AMSCO AP Government and Politics: Chapter 6 The Judiciary
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
amicus curiae brief
"friend of the court"; a brief filed in order to raise additional points of view in order to influence the decision of the court
appellate jurisdiction
the authority to review decisions made by lower courts
The U.S. Court of appeals has appellate jurisdiction
The Supreme Court has appellate and original jurisdiction
attorney general
the head of the Justice Department and the chief law enforcer of the United States
binding precedent
the decisions of higher courts that set the legal standards for similar cases in lower courts within the same jurisdiction
certiorari
"to make more certain"; losing parties can appeal based on this concept
common law
the body of court decisions that makes up part of the law
concurring opinion
an opinion that agrees with the result of a case but disagrees with the court's reasoning for the decision
constitutional courts
courts directly or indirectly mentioned in the Constitution
Department of Justice
represents the government in legal matters and provides the means for the enforcement of federal laws
discuss list
compiled by the chief justice, the list of cases on review that he thinks may be appropriate for the Court to hear
dissenting opinion
opinion of a case that a minority of the judges agree upon... does not become case law but will sometimes be referenced by judges in future court cases
diversity citizenship
cases in which two parties reside in different states
defendent
the party answering the action
Dred Scott v. Stanford
Supreme Court case in which it was ruled that black slaves were not citizens of the United States and could not claim any rights or privileges granted to white citizens
in forma pauperis
a petition filed with the U.S. Supreme Court by an indigent person; the $300 filing fee is waived for such petitions
injunction
a court order prohibiting a person from committing a certain act
judicial activism
the tendency of judges to interpret the Constitution according to their own views; often appears with loose constructionism
judicial review
allows the Supreme Court to declare a law or act unconstitutional after the fact; established in Marbury v. Madison
judicial self-restraint
judges should confine themselves to applying rules clearly stated in the Constitution; often appears with strict constructionism
litmus test
used to find where nominees stand on certain (controversial) issues
majority opinion
opinion of a case that a majority of the judges agree upon... becomes the law
written by the chief justice or the most senior justice on the majority
Marshall, John
Created the precedent of judicial review in the case of Marbury v. Madison; many of his decisions gave the federal government more power
original jurisdiction
-refers to where a case should be heard first
-U.S. District Court has original jurisdiction
-Supreme court has original jurisdiction and appellate
per curium opinion
collective and anonymous decision (often brief and without explanation)
Persuasive precedent
precedent which a judge is not obliged to follow, but is of importance in reaching a judgment
petition for certiorari
A formal request by one or more parties in a legal case for a the Supreme Court to grant a writ of certiorari, or to agree to hear the appeal
"cert"
petitioner
party that initiates a lawsuit
plaintiff
a person or party filing a lawsuit
plea bargain
a negotiation in which the defendant agrees to enter a plea of guilty to a lesser charge and the prosecutor agrees to drop a more serious charge
precedent
A decision in a previous court case that is used as the basis for a decision in a similar case.
respondent
the individual who responds to an appellate case, claiming why and how the lower court ruled correctly
Rehnquist, William
United States jurist who served as an associate justice on the United States Supreme Court from 1972 until 1986, when he was appointed chief justice
Roberts, John
Chief Justice of the Supreme Court
rule of four
Requirement that a case can only be heard by the Supreme Court if four justices vote to hear the case
senatorial courtesy
Presidential custom of submitting the names of prospective appointees for approval to senators from the states in which the appointees are to work.
solicitor general
Senior Justice Department attorney. Decides what cases the government will appeal to the Supreme Court, files amicus briefs with the Supreme Court in cases the government is interested in, and represents the United States before the Supreme Court.
sovereign immunity
the government is protected from suit unless it permits such a claim.
special legislative courts
courts created by Congress to hear matters of expert concern
stare decisis
Let the decision stand; decisions are based on precedents from previous cases
strict constructionist
a person who interprets the Constitution in a way that allows the federal government to take only those actions the Constitution specifically says it can take
Supreme Court
Final federal appellate court ("court of last resort"). Hears appeals from Circuit Courts (certiorari petition / rule of 4). Only hears "important" constitutional cases.
-Supreme Court Justices nominated by POTUS and serve for life
-appellate and original jurisdiction
torts
Intentional or unintentional acts performed by an individual and based on unreasonable conduct are known as
U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals
hears appeals from specialized trial courts, primarily the United States Court of International Trade and the United States Court of Federal Claims, as well as appeals from the district courts in patent cases and certain other specialized matters
- appointed for life, nominated by the president
-hear the case second
-appellate jurisdiction
U.S. District Courts
Trial courts in the federal court system in which almost all federal cases begin (first court to hear a case)
-courts of general jurisdiction
- judges appointed for life
-nominated by the president
-original jurisdiction
Warren, Earl
Chief Justice during the 1950's and 1960's who used a loose interpretation to expand rights for both African-Americans and those accused of crimes.
writ of certiorari
An order by a higher court directing a lower court to send up a case for review
inferior courts
-The lower federal courts, beneath the Supreme Court
-Article III courts
Judges Term
-all federal judges "shall hold their offices during good behavior" For Life
-This allows the judicial branch to operate independently from the other branches
Treason
only crime defined in the constitution
Leving war or giving aid or comfort to the enemy
Right to Jury Trial
-a citizens check on the judiciary
Federalist 78
written by Alexander Hamilton; talks about the federal judiciary; judiciary must depend on other two branches to uphold its decisions
Judiciary Act of 1789
In 1789 Congress passed this Act which created the federal-court system.
-one district existed in each state
- Defined the Supreme Court as 6 justices, or judges
riding the circuit
traveling to hold court in their assigned regions of the country
Federal Court System
The three-tiered structure of federal courts, comprising U.S. district courts, U.S. courts of appeal, and the U.S. Supreme Court.
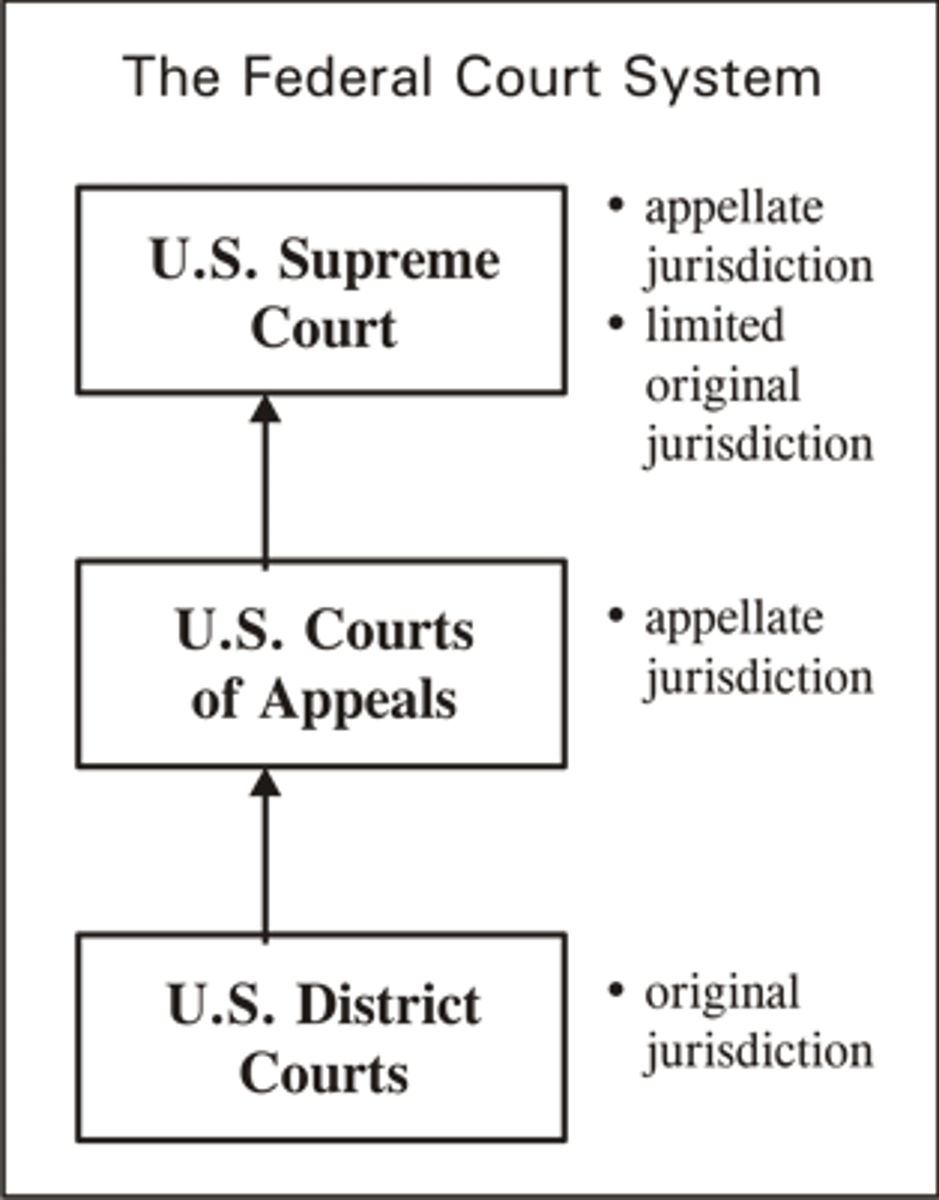
trial courts
-U.S. District courts are trial courts with original jurisdiction
-plaintiff (prosecution), defendant
-deals with crimes and civil cases
Federal Crimes
kidnapping,
mail fraud,
treason,
assassination,
counterfeiting
tax evasion
terrorism
drug trafficking
bank robbery
U.S. Attorneys
-Government lawyer that represents the US government at the district court level (trials).
-each of the 94 districts has one
civil cases
Court cases that involve a private dispute arising from such matters as accidents, contractual obligations, and divorce.
Lower burned of proof ="preponderance of the evidence"
attorney genral
the head of the department of justice
Suing the government
-The government can be sued only if it permits you too
-these cases are handled by the court of federal claims
Marbury v. Madison (1803)
Established judicial review
Getting Borked (Robert Bork)
Beginning with Robert Bork, this term means for the Senate to destroy a judicial nominee's confirmation through an attack on character, morals, and background.
Clarence Thomas
This man was an African American jurist, and a strict critic of affirmative action. He was nominated by George H. W. Bush to be on the Supreme Court in 1991, and shortly after was accused of sexual harassment by Anita Hill. Hearings were reopened, and he became the second African American to hold a seat in the Supreme Court.
nuclear option
a maneuver exercised by the presiding officer in the Senate that eliminates the possibility of filibusters by subjecting votes on certain matters to a simple majority vote
Denying Merrick Garland
McConnell announced the Senate would not hold a confirmation vote for any SCOTUS nominee until the election results of 2016
obama had nominated Garland
Trump won and nominated Neil Gorsuch
American Bar Association
largest national organization of attorneys,they're role is solely to evaluate the professional qualifications of candidates for all Article III judicial positions--the supreme court, the united states courts of appeals, and the United States District Courts
confirmation of nominees
senate votes to confirm nominees
simple majority needed
Senate's "Advise and Consent" power
The senate confirms presidential judicial nominees
Judicial checks Executive
-declare executive branch actions unconstitutional
-chief justice presides over impeachment trial
-Serve for life
-presides over presidential impeachment trial
Judicial checks Legislative
Rule federal and state laws unconstitutional
overturning precedent
Caused by societal change or if a judge decides that the case that set the precedent was wrongly decided
reversed decision by legal means
ideology
a system of ideas and ideals, especially one that forms the basis of economic or political theory and policy.
liberal
conservative