Genetics and Meiosis
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
know how to do punnet squares too they arent included here bc its easier to just find practice problems and theres nothing to remember about them tbh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Heredity
The act of passing genes onto your descendants
Dominance
A allele that displays a phenotype even if only one dominant allele is present.
In pedigrees, the phenotype never skips generations.
Ex: Aa would display the “A“ allele phenotype because the “A“ allele is dominant.
Recessive
A alleles that will only display a phenotype if all alleles are recessive.
In pedigrees, the phenotype can skip generations.
Ex: aa displays the “a“ phenotype, Aa does not display the “a“ phenotype. “a“ must be a recessive allele.
Phenotype
the physical characteristics of an organism displayed based on their genotypes.
Genotype
The physical combination of genes of an organism
Heterozygous
A combination of two different alleles
Ex: Aa is a heterozygous combination.
Homozygous
A combination of two identical alleles
Ex: AA is a homozygous combination.
Allele
Variations on genes that lead to different physical traits. You receive different ones from each parent.
Genes
Segment of DNA that codes for proteins or RNA molecules.
Trait
Characteristics that can be passed hereditarily
mendel’s laws of inheritance: law of dominance
Some alleles are dominant over other alleles.
mendel’s laws of inheritance: law of segregation
Each parent can only provide one allele to each of their descendants.
mendel’s laws of inheritance: law of independent assortment
The assignment of alleles is independent of the other(?)
Ex: in pea plants, the distribution of round vs wrinkled seeds is independent of the distribution between yellow and green seeds.
Mendel’s Experiments
Experiments with pea plants which laid the groundwork for our understanding of genes
Might not need to know the specific term name
Monohybrid crosses
Experiment examining the inheritance of one allele.
Dihybrid Crosses
Experiment examining the inheritance of two different alleles.
Incomplete dominance
The phenotype of a offspring is merely a blend of the dominant alleles from the parents.
Ex: Red and White flowers produce a pink offspring.
Codominance
The offspring displays a simultaneous combination of both dominant alleles from the parents.
Ex: Red and White Flowers produce a offspring with alternating red and white petals
Sex-linked traits
Traits that are passed down specifically based on sex.
This makes it such that pedigrees can reveal sex-related traits if the traits are only present in one sex.
Also makes males more susceptible to sex related illness/trait as their “X“ chromosome only has one copy, thus if a X chromosome has a recessive illness/trait and is passed to a male offspring, the male offspring is guaranteed to have the trait/illness.
Autosomes
Non sex-related chromosones
Human chromosome #
23 pairs, 46 chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes
Pairs of identical coding chromosomes, with each containing a different combination of alleles from each parent.
Pedigree
Family tree that displays the presence of traits across generations
Square in pedigree
Male
Circle in pedigree
female
Dashed/partially filled in pedigree
Carrier
Carrier
An individual who carries a diseased allele but is not afflicted with it. Can pass the disease onto descendants.
Fully filled in on pedigree
Diseased, displays phenotype
Polygenic inheritance
Alleles that are additive and produce different phenotypes based on combinations. Multiple genes determine one phenotype.
Ex: genotypes with aabbcc determine skin color, with the more dominant alleles resulting in darker skin. aabbcc would be the lightest shade, while AABBCC would be the darkest. Combinations of the alleles lead to distinct phenotypes, like AaBbCc leading to a medium shade.
Pleiotrophy
Single gene expresses multiple phenotypes.
Haploid
Containing one set of chromosones. Symbol is n
Diploid
Containing two sets of chromosones, one from each parent. Symbol is 2n
Meiosis I
Replication of chromosomes and genetic diversity promoted by crossing over
Interphase I
Genetic material, one chromatid from each parent, are replicated to form two homologous chromosomes, each containing genetic material from one parent.
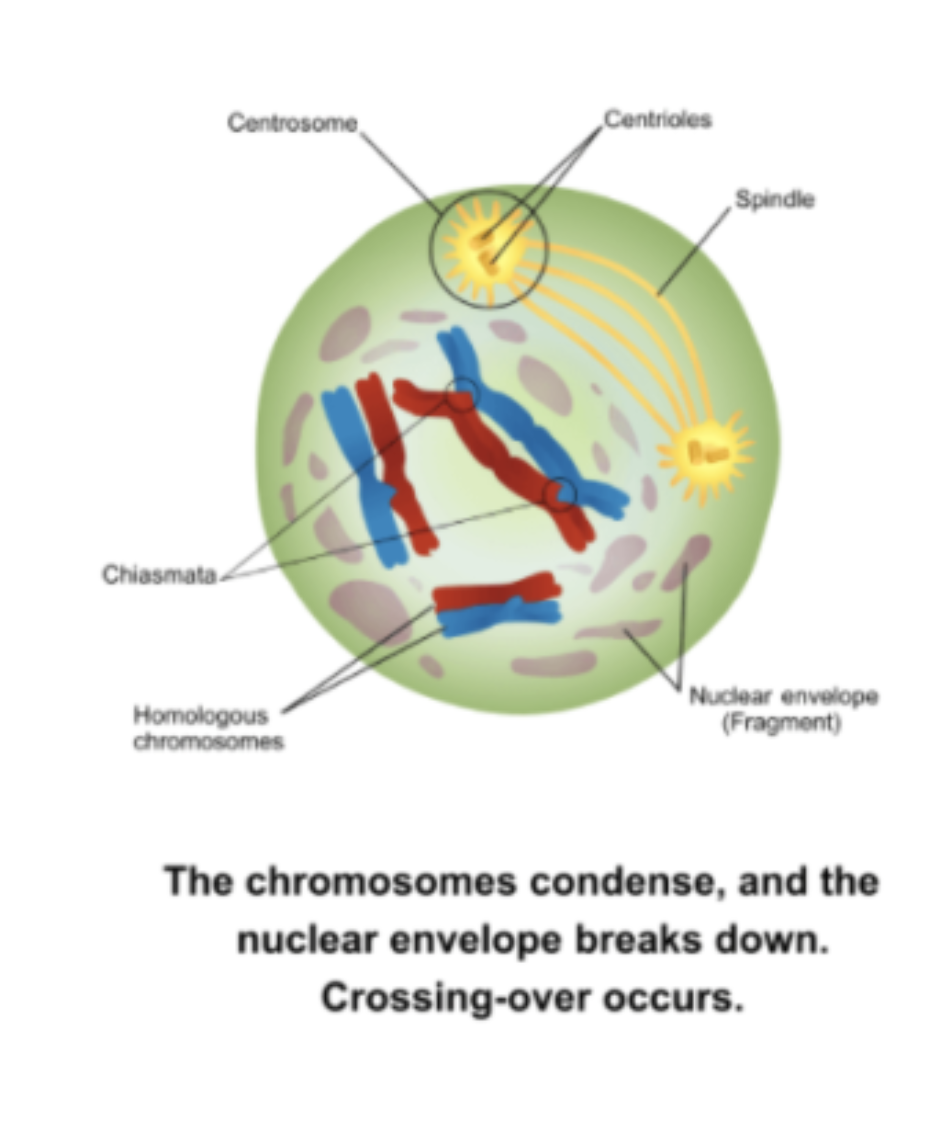
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes crossover to form tetrads, spindle extends from centrioles. The nuclear membrane dissolves.
Tetrads
A pair of homologous chromosomes tightly intertwined during prophase
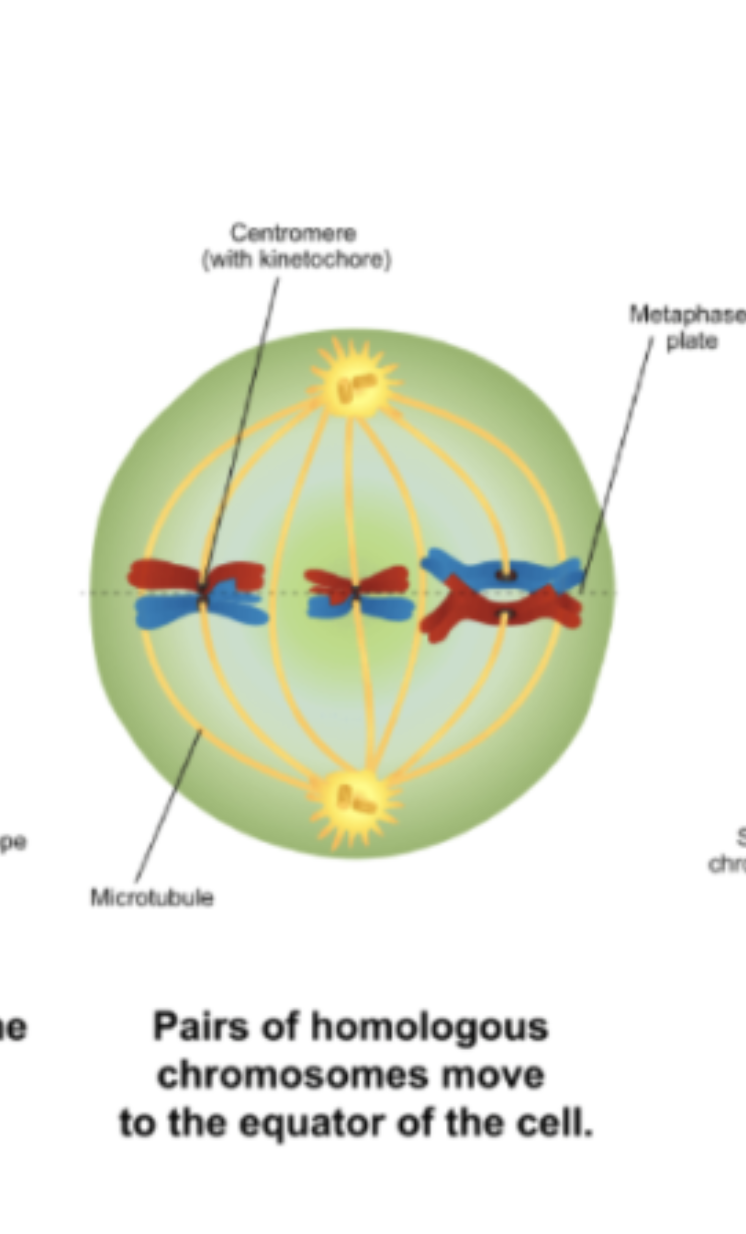
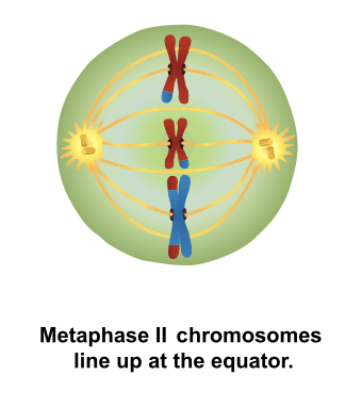
Metaphase I
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, spindles connect to centromeres
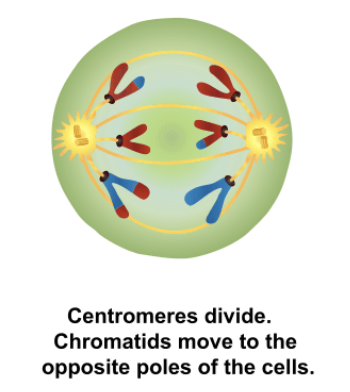
Anaphase I
Spindles begin to retract, pulling the homologous chromosomes apart.
Crossing Over
Process in anaphase I where intertwined homologous chromosomes are pulled apart, diversifying the child with alleles from each parent
Meiosis II
Process identical to mitosis but with haploid gamete cells as both daughter and parent cell
Cells before meiosis I
In Interphase, the gametes are diploid
Cells after meiosis I
After anaphase, the cells are haploid gametes
Cells before and after meiosis II
The cells remain haploid for the entirety of this process.
Synapsis
Intertwining of homologous chromosomes prior to crossing over
Gamete Cells
Haploid sex cells which can combine with other gamete cells to produce a zygote.
Zygote
The first cell of a new organism, made from the fusion of two gamete cells from each parent. It is diploid.
Somatic Cells
Diploid body cells
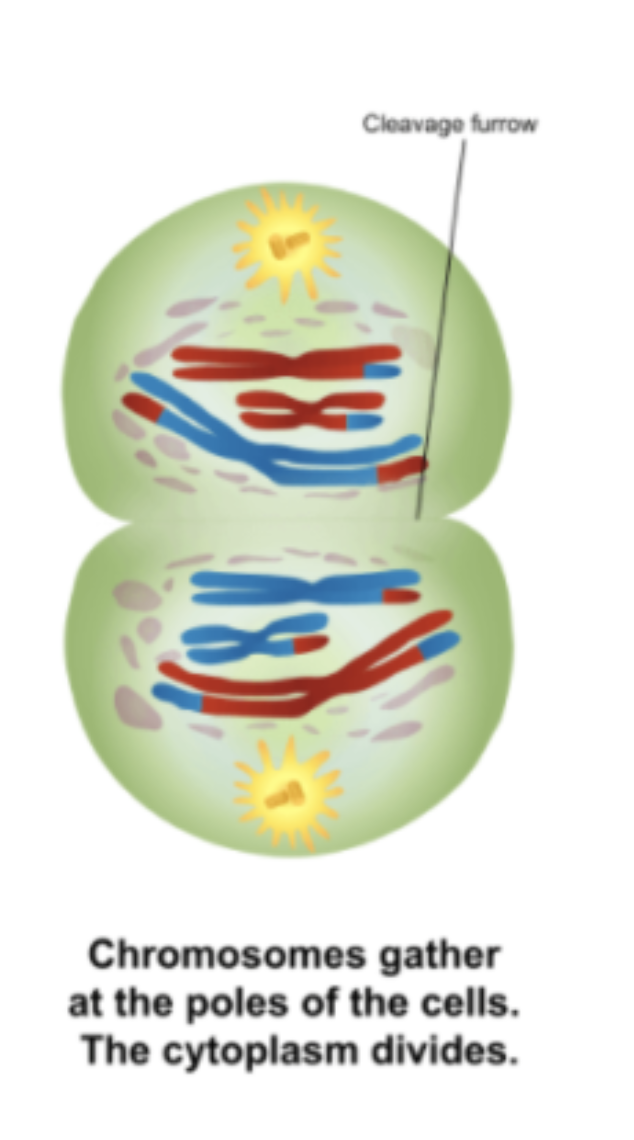
Telophase I
Chromosomes reach the poles and the nuclear membrane reforms. The sister chromatids still remain attached to form chromosomes, the homologous chromosomes are simply separated with one going into each daughter gamete.
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
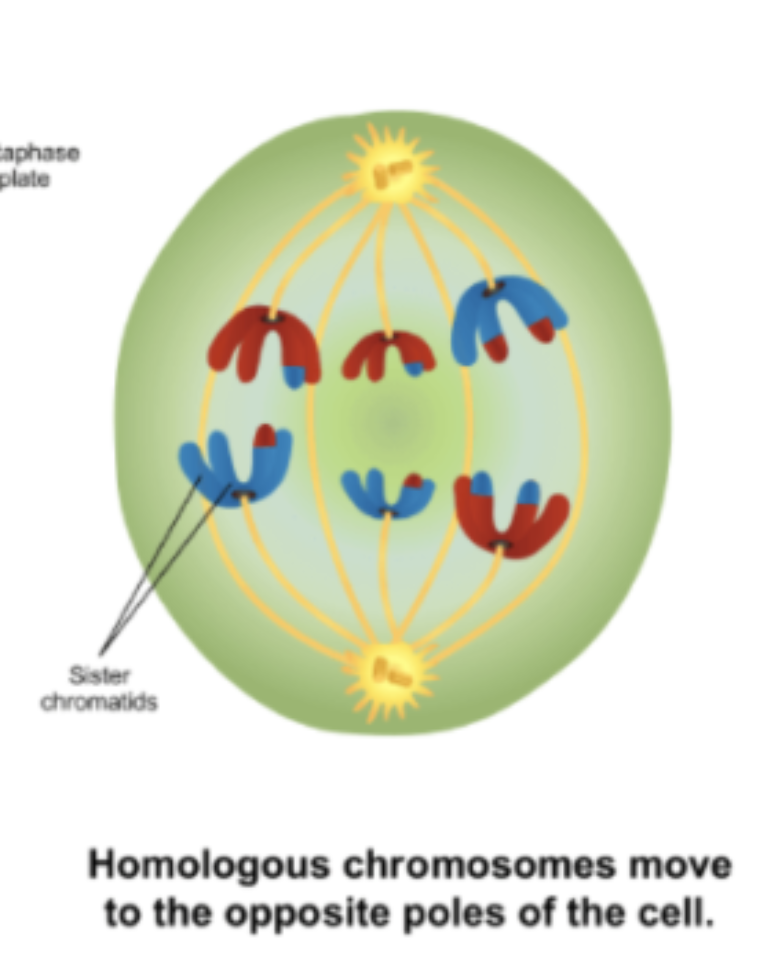
Telophase I
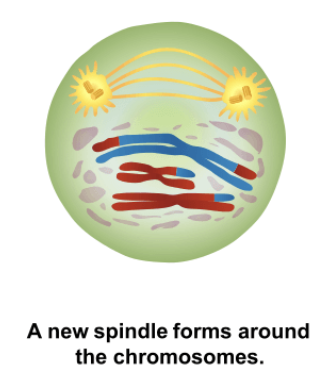
Prophase II
Metaphase II
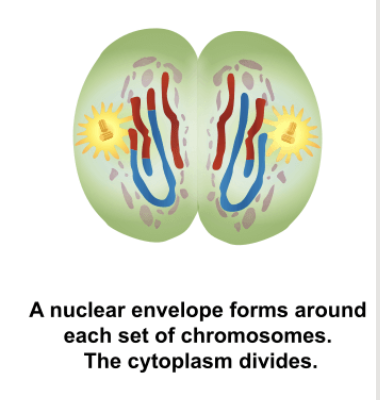
Telophase II
Anaphase II