Polar &/or Charged Carbon-Containing Molecules/Groups
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biochem Outcome 2 Cluster
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
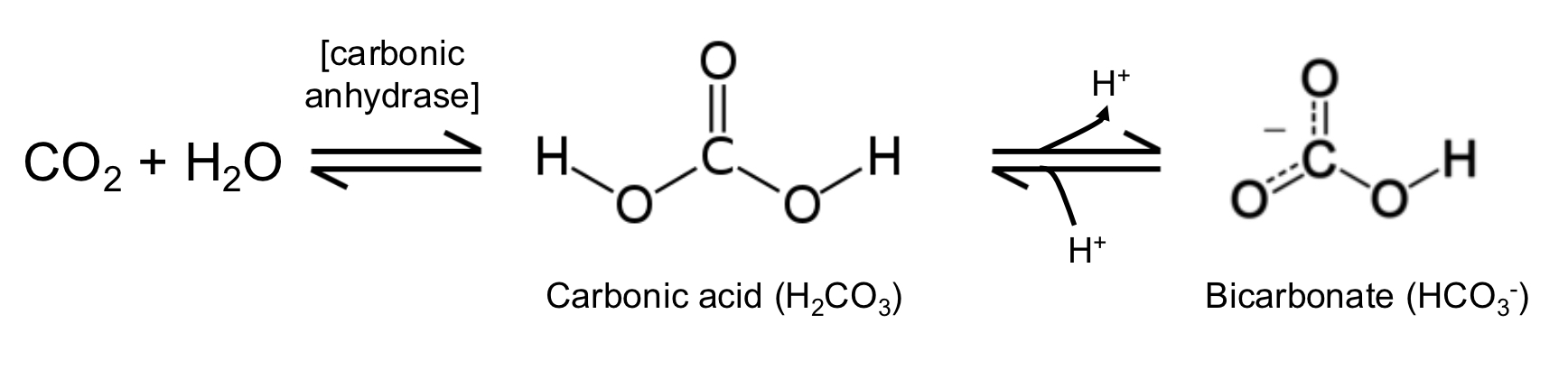
bicarbonate
derived from carbon dioxide via the carbon anhydrase reaction & functions both as a potential proton-absorbing buffer compound & as a source of carbon for metabolic carboxylation reactions
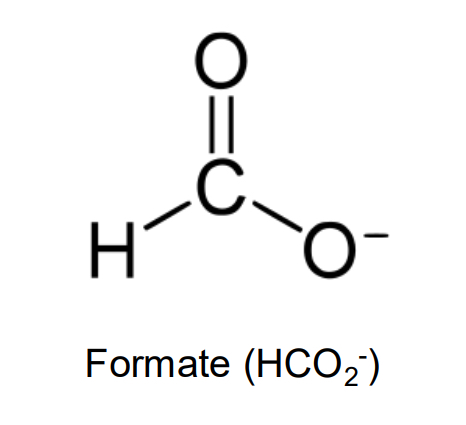
formate
important single-carbon anion, being the deprotonated conjugate base of formic acid (H2CO2)
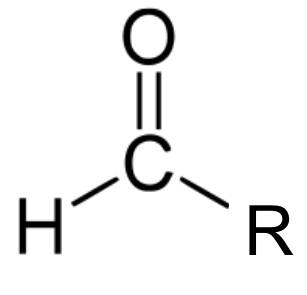
formyl group
derived from formate, also common
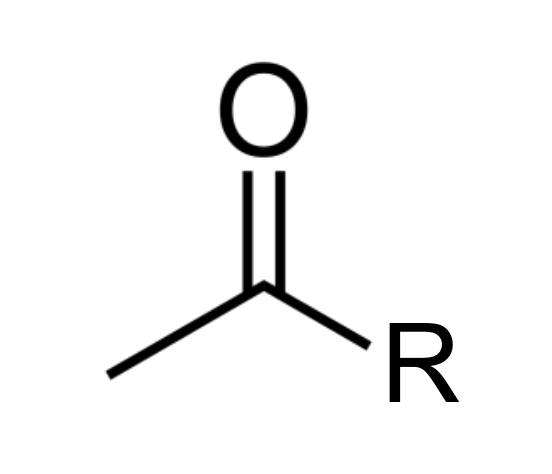
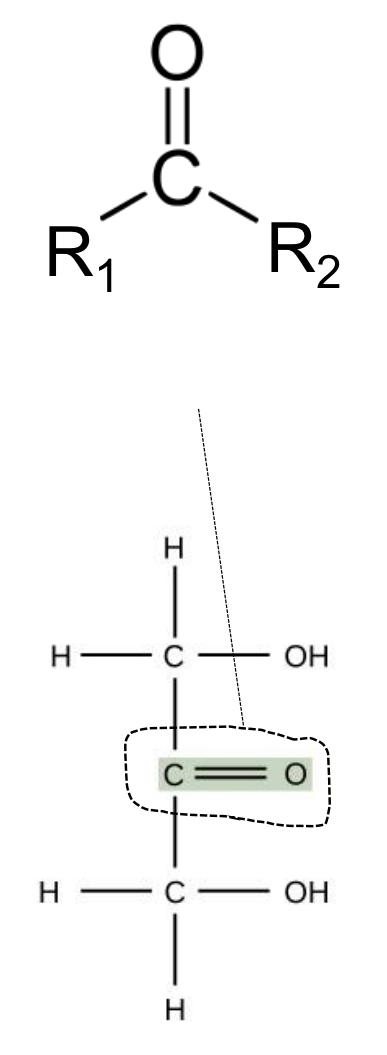
carbonyl group
any carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom; carbonyl groups may be found in either a ketone or aldehyde form
carobonyls
are also often found within other groups, e.g., carboxyl & carboxamide groups
carbonyl (aldehyde)
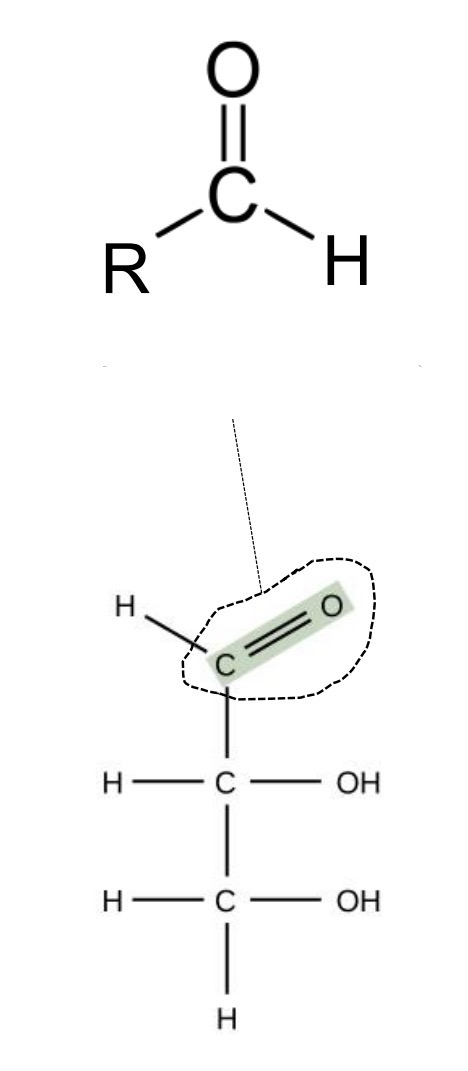
carbonyl (ketone)
carboxyl groups
the most common ionizable weak acid group found in biomolecules & can reversibly interconvert between a polar, protonated form & a charged (anionic) deprotonated conjugate base form
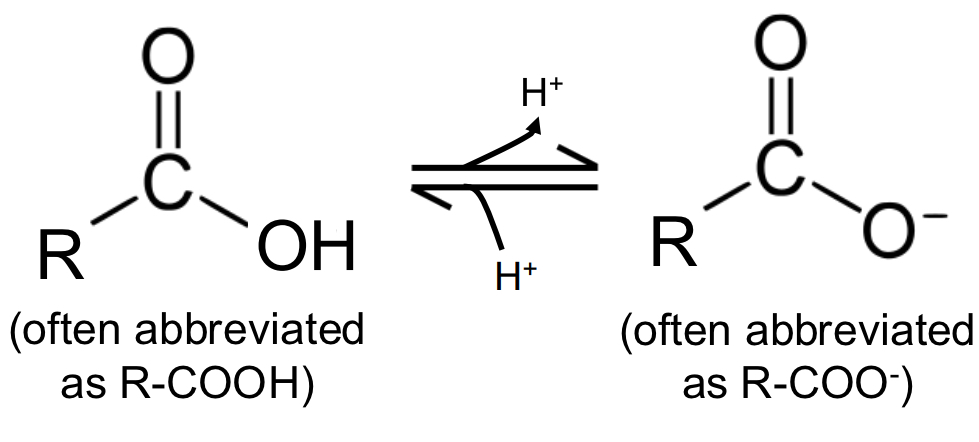
deprotonated (anionic) form
the predominant form at neutral or near-neutral pH
many key metabolic intermediates are
carboxylic acids (or more precisely carboxylates, when in their deprotonated conjugate base forms, that would predominate in biological aqueous solutions)
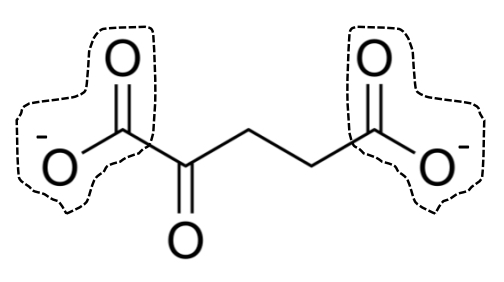
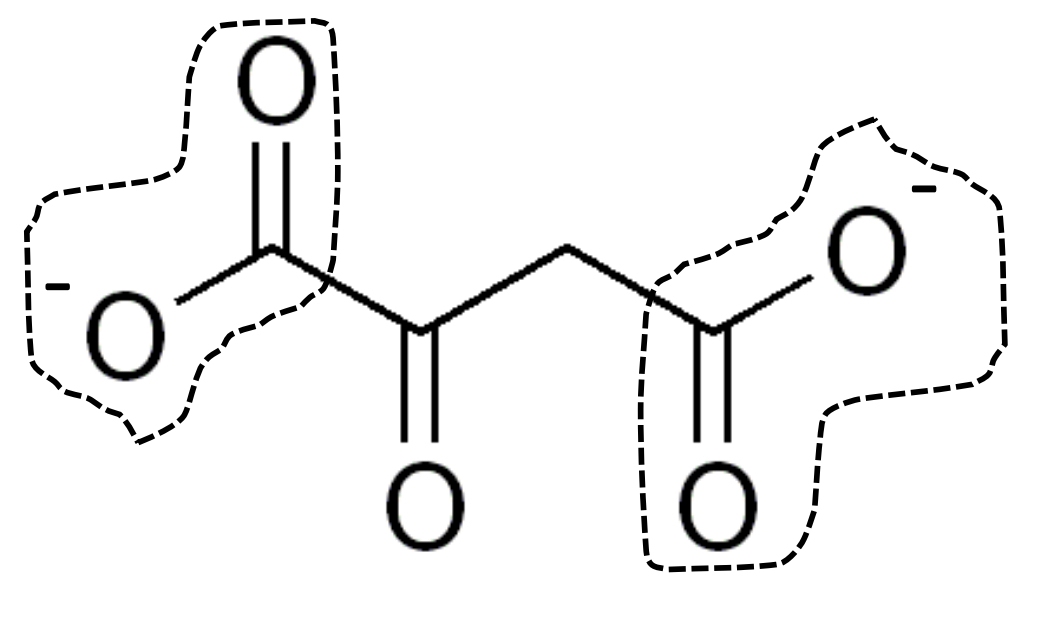
α-ketoglutarate & oxaloacetate
also contain additional ketone carbonyl groups
α-ketoglutarate
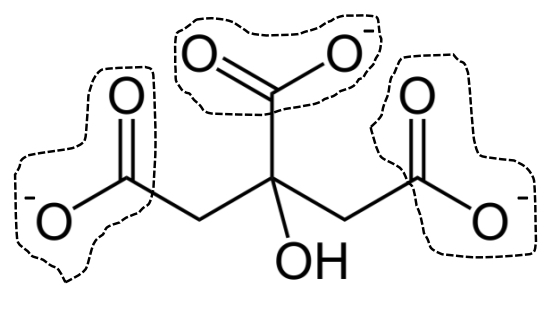
citrate
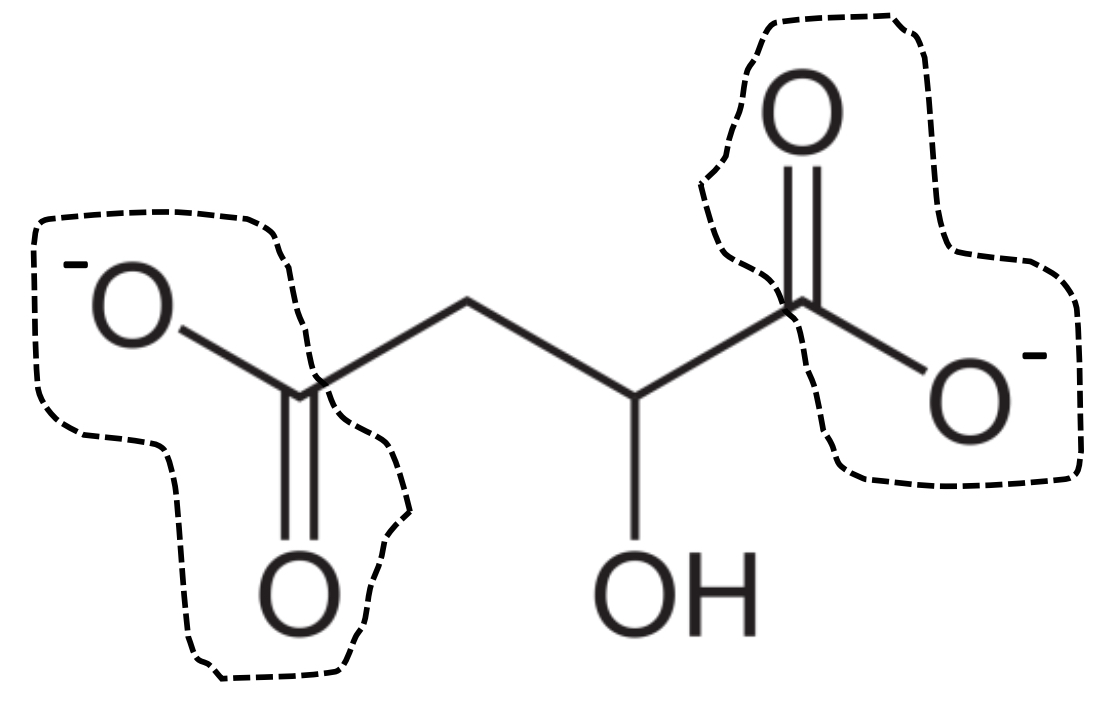
malate
oxaloacetate
acetic acid
2-carbon compound that acts as a weak acid & will be predominantly deprotonated to the anionic conjugate base acetate at neutral or near-neutral pH; acetyl groups are also derived from acetate

acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
metabolically most important form of acetate/acetyl, which features an acetyl group joined in a thioester linkage to coenzyme A
Coenzyme A
the thioester S atom + everything else to the right
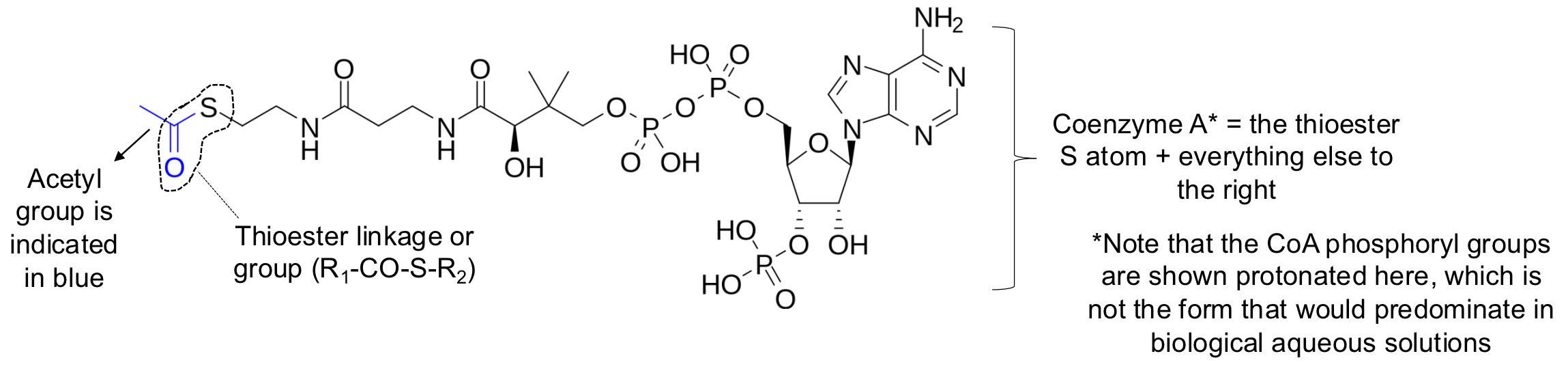
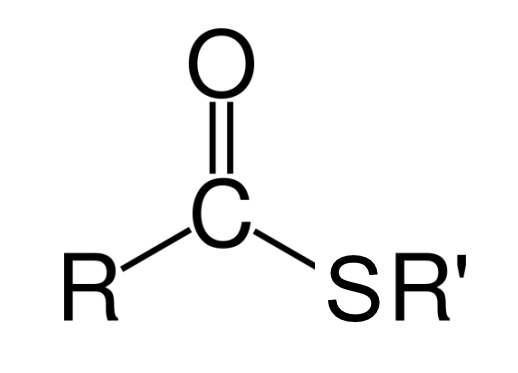
thioester group
essentially a substituted form of the much more common ester groups, with the sulfur replacing an oxygen in the ester
“thio-”
refers to sulfur
ethers
closely related to ethers
thioester linkage or group (R1-CO-S-R2)
ester linkage or group (R1-CO-O-R2)
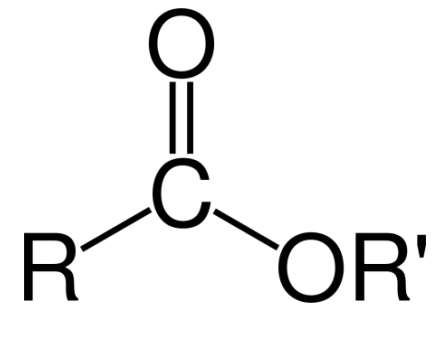
phosphate ester
another important substituted ester
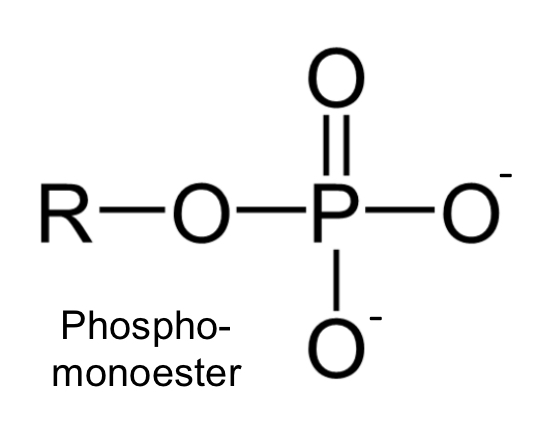
phospho-monoester
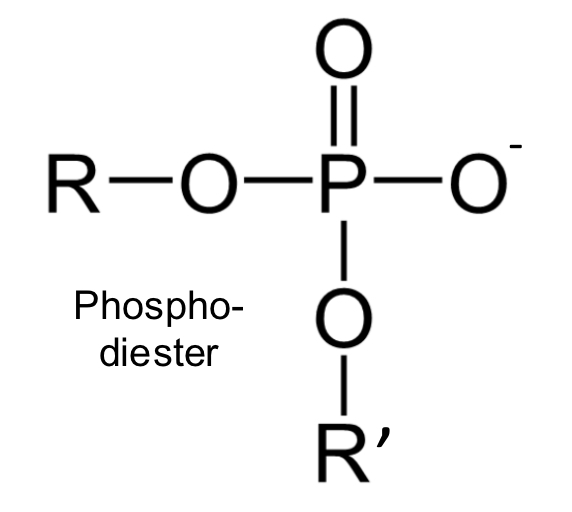
phospho-diester
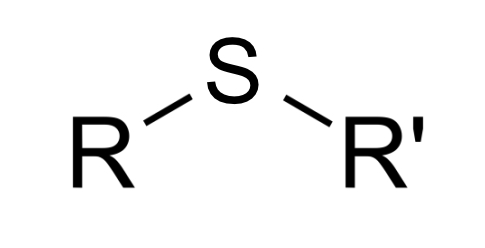
thioether linkage or group (R1-S-R2)
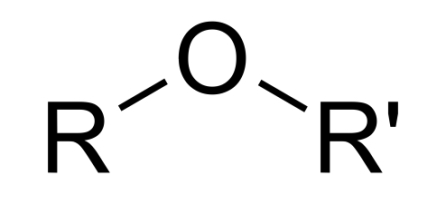
ether linkage or group (R1-O-R2)
acetyl group