Non-Communicable Disease Epidemiology Final Exam
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Natural history (def)
Typical progression of a disease in an individual from its beginning until its final outcome without treatment
Stages of disease (3; interventions)
Predisease: health promotion and specific protection
Latent disease: Early diagnosis and treatment
Symptomatic disease: Disability limitation, rehabilitation
Primary prevention (methods)
3 E's
Education
Environmental change
Enforcement/legislation
Population strategies (def, key factors)
Bell curve -> shift risk factor distribution in the population
Move everyone down 5lbs or lower chol
Radical
Benefit-to-risk ratio low
High-risk strategies (def, key factors)
Screening and aggressive treatment
Behaviorally inappropriate
Difficult to identify
Risk scores: Framingham, SCORE
Secondary prevention (methods)
Early detection
Screening
Tertiary prevention (methods)
Prevent and delay development of acute/chronic complications
COPD (cases, def, types)
210 million cases/year
Chronic bronchitis/emphysema
Decreased elasticity of the lung
Asthma (cases, prevalence, why deaths)
300 million cases/year
Increasing in prevalence
Deaths related to lack of proper treatment
Occupational lung diseases (examples)
Pneumoconiosis
Occupational asthma
Work-aggravated asthma
Sleep apnea (%, sequelae)
25% men, 10% women
Untreated -> hypertension, stroke, cardiac failure
Hospital-based cancer registry (limitation)
Only the people visiting that hospital
Population-based registry (US, when, who, what)
USA: Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Result (SEER) program
started 1973
36% of population
"tracks the incidence of persons diagnosed with cancer during the year and collects follow-up information on all previously diagnosed patients until their death."
Age standardization (def, use)
Apply rates to a relevant population standard
Take away impact of age on epi
Account for differences in age structure of the population/s being considered
Geographical variation (factors)
- Genetics
- Lifestyle
- Environmental factors
- Screening
(migrant studies)
Migrant studies (def/use)
Determine if causes are genetic or environmental
Lung cancer (cases)
2.48 million cases, 1.82 million deaths (g)
2,500 cases, 1.9k deaths (I)
Most common overall
Lowest 5-year survival rate (1.7/10)
90% from smoking
Lung cancer (trends)
-Higher in men, but decreasing
-Increasing in women, effects from smoking in 60/70s
Lung cancer (risk factors)
-Age
-M>F
-SEG: lower>upper
-Smoking
-Dose-response relationship, no safe level
Doll and Hill (type, years, focus, results)
Cohort study of doctors
1954
Cases with lung cancer, controls without
Smoking & lung cancer link
Lung cancer (prevention)
Primary: stop smoking
Secondary: screening?
Breast cancer (cases)
2.31 million
3.6K (i)
Second most common after lung
Breast cancer (incidence/mortality)
Highest incidence in the West
Higher deaths in Africa/LMICs
Breast cancer (risk factors)
-increasing age
-SEG incidence higher in upper, mortality higher in lower
-age at menarche/menopause
-age at first pregnancy (over 30 >risk, under 20
Breast cancer (prevention)
Modify lifestyle factors
Awareness and screening
Treatment and specialist centers
Colorectal (cases)
1.9m (g)
2.5k (i)
Third most common
Second leading cause of cancer deaths (900k/year)
Colorectal (risk factors)
-Family history
-Increasing age
-Gender no
-SEG no
-Ulcerative colitis 2-8.2
-Lifestyle
-Diet
Colorectal (prevention)
Diet
Exercise
Screening
Prostate cancer (cases)
1.4m (g)
4.1k (i)
Second-most common diagnosed among men
Mort low in West, high in Africa
Prostate cancer (risk factors)
-Increasing age
-Race (AA men higher, Asian men lower)
-Development of prostate
-Family history
-Diet
-Smoking
-Older paternal age
Prostate cancer (prevention)
Uncertain
General health health diet
Cervical cancer (cases)
662k (g)
250 (i)
350k death g
Cervical cancer (geography, progression)
High in Africa
10-15 year progression from CIN to CC
CC (risk factors)
-High risk HPV infection (12 strains, especially 16/18)
-HIV
-Smoking
-Oral contra
-High parity
-Low SEG
-Immunodeficiency
-Diethylstiboestrol during preg
Framingham study (type, location, when, goal)
Longitudinal CV cohort study
Massachusetts
1948-now
Identify risk factors for CVD
Nurse's health study (when, what)
1976
Risk factors for major chronic disease in women
Doll and Hill (what, when, who)
Link between smoking and cancer/diseases
1950s
British doctors
Skin cancer (cases)
1.5m (g most common)
11k (i most common, 90% non-melanoma skin cancers, remainder melanoma)
Skin cancer (types)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma
- Both chronic ulcers scars, burns; sun exposure
Malignant melanoma
- Naevi/moles, childhood sunburn/intermittent sun
Skin cancer (trends)
Trending up in incidence and mort
Often caught early
High 5 year survival and rising since 90s
Skin cancer (risk factors)
-Age
-SEG lower>upper
-Ethnicity
-Family
-Phenotype
-Pigmentation disorders
Skin cancer (prevention)
Primary: hats, suncream, protect children, avoid lamps/beds
Secondary: early diagnosis, awareness
Injury (definition, key stats)
Damage to the body from acute exposure to thermal, mechanical, electrical or chemical energy or from absence of essentials such as o2
Most common cause of death for 1-44 years
35% of all ER visits
General model for injury control
Monitor incidence
Identify risk factors
Intervene
Evaluate
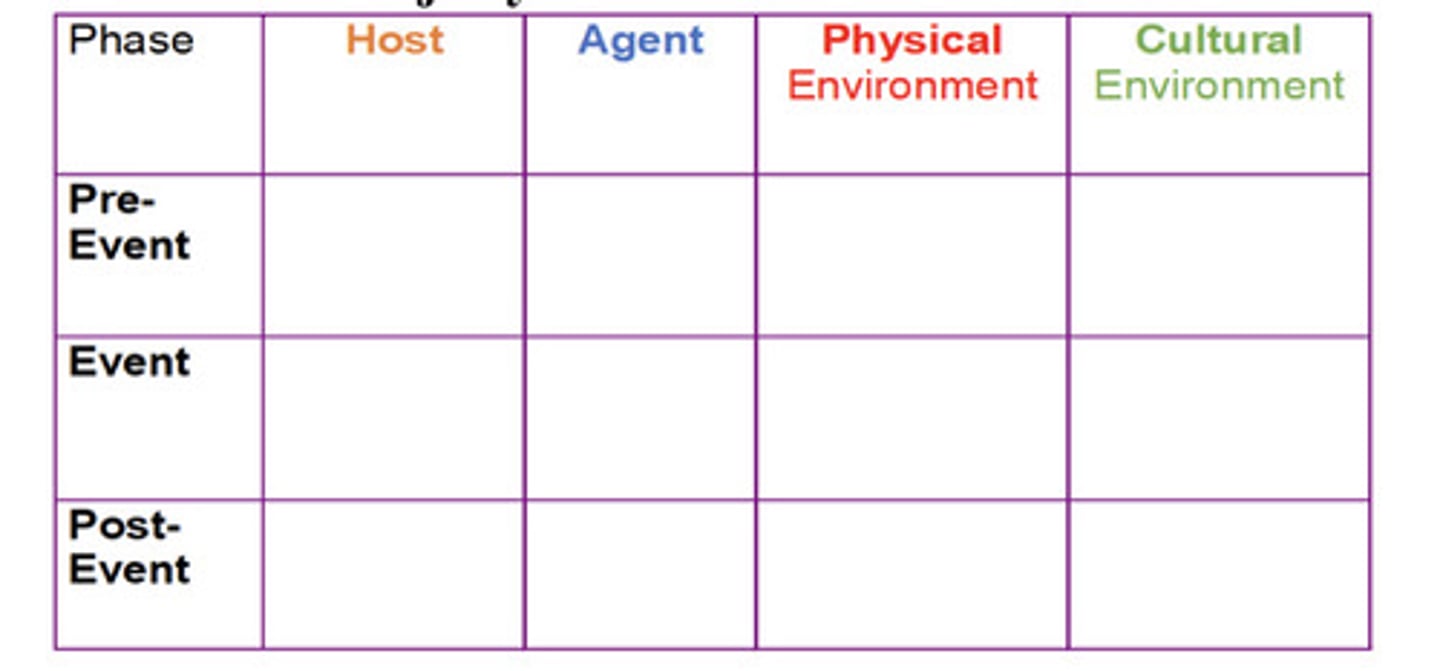
Haddon Phase Factor Matrix (what is, 6 factors)
Phases relevant to the risks posed by the agent, host and environment
Pre-event, Event, Post-event
5 E's of incident prevention
Epidemiology
Education
Enforcement
Engineering
Evaluation
Screening vs diagnostic test
Screening = identifies asymtomatics at risk of disease
Diagnostic = determines presence or absence of disease in symptomatics
Positive predictive value (def, equation)
probability a person with a positive test actually has the disease; true positive
= true positive/total positives
Negative predictive value (def, equation)
Prob person with a negative test is truly disease-free; true negative
= true negatives/total negatives
Sensitivity (def, equ)
test's ability to correctly identify true positives/people with disease
= true positive/(true positive+false negative)
Specificity (def, equ)
Ability of test to correctly identify true negatives
= true negatives/(true negative+false positive)
Lead-time bias (def)
Live with disease longer because it was diagnosed earlier
Length bias (def)
screening tends to detect more slow-growing/indolent cancers; aggressive cancers move faster so less likely to be picked up
Benefits of screening
-Improved prognosis
-Reassurance for ppl with negative tests
-Less radical treatment
Disadvantages of screening
-Longer "illness" if prognosis unchanged
-False reassurance for false negatives
-Anxiety/unnecessary medical intervention
-Cost
Considerations for starting a screening program
-Management
-Population register
-Call-recall system
-Facilities
-Fears/anxiety
-Treatment
-Quality assurance
Junger and Wilson criteria (use, 9)
To introduce a screening program. Must be:
-Relatively common
-Seriously debilitating
-Treatment acceptable to population
-Facilities available for treatment
-Recognized treatment available
-Recognized identifiable preclinical phase
-Natural history understood
-Treatment of preclinical disease more effective than treatment of symptomatic
Wilson & Jungner screening test criteria (7)
-Simple and quick
-Specific
-Sensitive
-Repeatable
-Accurate
-Inexpensive
-Acceptable
Criterion of positivity (def, considerations)
Test value at which screening test outcome is considered positive
Weigh cost of false positives vs negatives, anxiety and costs vs false sense of security
Decreased criterion of positivity =
sensitivity increase, specificity decrease
Increased criterion of positivity =
sensitivity decrease, specificity increase
Breast cancer screening (test, evidence, issues, rec)
Mammography
Reduction of mortality 20% in 50+
Overdiagnosis/treatment
Yes
CC/CIN screening (test, rationale, rec)
Smear and cytology/HPV and reflex cytology (more sensitive)
Smear tests can detect CIN which always precede CC
Yes
Colorectal cancer screening (test, evidence, rec)
Meets ALL disease criteria
Test = fecal immunochemical test
Early detection and removal = reduction in incidence and mort
Yes
Lung cancer (evidence, rec)
Limited evidence, only one RCT showed reduced mort
US rec yes for at risk, EU waiting on more trials
Prostate cancer screening (evidence, tests, rec)
Mixed evidence, no reduction in mortality
Tests = prostate specific antigen (PSA), digital rectal exam
US and EU no
EU running PRAISE-U project to identify cost-effective early detection programmes for prostate cancer
Interval cancer (def, examples)
Cancers diagnosed between routine screening appts
Breast, CC, Colorectal
Interval breast cancer (causes)
Mammographically occult
True interval
Missed abnormality (false neg), subtle signs
Obesity (trends/stats)
3x since 1975
1 in 8 people in 2022
1.18 association with all-cause mort in OB
23% Irish adult OB, 1 in 5 children
BMI (pos/negs)
Pos: quick, simple, inexpensive
Neg: Crude, doesn't take body comp into account, can't be used in children, underestimates prevalence of OW&OB
Metabolically healthy OB (def)
absence of metabolic abnormality in OB person
OB as public health concern (conditions, sequlae)
Metabolic syndrome, T2D and CVD
Higher risk of premature death and all-cause mort
Childhood OB has lifelong impacts
Negative social/econ consequences
Costs to individuals and systems
T2D (def, trends)
Body cannot effectively use insulin, damage to nerves, vessels, eyes, kidneys
4x increase in 18+ with diabetes
Rising faster in LMICs
14% of adults in 2021
90% potentially avoidable
T2D Ireland (stats)
9.5% in 2015
7th in world for diabetes-related health exp. per person
Stable in adults but rising in primary school
Pre-diabetes (def, test, prog)
Abnormal glucose reg but not past threshold
Impaird fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
70% will develop overt T2D
T2D risk factors
-Age
-Family history
-Gestational dia
-OB
-Sendintary
-Smoking
-Very low birth weight
-Depression, antipsychotics
-ART
-Diet
Building a cancer strategy (steps)
FROM PREVENTION TO Palliative andd prediction
1 Population data
2 Diagnosis
3 Treatment
4 Palliative care
Predicting future trends
Building a cancer strat: Population data (considerations)
Primary prevention
Secondary prevention (screening)
Building a cancer strat: diagnosis (considerations)
Facilities available
Building a cancer strat: Treatment (considerations)
Current types and numbers of cancer by age and sex
Personnel required
Hospitals
GP/primary services
Building a cancer strat: Palliative care (considerations)
Cure/survival rates
Where do people like to die
Palliative care specialists
Projections
Testing in series (def, s/s effect)
BOTH screening tests must be pos/abnormal for positive result
Lower sensitivity, higher specificity
Testing in parallel (def, s/s effect)
EITHER test is pos/abnormal = pos screening result
Higher sensitivity, lower specificity
Positive predictive value (PPV) (def, equ)
True positives, person with pos result actually has disease
True positives/total positive on test
Negative predicative value (NPV) (def, equ)
True negatives, person with neg result does not have disease
True negatives/total negative on test
Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC curve) (def, setup, interp)
Graphic determination of test accuracy
Sensitivity on Y vs 1-specificity on X
More area under the curve is GOOD: 1 is perfect, .5 is random, >.5 is model worse than guessing
No discrimination is BAD
Likelihood ratio (def, interp)
Commentary on test quality ;probability of getting a result if the person has the condition vs if they were healthy
Good test has high ratio
LRpos>10 and LRneg<0.1 = convincing evidence
LRpos>5 and LRneg<0.2 = strong evidence
LR+ (def, equ)
Probability of getting a positive result if person is diseased vs healthy
Equ = Likelihood of + test in diseased person / likelihood of + in a healthy person
LR- (def, equ)
Probability of getting a negative result if person is diseased vs healthy
LR neg = (1-sensitivity)/specificity
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) (def, examples)
Conditions of the heart and blood vessels, all stemming from atherosclerosis
-Coronary heart disease (CHD)
-Cerebrovascular disease
-DVT
-Pulmonary embolism
CVD public health significance (stats)
#1 cause of death and premature death globally
19.8m in 2022
32% of all global deaths (75% of which LMIC)
38% of premature deaths
Most can be prevented
CVD and COVID (relationship)
Pre-existing CVD = worse outcomes, greater risk of death from COVID
COVID can induce CVD symptoms
Descriptive epidemiology (def)
Describes distribution and occurrence of a disease
Who, what, where, when
Analytical epi (def)
Analyzing relationship between disease and risk factors
Formulation and testing of etiological hypotheses
Experimental epi/prevention strategies
Descriptive epi CVD (list)
Age: Atherogenesis and lifestyle begins in childhood, increase in m's starts from 30
Gender: mort more common among men, affects women equally but older; women have gender-specific risks
CVD trends (over time, location)
Doubling of cases 1990-2023
Prevalence higher in E EU, C Asia, N Africa, ME, N America, Australia; mort higher in E EU, N Africa, C Asia
CVD deaths leading causes
CHD/ischemic heart disease and stroke
CVD in Ireland (stats)
56% reduction from 1985-2006
48% due to risk factor improvements
56% reduction from 2000-15
60% from improvements in treatment
CVD risk factors
Elevated total or LDL chol
Low HDL
Hypertension
Smoking
Diabetes
Family history
Age
OB
Psychosocial
Diet
Inactivity
HDL (def, implication)
High-density lipoprotein
Confers protection against CVD?