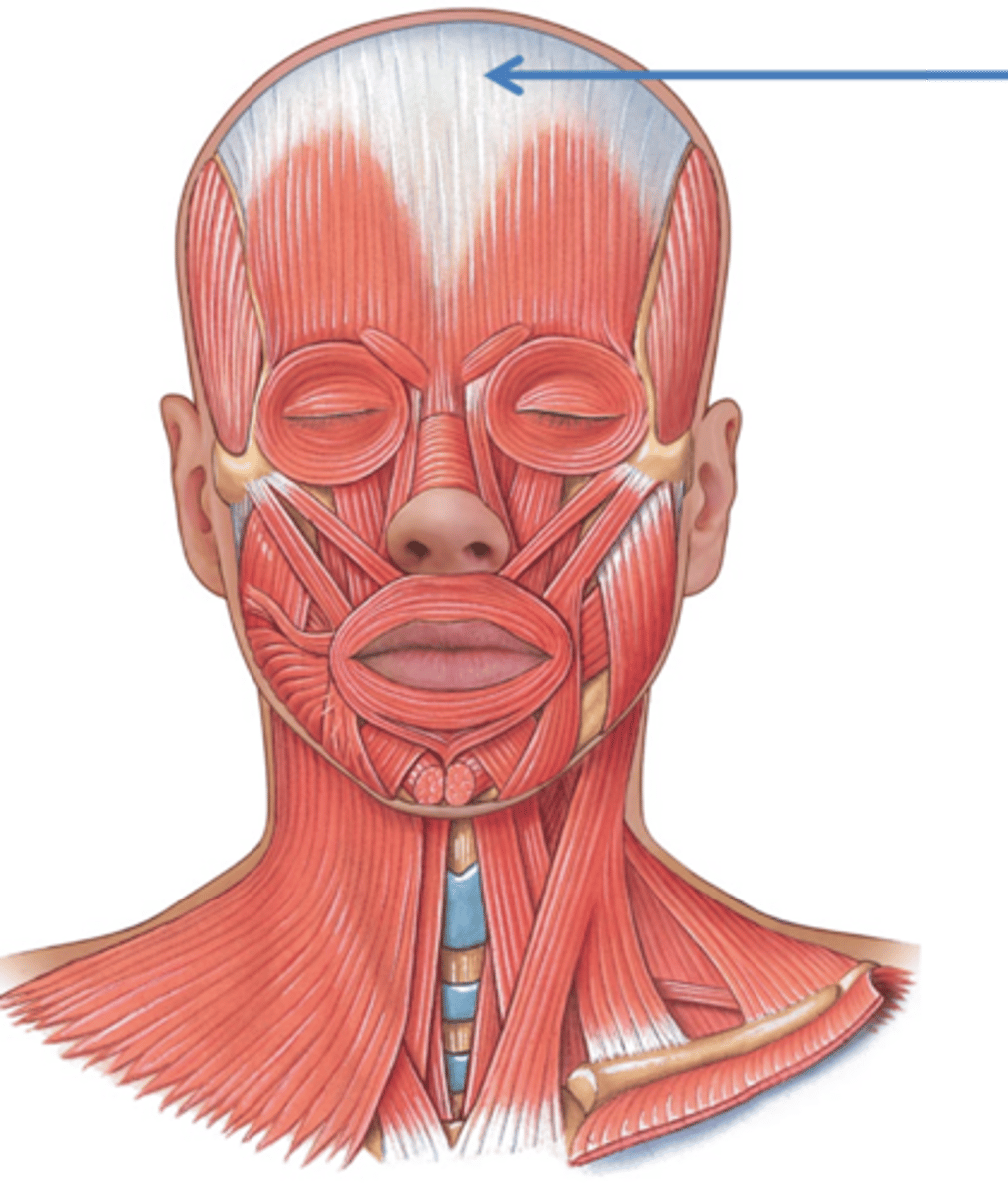
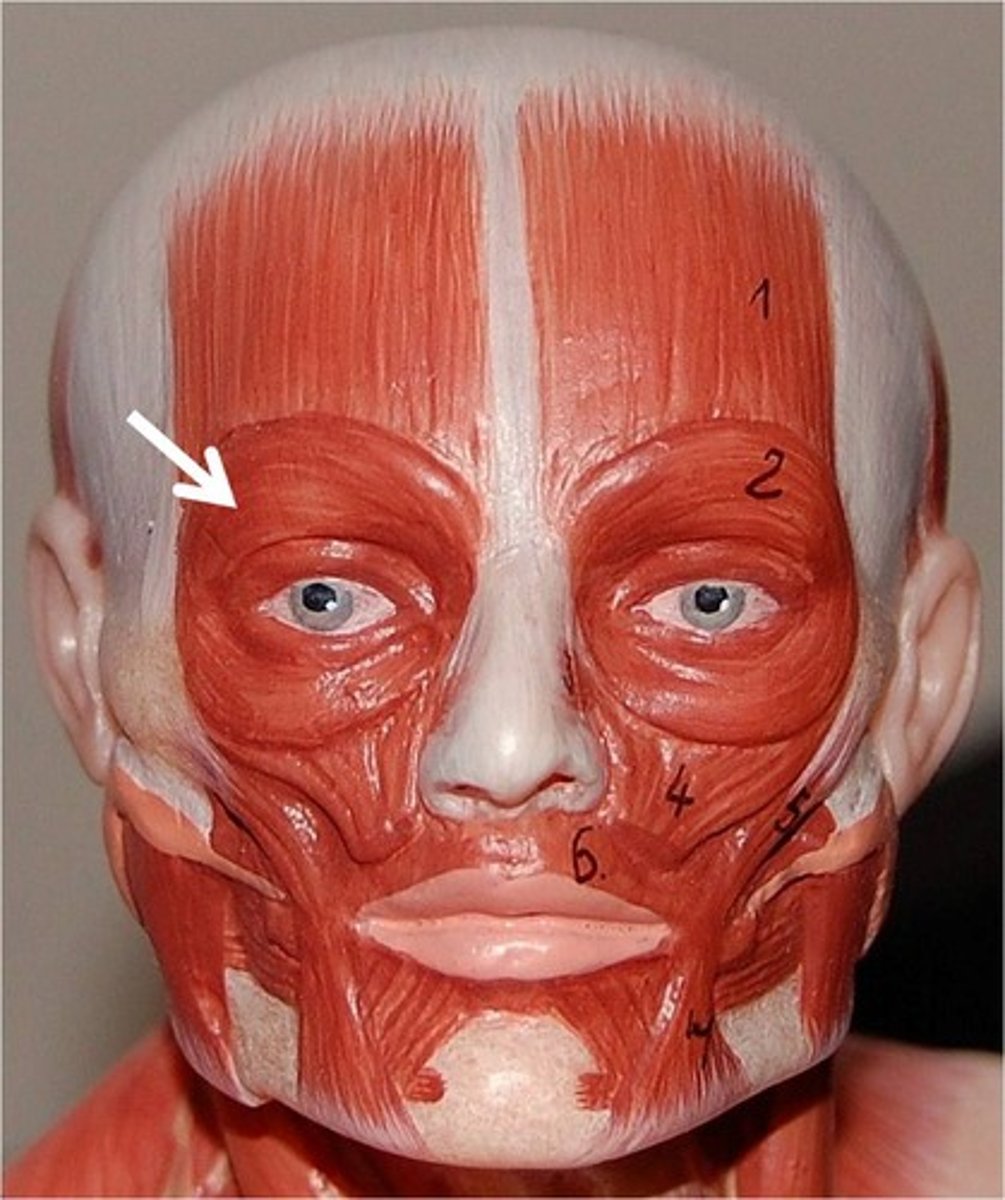
orbicularis oculi
closes eye
orbicularis oris
kissing muscle

masseter
prime mover of jaw closure

temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible

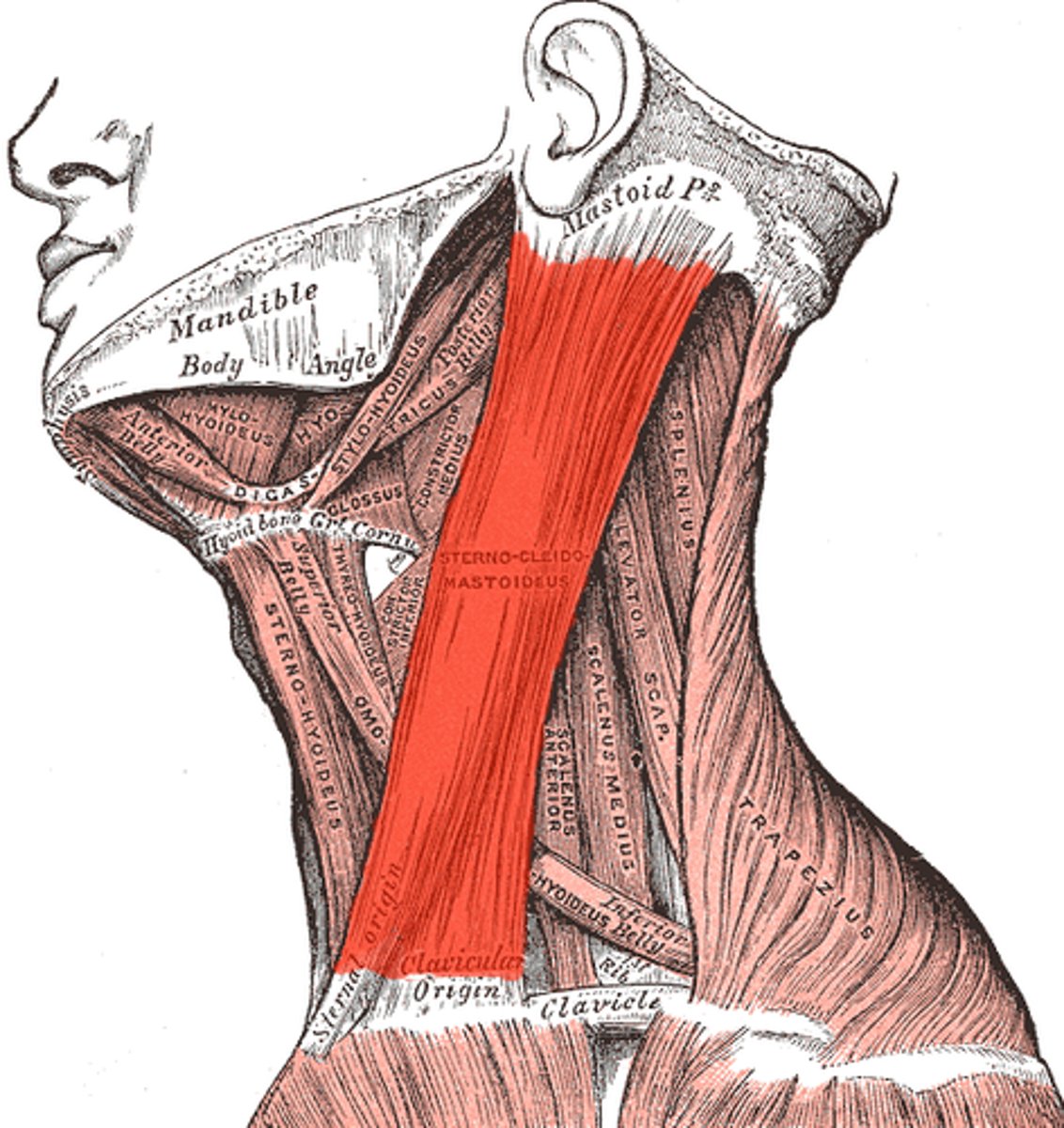
sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck; rotates head
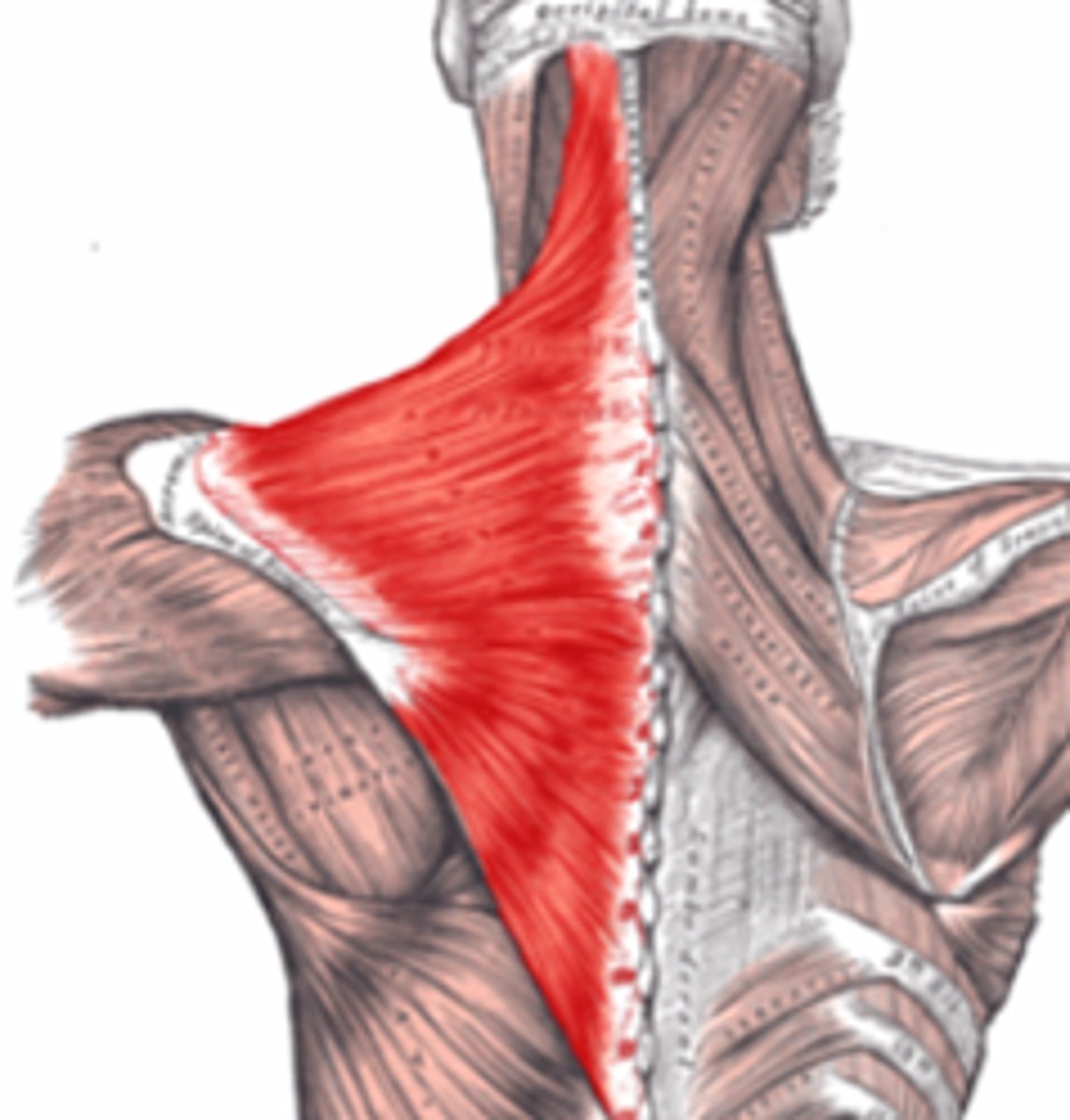
trapezius
upper back
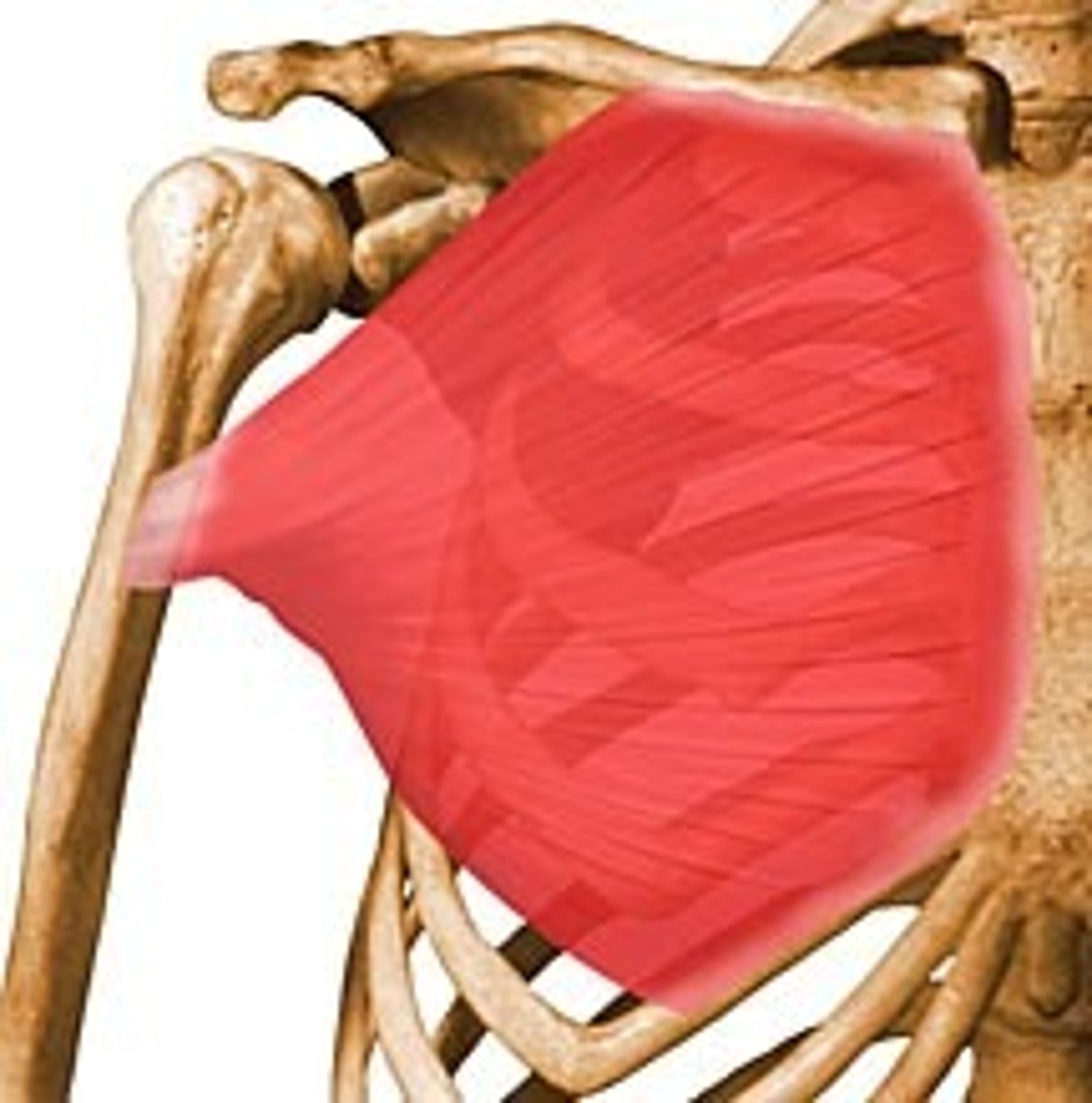
pectoralis major
Adducts and flexes humerus
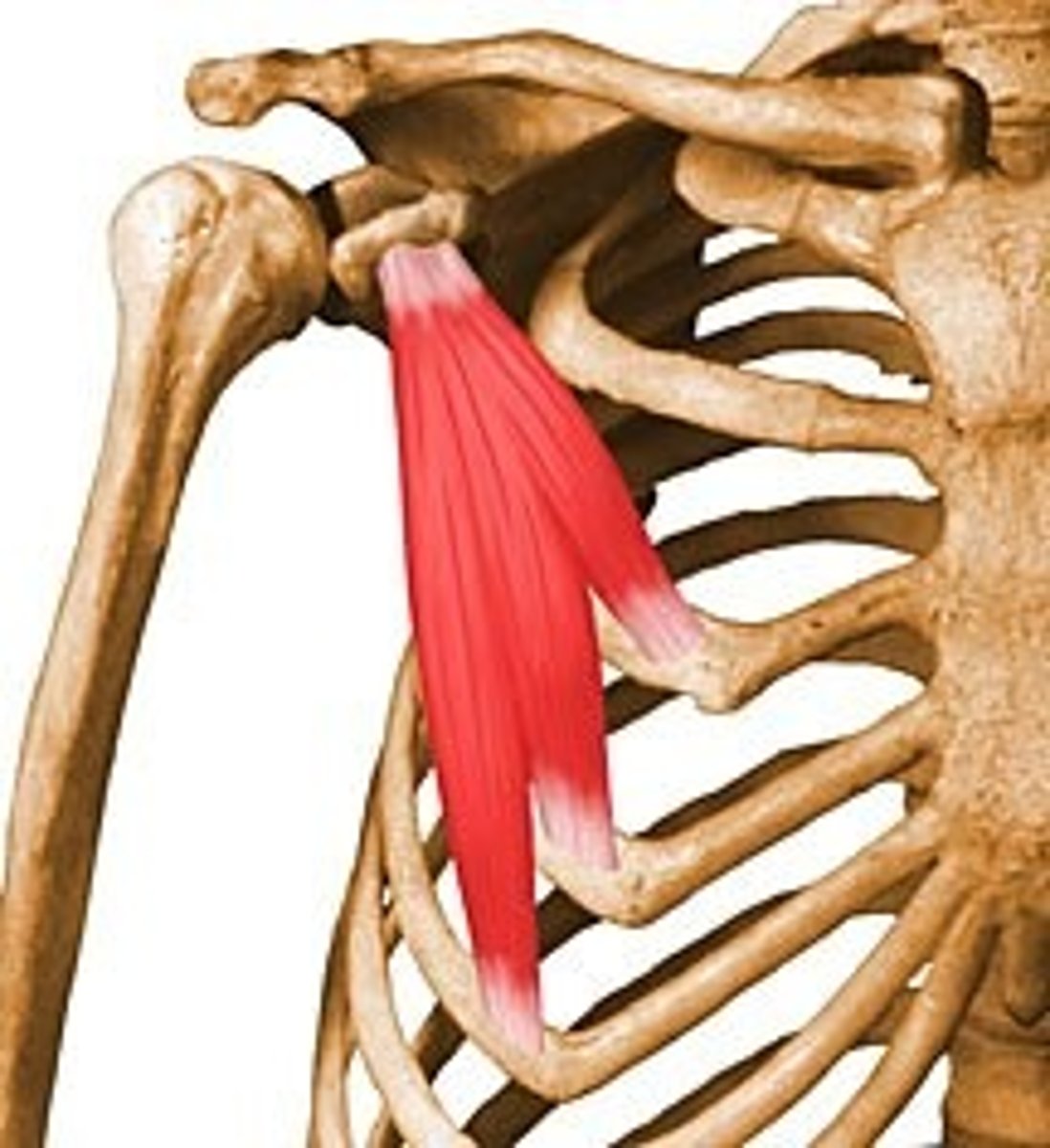
pectoralis minor
protracts and depresses scapula
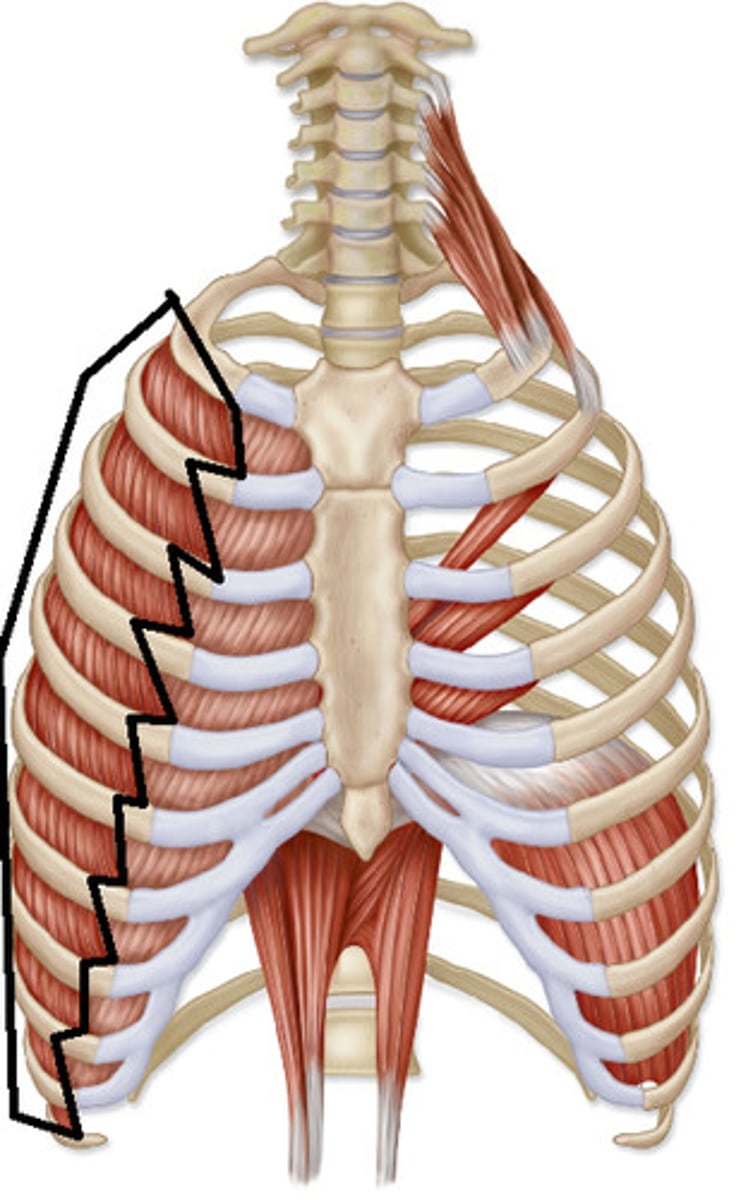
internal intercostals
depress ribs
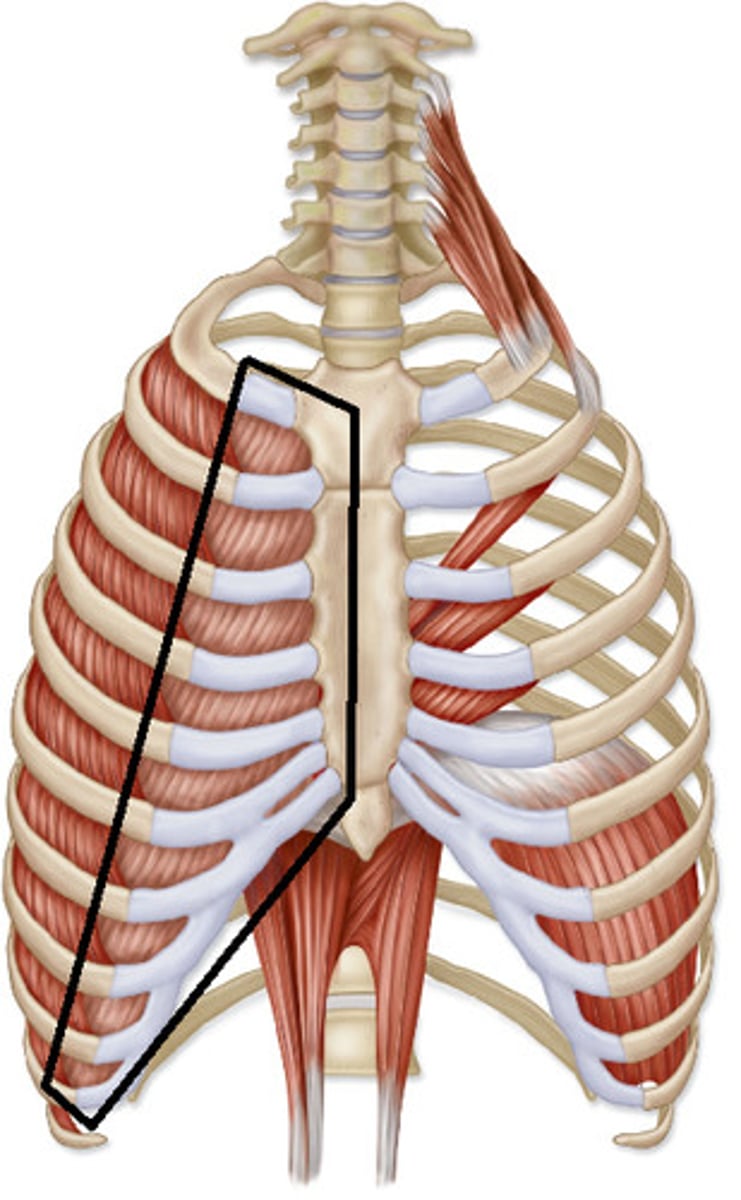
external intercostals
elevates ribs
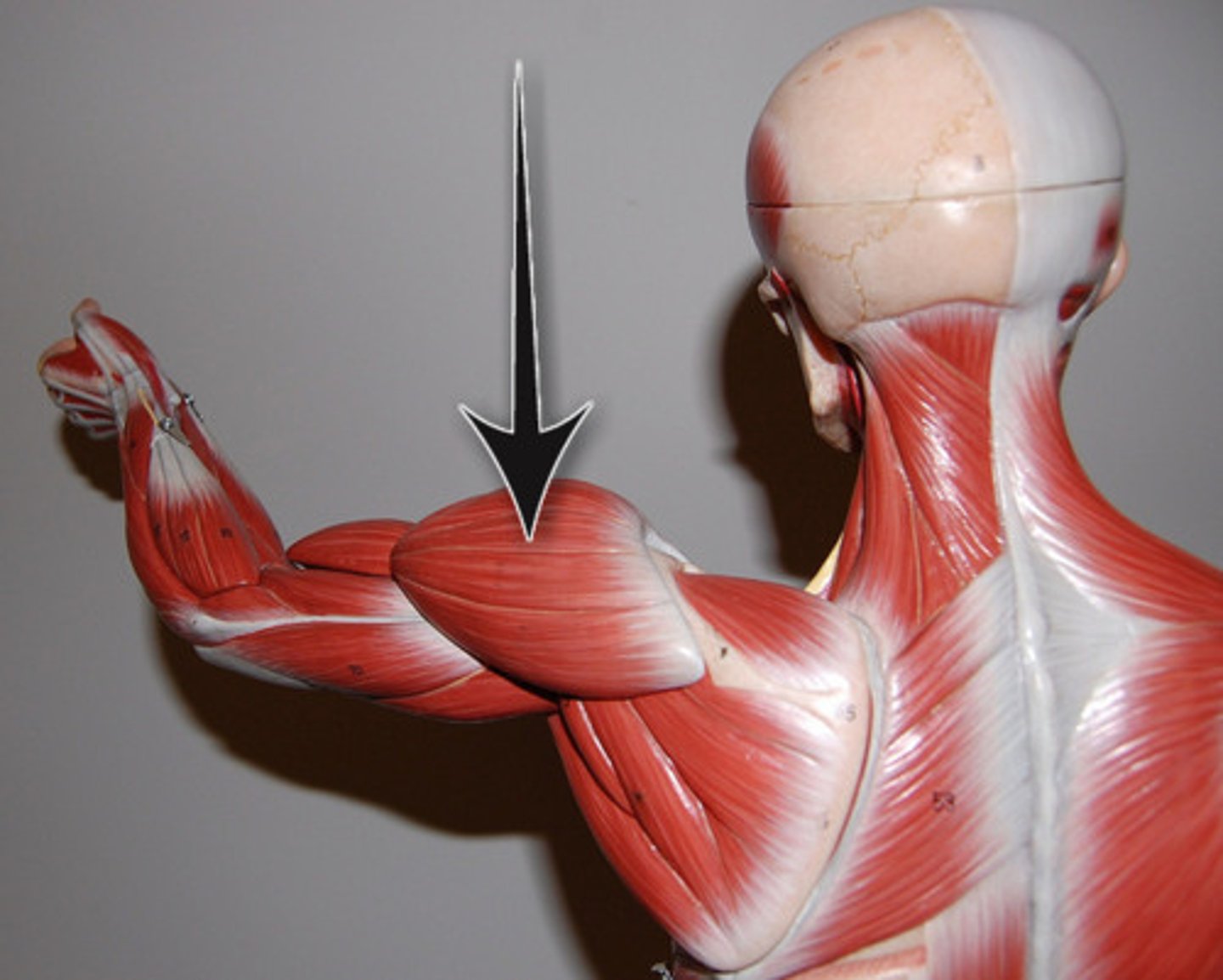
deltoid
abducts arm
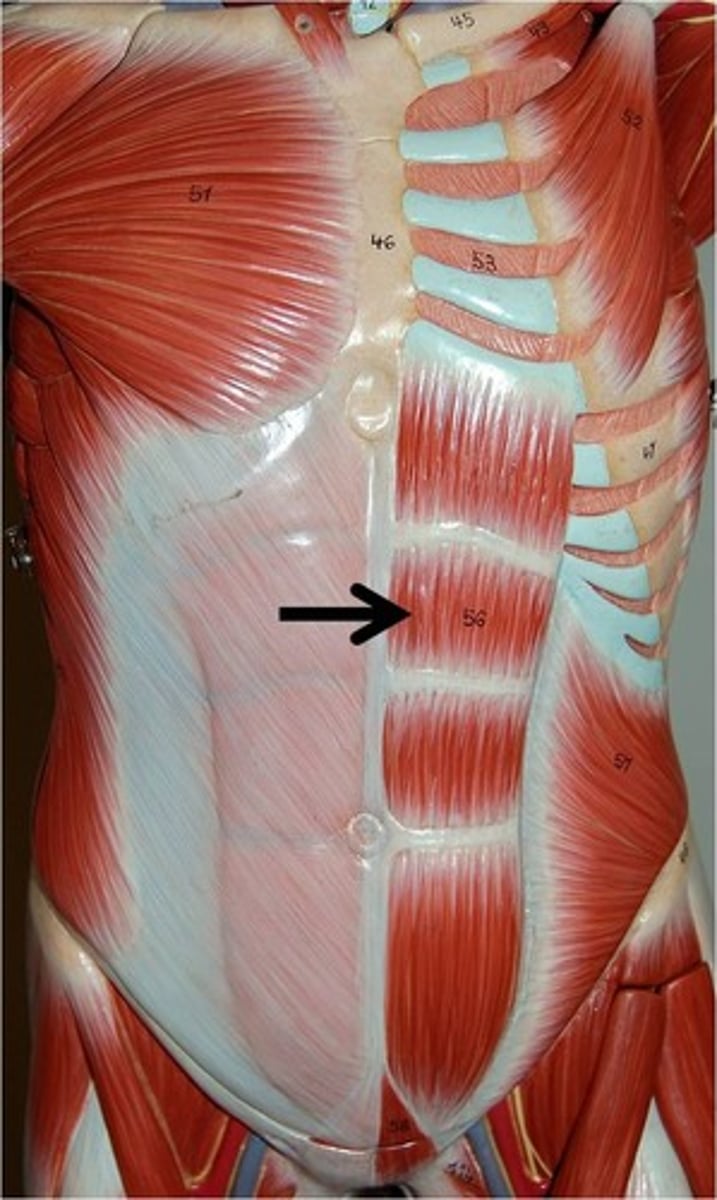
rectus abdominis
flexes vertebral column
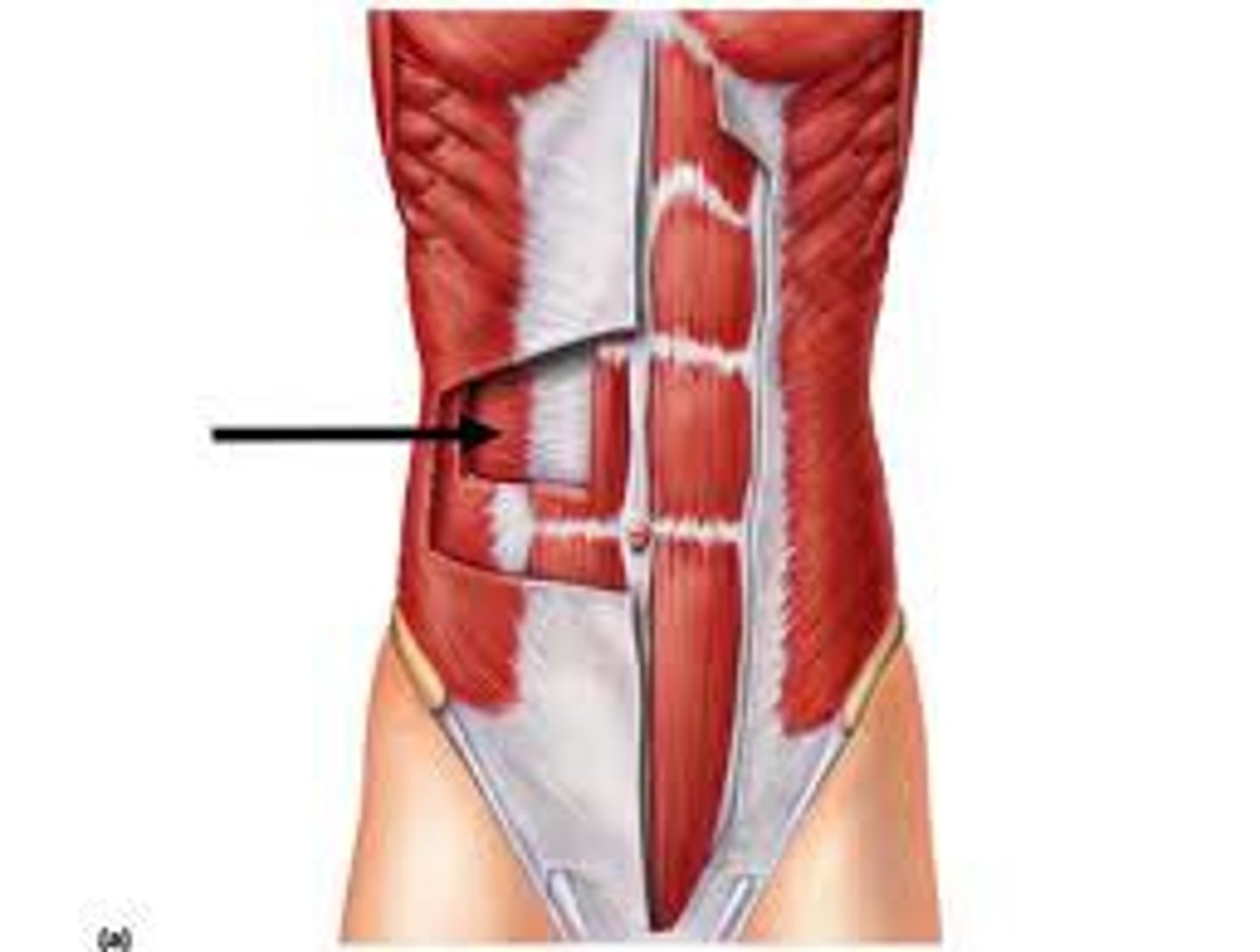
external oblique
compresses abdomen

internal oblique
compresses abdomen

transversus abdominis
compresses abdomen
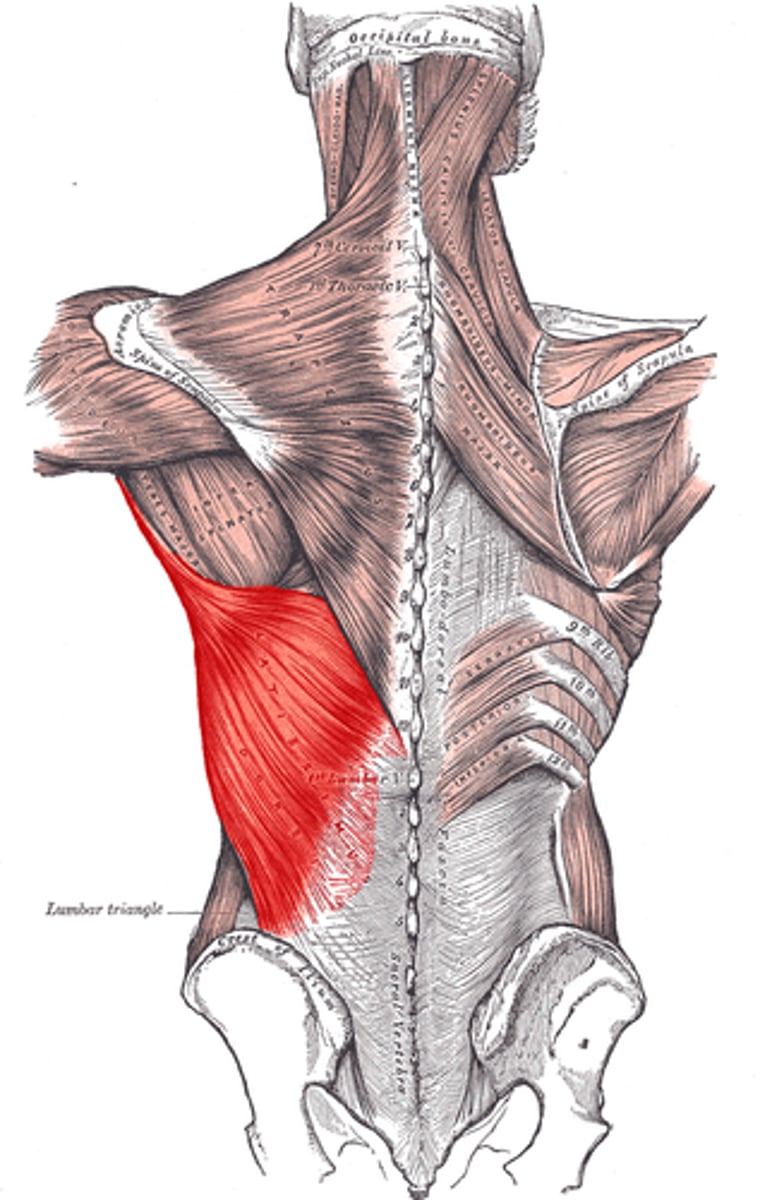
latissimus dorsi
extends and adducts humerus
triceps brachii
extends forearm at elbow
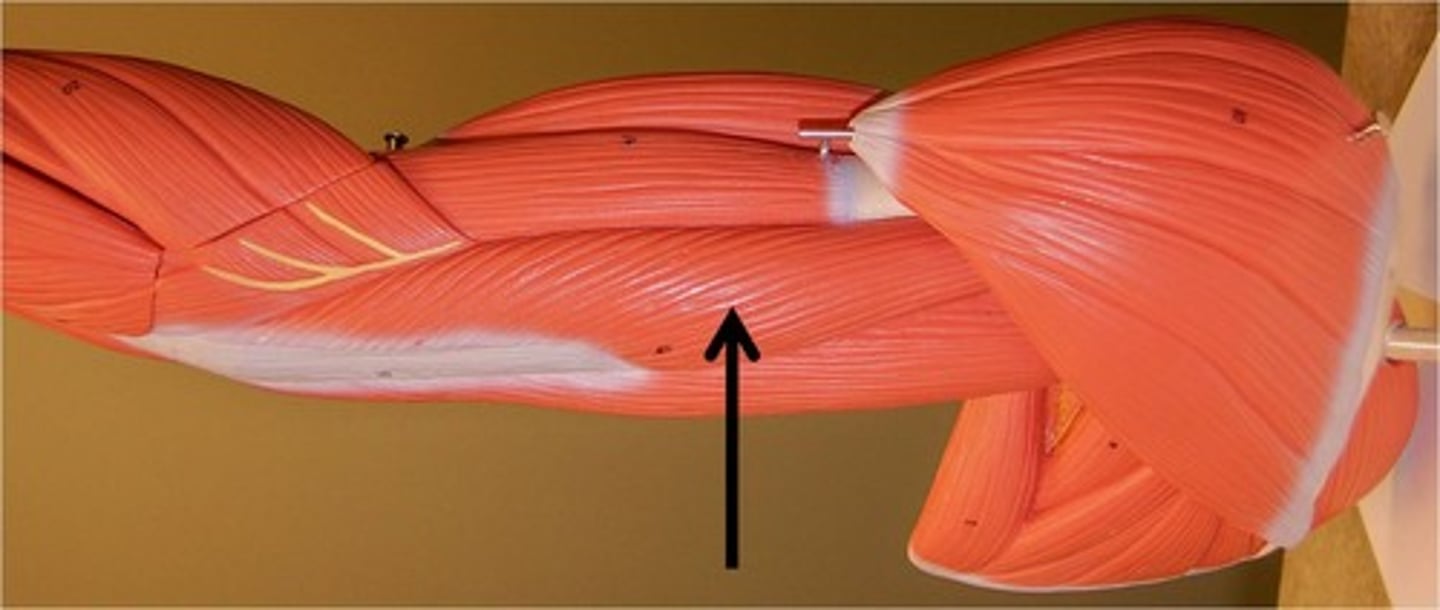
humorus
triceps brachii origin
olecranon process of ulna
triceps brachii insertion
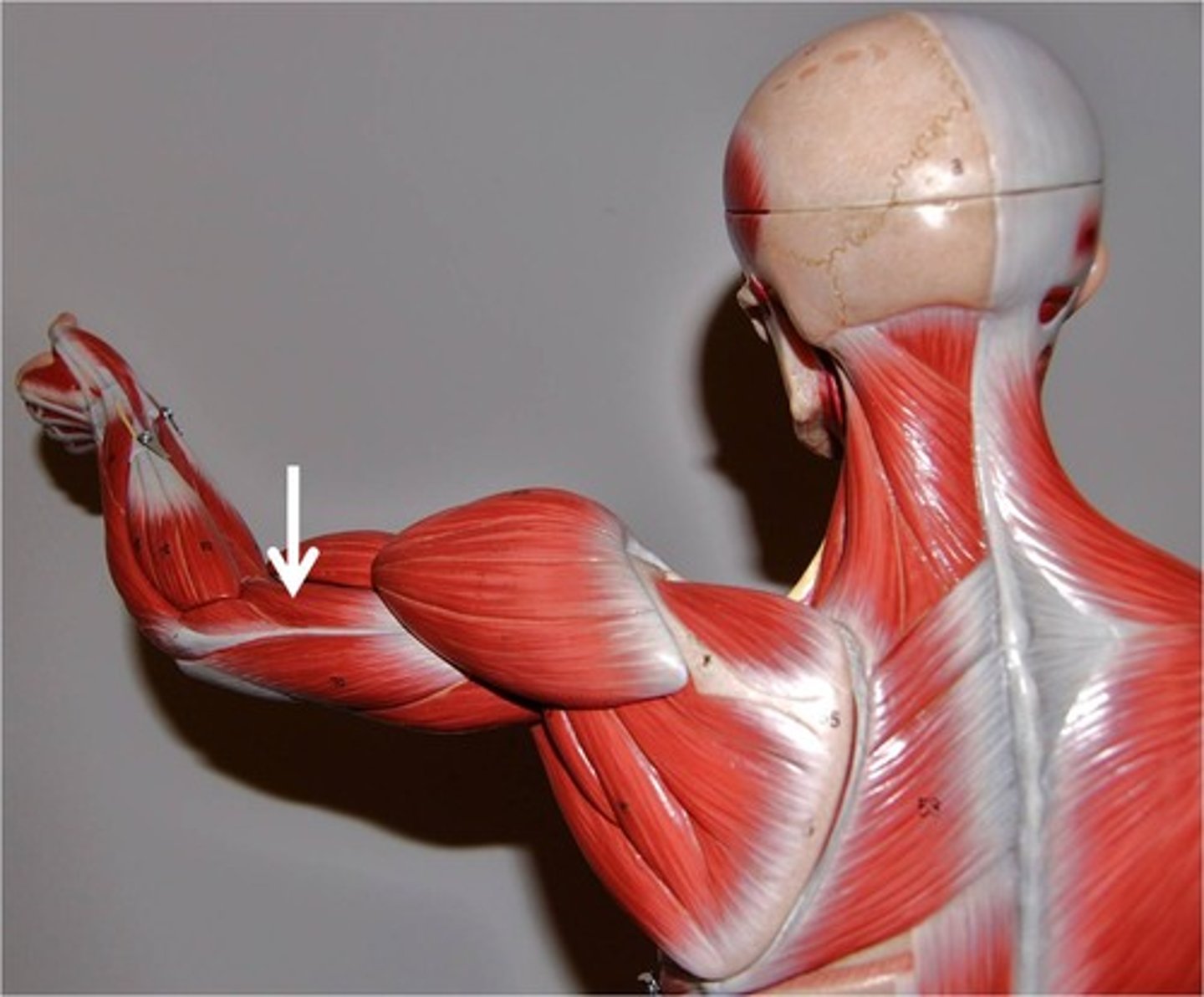
biceps brachii
Flexes and supinates forearm
scapula
biceps brachii origin
radius
biceps brachii insertion
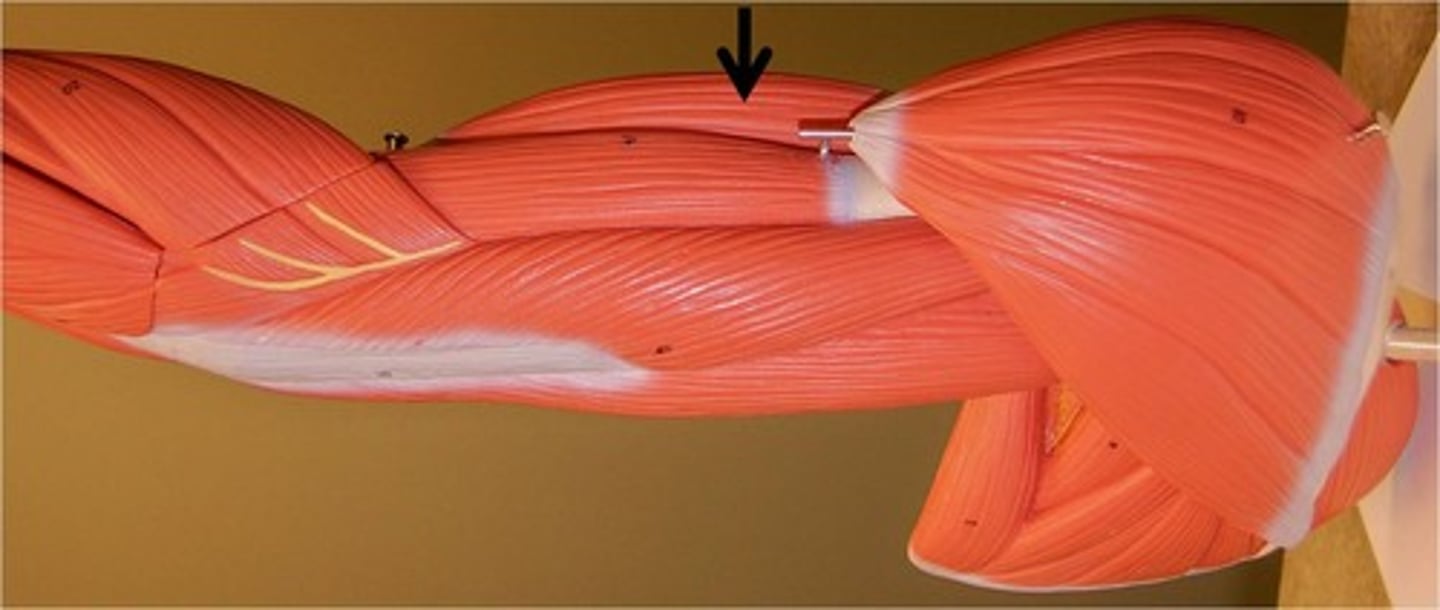
brachialis
flexes elbow
humerus
brachialis origin
ulna
brachialis insertion
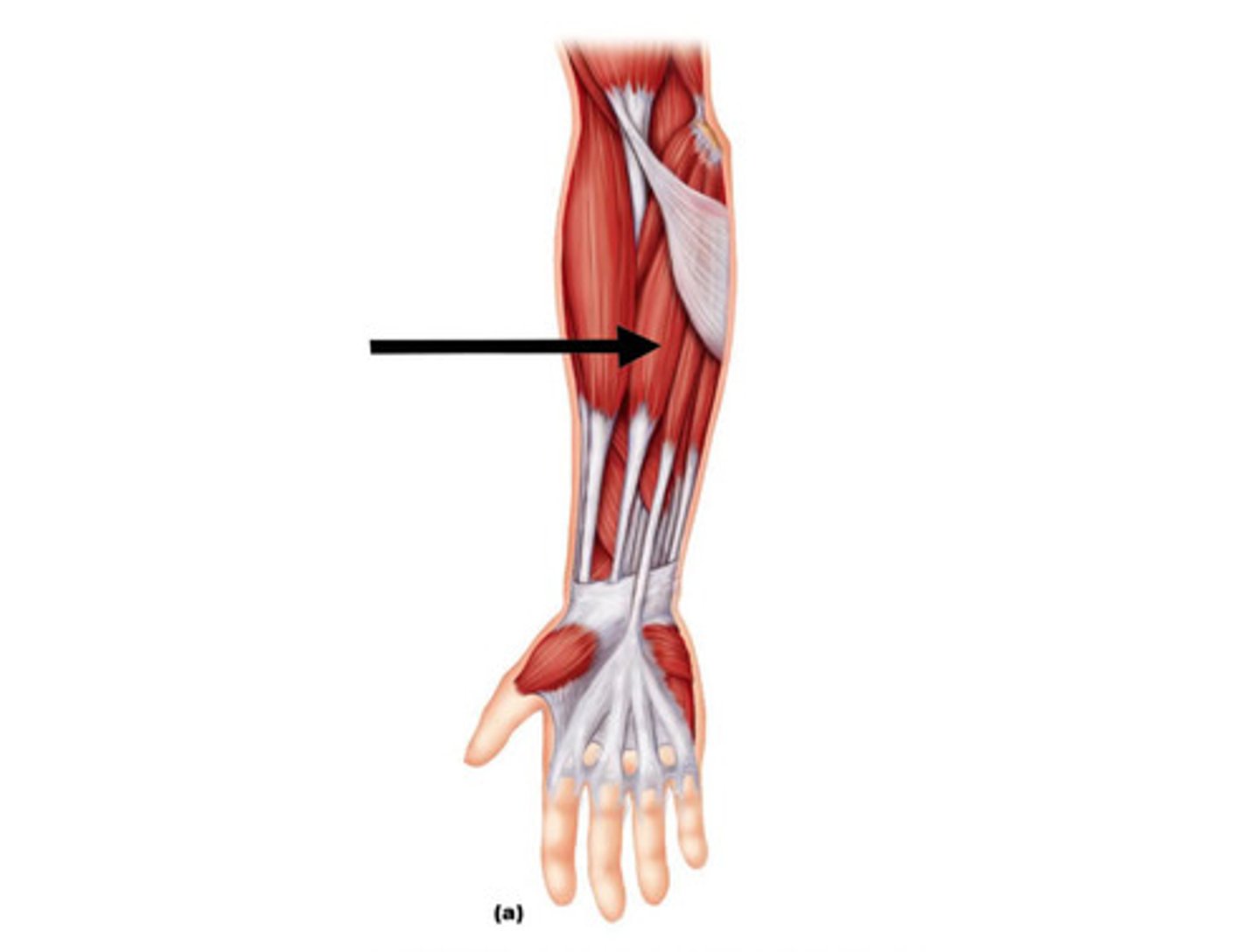
extensor carpi radialis longus
Extends wrist and abducts hand
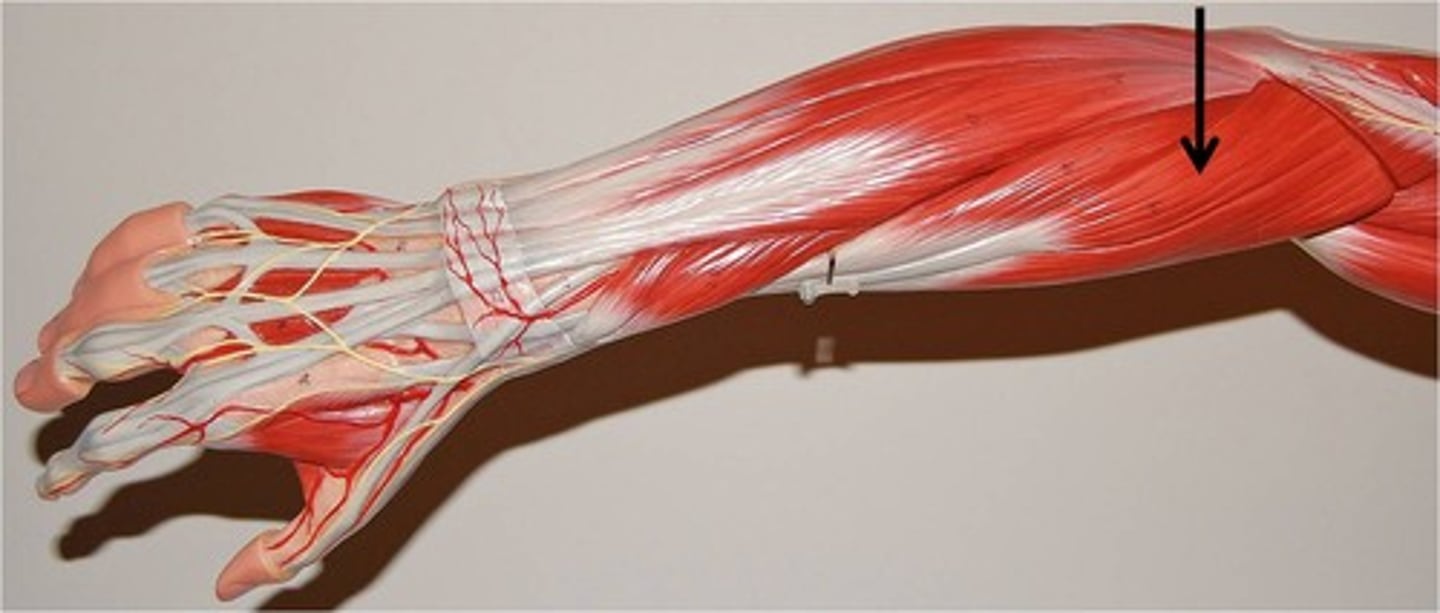
extensor digitorum
Extends fingers and the wrist
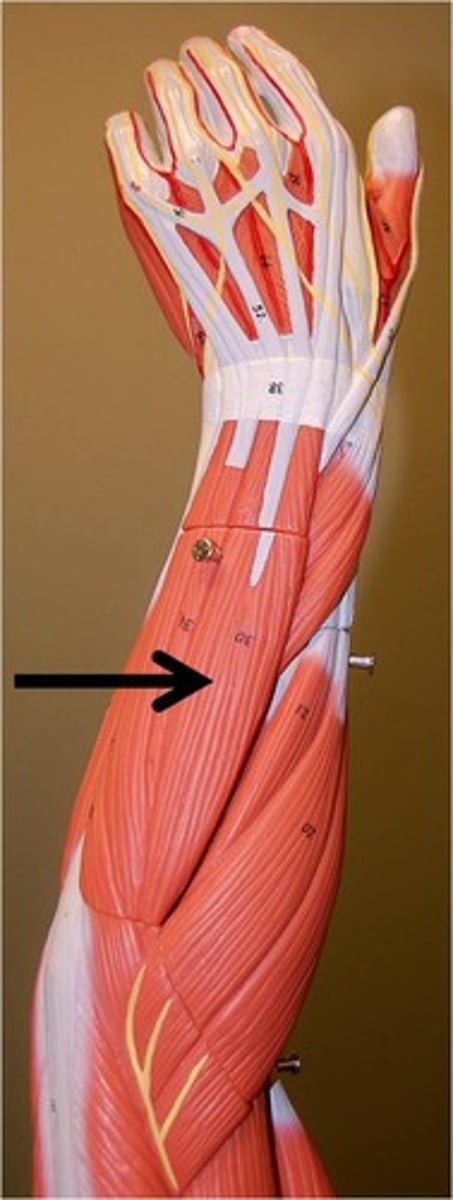
flexor digitorum superficialis
flexes wrist and middle phalanges of fingers 2-5
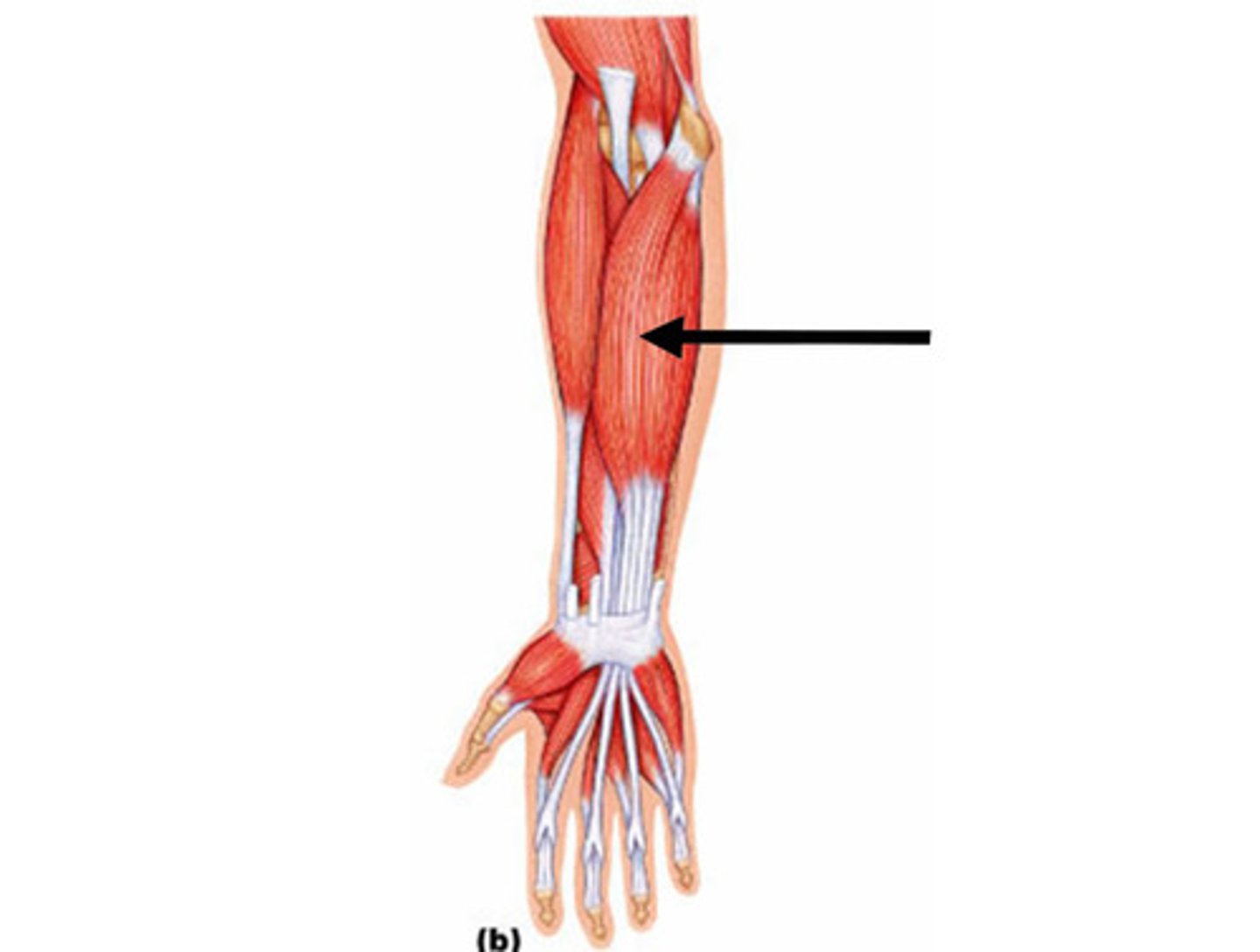
flexor carpi redialis
flexes and abducts wrist
gluteus maximus
extends thigh
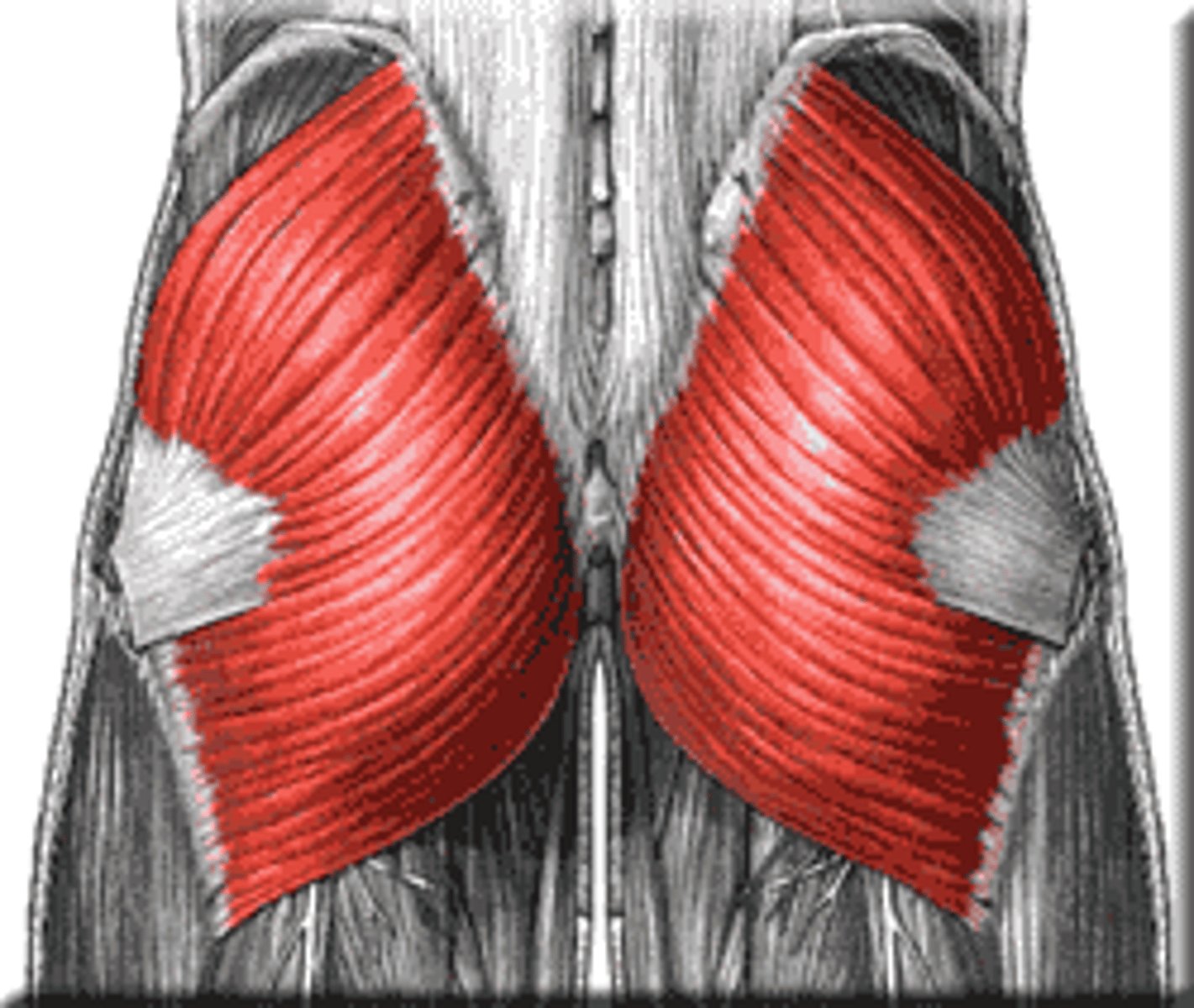
gluteus medius
abducts and medially rotates thigh
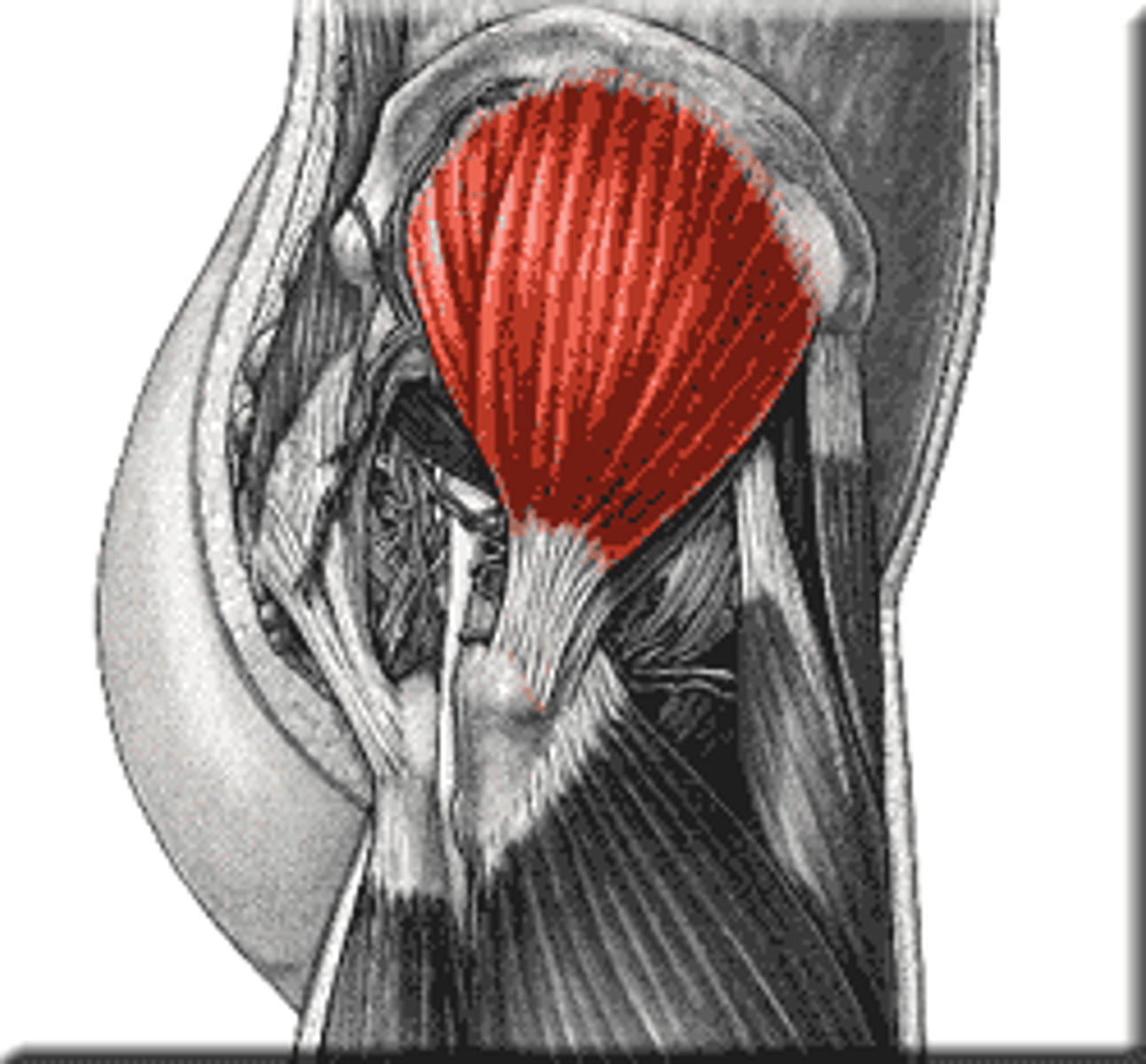
sartorius
Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh at the hip; flexes knee
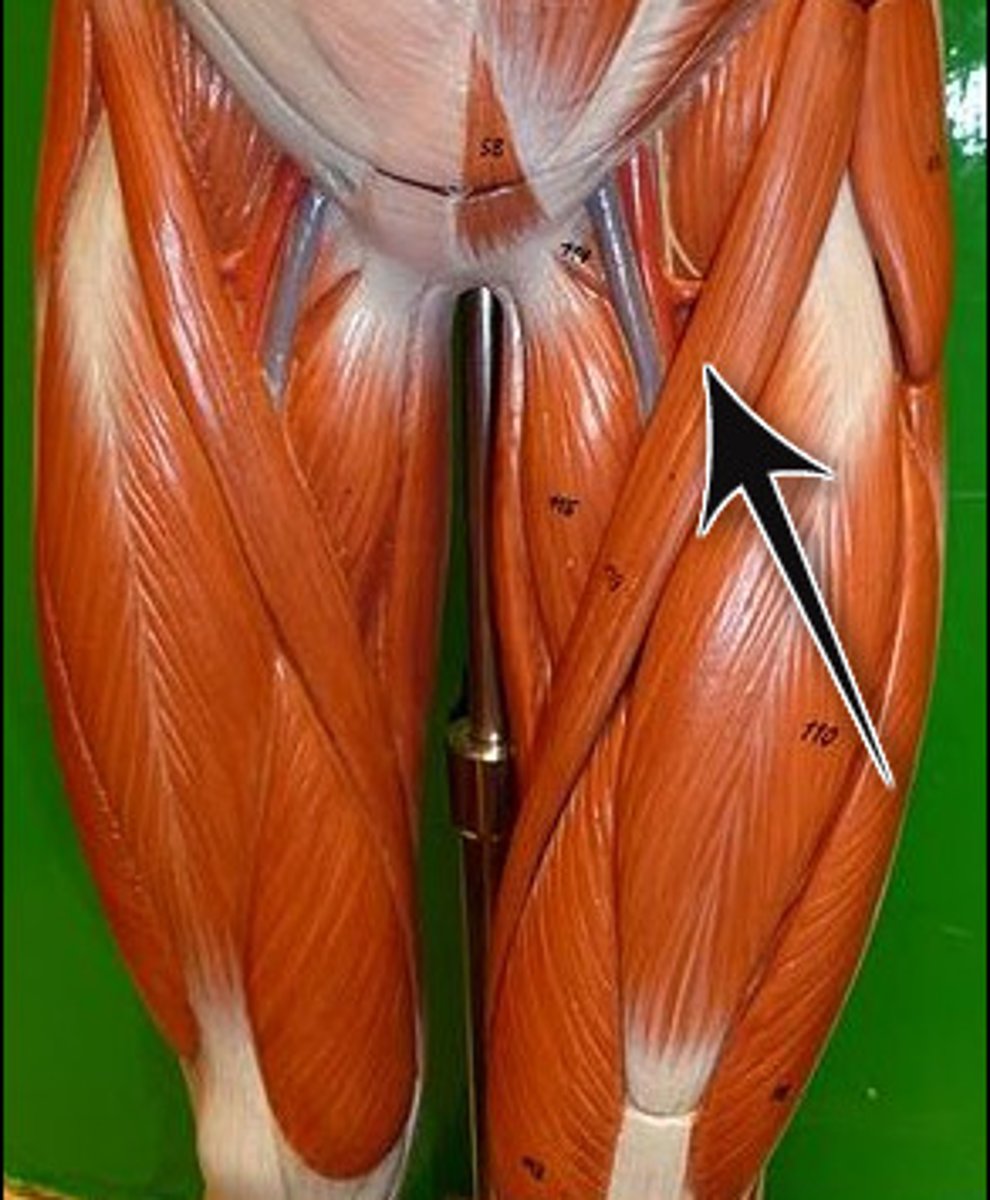
gracilis
adducts thigh
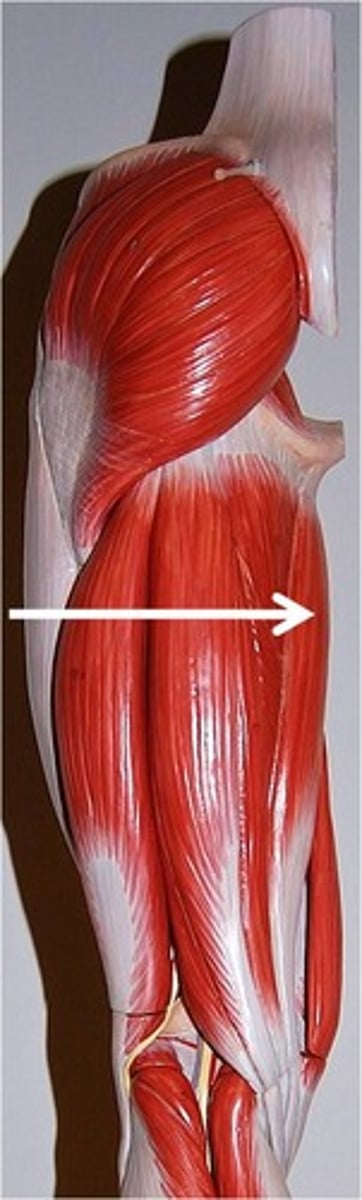
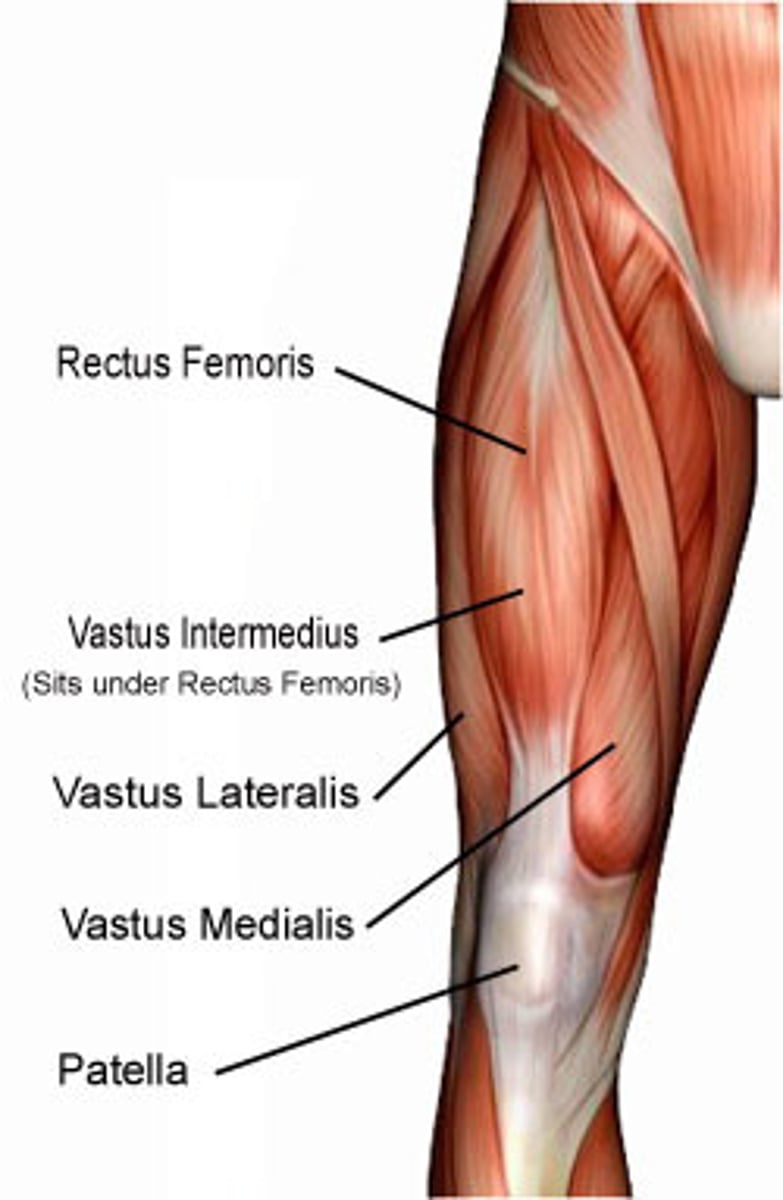
quadriceps femoris
Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius.
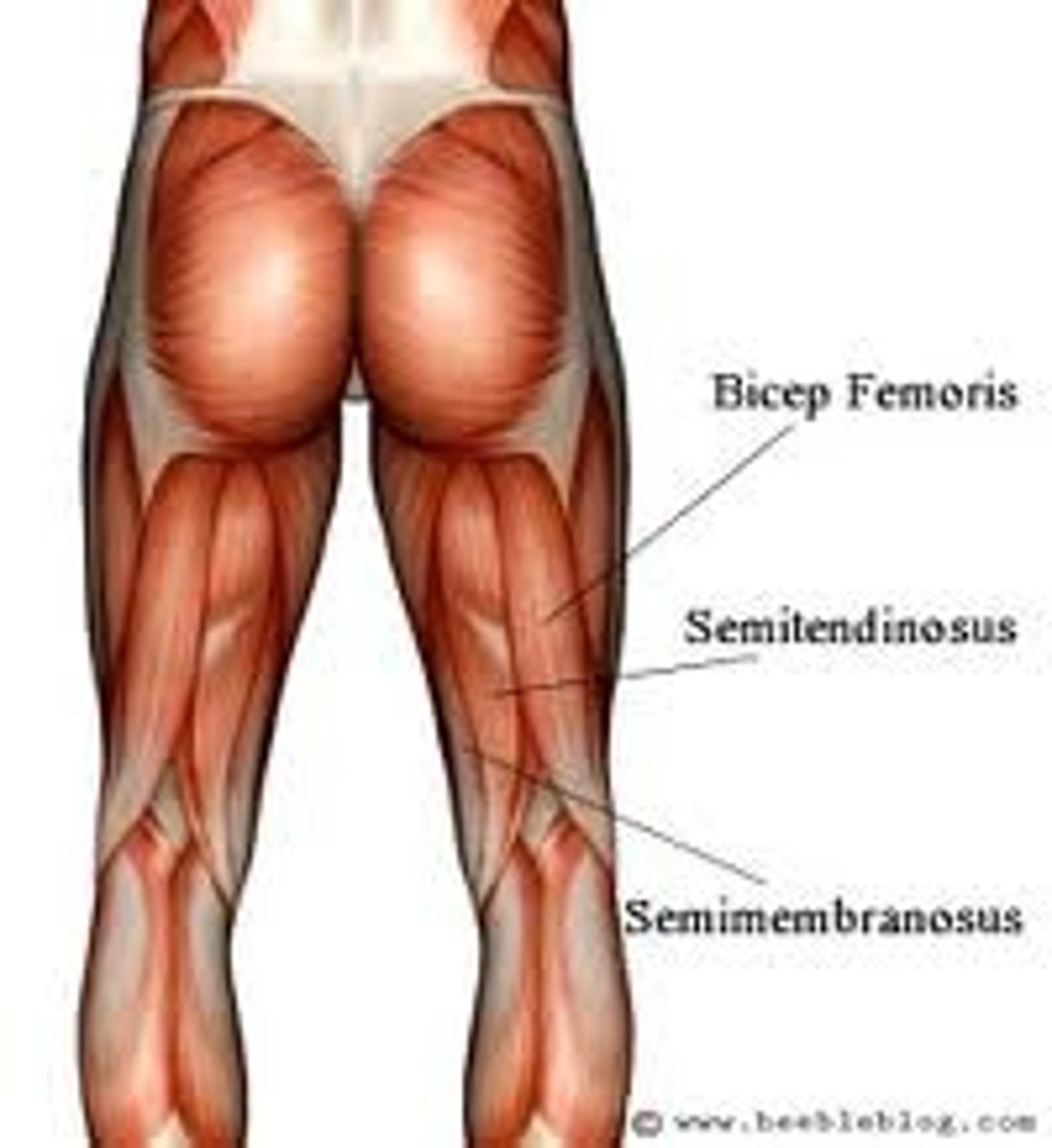
hamstrings
biceps femoris, semimembranosus
Gastrocnemius
plantar flexes foot
femur
gastrocnemius origin
calcaneus
gastrocnemius insertion
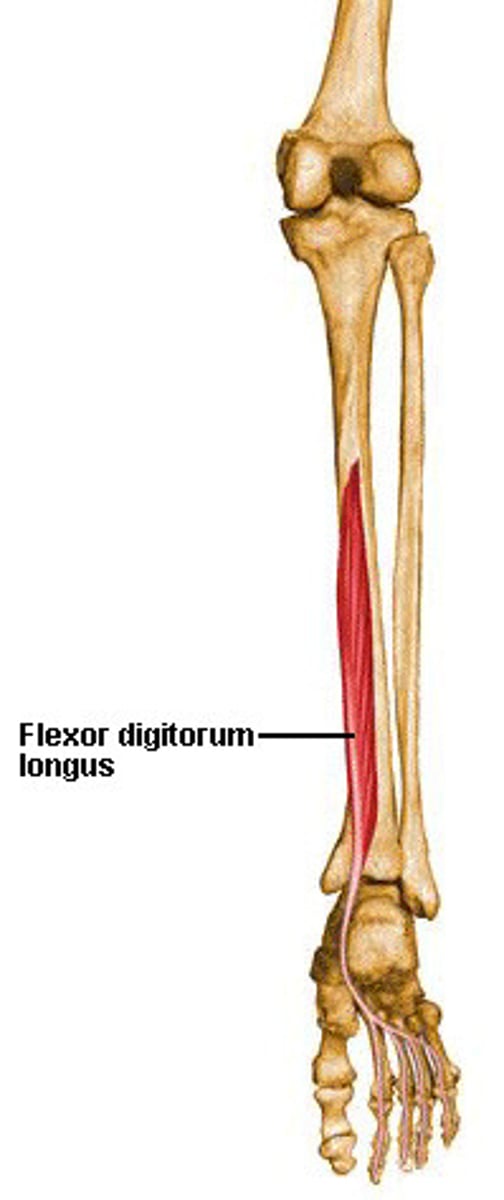
flexor digitorum longus
flexes toes
tibia
flexor digitorum longus origin
distal phalanges of digits 2-5
flexor digitorum longus insertion
extensor digitorum longus
extends toes
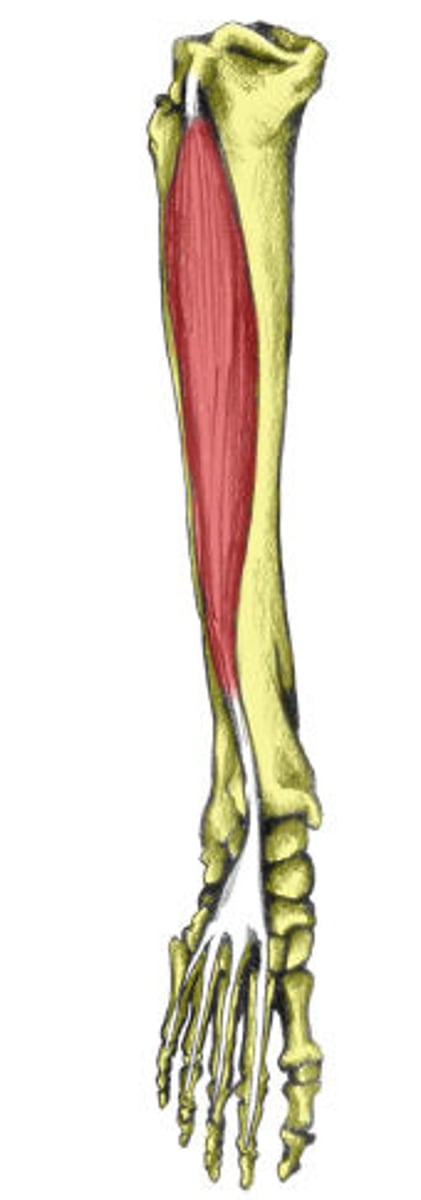
extensor digitorum longus origin
tibia/fibula
extensor digitorum longus insertion
middle and distal phalanges of toes 2-5
tibialis anterior
dorsiflexes and inverts foot
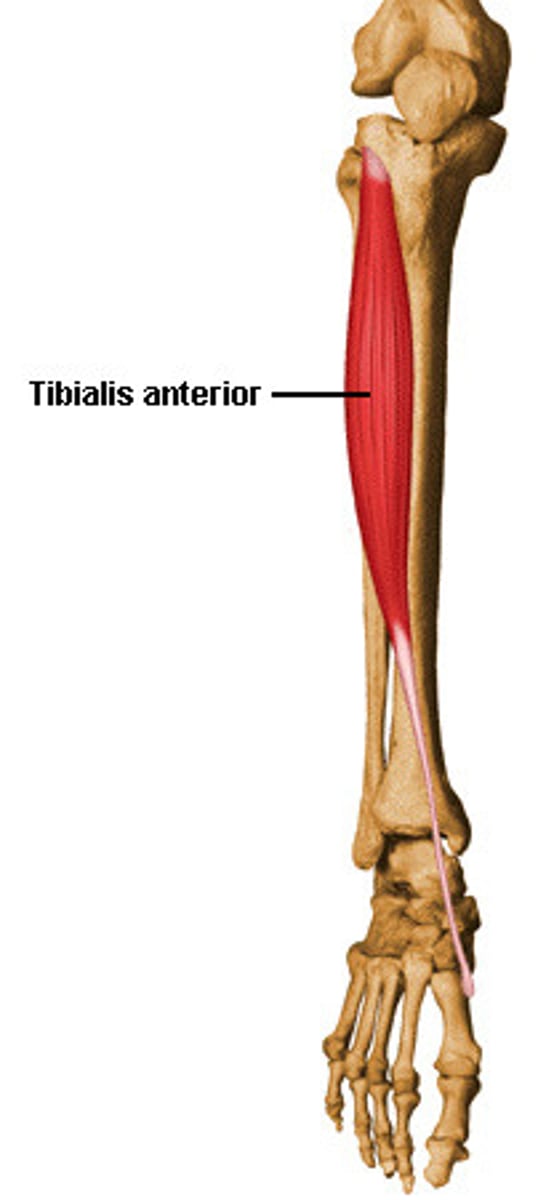
tibia
tibialis anterior origin
tibialis anterior insertion
1st metatarsal
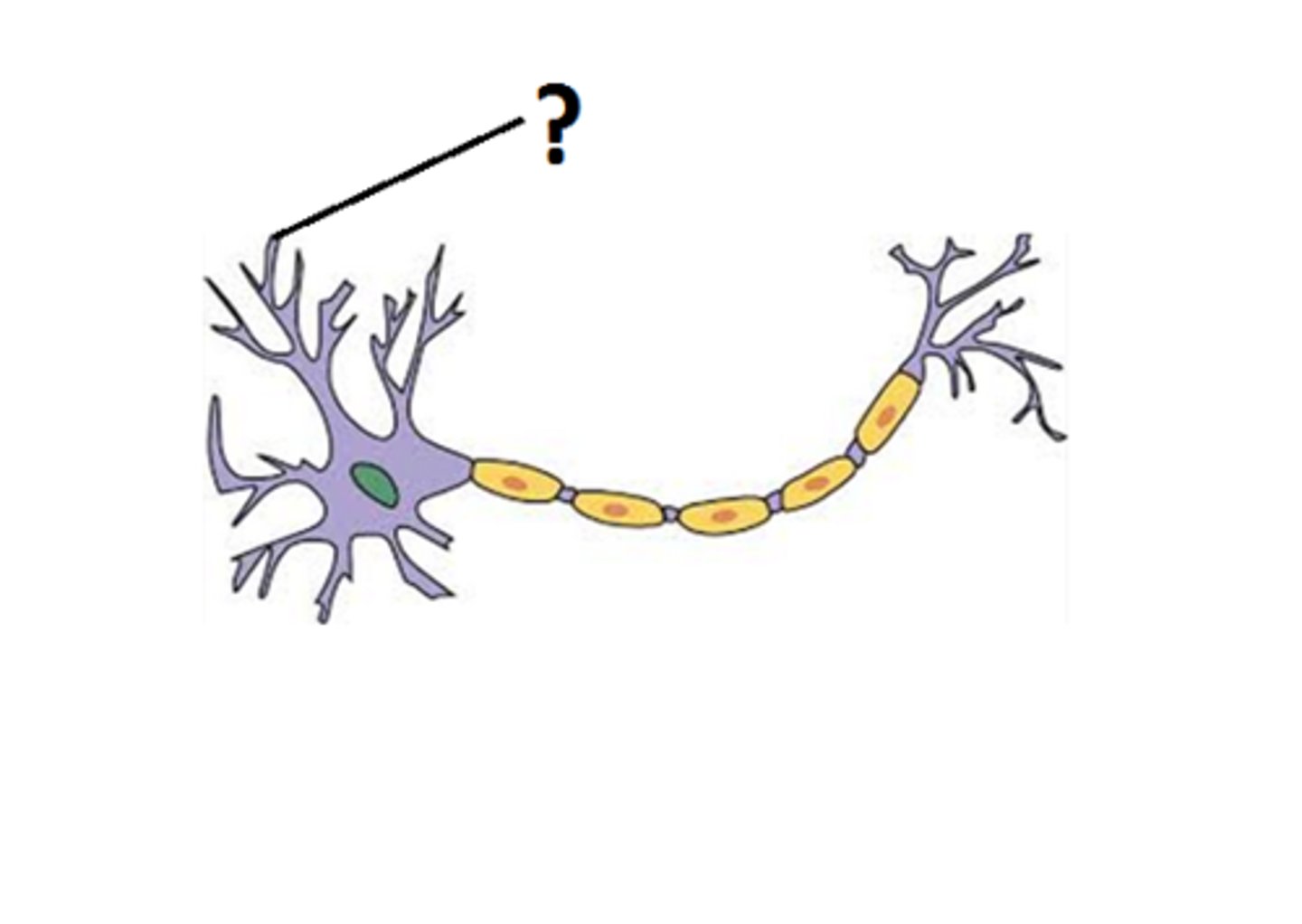
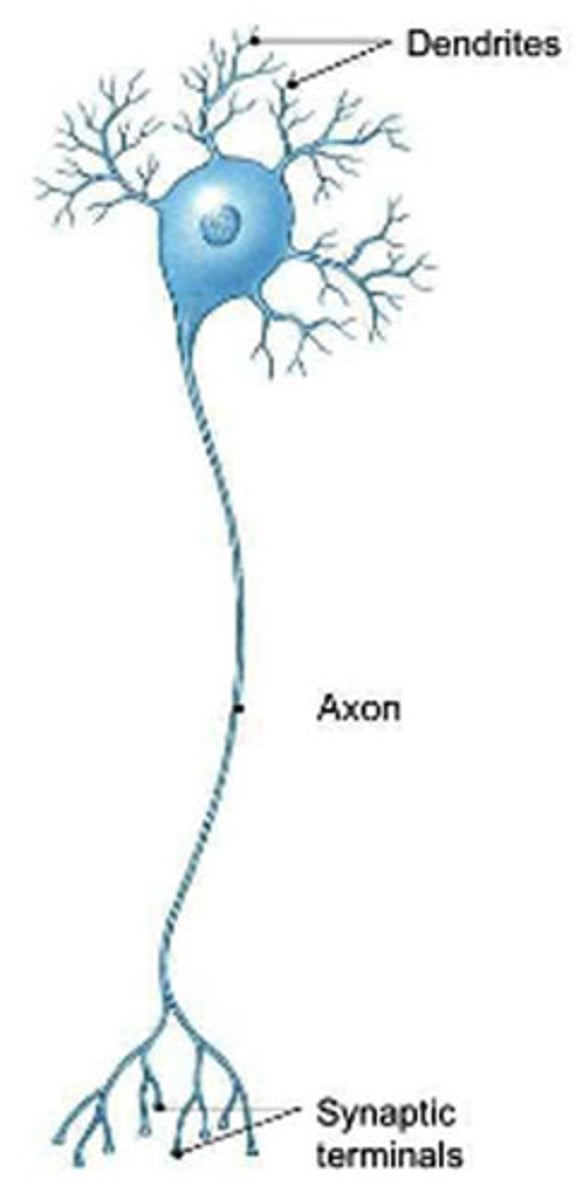
dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
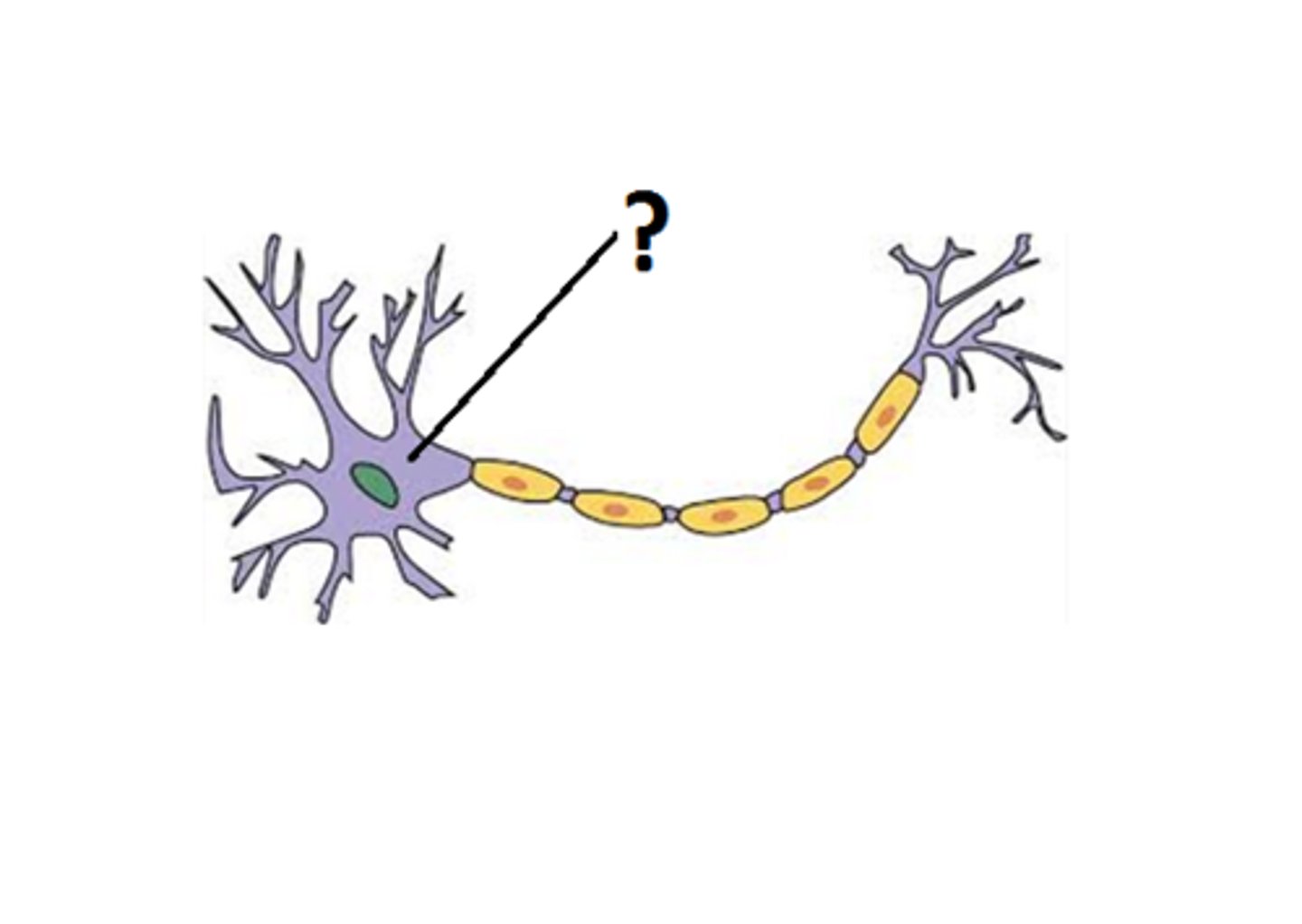
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
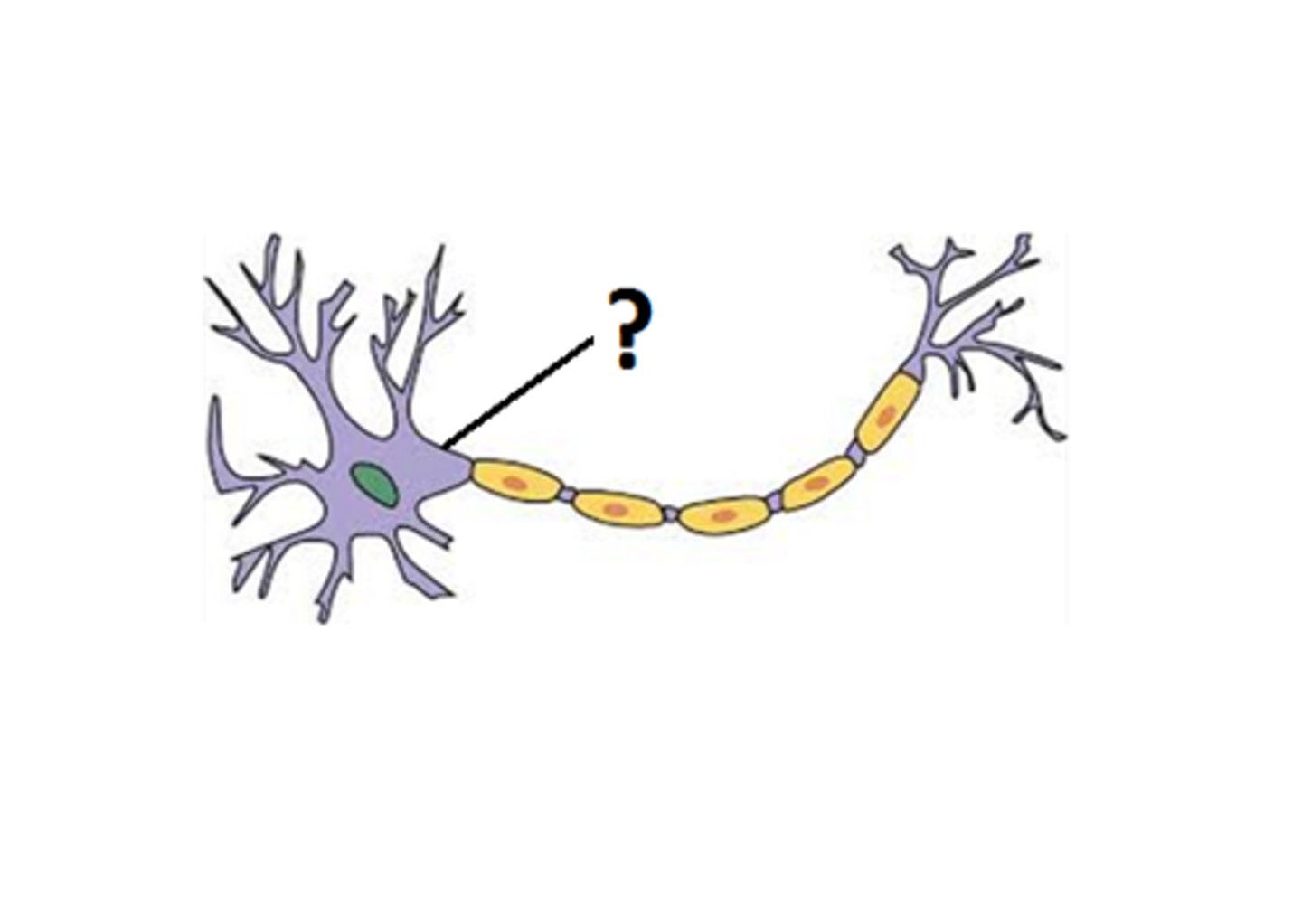
axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
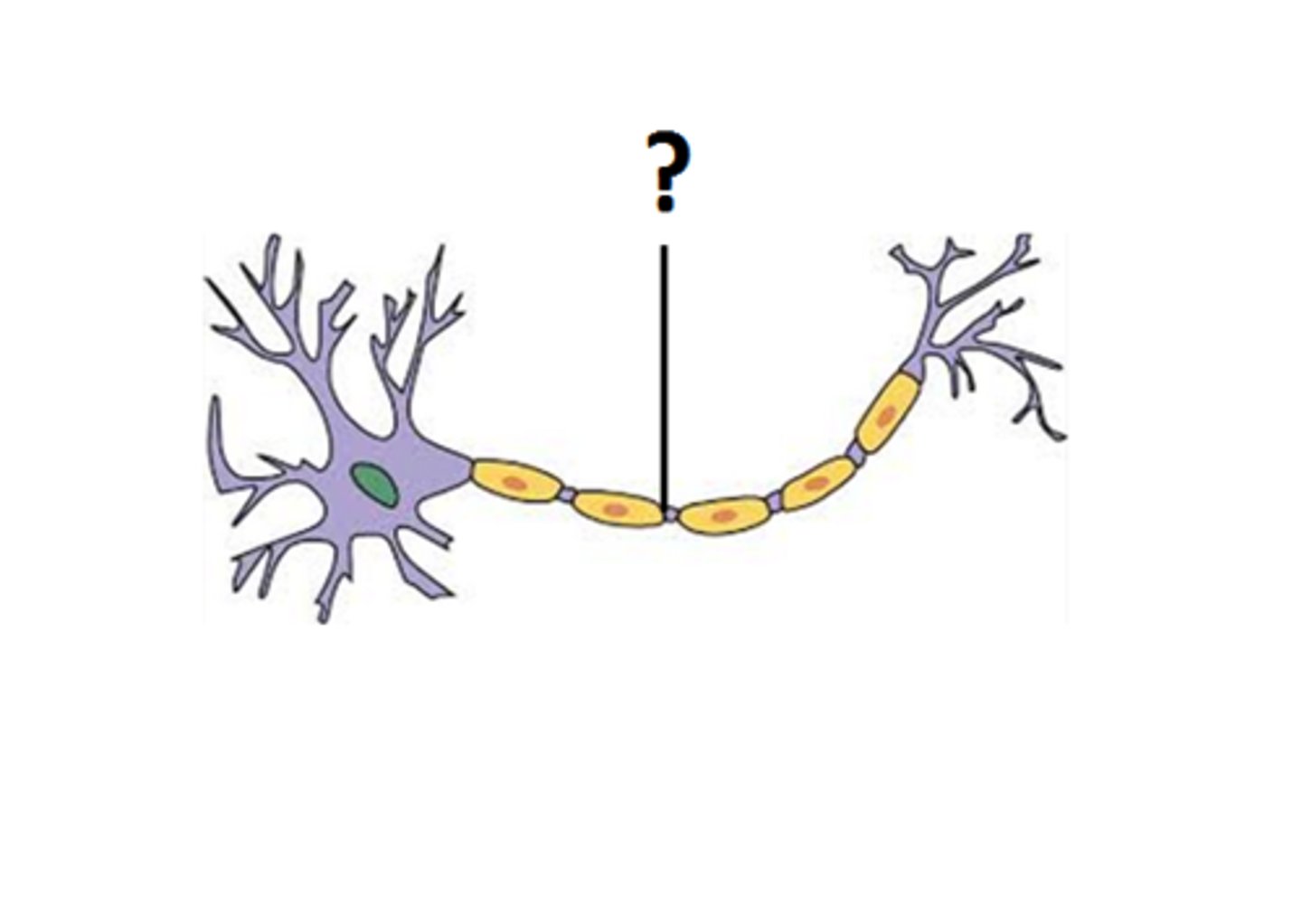
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
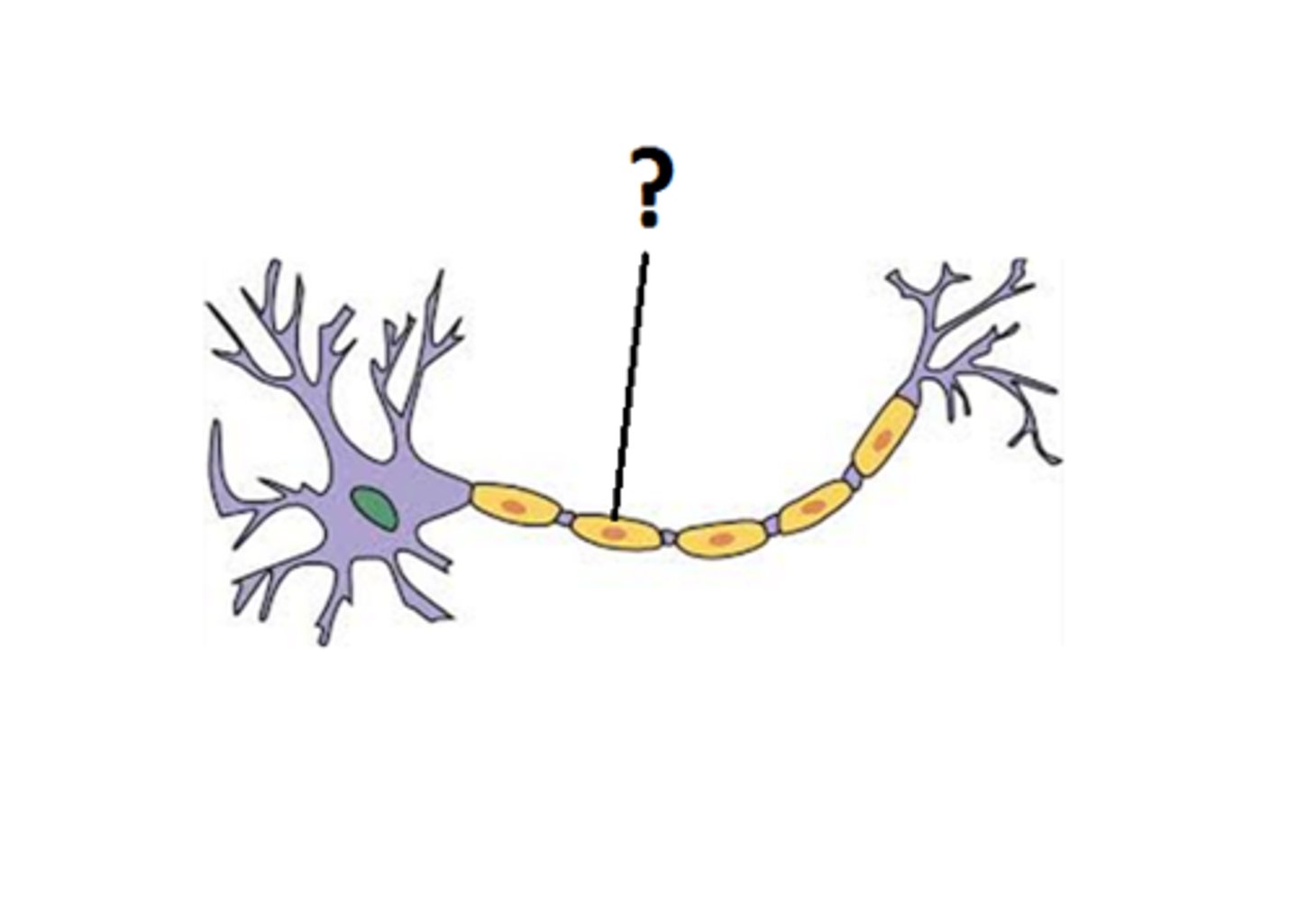
Node of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
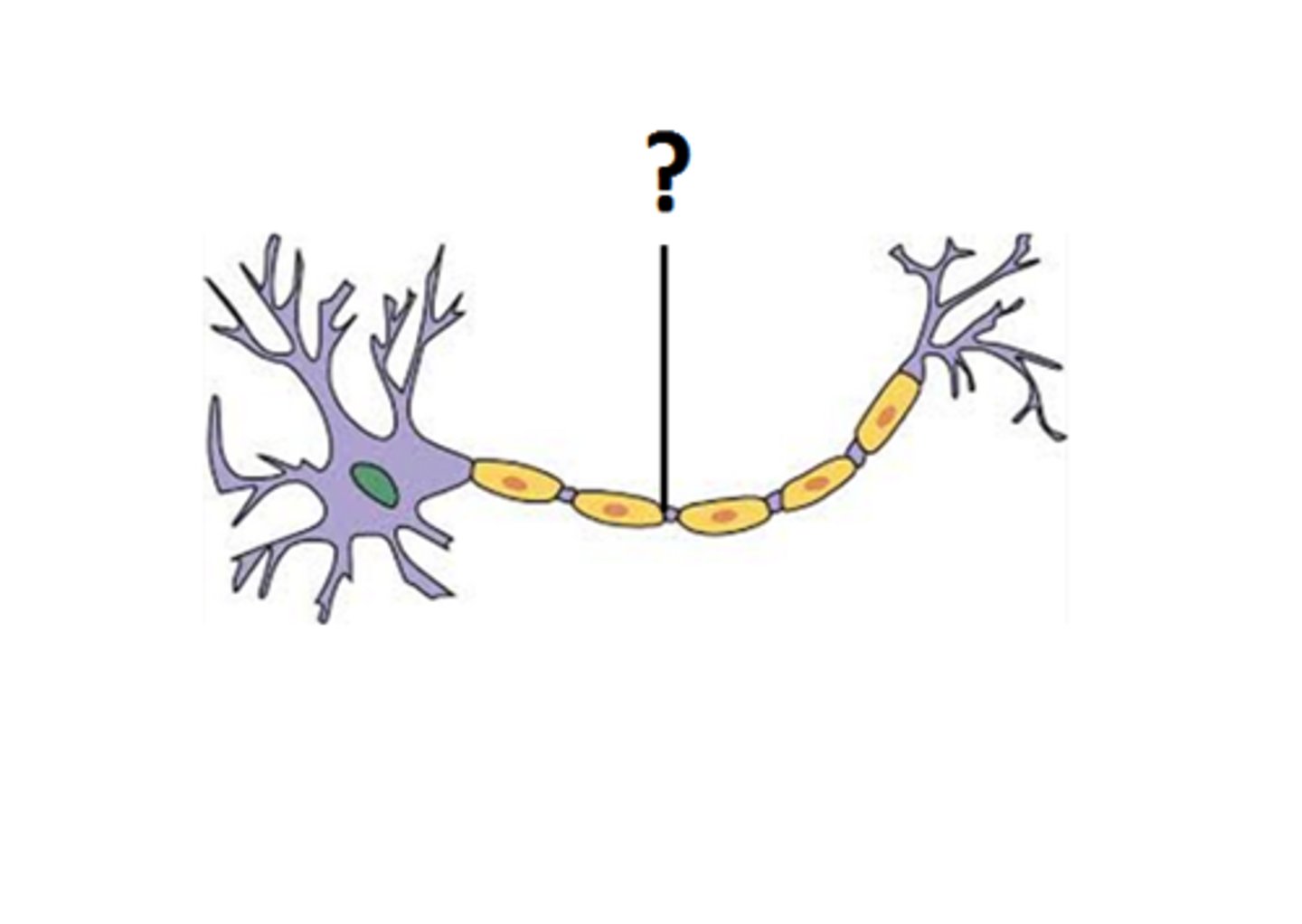
Axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
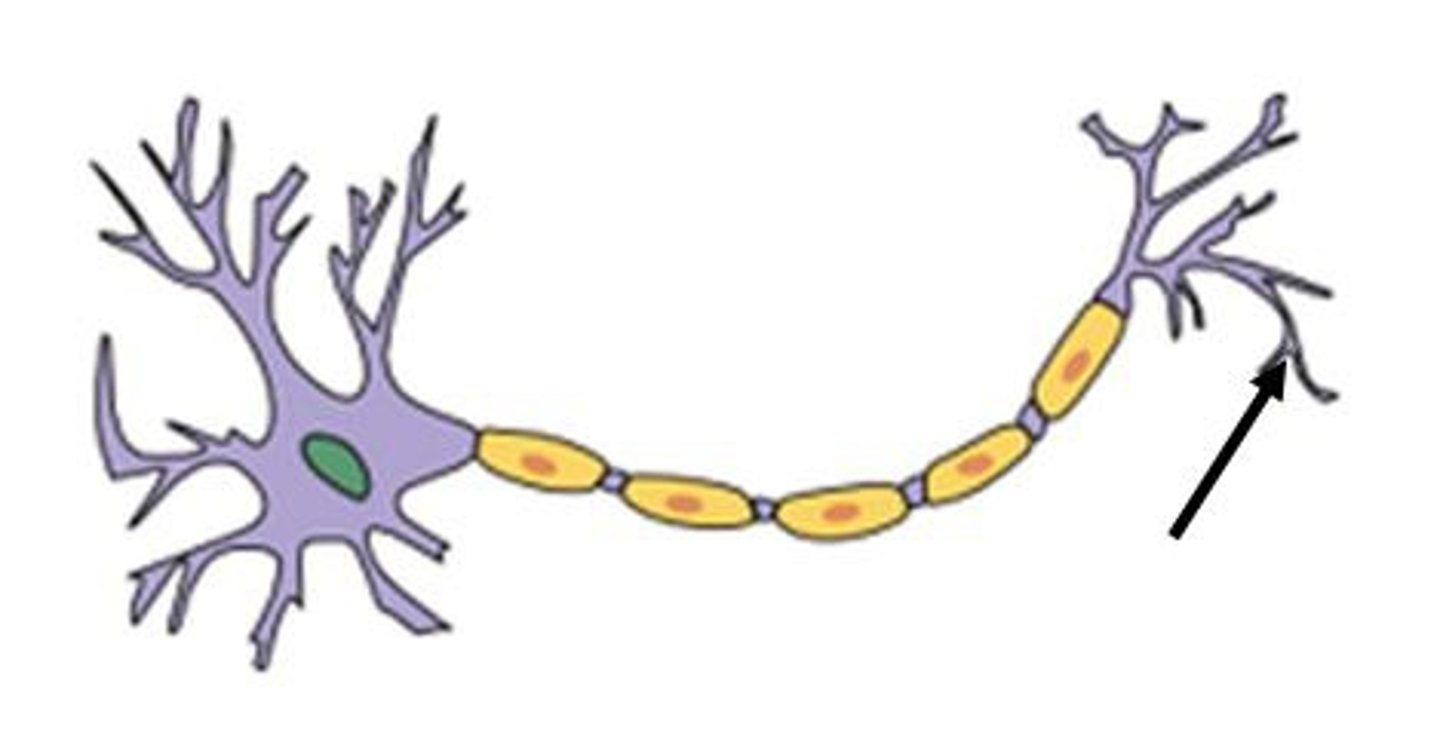
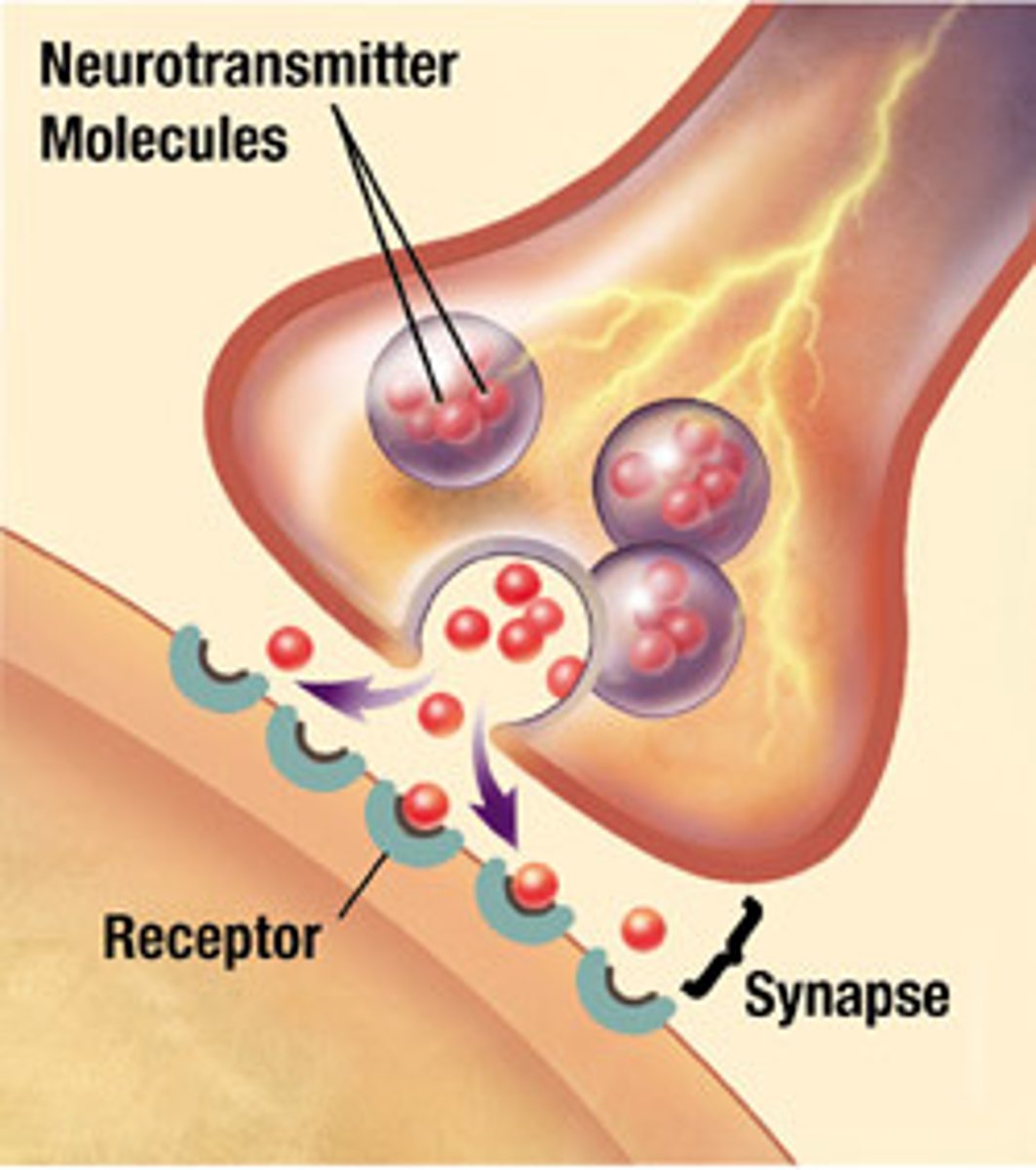
synapse
Gap between neurons
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
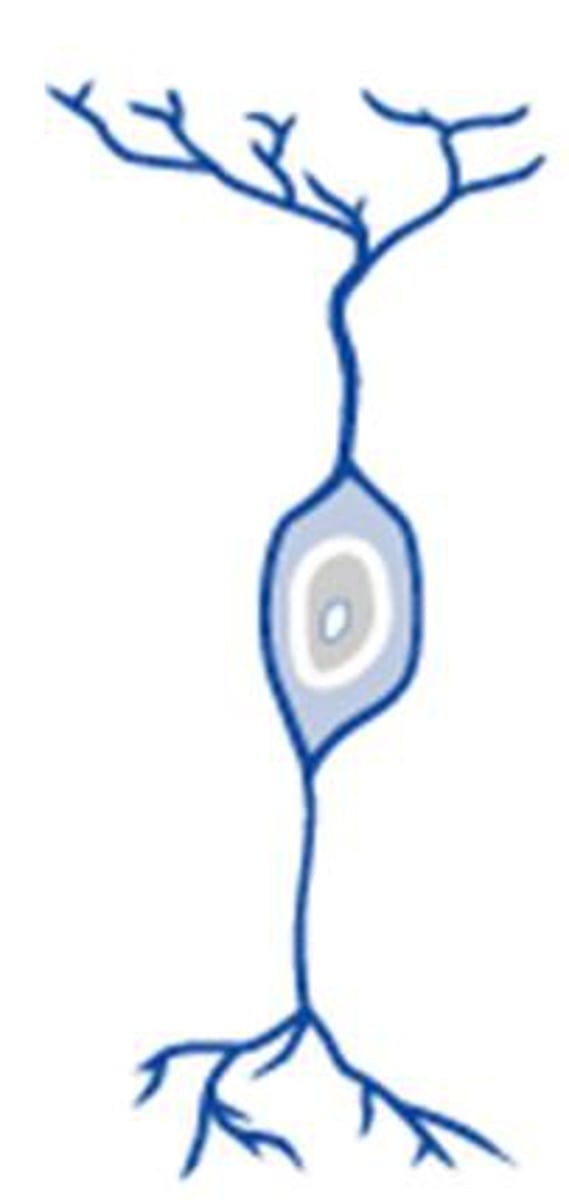
bipolar neuron
a neuron with one axon and one dendrite attached to its soma
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
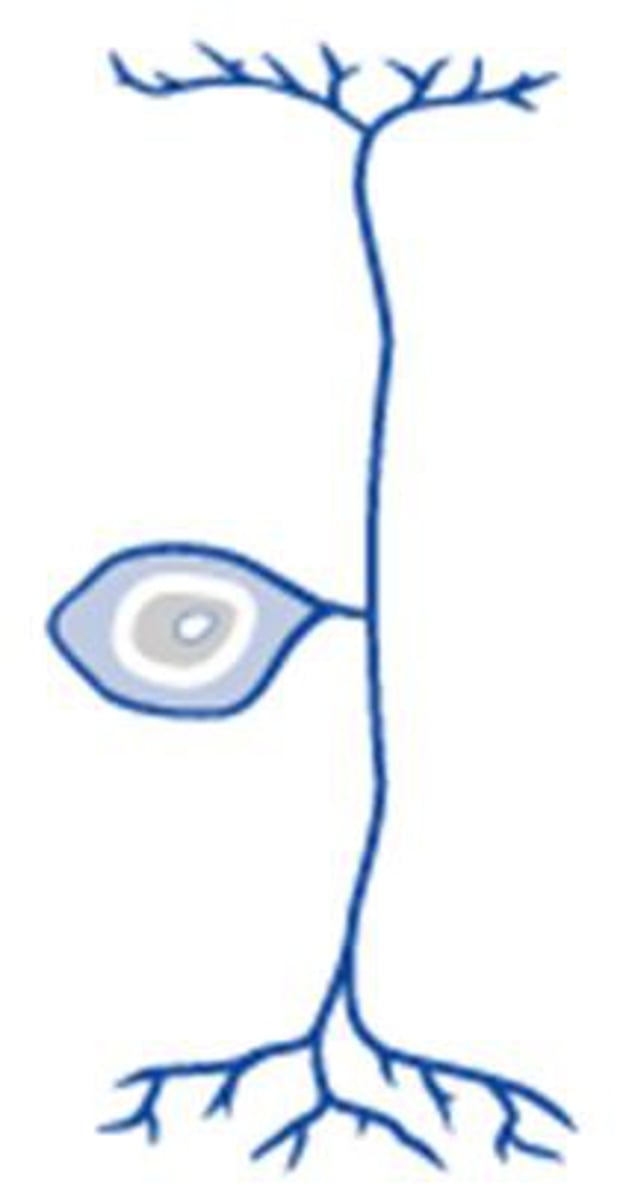
Sensory (Afferent)
transmits action potentials from receptors to CNS
Motor (efferent)
transmits action potentials from CNS to effectors (muscles, glands)
Interneurons (association)
connect sensory and motor neurons
Nuclei
Groups of Cell bodies in the CNS
Ganglia
Groups of cell bodies in the PNS
Tract
Bundle of axons in the CNS
Nerve
Bundle of axons in the PNS
Conus medullaris
end of the spinal cord
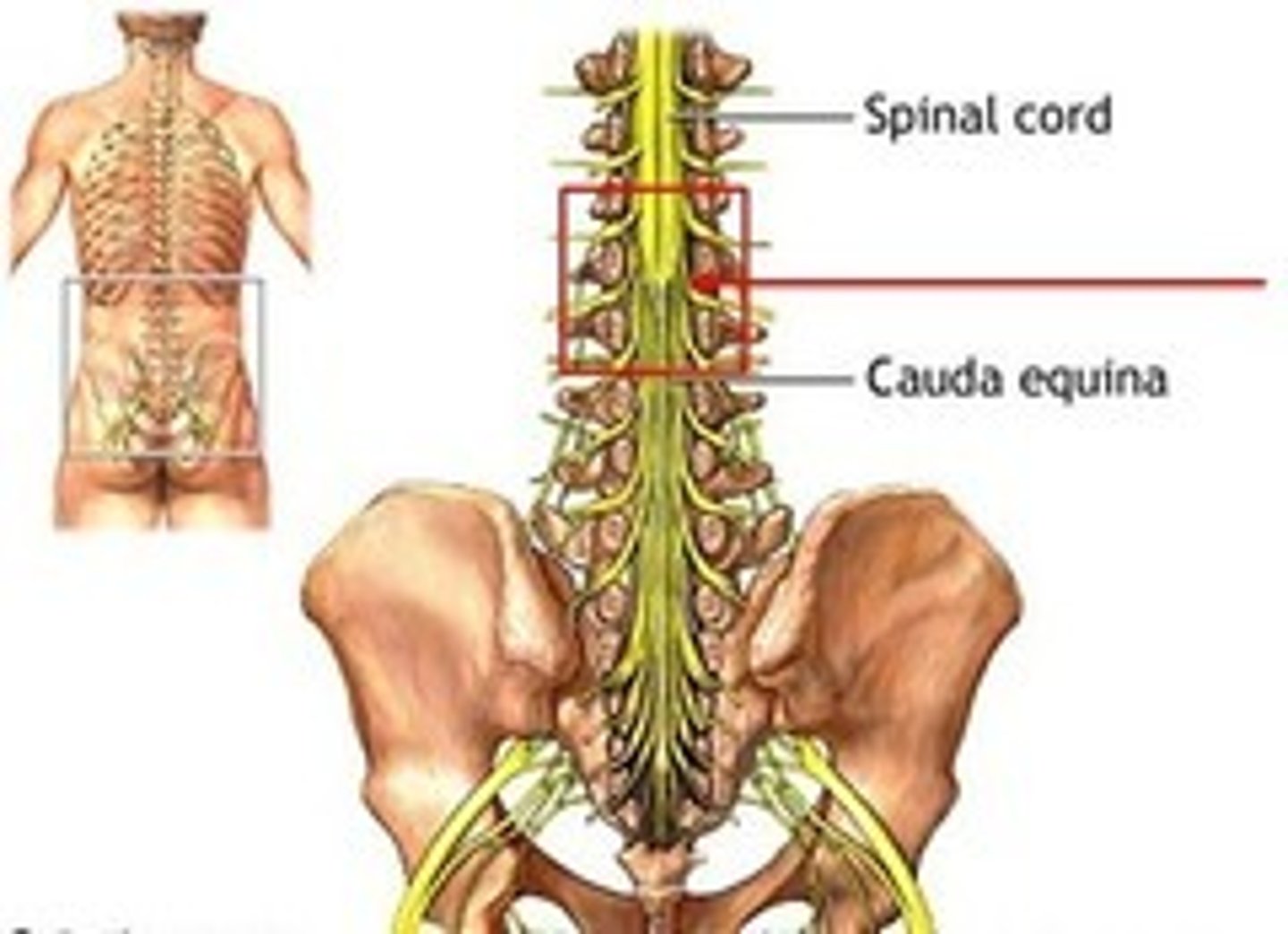
Filum terminale
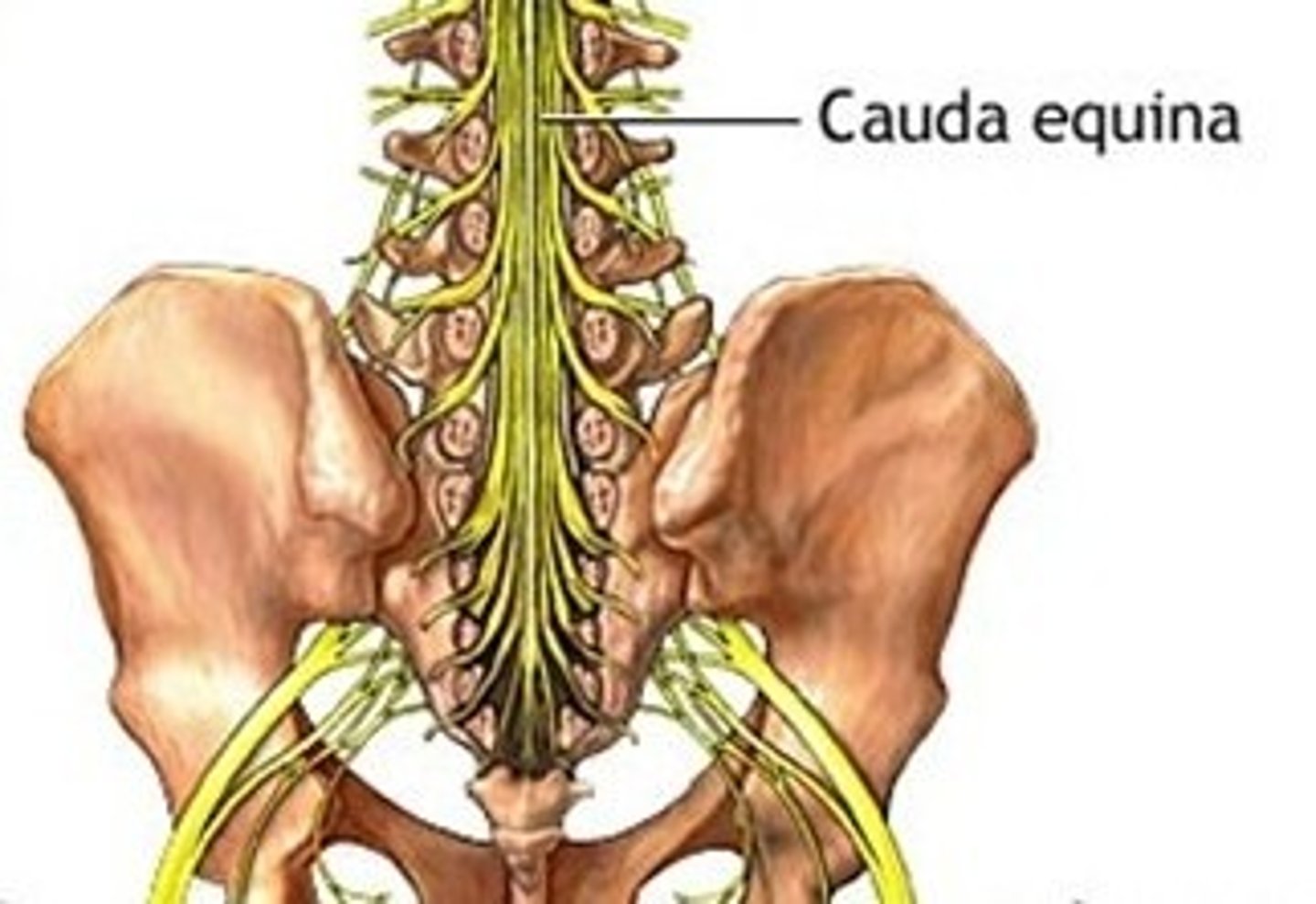
cauda equina
meninges (Spine)
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater

dura mater (spine)
1 layer in spine and is fat filled
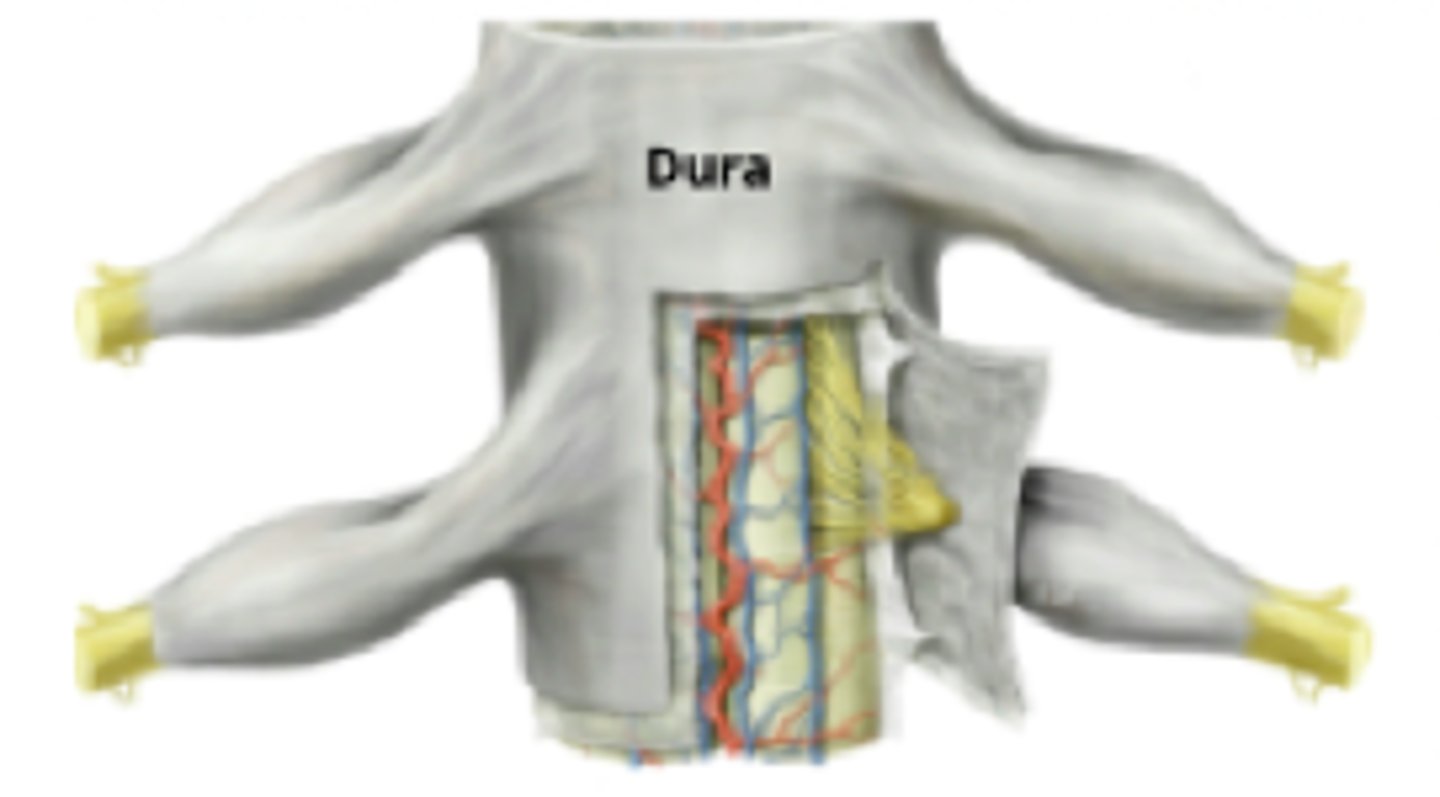
arachnoid mater (spine)
middle layer of the meninges
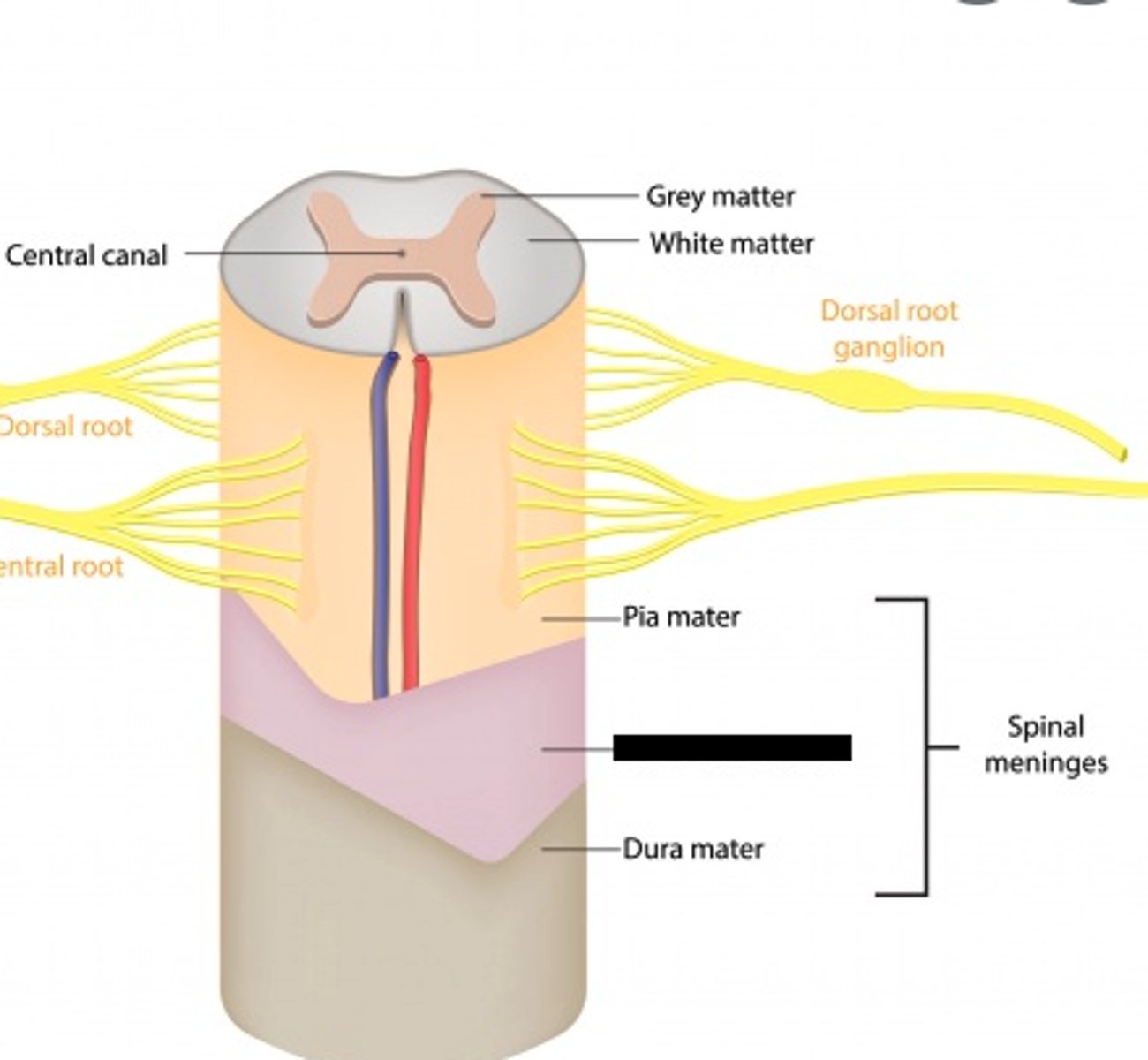
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
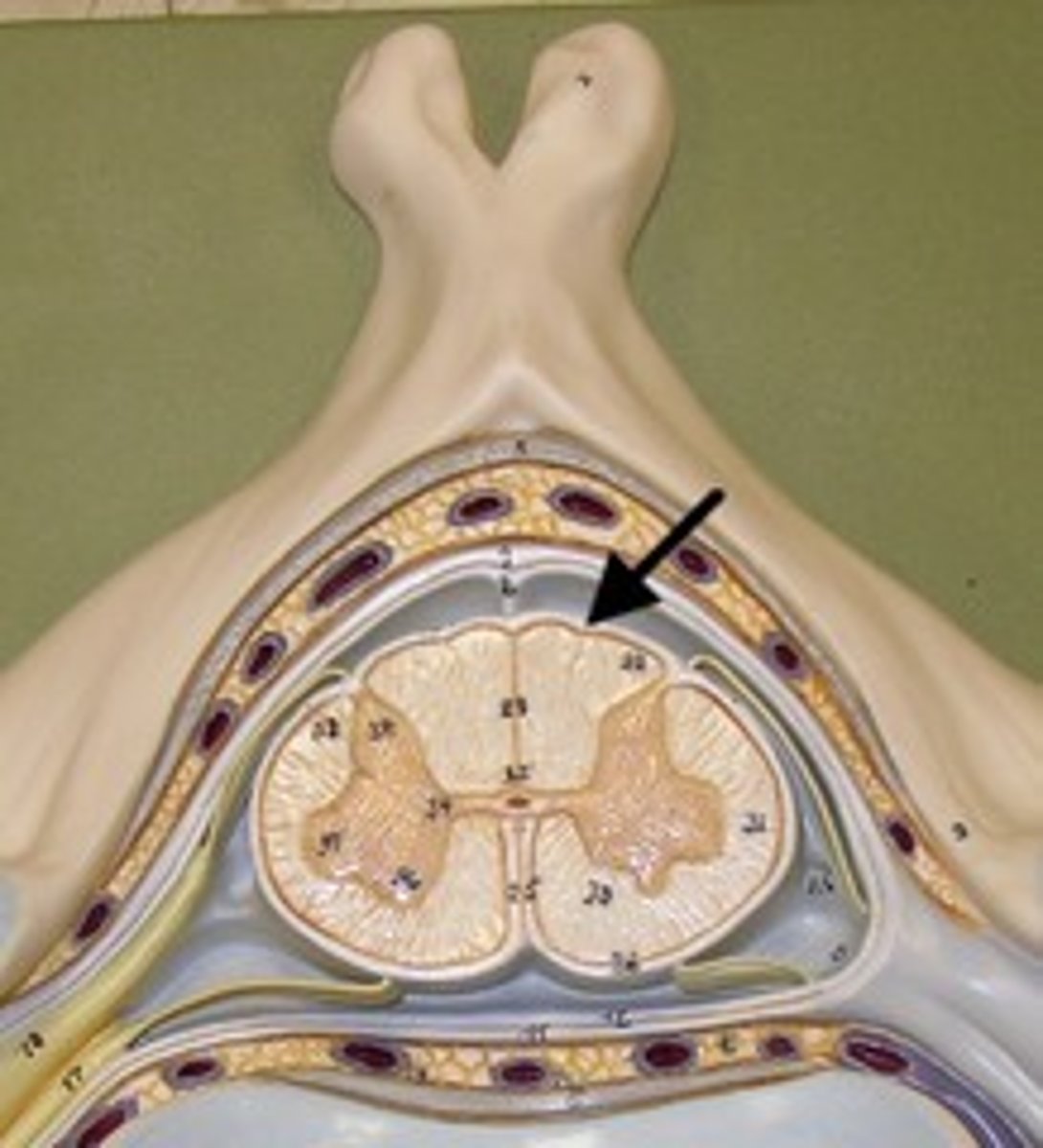
white columns (White Matter)
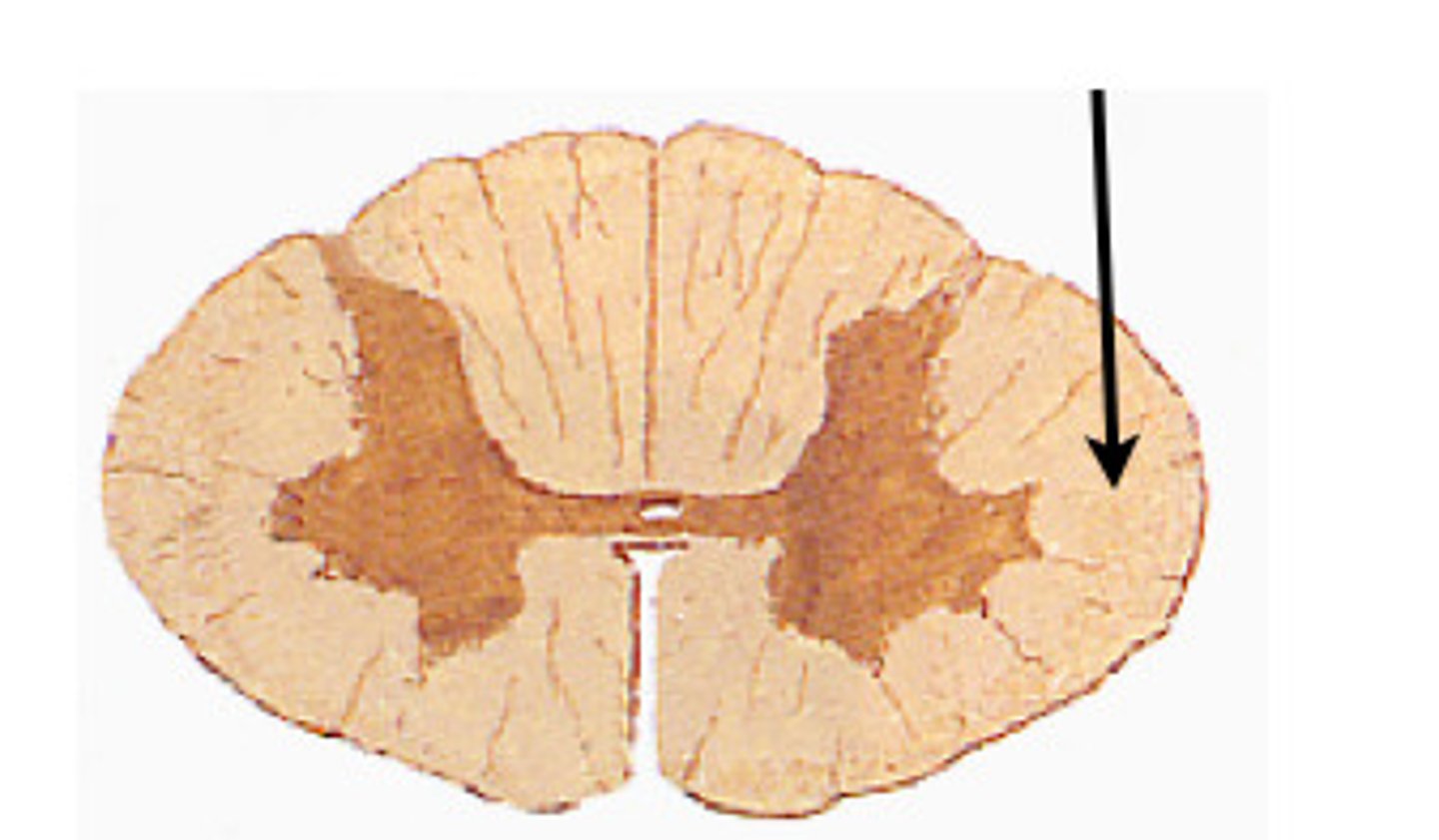
gray commissure (Gray matter)

dorsal root
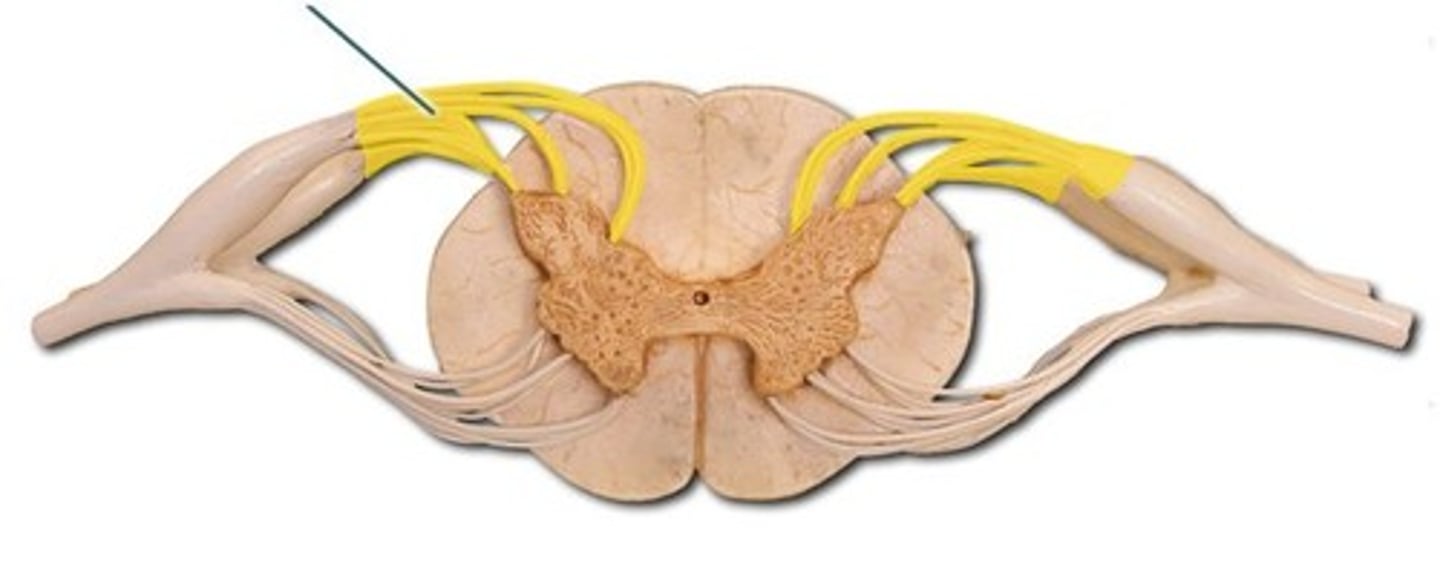
dorsal root ganglion
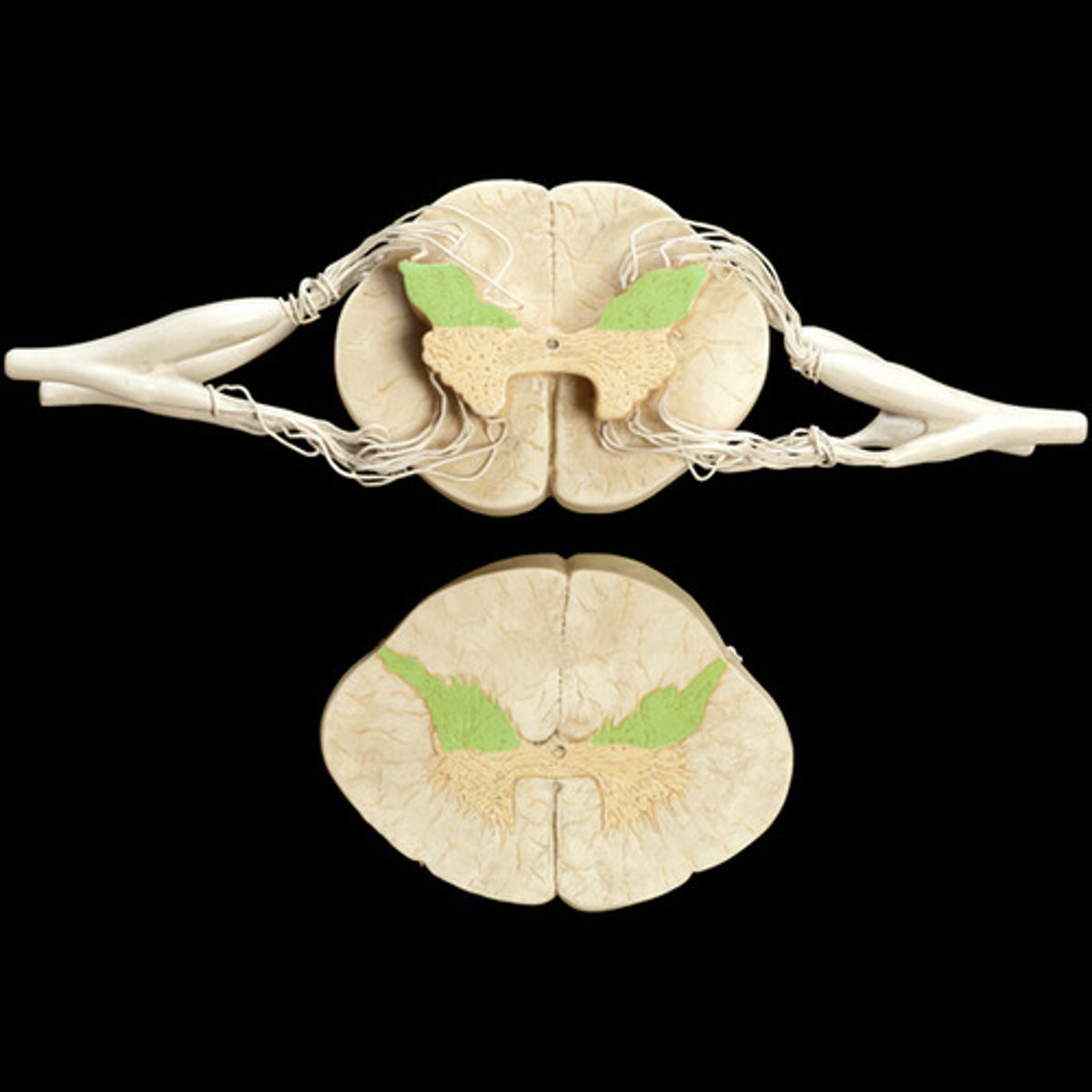
dorsal horns
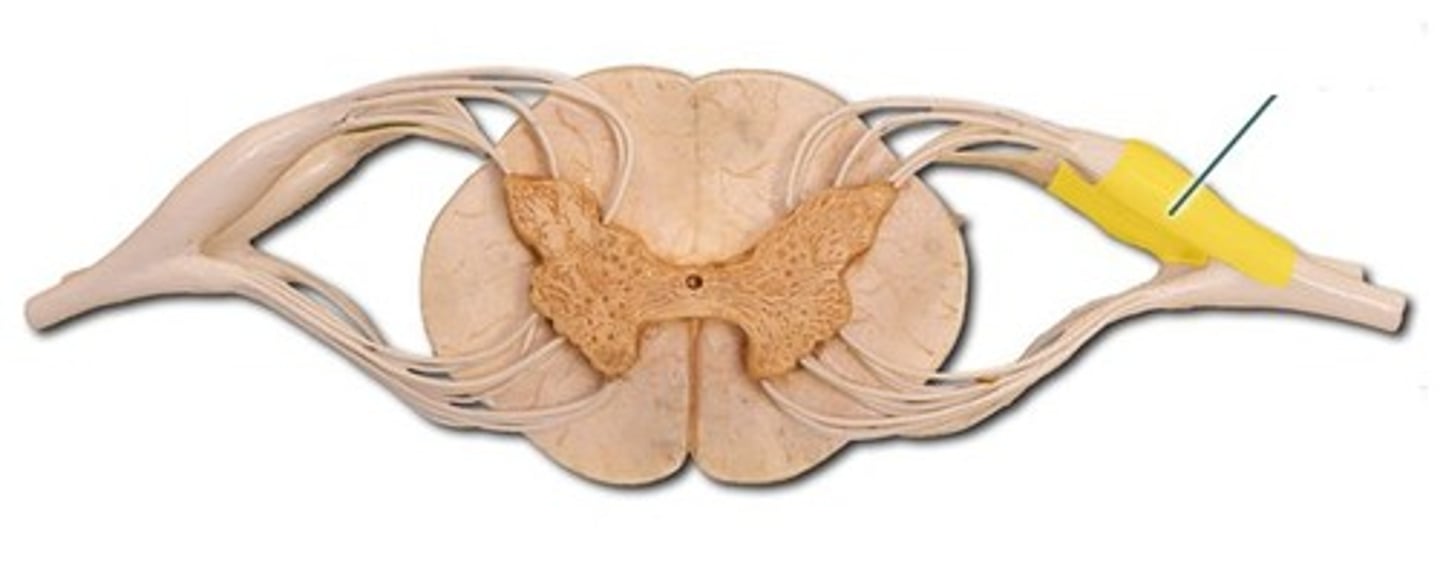
ventral root