Psychology 2e: Social Psychology Key Concepts and Theories
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is social loafing?
The exertion of less effort by a person working together with a group.
What happens to group performance on easy tasks due to social loafing?
Group performance declines.
What is prejudice?
A negative attitude and feeling toward an individual based solely on their membership in a particular social group.
Define stereotype.
A specific belief or assumption about individuals based solely on their membership in a group.
What is discrimination?
A negative action toward an individual as a result of their membership in a particular group.
What are the two types of attitudes in the Dual Attitudes Model?
Explicit (conscious and controllable) and implicit (unconscious and uncontrollable).
What is racism?
Prejudice and discrimination against an individual based on race.
What is ageism?
Prejudice and discrimination toward individuals based solely on their age, typically against older adults.
Define homophobia.
Prejudice and discrimination of individuals based solely on their sexual orientation.
What is sexism?
Prejudice and discrimination toward individuals based on their sex.
What are the two forms of sexism?
Hostile sexism (negative feelings toward women) and benevolent sexism (offering protection to women who conform to traditional roles).
What is a self-fulfilling prophecy?
An expectation held by a person that alters their behavior in a way that tends to make it true.
What is confirmation bias?
The tendency to seek out information that supports our stereotypes and ignore information that is inconsistent with them.
Define in-groups and out-groups.
In-groups are groups we identify with; out-groups are groups we view as fundamentally different from us.
What is in-group bias?
Prejudice and discrimination because the out-group is perceived as different and less preferred than our in-group.
What is aggression?
Seeking to cause harm or pain to another person.
Differentiate between hostile aggression and instrumental aggression.
Hostile aggression is motivated by anger with intent to cause pain; instrumental aggression is motivated by achieving a goal without intent to cause pain.
What does the Frustration Aggression Theory state?
When humans are prevented from achieving an important goal, they become frustrated and aggressive.
What is bullying?
Repeated negative treatment of another person over time, including physical, verbal, or psychological harm.
What is the bystander effect?
The phenomenon where a witness does not volunteer to help a victim in distress due to diffusion of responsibility.
What is prosocial behavior?
Voluntary behavior with the intent to help other people.
Define altruism.
The desire to help others even if the costs outweigh the benefits of helping.
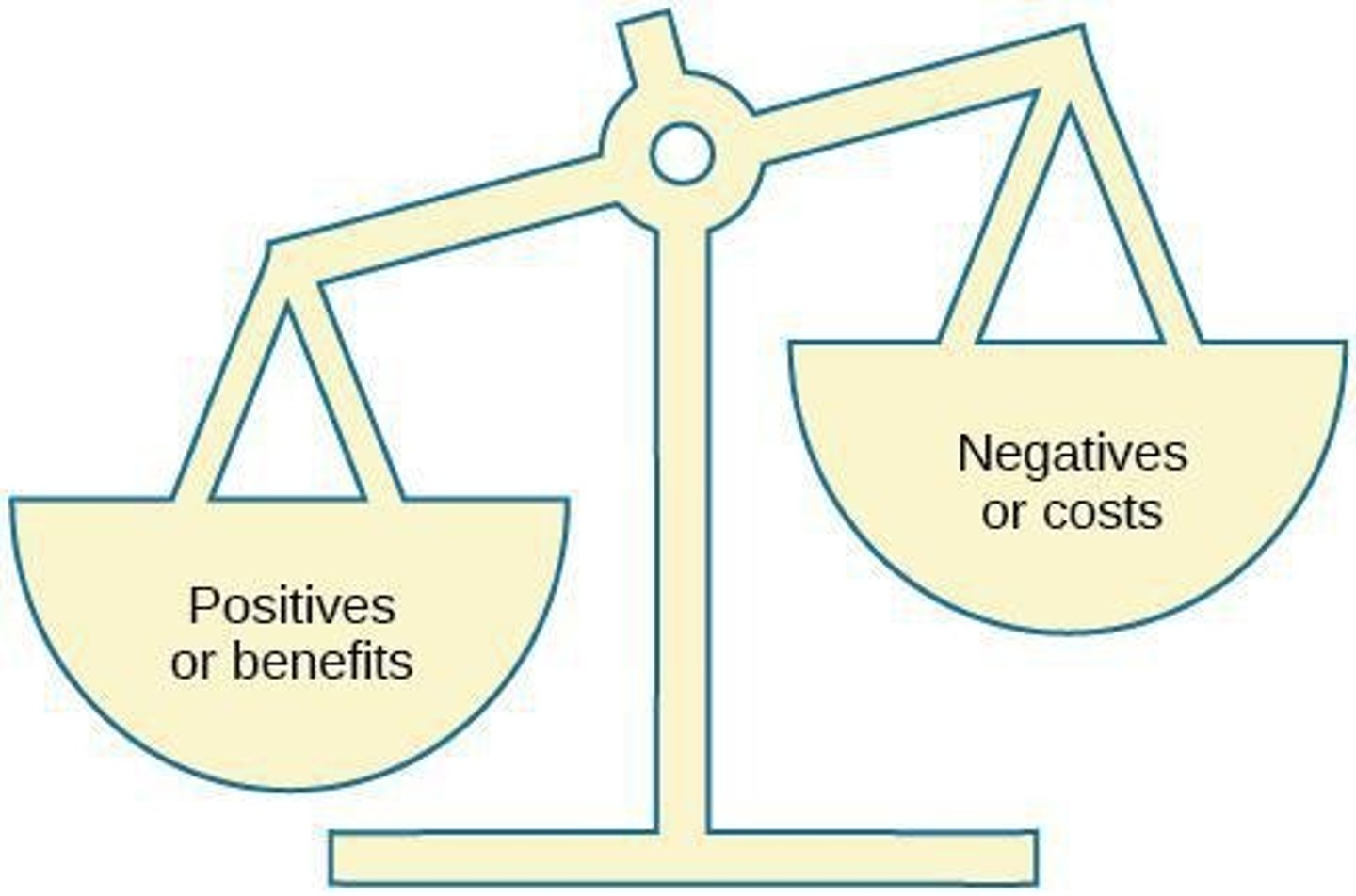
What is social exchange theory?
The idea that people keep track of the costs and benefits of forming and maintaining a relationship.
What factors influence who we become friends with?
Proximity, similarity, and homophily.
What is the matching hypothesis?
The tendency for people to choose partners they view as equal in physical attractiveness and social desirability.
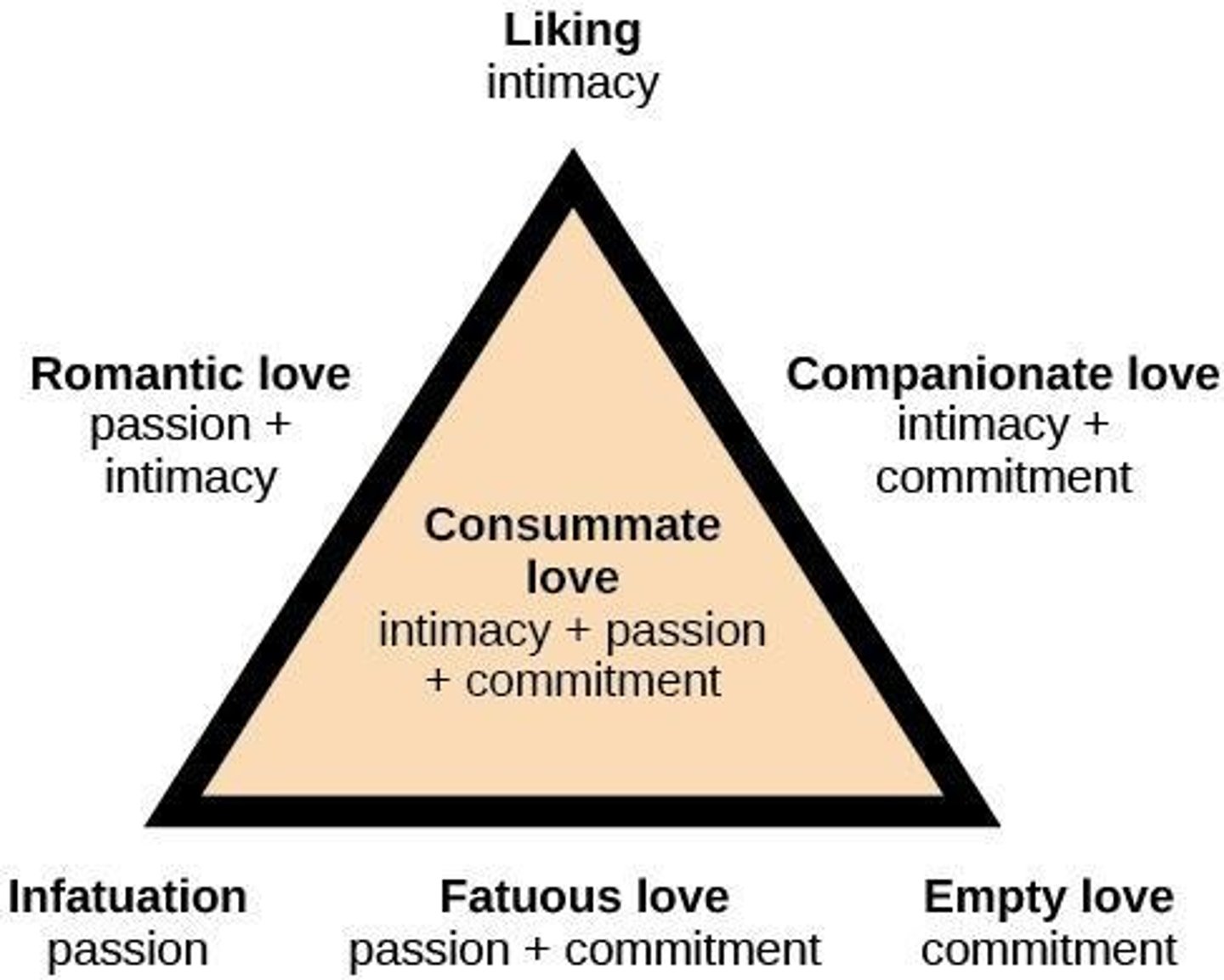
What are the three components of Sternberg's Triangular Theory of Love?
Intimacy, passion, and commitment.