Physics Remove Summer Exam
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Energy Stores
Kinetic, gravitational potential, electrostatic
Nuclear, elastic potential thermal, chemical, magnetic
Energy Transfers
By Radiation - e.g: light, sound
By Heating - due to a temperature difference
Mechanical - using a force
Electrical - using a current
Sankey Diagram
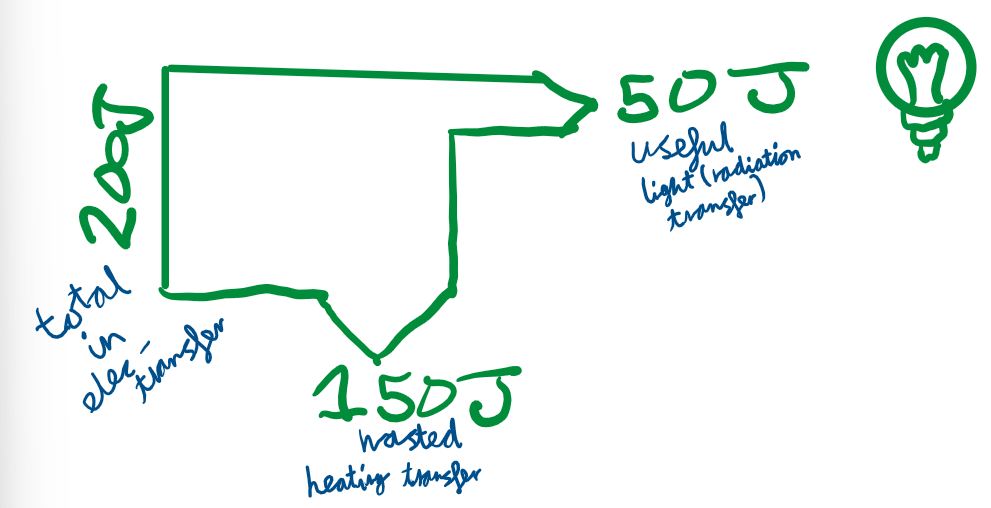
What is the conservation of energy?
The idea that energy can not be created or destroyed.
Efficiency =
useful output energy / total energy
Power (W) =
Energy Transferred (J) / time (s)
What is work?
When a force acts on an object and moves the object in the direction of force.
Work Done (J) =
force (N) x distance (m)
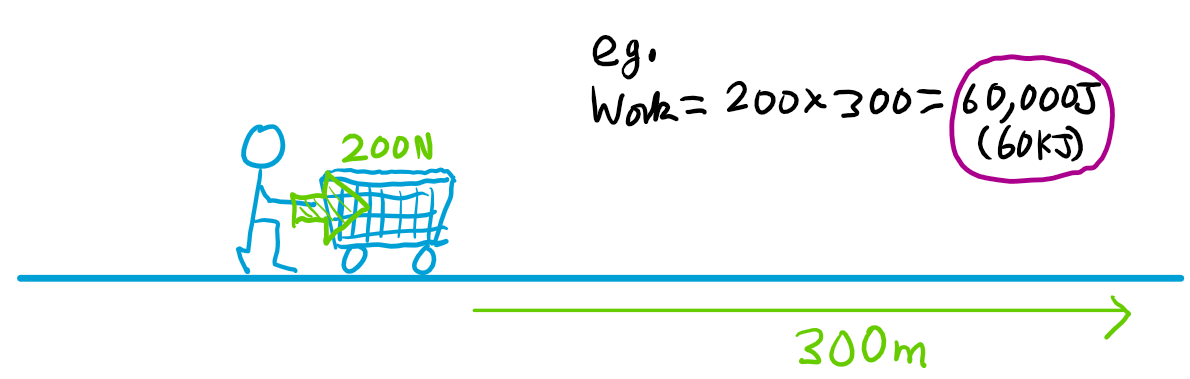
1J =
1N x 1m
What is Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE)?
This is the energy an object has due to how high above the ground it is.
Change of GPE = m x g x h
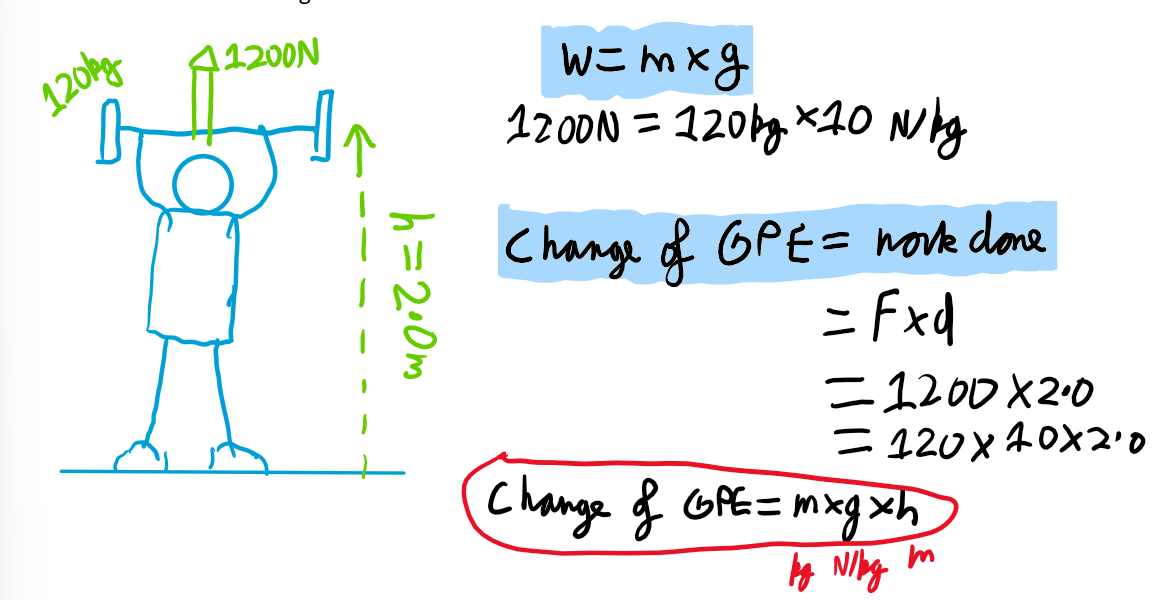
Kinetic Energy (K.E0 =
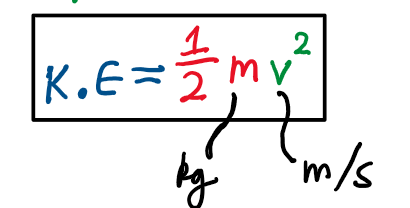
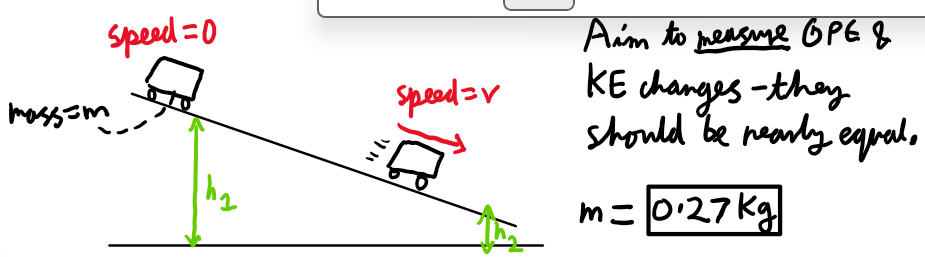
GPE to KE energy expermient:
Objects can be charged by
Rubbing/friction
Charge is measured in
Coulombs (C)
When two opposites attract
+loses electrons
-gains electrons
Current from
to -
Amps (A/I) =
Coulombs per second
Charge (C/Q) =
Amps(A/I) x time (s/t)
Voltage =
Energy Transferred (E) / Charge (C/Q)
Power (W) =
Amps (A) x Voltage (V)
Energy (J) =
Power (W) x Time (s)
or A x V x s
In series circuits
In parallel circuits
Currents are equal.
Currents add up logically.
More then one element means
They will also add up logically.
Slowly 'spend' energy.
Any path taken must add up to right amount of volts.
Voltage is
The difference in electrical energy for each coulomb between 2 points in a circuit.
Live wire
Brown
Neutral wire
Blue
Earth wire
Green and Yellow
Normal mains only has
Live and neutral wires because it has a fuse in the live wire
The fuse melts when
The current becomes bigger than the fuse. This disconnects the live wire.
The fuse protects
The device from too much current.
People from fires that can be caused by too much current.
The Earth wire
Sends energy back into the ground in emergencies. This does not protect people and their hearts fast enough.
Insulation
Metal wires have plastic sheaths.
Double insulation
Devices with plastic casing and sheaths - 2 layers. Does not need Earth wire.
Circuit Breaker Electromagnetic
If the current becomes too large, the magnetic field of solenoid becomes strong enough to pull down the soft iron.
Circuit Breaker Electronic
These devices monitor currents in the live and neutral.
If a difference is detected, the circuit is broken and the live is disconnected.
This can prevent electrocution.
Mains plug
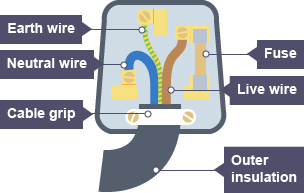
Earth wire need for
Devices with metal cases
Current is the same as
Amps
Volt =
Joule per coulomb
Difference between direct and alternating current
Direct Current is continuous and in one direction.
Alternating current constantly changes direction.
Distance Time Graph Shapes
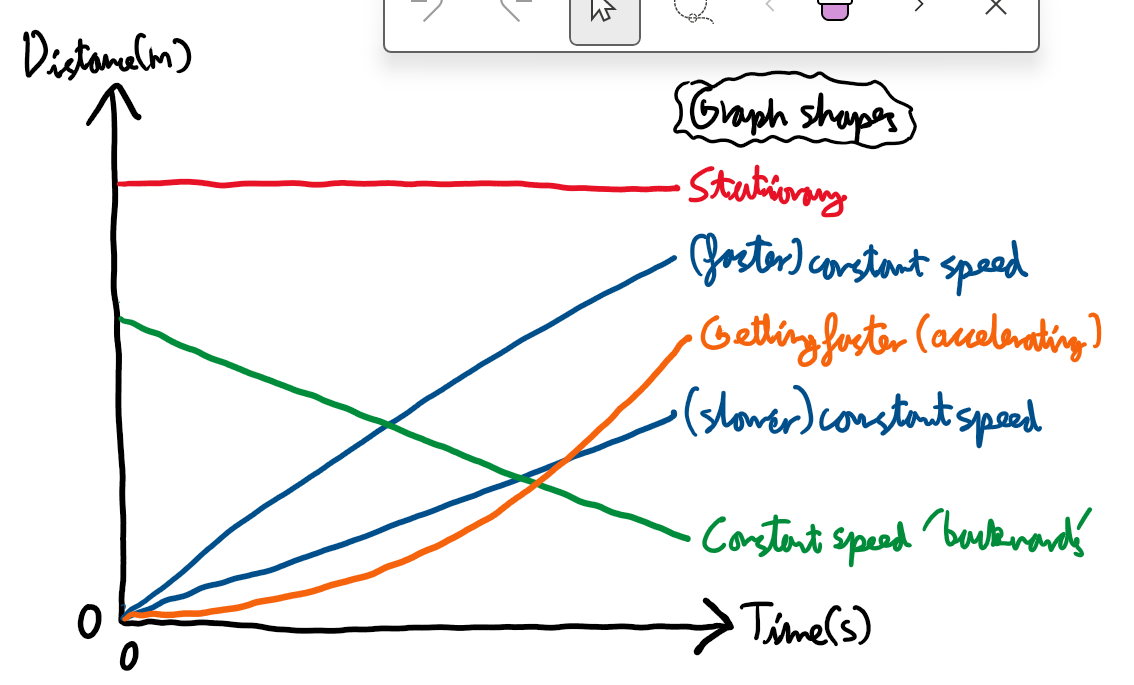
What does the gradient give in a distance time graph?
The speed
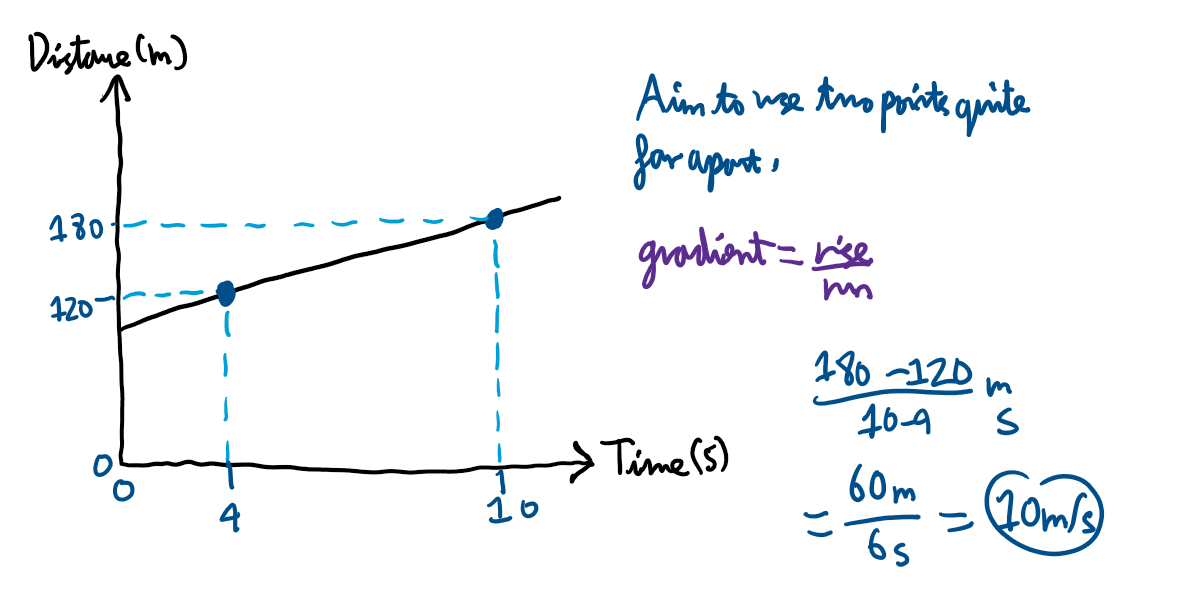
Example of determining speed in a distance time graph:
Acceleration =

Acceleration Symbol Equation

Acceleration can mean:
Increasing speed
Decreasing speed
Changing direction of the velocity (with or without changing speed)
Acceleration Experiment:
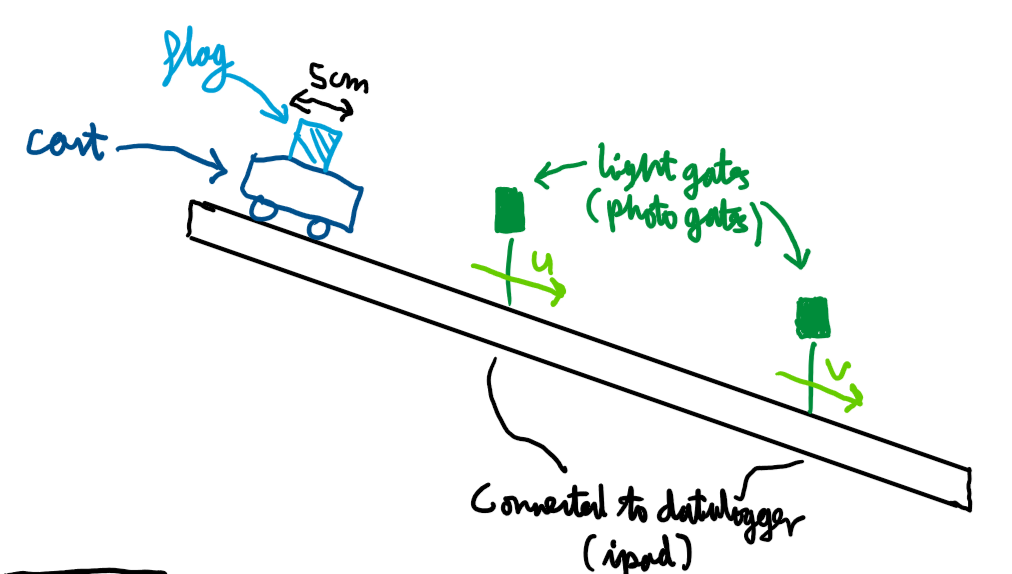
Velocity Time graphs constant velocity
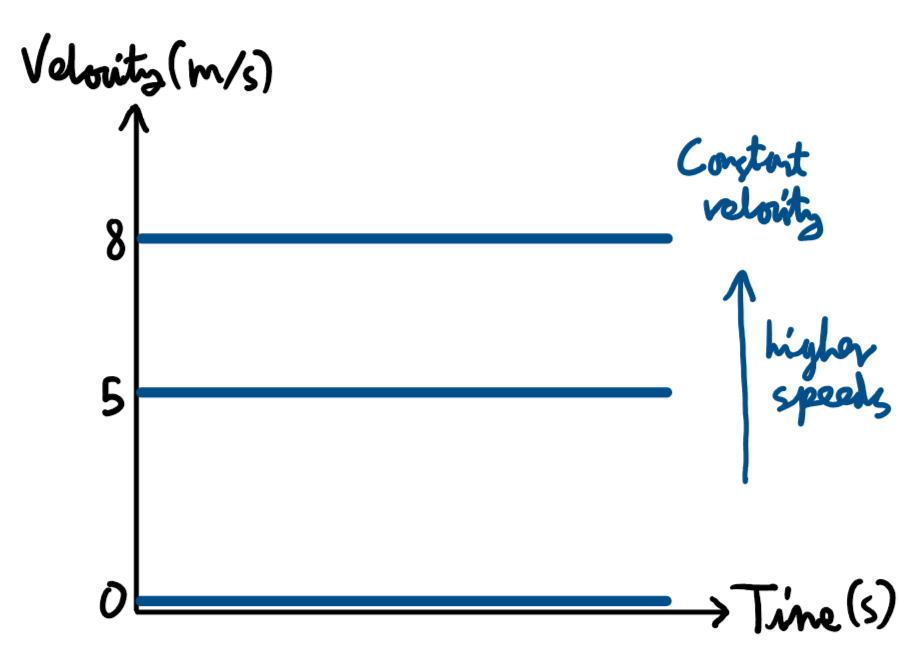
What does the gradient of a velocity time graph give?
Acceleration
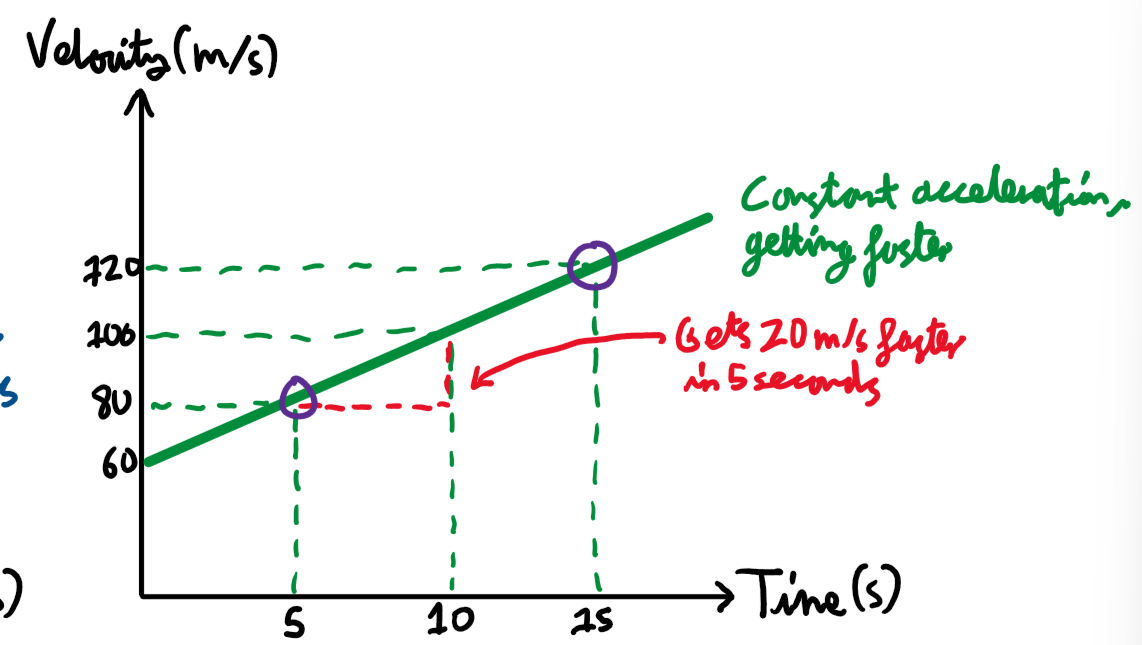
Velocity Time graphs constant acceleration
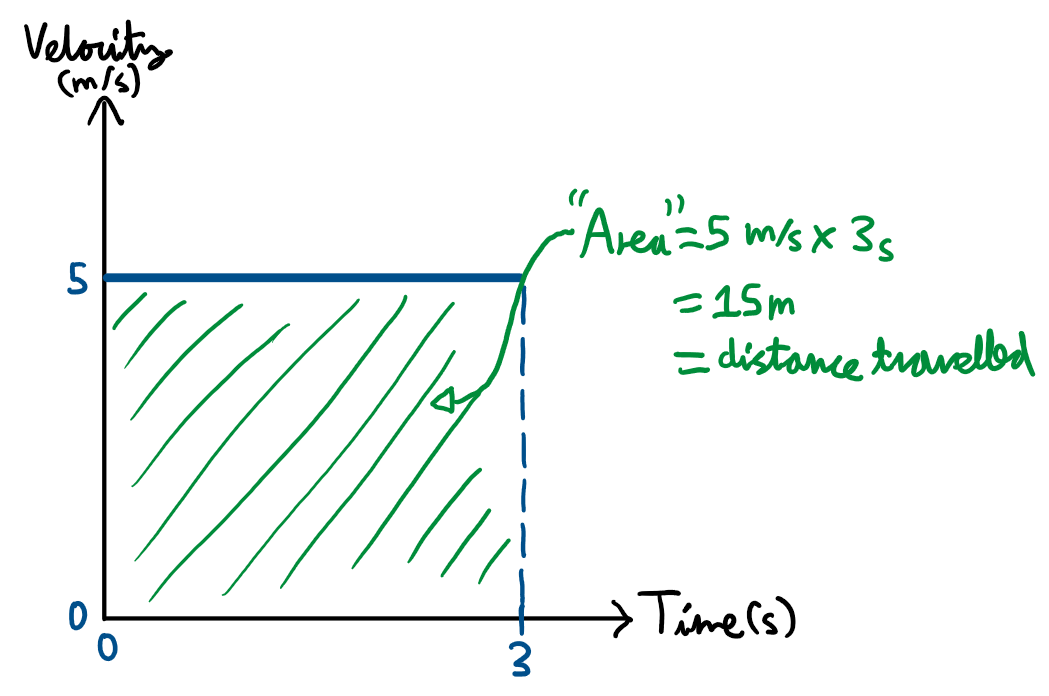
What does the area of a velocity time graph give you?
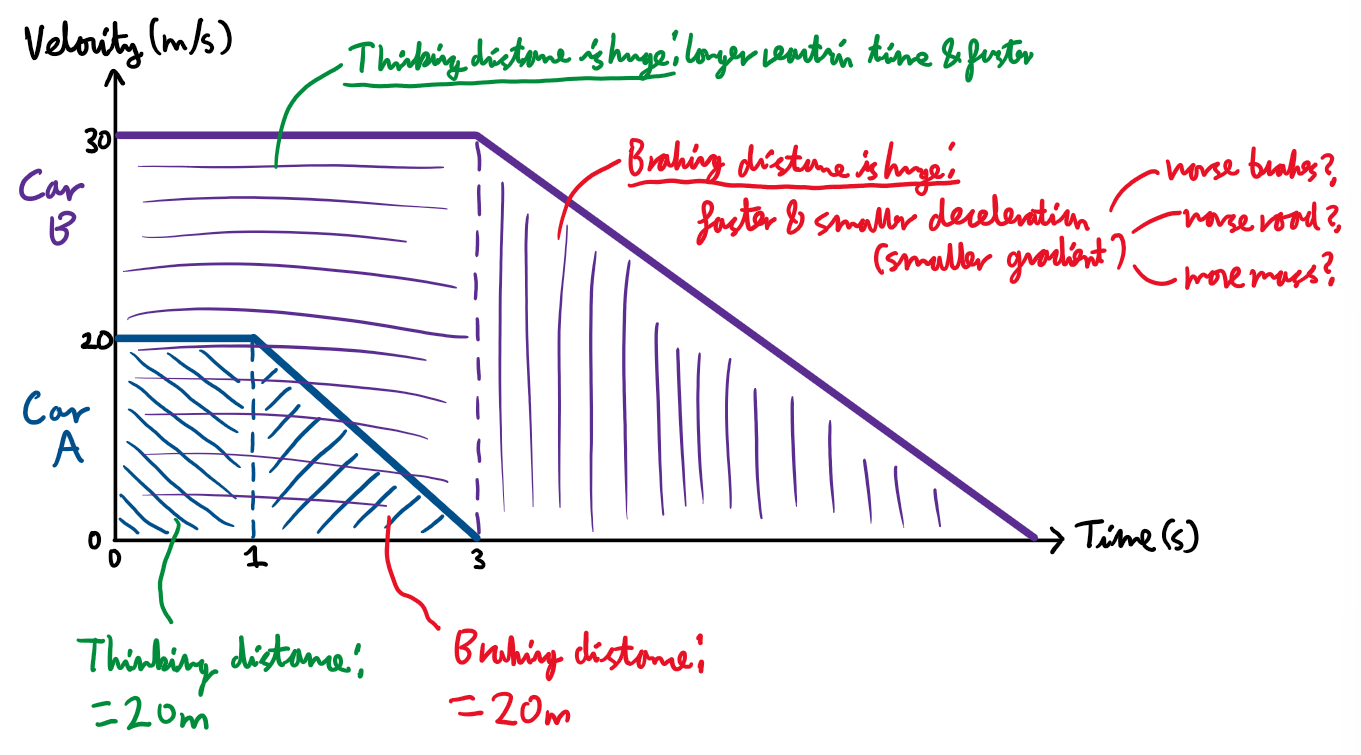
Stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance
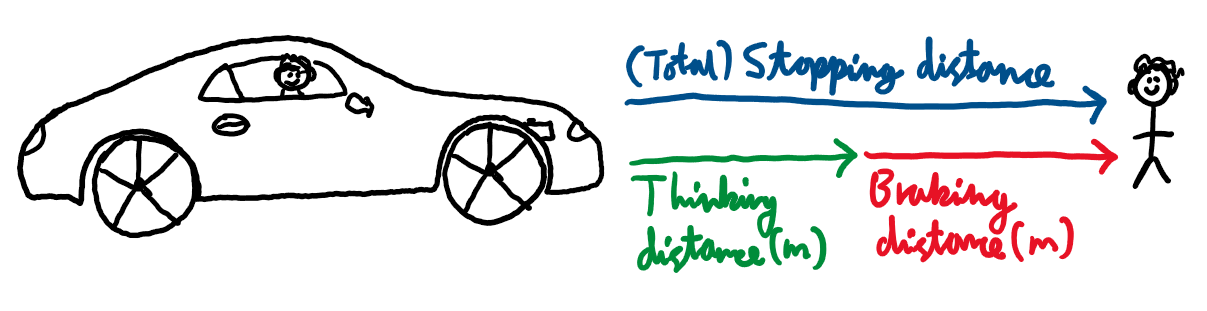
Stopping distance =
Thinking distance + braking distance
Factors that increase thinking distance:
(Old) age
Alcohol
Tiredness
Distraction
Disability
Factors that increase braking distance:
Road surface (ice/mud/wet)
Bad tyres
Weak/faulty brakes
Downhill
Weight/mass of car
Graph showing thinking and braking distance:
What is an isotope?
An atom of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What might an unstable atom do?
It may undergo radioactive decay and/or change into another element.
What is special about radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is a random process. We can not predict when an individual atom will decay.
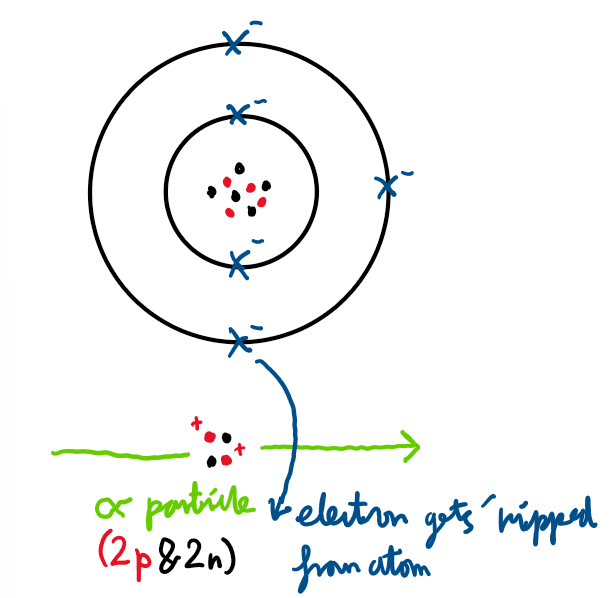
What is ionisation?
The process of an atom becoming an ion (losing electrons).
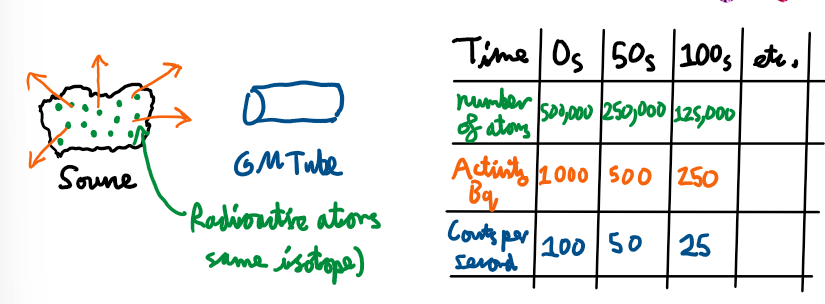
Ways to detect ionising radiation
A Geiger-Muller Tube and counter or photographic film.
What is background radiation?
It is the day to day radiation caused by objects containing radioactive isotopes.
Examples of background radiation:
Living things, building materials (brick,concrete) and food.
What are alpha, beta and gamma particles?
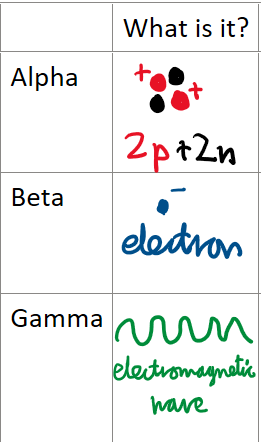
How are alpha, beta and gamma particles created?
They are randomly emitted from unstable nuclei.
Charge of alpha, beta and gamma:

Range in air for alpha, beta and gamma:
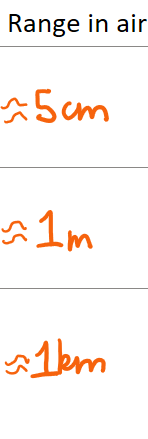
What are alpha, beta and gamma particles blocked by?

Alpha, beta and gamma ionising ability:

Three safety methods when dealing with radiation sources:
Short time, large distance and tongs
Where does ionising radiation from space come from?
Our planet receives cosmic rays which are high energy particles from space.
Absorption / penetration of ionsing radiation experiment:

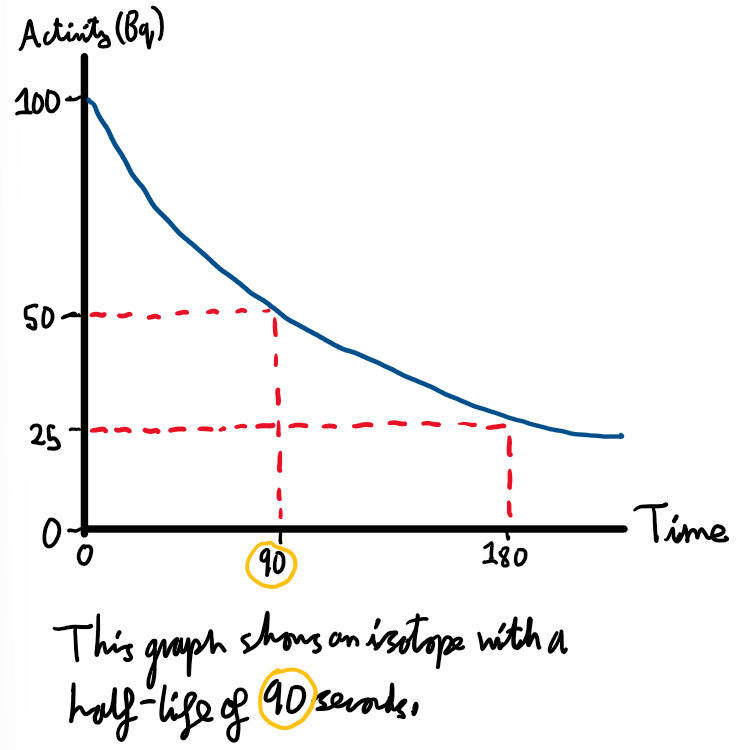
What is a half-life.
The half-life of an isotope is the time in which the activity of the source, counts recorded or number of radioactive atoms will halve.
Graph of a half-life
What is activity and what is it measured in?
Activity is the number of radioactive decays per second measured in Becquerels (Bq).
Half-life example
Alpha charge
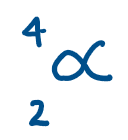
Beta Charge
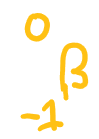
Gamma charge

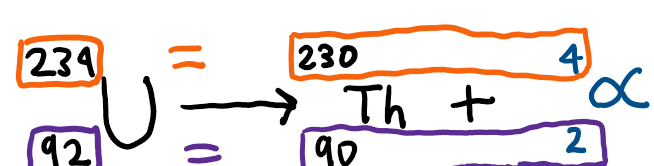
Nuclear equation for radioactive decay example
Some radioactive isotopes…
decay to produce isotopes that are again reactive leading to chains forming.
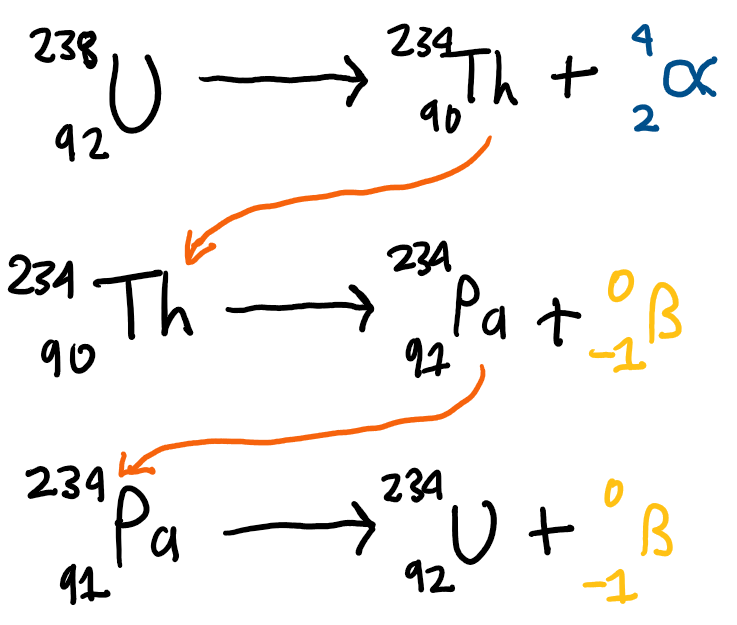
Some radioactive materials…
stay radioactive for a very long time and emit a lot of radiation.
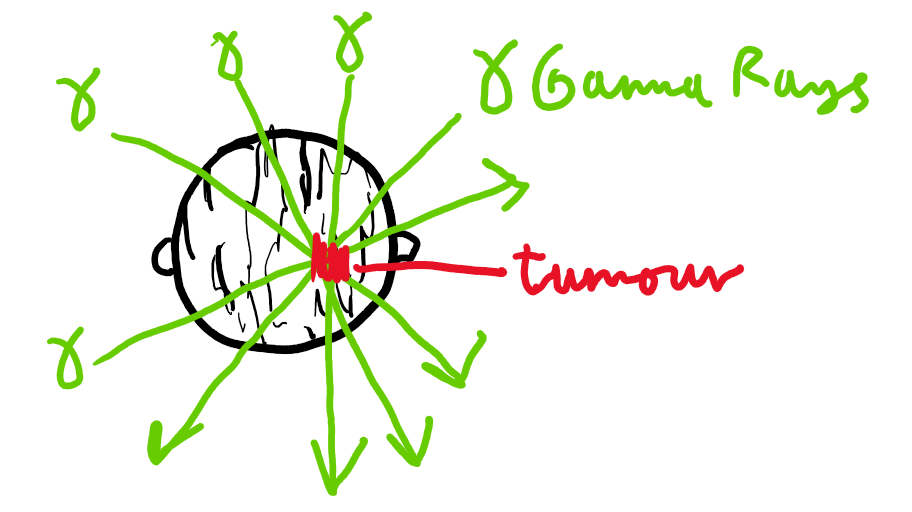
What is a use of radioactivity relating to cancer:
Cancer treatment - radiotherapy:
Gives a high dose of gamma rays to the tumour, aiming to kill it.
What is a use of radioactivity relating to manufacturing:
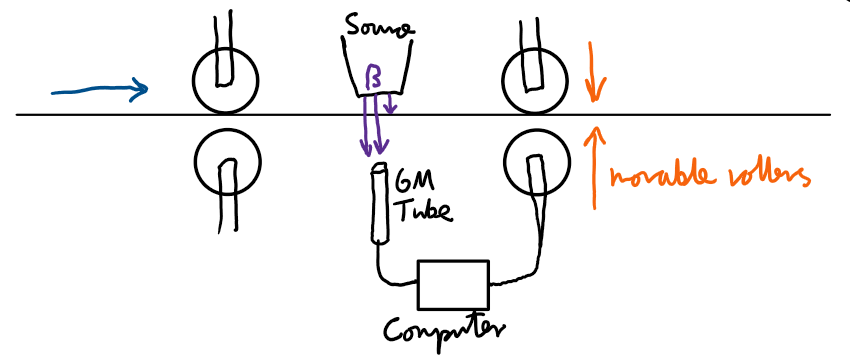
Thickness monitoring: e.g manufacturing aluminium foil:
Controls thickness of the foil.
Some betas will pass through and some will get blocked.
If the thickness changes, the amount that go through will change.
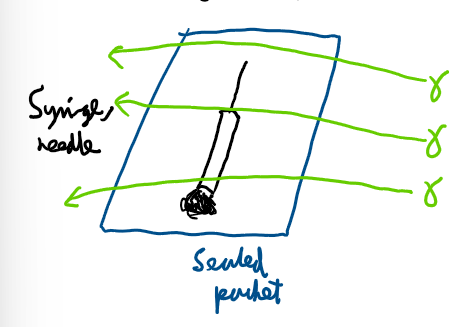
What is a use of radioactivity relating to sterilising:
The gamma rays kill bacteria.
E.g, syringe is perfectly clean.
What are some dangers of ionising radiation?
Cause mutations in living cells, can become cancerous.
Damage cells and tissue, can’t function properly.
Why does disposal of reactive waste need to be hidden?
Security guards and a safe location is needed so that no one tries to steal the waste and use it dangerously.
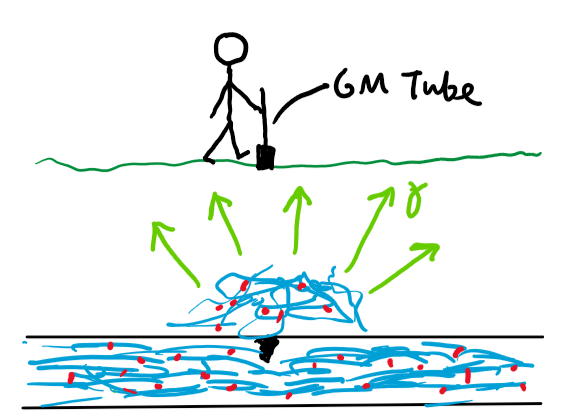
What is a use of radioactivity relating to movement?
Tracers:figuring out where something goes
Put some of the radioactive isotope into what you want tot trace and find out where it goes with the GM tube.
What is contamination?
This is when we get radioactive materials on ourselves, clothes, equipment or buildings.
This leads to irradiation.
What is irradiation?
This is when our bodies are blasted by ionising radiations.
What is thermal energy?
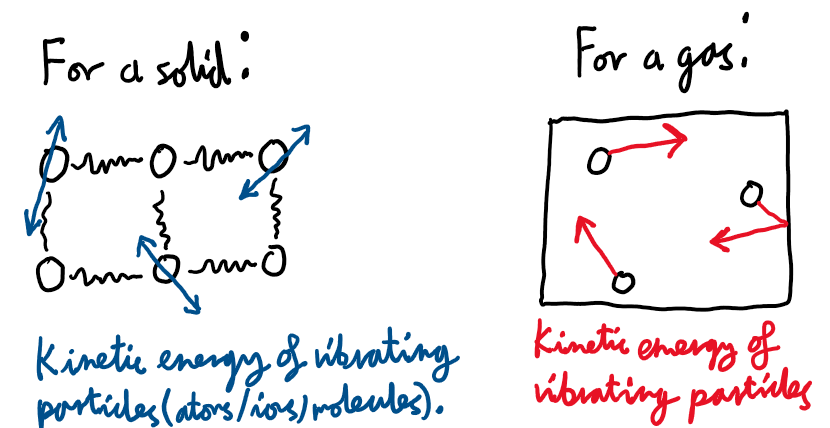
What is temperature?
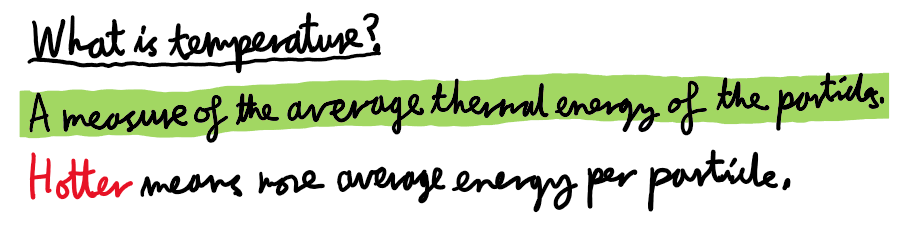
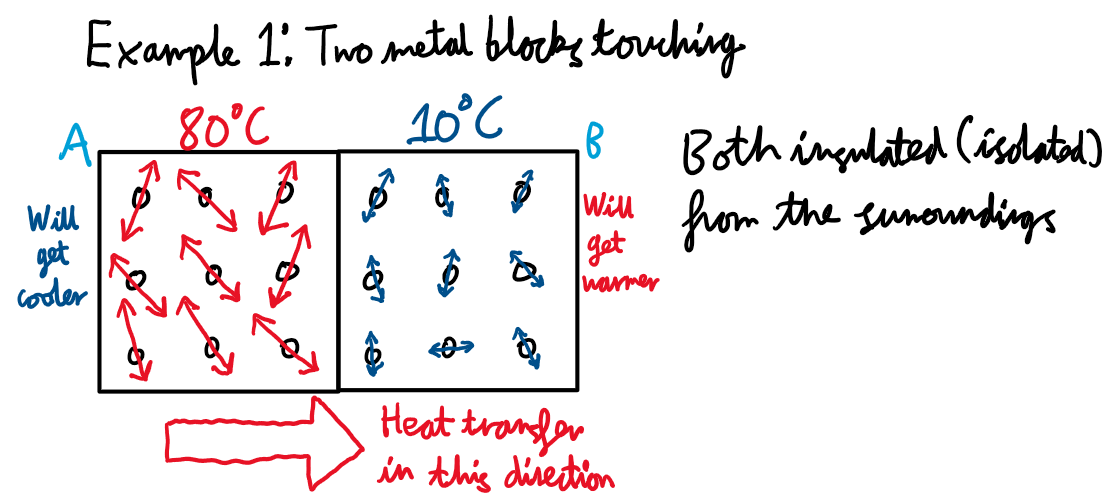
Transfer of thermal energy due to temperature difference
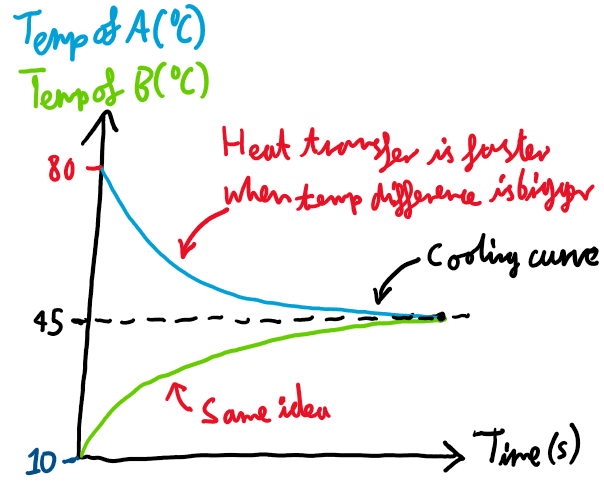
Two blocks touching heat graph
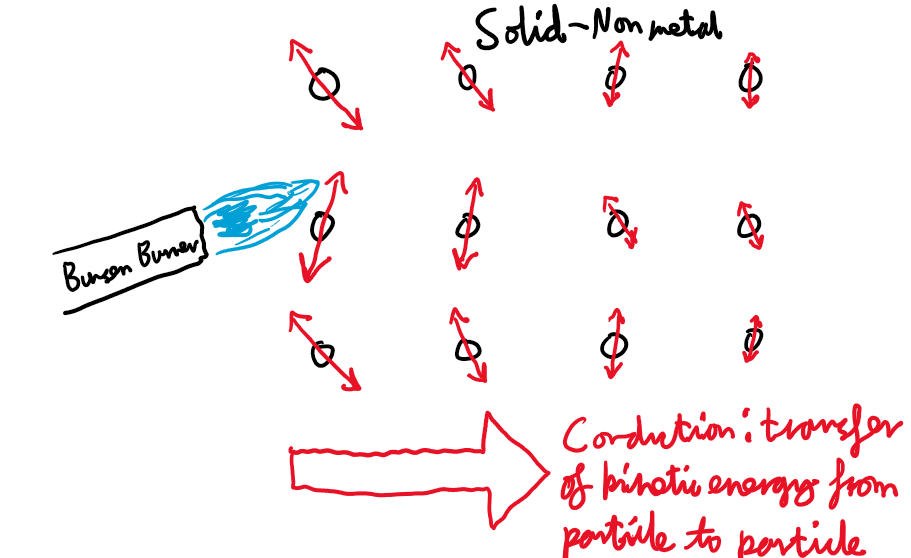
What is conduction?
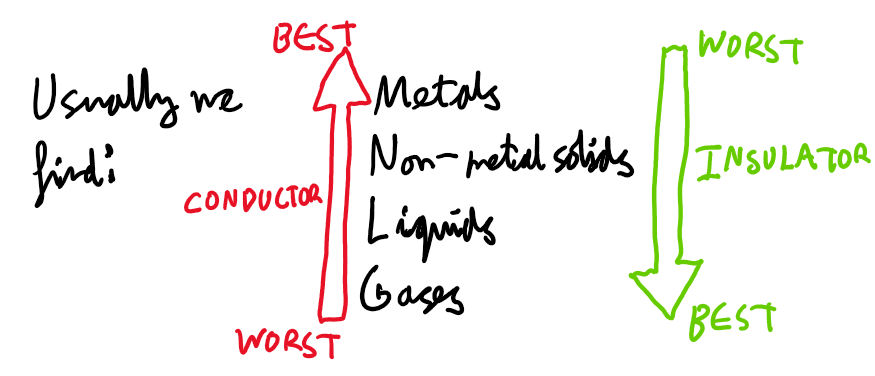
Conductors and Insulators
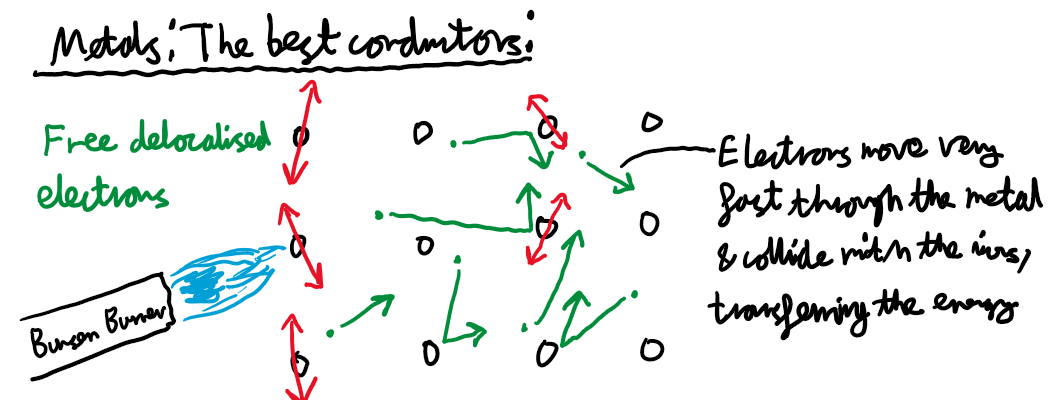
Metals: The Best Conductors
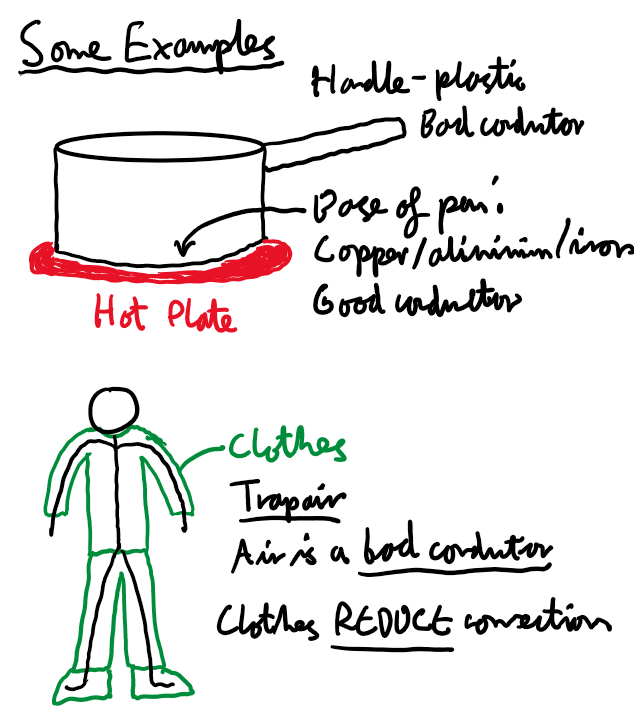
Conduction Examples
What is convection?
Thermal energy being transferred from one place to another by the movement of fluids of gases.