Unit 5: Electromagnetism
0.0(0)Studied by 141 people
0%Unit 5: Electromagnetism Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/21
Last updated 10:05 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
Electromagnetic field
A physical field that arises from the presence of electrically charged particles and affects the behavior of those particles.
2
New cards
Electric field
A region of space around an electrically charged particle or group of particles, in which other electrically charged particles experience a force.
3
New cards
Magnetic field
A region of space around a magnet or moving electric charge, in which other magnets or moving electric charges experience a force.
4
New cards
Electromagnetic waves
A type of wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which propagate through space at the speed of light.
5
New cards
Coulomb’s Law
A fundamental law of electrostatics that describes the interaction between electric charges.
6
New cards
Gauss’s Law
A fundamental law of electromagnetism that relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the charge enclosed within that surface.
7
New cards
Faraday’s Law
A fundamental law of electromagnetism that describes how a changing magnetic field induces an electric field.
8
New cards
Ampere’s Law
A fundamental law of electromagnetism that relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electric current flowing through that loop.
9
New cards
Maxwell’s Equations
A set of four partial differential equations that describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields and their interactions with charged particles.
10
New cards
**Magnetic flux**
It is the measure of the strength of a magnetic field passing through a given area. It is denoted by the symbol Φ and is measured in Weber (Wb) or Tesla meter squared (Tm²).
11
New cards
Φ = B \* A \* cos(θ)
Magnetic flux Formula
12
New cards
EMF = -dΦ/dt
Electromagnetic Induction Formula
13
New cards
ε = -dΦ/dt
Lenz's law Formula
14
New cards
L = NΦ/I
inductance of a circuit formula
15
New cards
inductor
A passive electronic component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it.
16
New cards
LR circuit
A circuit that consists of a resistor (R) and an inductor (L) connected in series. When a voltage is applied to the circuit, the current that flows through the circuit changes over time due to the inductor's behavior.
17
New cards
LC circuit
a type of resonant circuit consisting of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C) connected together.
18
New cards
f = 1 / (2π√LC)
**resonant frequency** of an LC circuit formula
19
New cards
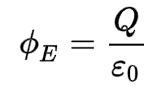
Gauss's Law for Electric Fields
This equation states that the electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed within the surface.
20
New cards
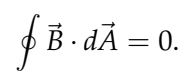
Gauss's Law for Magnetic Fields
This equation states that the magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero.
21
New cards
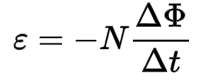
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
This equation states that a changing magnetic field induces an electric field
22
New cards
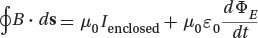
Ampere's Law with Maxwell's Correction
This equation relates the magnetic field to the current density and the rate of change of the electric field.