ap psychology: research unit
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
theory
possible explanation of a phenomenon → helps validate
example - the more you see someone, the more you like them
THEORY AND HYPOTHESIS ARE NOT THE SAME
hypothesis
testable prediction of an outcome (or a study) → helps form
example - subjects will more likely want to play a game with people they saw earlier opposed to people they just met
operationalization(operational definition)
how is it measured?
(is the measure good/fair/makes sense?)
how variables in a study are measured
types of measures
survey, test, inventory
validity
is it accurate?
reliability
is it CONSISTENT?
population
group of people who possess a certain characteristic (who I may want to study)
sample
smaller group that represents the population
the group participating in the study
internal validity
measure assesses what it is supposed to
external validity
sample represents the population → results from sample can be applied to population
random sampling
people from the population who are chosen randomly → good external validity
sample bias
poses the greatest threat to external validity → poor external validity
case study
poor external validity
rare concept with much info
provides the most detailed qualitative information
allows you to collect a lot of information from something rare or unusual that is likely not possible with other research methods
a type of a research method that you can’t really conduct repeat and experiments on so you use the all information that is already available
meta analysis
uses previous studies and puts it all together
experiment
study 1, study 2
variables that can be manipulated
observational study
naturalistic → variables you can’t control
laboratory → artificial
pro and con of experiment
infer cause and effect
can be complex
variable: dependent
it’s affected/depends on the independent variable
you can’t control
variable: independent
the variable you can control and change
variable: control/controlled
the variable you keep the same throughout the experiment
variable: extraneous
variables you can’t control
confounding
interferes with the influence of the independent variable
a kind of extraneous variable that is messing things up; makes things confusing
variables that adversely affect an outcome of a study that we cannot control and/or are not aware of
the effect of extraneous/confounding variables
researchers take into account extraneous variables because the whole experiment must be considered invalid if another variable affects the study because the experiment is longer testing one’s variable’s affect on the other
control group
no special treatment
experimental group
gets special treatment
ethics
IRB approval
confidentiality
informed consent
no coercion
minimized risks
deceptions when necessary
debriefing
IRB (Institutional Review Board)
approves any kind of research before it starts
reviews research purpose
will accept or reject and ask you to revise
looks at research ethics
they do NOT fund the study
confidentiality
the participant can tell whoever but the research has to make sure the participant’s identity is kept a secret unless it’s an emergency like they’re going to hurt themselves
informed consent
participant has to give you their consent to do the experiment unless you’re in a public space like a mall
no coercion
researcher cannot force a participant to do anything nor can they offer money
minimized risks
ALL research has risks but it is always better to have less risks
the IRB asks “does the benefits outweigh the risks?” example - coronavirus vaccine
deception when necessary
it is permitted under certain circumstances
debriefing
tell participants about all the aspects of the study (what is going on, the purpose, hypothesis, etc.) following participation in a study
random assignment
each person has an equal chance of being in either the control or experimental group
avoids experimental bias
double blind procedure
neither the researcher nor the participant knows the participant assignment
avoids experimental bias
single blind procedure
the researcher knows the assignment of the participant while the participant does not know their assignment
experimenter bias
researcher influences results
sometimes deliberate, sometimes not
social desirability bias
appealing better than one is in a study
examples - rating oneself better, knowing like you have knowledge
placebo effect
“fake pill” → healing response
expectation of healing → healing response
hawthorne effect
knowing you’re being studied which facilitates behavior
correlation
the relationship between two variables
NOT CAUSATION (just because there’s a correlation between two variables does not mean one variable caused the other variable to happen)
spurious correlation
a misleading/non-existent relationship
two variables that appear to correlate but in fact do not
positive correlation
same direction: A↑ B↑ and A↓ B↓
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE DO NOT REFER TO GOOD AND BAD
negative correlation
opposite direction: A↓ B↑ and A↑ B↓ (inverse)
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE DO NOT REFER TO GOOD AND BAD
correlation coefficient
direction → positive (+) or negative (-)
strength of relationship → how much do the dots look like a line? (number from 0 to 1)
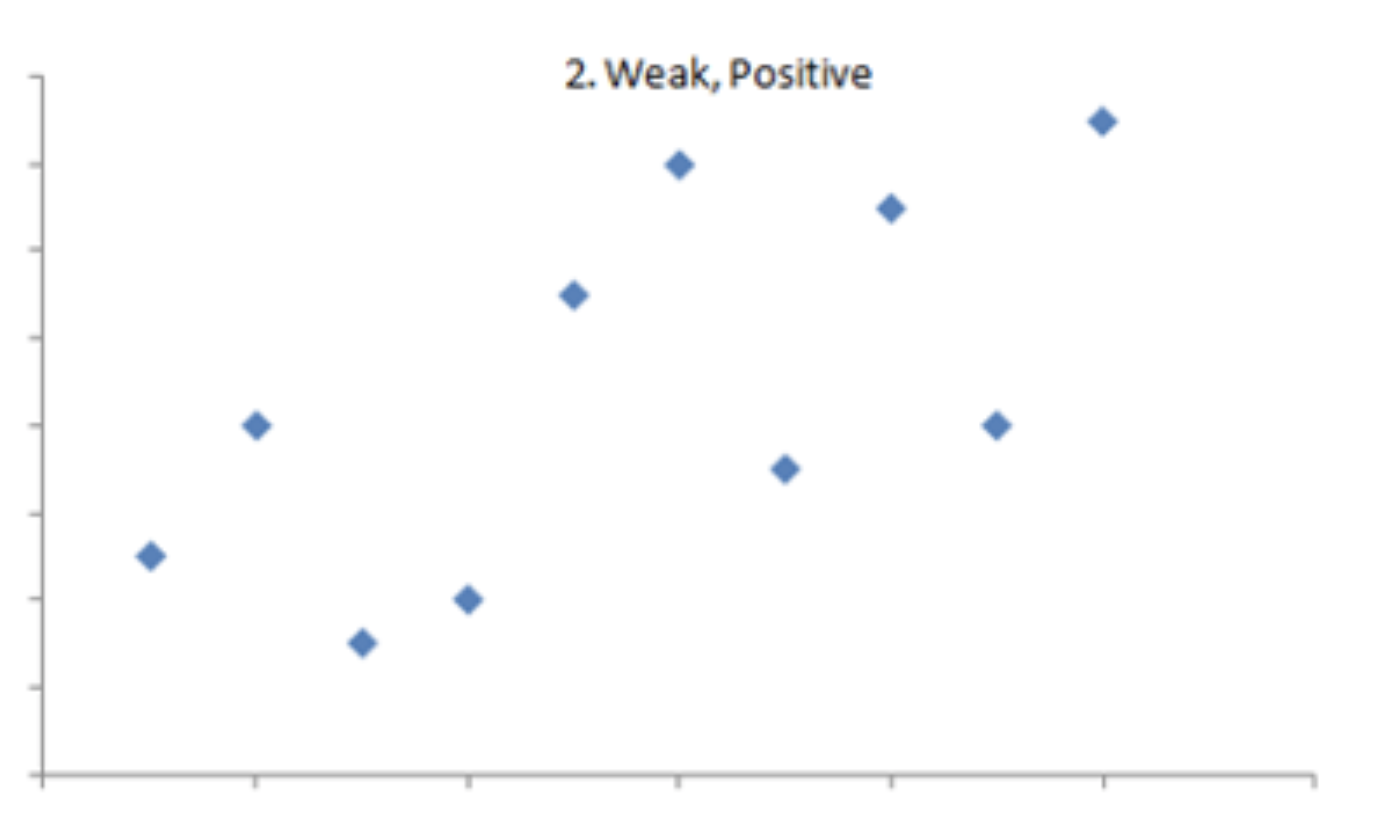
0.2
weak correlation, dots are going in a positive up direction
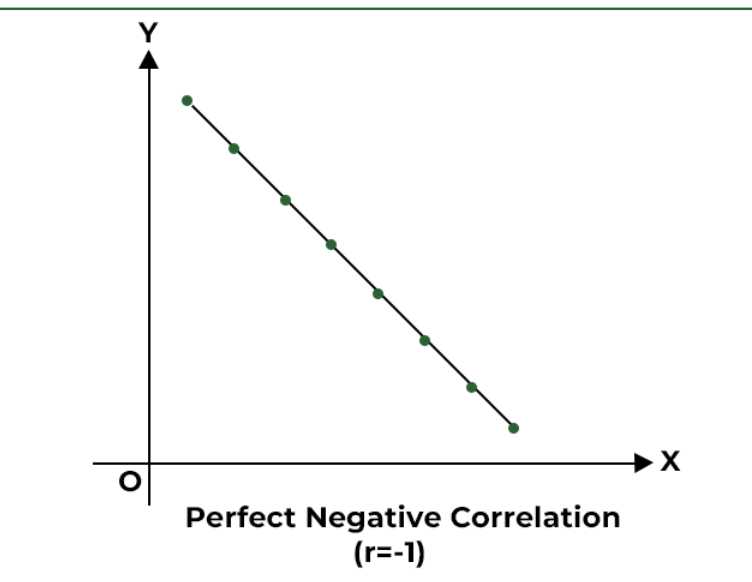
-1.0
perfect correlation, dots made a straight line that is going in down negative direction
mean
the average
most easily affected by extreme scores
median
middle value
is the middle of all vales
mode
most frequent mode
can be more than one
mode is the highest point
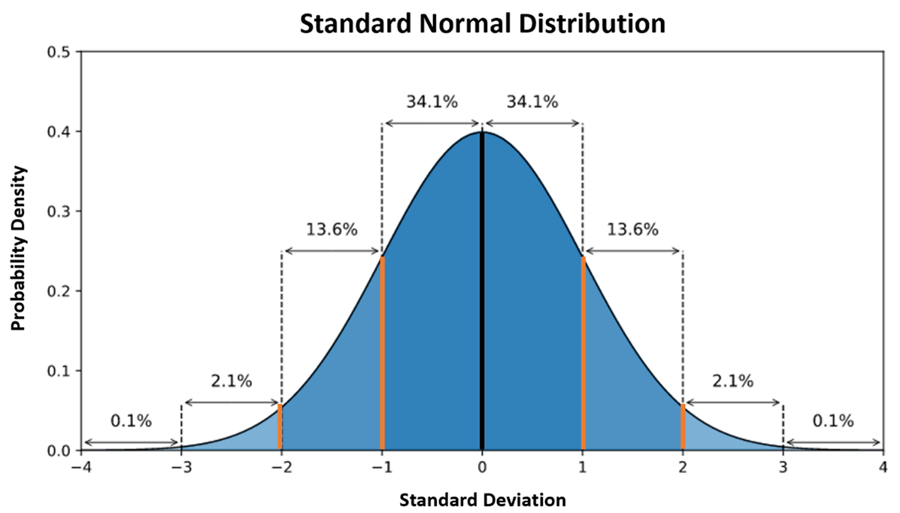
normal distribution
mean=median=mode
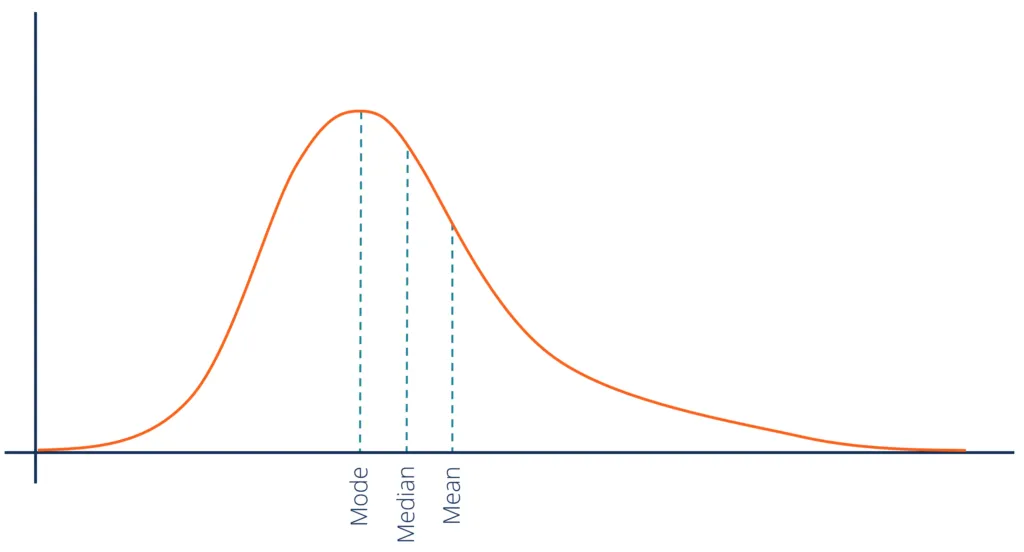
positive skew
mean>median>mode
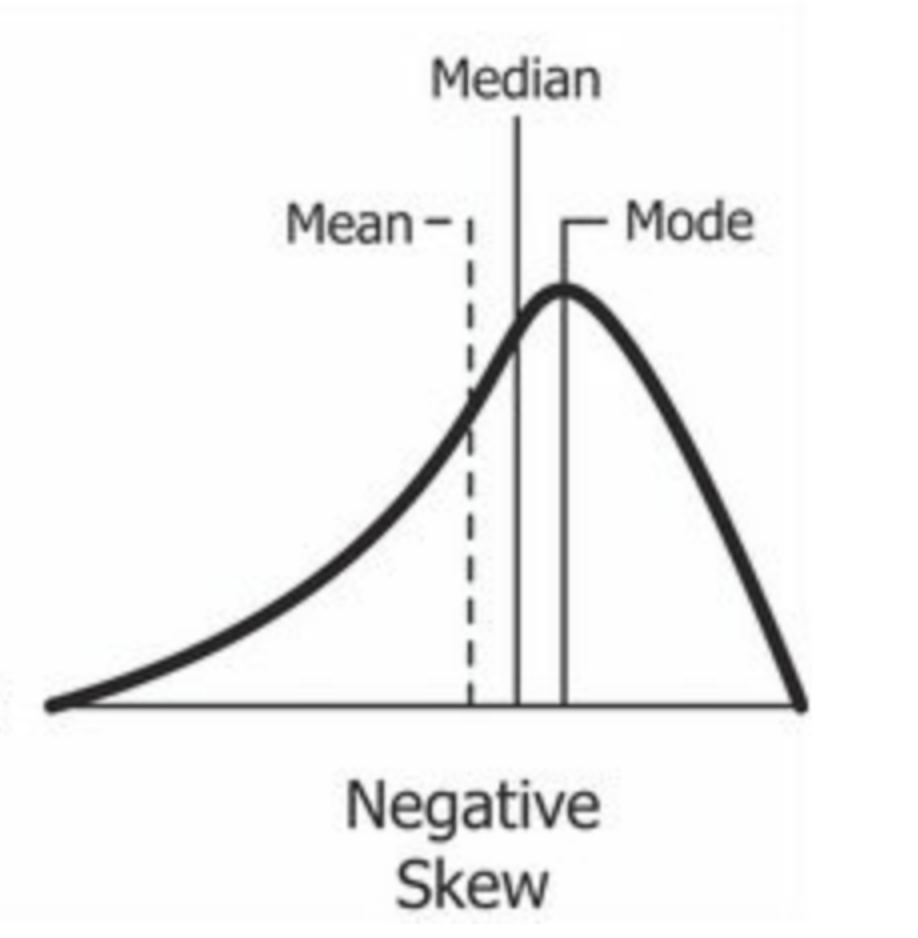
negative skew
mode>median>mean
measures of spread
=measures of variation
range equals
highest-lowest
standard deviation
standard measure or variability
can compare one variable to another
standard deviation equals
square root of variance
☆ the higher the SD, the bigger the spread
variance equals
square of standard deviation
☆ the higher the SD, the bigger the spread
EX: 100 mean (0 SD)
1 above: 110
1 below: 90
SD is 10
z-score
number of standard deviations above or below the mean
z score equation
z score = score-mean/sd
if the mean of test scores was 100 and the standard deviation was 15, what is the z-score of a person who got 130?
130-100=30 30/15=2
(consider a normal distribution) given a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 5, what percentage of participants had a score between 45 and 55?
68%
percentile
what percentage of population did a value outscore? → add up everything to the left of the value
percentage is the same as _____
percentile
suppose a person has a score of 1.0. what is that person’s percentile?
84
what is the percentile of someone who score corresponds to a z-score if -1?
16th percentile (or 15.5 if you don’t round)
concluding an effect or difference exists →
conclusion is wrong →
type 1 error → chance of this → p-value
any p-value equal or less than this is acceptable
0.05
statistical significance
→ low type 1 error probability
→ confidence that difference/effect exists
→ “not due to chance”
t-test
compares means of two groups
ANOV
compares means of 3 or more groups
hindsight bias
“I knew it all along” ← after conducting research and coming to a conclusion, you feel like this
confirmation bias
belief → seeks evidence that supports
belief → ignores evidence that goes against
construct validity
theoretical concept
does the test accurately assess the theoretical concept?
criterion validity
specific skills
does the test accurately measure a certain set of skills?
content validity
measure that accesses how well a test or other assessment tool covers all relevant aspects of a construct
do the test items collectively fully cover the theme being assessed?
concurrent validity
measure that accesses how well 2 tests or assessments agree when they were taken at the same time
does the test correlate well with an already established test?
predictive validity
ability of a test or measurement to predict a future outcome, such as behavior, performance, or disease
face validity
does the test look like a legitimate test?
test- retest reliability
does administering the SAME test give you similar results?
parallel forms reliability
do different test versions with similar content yield similar results?
inter-rater reliability
do obsevers of the same event rate it the same way?
split half reliability
is there consistency WITHIN the test?