Prions, Mad Cow Disease and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (9/9)
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Liu (Lecture 26)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are transmissible spongiform encephalopathies?
fatal neurodegenerative disease caused by prions
long incubation time before symptoms show up
Scrapie the sheep
prototypic prion disease
“scrapie” describes infected sheep that constantly scraped objects while their brains were being degenerated
What is Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)? What is the incubation time? What 2 distinct features of this disease?
Mad Cow disease that results from feeding cattle with and bone meal contaminated from scrapie sheep
incubation time ~5 yrs: most cattle did not manifest disease bc they are sacrificed between 2-3 yrs
Cows are unable to stand, holes/spongiform in brain tissue
Who discovered human creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)? What does it look like? Who does it affect the most?
first described by Hans Herhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob
sponge-like lesions in brain, amyloid fibrils are misfolded prions that accumulate in the brain
most common human prion disease: affects ages 45-75, mostly 60-65
Is there a diagnostic test for CJD? What do you do first? How can you confirm CJD?
there is no single diagnostic test for CJD
first, rule out treatable forms of dementia such as encephalitis or chronic meningitis
confirmation: brain biopsy or autopsy
describe a brain biopsy. Why is it strongly discouraged?
remove small piece of tissue from brain so that ic an be examined by the neurologist
discouraged bc correct diagnosis doesn’t help the pt, unless its needed to rule out a treatable disorder
What are the 3 major categories of CJD? How common is each category?
85% sporadic CJD
10-15% hereditary (familial) CJD: 100% penetrance, carriers will eventually develop disease
<1% acquired CJD
What are some symptoms of CJD?
altered behavior, dementia, memory loss, impaired senses, delirium, premature senility, uncontrollable muscle contractions
Acquired CJD
acquired from human or from BSE
What is the difference between CJD and vCJD (variant from BSE)
CJD:
median age at death: 68
median duration: 4-5 mo
S&S: dementia, early neurological signs
vCJD:
median age at death: 28
median duration: 13-14mo
S&S: prominent pscyhiatric/behavioral symptoms, delayed neurological signs
What is Human Kuru?
infection through ritualistic cannibalism
endemic disease prevalent among New Guinea highland Natives
What are some features of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
resistant to chemicals, ionizing radiation, heat
do not present virus morphology in electron microscopy
not assoc w foreign nucleic acid isolated from infected host cells
proteinaceous, filterable
multiplies slowly in cell culture, no cytopathic fx
do not elicity inflamm rxn or antibody formation in host (nonimmunogenic)
responsible for plaques and abnormal fibers forming in brain
transmission: intimate contact with infected tissues and secretions
define prions.
causative agent of spongiform encephalopathies
proteinaceous infectious particles that are devoid of nucleic acid and composed of a modified form of the prion protein
what are prions designated as? Where is it present?
PrP
present in normal healthy people (aka PRP^c)
diseased form of prion: PrP^sc “scrapie”
Location: on the cell surface through glycosylphosphatidyl inositol (GPI) moiety
What is human Prp encoded by?
single copy of PrP gene on chromosome 20
other species have a single copy PrP gene in genome
prion gene from 40 different species has been sequenced except
chickens
other than chickens, prion protein from other species is similar to human prion protein
before the discovery of prions, what was thought to be the cause of TSE?
slow virus
associated with the fact that incubation is very long.
How does prion protein sequence identity across species relate to the prion transmission barrier?
Prion diseases transmit more easily between species whose PrP proteins are highly similar.
Human PrP shares:
99% identity with chimpanzee PrP → very low transmission barrier.
92% with sheep, 90% with cow, 90% with mouse PrP → moderate barrier.
41% with chicken PrP → very high barrier; transmission unlikely.
PrP^c knockout mice
apparently healthy mice that are resistant to prion disease and unable to replciate prions
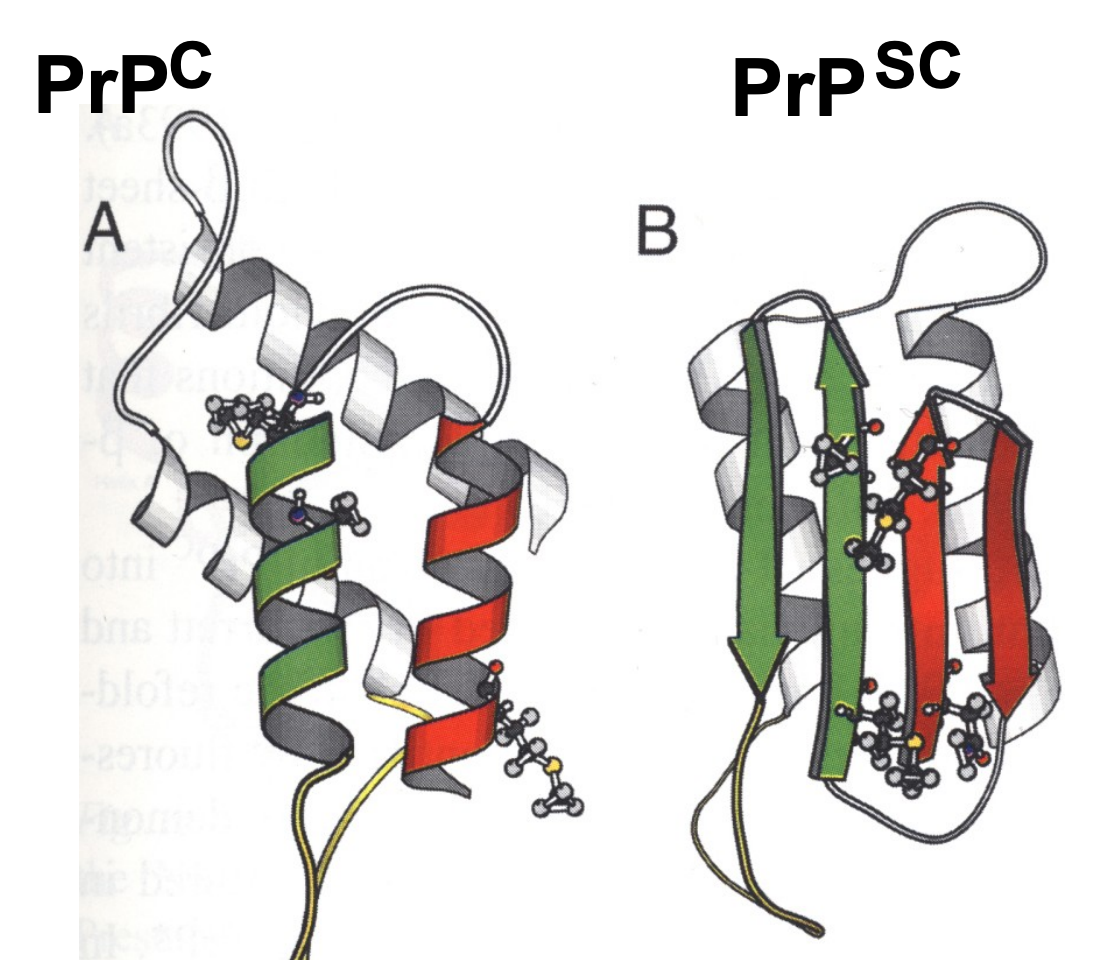
describe the moa of prion diseases
conformation change: PrPc is unfolded and refolded into PrPsc — alpha-helical sturcture converted into beta-sheet
accompanied by physico-chemical property changes > eventual deposition of amyloid fibrils > tangles the brain
simplified moa of prion diseases
PrPsc can induce PrPc to be converted into PrPsc
PrPsc conformation enciphers prion diversity
What type of mutations do inherited and sporadic CJD results from?
Inherited CJD results from germline mutations in the prion gene
sporadic CJD can results from somatic mutation of the prion gene
whether CJD can be resulted from spontaneous conversion of PrPc into Prpsc in the absence of a mutation remains to be determined
Epidemiology of BSE and vCJD. What did epidemiologicaland and experimental studies show?
1994 in teenagers and young adults eventually labeled as vCJD occurred in the Great Britain
Studies show: vCJD is result of prions being transmitted from cattle with BSE to humans through consumption of contaminated beef products
Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker (GSS) Syndrome
rare, familial, fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects pts from 20-60 yrs
incidence: 1 to 10 per 100 million
what type of mutation does GSS have?
point mutation in prion gene that leads to deposition of Prp amyloid
change in codon 102 from proline to leucine
what are some symptoms of GSS?
developing dysarthria (difficulty speaking) and cerebellar ataxia (unsteadiness) and then the progressive
Is there a cure or treatment for GSS?
NO, it has a longer clinical course compared to other prion diseases, pts rarely survive longer than 5 yrs
what type of mutation occurs to create fatal familial insomnia?
genetic form is caused by dual mutations in prion gene:
substituted aspartic acid by asparagine at codon 178
methionine at the position 129
what is fatal familial insomnia? Are there any distinct triggers?
very rare prion disease due to selective degeneration of the dorsal medial nuclei of the thalamus, which controls sleep
results in reduced sleep and evenutally the inability to sleep
sporadic and genetic forms
autosomal dominant disease
It strikes during middle age and results in death. It has no apparent trigger, patients last up to 3 yrs
SEQ the 4 stages of fatal familial insomnia
onset: panic attacks, unfounded phobias that last 4 mo
severe insomnia, worsening panic attacks and hallucinations that last 5 mo
complete insomnia, rapid wt loss that last 3 mo
dementia, unresponsiveness that last 6 mo
FFI is eventually fatal
What is the history of FFI? Who is Silvano and Michael Corke
Italian man in Venice 1765. Family secret for generations
stopped being a secret with Silvano who went to University of Blognea and filmed his final months with FFI
donated brain to research > structure in thalamus was spongy and degraded
Michael Corke: in Chicago had trouble sleeping, died after not sleeping for 6 mo
DNA sequencing found 2 mutations in prion gene for FFI
Species Barrier (prion related issue)
prolongation of incubation period when prions are transferred form one speciesto another
on second passage of prions in same species, incubation decreases than remain constant on subsequent passage
how prion proteins pass the BBB?
not completely understood
partially bypass BBB
retrograde spread through thoracic spine peripheral nerves
involvement of immune cells
directly cross BBB
PrPsc oligomers can cross BBB without disruption