PED - Ethics: informed consent
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4 types of consent , what is required for valid consent , 4 criteria used when assesing caoacity , practical terms considered and gillick competence and how it differs from fraser guidelines
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is consent ?
“permission for something to happen or agreement to do something”
Examples:
• One can consent to many things;
– Sharing of information
– Sexual intercourse
– An operation
What are the types of consent ?
Informed
the patients understanding - the risks , benefits , the information given
Explicit
verbal or written - a signature
Implied
caution required eg . asking are you here for this, pulls up sleeve for bp check
Proxy
eg . a court may consent on behalf of a child
note- an intervention with. a patient without consent = assault
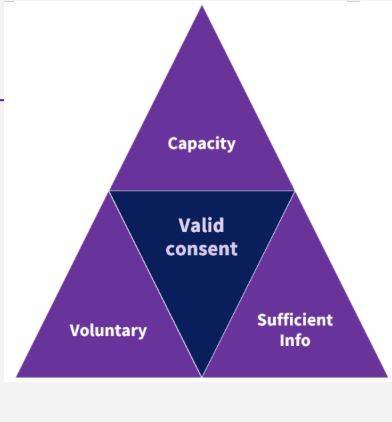
What is required for the consent to be valid ?
Have capacity to give consent
Be acting voluntarily
Have sufficient , balanced information to allow them to make an informed decision
Be capable of using and weighing up the information provided
Understanding the consequences of not giving consent
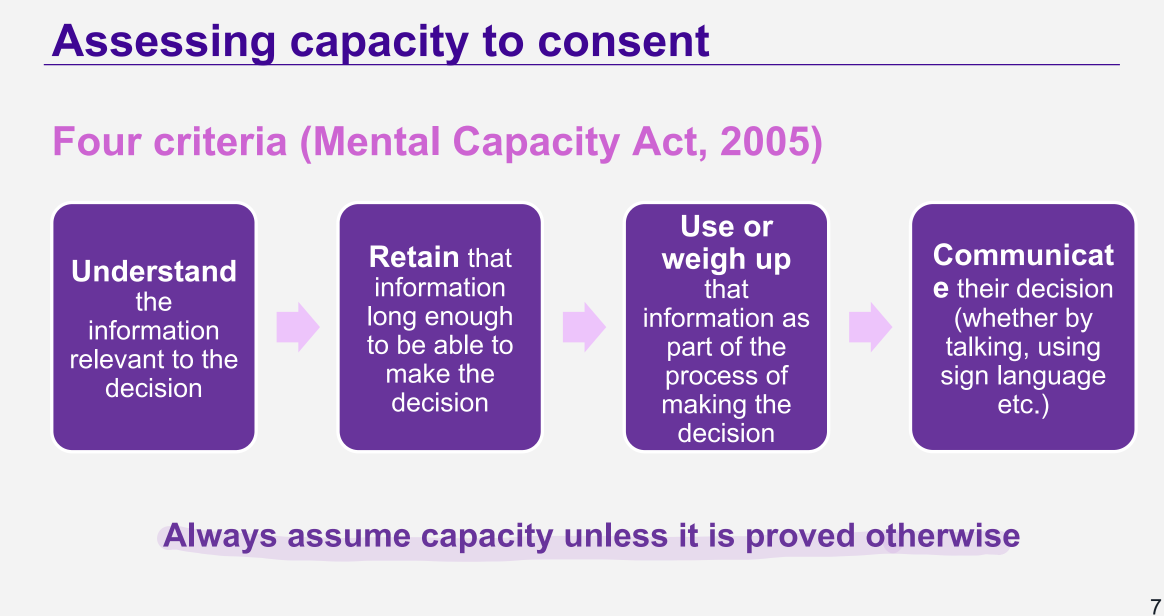
What is the mental capacity act 2005 criteria for assessing capacity ?
alway assume capacity unless it proved otherwise
4 criteria:
understand
retain
use or weigh up information
communicate their decision
What are the rules related to capacity?
Do not assume if someone lacks capacity on one occasion in relation to one thing that they lack capacity for all decisions
● A person’s capacity to consent may be temporarily affected by other factors, e.g. fatigue, effects of alcohol
● Do not assume someone lacks capacity based just upon their age, disability, beliefs, condition or behaviour
● Do not assume someone lacks capacity because they make a decision that you disagree with
● Take all reasonable steps to help and support people to make their own decisions
What are material risks ?
when discussing a medicine , prescribers should tell patients about:
Material risks 🇦:
a risk that a reasonable person would want to know or that this particular patient would want to know
focus on patients perspective in his or her specific circumstances
advise of serious side effects and common side effects
reasonable alternatives - may include not taking medicines
What must be done when obtaining consent ?
information given needs to be clear,accurate and presented so they can understand
don’t make assumptions about their level of knowledge
give opportunity to ask questions
it is ongoing process , can’t be presumed because it was given previously
people with capacity are entitled to withdraw their consent at any time
what is the structure of a consultation ?
good intro - hi my name is,role, ask for patient identifiers
golden minute - how can i help you
LCIF - lifestyle,ideas,concerns,expectations,feelings
discuss material risks - concerns specific to the particular patient - risk of harm to baby
reasonable alternatives - what are the consequences to her and baby if do nothing ?
What are the age definitions ?
adult 18+
young person - 16 or 17 yrs old
child - under 16 yrs
What do you consider when a young person or child might have capacity ?
They may have consent to some services but not others:
asses maturity and understanding
consider the complexity and importance of decision
young people and children should be involved as much as possible in decisions about their care , even when they are not able to make decisions on their own
How does capacity work with young people ?
young people are presumed to have capacity unless evidence to suggest otherwise
asses capacity the same way as for an adult ( the 4 MCA CRITERIA )
encourage young people to involve their parents in making important decisions
but pharmacists should respect a competent young persons request for confidentiality
How does capacity work with children ?
children are not presumed to have capacity to consent Pharmacist decides if a child can give consent base on if :
the treatment is in their best interest
they have maturity and the ability to understand the information given
they understand what they are consenting to
if pharmacist is satisfied — no additional parental consent is required
What is gillick competency ?
“As a matter of Law the parental right to determine whether or not their minor child below the age of sixteen will have medical treatment terminates if and when the child achieves sufficient understanding and intelligence to understand fully what is proposed.”
What is fraser guidelines ?
They apply specifically to giving contraceptive advice to girls under 16
1. that the girl will understand the advice
2. that she cannot be persuaded to inform her parents or to allow the HCP to inform the parents that she is seeking contraceptive advice
3. that she is very likely to continue having sexual intercourse with or without contraceptive treatment
4. that unless she receives contraceptive advice or treatment her physical or mental health or both are likely to suffer
5. that it is in her best interests to get contraceptive advice, treatment or both without the parental consent” (Gillick v West Norfold, 1985).
What is different about gillick competency?
not specific to contraception
competency depends on what the child is consenting to - decided by professional
a gillick competent child can refuse treatment - can be overruled by parental responsibility if severe consequences
a gillick non-competent child cannot refuse treatment
a child’s view should still be considered , regardless of competence
Summary
Consent is vital
• Those 16+ have capacity to consent unless they do not meet one of the four
criteria
• Those 15 and under might be competent to consent themselves- gillick competency