PSYC101: Chapter 11 - Stress, Coping, and Health
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Stress
The tension, discomfort, or physical symptoms that arise when a situation called a stressor — a type of stimulus — strains our ability to cope effectively
Clinicians Illusion
Suggests people who are practicing psychologists will see people often in need of psychological help or have poor coping problems, therefore thinking these things are more common and severe than they really are
Stressors as Stimuli
Stimuli that causes stress and negative experiences—something out in the environment that impacts our inner world
Stress as Transaction
Stress is subjective
Primary appraisal: initial decision regarding whether an event is harmful or irrelevant, neutral, positive
Secondary appraisal: perceptions regarding ability to cope with an event that follows a primary appraisal
Coping
degree to which we think we can adapt to the stressor
problem-focused coping: addressing stress head on (studying & preparing)
emotion-focused coping: changing our emotions in response to the stressor (watching tv)
Often used when we cant control the situation
Stress as a response
Physiological and psychological responses to stressful events or experiences
Social Readjustment Rating Scale (SRRS)
Participants rate anticipated difficulty (readjustment) of 43 events
Hassle
Minor annoyance or muisance that strains our ability to cope, can build up
Potential hassles become hassles when we appraise them as such
Physiological Measures of Stress
Heart rate and blood pressure
EEG (brain activity)
Hormonal Testing (cortisol and adrenaline)
Galvanic skin response measures
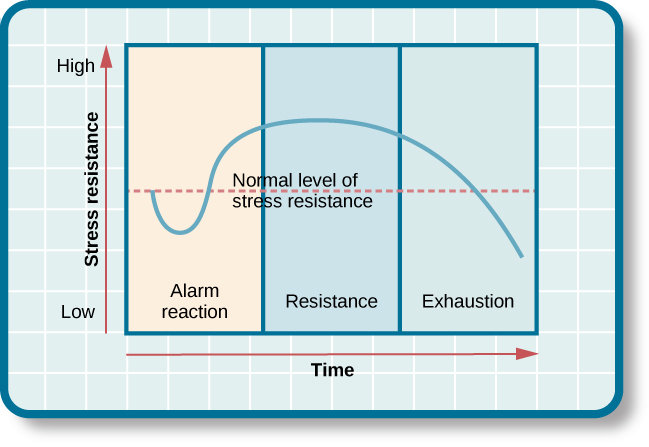
General Adaptation Syndrome
Peoples Responses to a stressor are similar, regardless of the type of stressor:
Alarm Reaction: Fight or Flight response, initial response to stress (short)
Resistance: Adapt to stressor; physiological responses lessened, but still higher than baseline
Exhaustion: No longer able to adapt to the stressor, body becomes depleted
Eustress
Stress can be good! It is a motivator
HPA Axis
Chain reaction of hormonal response lead to release of cortisol
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Adrenal Glands
Hypothalamus Activated → Releases hormones→ causes pituitary gland to release hormones→ causes Adrenal Glands to release Cortisol
Sympathetic Nervous System in Stress
Immediate response: adrenaline, heart rate, vasodilation, airways, sweat
Parasympathetic reduces stress response: slowing heart rate, breathing, etc.
Symptoms arent either/or, they’re constantly operating to maintain homeostasis
Variations in Stress Responses
Individual Differences: Perception/Interpretation, Coping Strategy, Type and degree of stress: acute or chronic
PTSD: Mental condition caused by highly stressful event
Gender Differences: Men exhibit more fight more flight (prefrontal cortex overly activated) Women “tend and befriend” (oxytocin)
Factors in Coping
Social Support
Individual Differences
Coping Strategies: Problem-focused vs. emotion-focused
Control: Belief that a stressor can be controlled
Behavioural Control: control behaviours
Cognitive Control: control thoughts
Informational Control: seek out info to manage (proactive coping)
Decisional Control: chose alternate courses of action
Emotional control: suppress or express emotions
Catharsis
Individual Differences in Coping
Hardiness: set of attitudes marked by a sense of control over events, commitment, and courage and motivation to control stressful circumstances
Optimism: tendency to view life’s events more positively
Hostility and Competitiveness are associated w/ worse health outcomes
Spirituality and Religion: sense of something greater
Rumination: excessive, repetitive thoughts that interfere with other forms of mental activity