ch302 exam 4
5.0(8)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:44 PM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
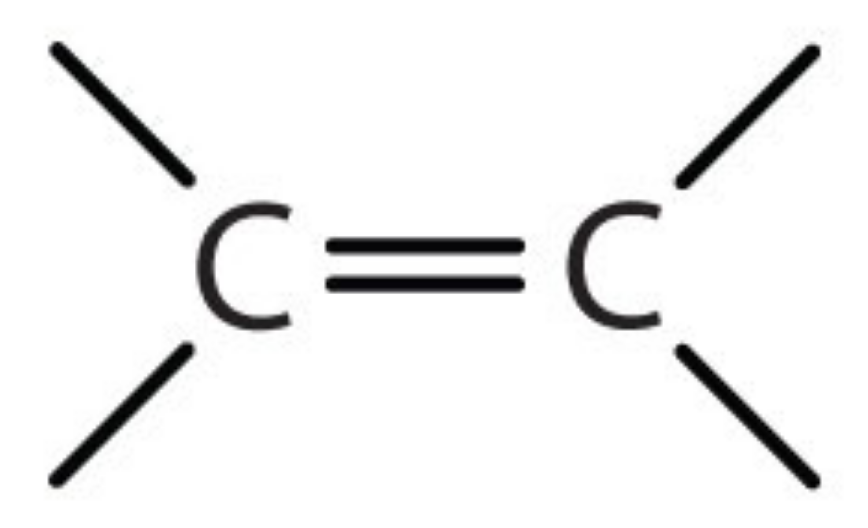
Name the functional group
alkene
2
New cards
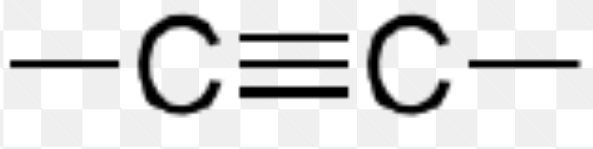
Name the functional group
alkyne
3
New cards
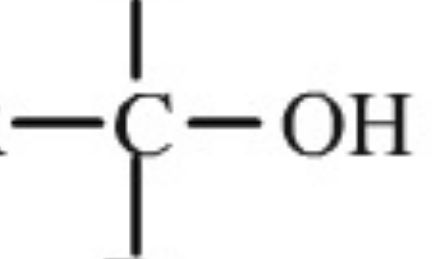
Name the functional group
alcohol
4
New cards
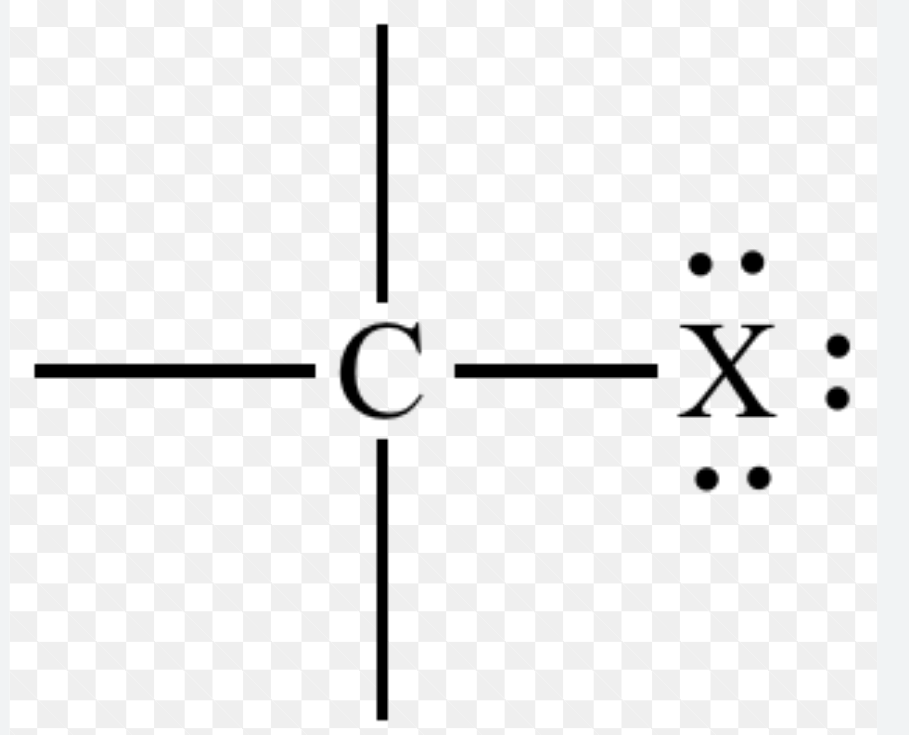
Name the functional group & list what “X” could be
haloalkane, Cl, Br, I
5
New cards
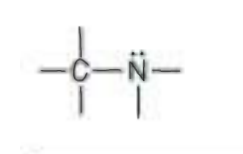
Name the functional group
amine
6
New cards
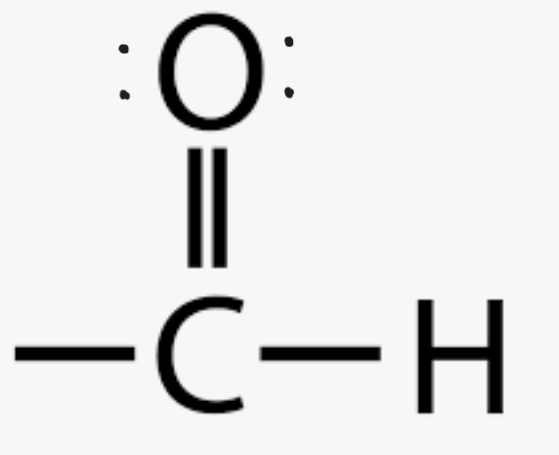
Name the functional group
aldehyde
7
New cards
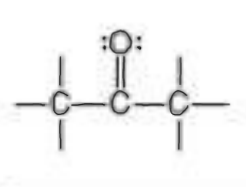
Name the functional group
ketone
8
New cards
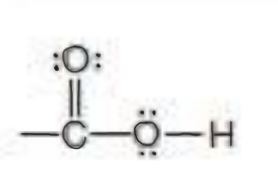
Name the functional group
carboxylic acid
9
New cards
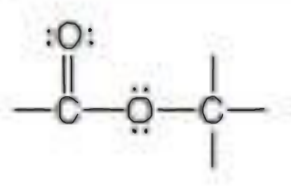
Name the functional group
ester
10
New cards
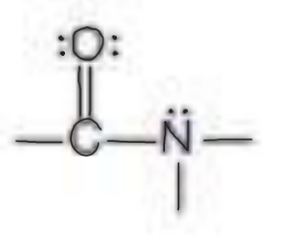
Name the functional group
amide
11
New cards
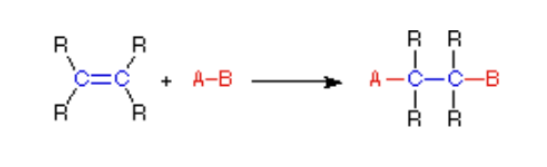
does the picture show a(n) addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement reaction?
addition
12
New cards
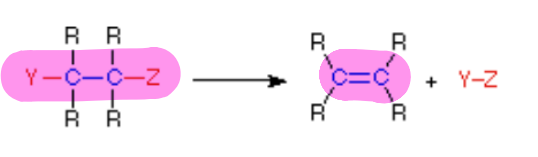
does the picture show a(n) addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement reaction?
elimination
13
New cards
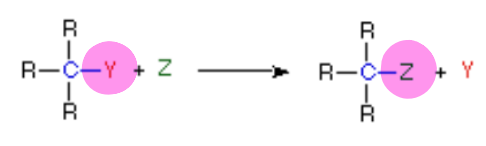
does the picture show a(n) addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement reaction?
substitution
14
New cards
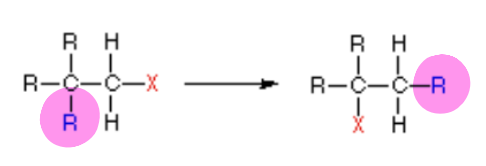
does the picture show a(n) addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement reaction?
rearrangement
15
New cards
basic building blocks of fatty acids =
carboxylic acids, hydrocarbons
16
New cards
basic building blocks of carbohydrates =
monosaccharides, polysaccharides
17
New cards
basic building blocks of polypeptides =
amino acids
18
New cards
basic building blocks of DNA and RNA nucleic acids =
nucleosides (nitrogen base, phosphate, sugar)
19
New cards
polysaccharides are formed from what kind of bonds?
ether
20
New cards
triglycerides are formed from what kind of bonds?
ester
21
New cards
polypeptides are formed from what kind of bonds?
amide
22
New cards
Which organic polymers are formed by condensation rather than addition?
polyester, polyamide
23
New cards
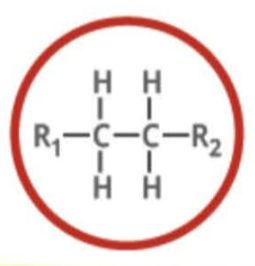
Name the functional group
alkane
24
New cards
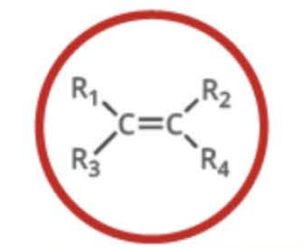
Name the functional group
alkene
25
New cards

Name the functional group
alkyne
26
New cards
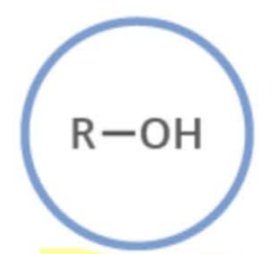
Name the functional group
alcohol
27
New cards
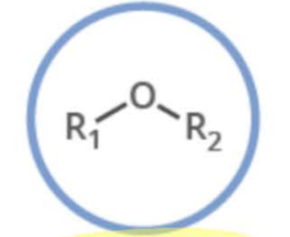
Name the functional group
ether
28
New cards

Name the functional group
haloalkane
29
New cards
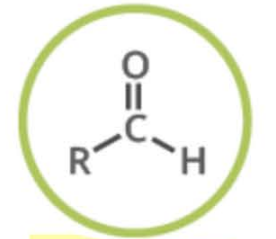
Name the functional group
aldehyde
30
New cards
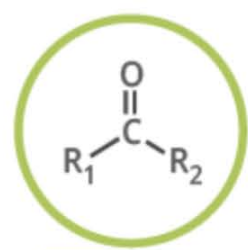
Name the functional group
ketone
31
New cards
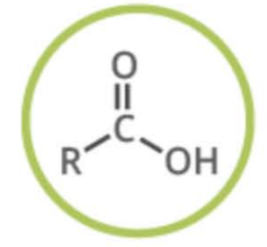
Name the functional group
carboxylic acid
32
New cards
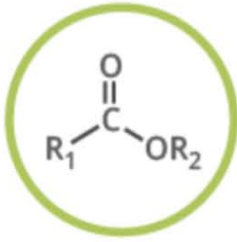
Name the functional group
ester
33
New cards
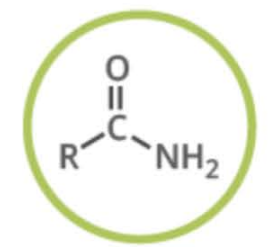
Name the functional group
amide
34
New cards
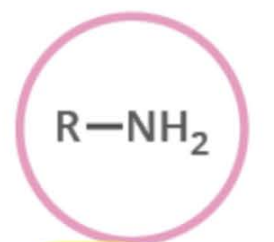
Name the functional group
amine
35
New cards
**name the bond formed by the following:**
polyester: alcohol + carboxylic acid
polyester: alcohol + carboxylic acid
ester
36
New cards
**name the bond formed by the following:**
polyamide: amine + carboxylic acid
polyamide: amine + carboxylic acid
amide
37
New cards
**name the bond formed by the following:**
triglycerides: glycerol + carboxylic acid
triglycerides: glycerol + carboxylic acid
ester
38
New cards
**name the bond formed by the following:**
sugars: alcohol + alcohol
sugars: alcohol + alcohol
ether
39
New cards
**name the bond formed by the following:**
proteins: amine + carboxylic acid
proteins: amine + carboxylic acid
amide
40
New cards
collision theory is based on _______. this means Ek= 1/2 kT = 1/2 mv^2
kinetic molecular theory of gases
41
New cards
a _______ must occur for a reaction to happen
collision
42
New cards
a collision must have ____ and ______ of collision
sufficient energy, correct orientation
43
New cards
Is ozone catalysis homogenous or heterogenous? What is the catalyst?
homogenous, Cl
44
New cards
What is the overall reaction in ozone catalysis? (in the form reactants, products)
O3 + O, 2O2
45
New cards
Is the Haber process exothermic or endothermic? What is the catalyst? Is it homogenous or heterogenous?
exothermic, FeO (iron powder), heterogenous
46
New cards
For catalytic converter reactions, list what goes in and out. (in the form reactants, products)
NO2 + CO + HC, N2 + CO2 + (CH)2
47
New cards
What gets reduced in the catalytic converter reactions? To what?
NO2, N2
48
New cards
What gets oxidized in the catalytic converter reactions? To what? (separate the 2 by a forward slash)
CO, CO2 / HC, H2O + CO2
49
New cards
Transition state theory is based on (energy/collisions) not (energy collisions)
energy, collisions
50
New cards
Transition state theory is most easily depicted on a reaction profile of
E vs t
51
New cards
the top of the activation barrier is the _____ or _____.__ It is theoretical, not an “ “
transition state, activated complex, intermediate
52
New cards
at the top of an energy hill, a transition state is (equally/more) likely to fall left or right
equally
53
New cards
an energy hill called the _____ rises positively above the thermodynamic profile. This barrier is what (nonspontaneous/spontaneous) processes don’t happen.
activation barrier, spontaneous