Electricity and Magnetism
0.0(0)Studied by 8 people
Card Sorting
1/20
Last updated 4:08 AM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
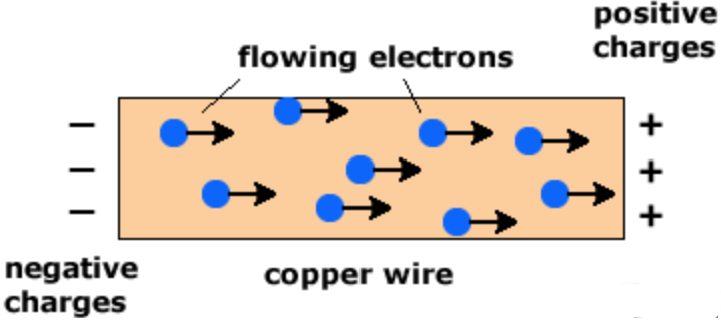
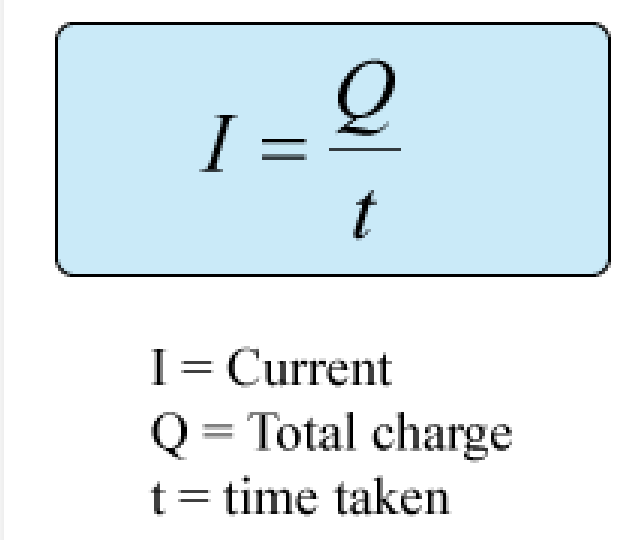
Electric Current (I)
Flow of charge (electrons) in a fixed direction.
* Measured in Amperes (A)
* Only measured in a series circuit
* Measured in Amperes (A)
* Only measured in a series circuit
2
New cards
Static Electric Current
A current that does not move/flow.
3
New cards
Electric Charge (C)
Imbalance in the number of protons and electrons.
* Measured in coulombs (C)
* Measured in coulombs (C)
4
New cards
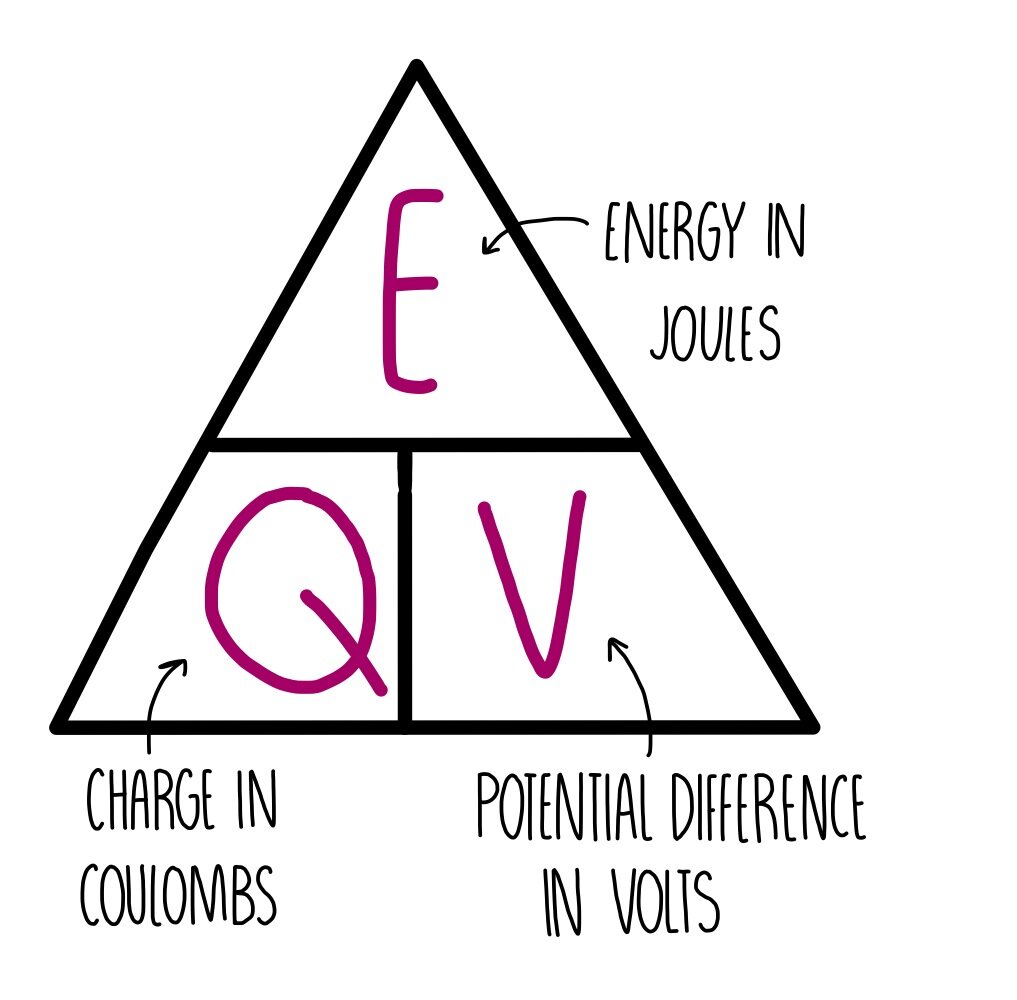
Voltage (V)
When one joule of energy is given to one coulomb.
* V= E/Q(C)
* V= E/Q(C)
5
New cards
Electron Pumps
‘Pump’ electrons by pulling them from one end of a wire and pushing them into the other.
* Convert chemical energy to electricity.
* (E.g: Cells/batteries)
* Convert chemical energy to electricity.
* (E.g: Cells/batteries)
6
New cards
Cell
Transfers energy to electrons.
7
New cards
Battery
Two or more cells.
8
New cards
Conductor
Materials that allow electrons to pass through them well.
* (E.g: Metals have free electrons between atoms, making them great conductors)
* (E.g: Metals have free electrons between atoms, making them great conductors)

9
New cards
Insulator
Materials that do not allow electrons to pass through them well.
* (E.g: Rubber has tightly bound electrons)
* (E.g: Rubber has tightly bound electrons)
10
New cards
Semi-Conductor
Materials that are neither conductors nor insulators.
* (E.g silicon and germanium are good conductors when warm, poor when cold)
* (E.g silicon and germanium are good conductors when warm, poor when cold)
11
New cards
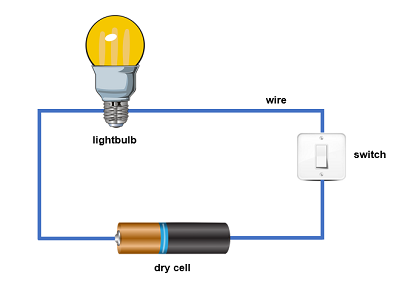
Electric Circuit
A continuous path of wires and electrical components where electrons can flow. Controlled by a switch between two terminals of a cell or battery.
12
New cards
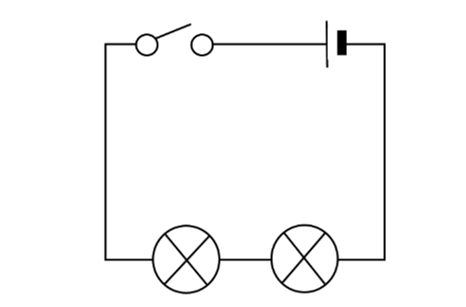
Series Circuit
A circuit with only one electric current flows throughout.
* I₁ = I₂ = I₃ = I₄
* I₁ = I₂ = I₃ = I₄
13
New cards
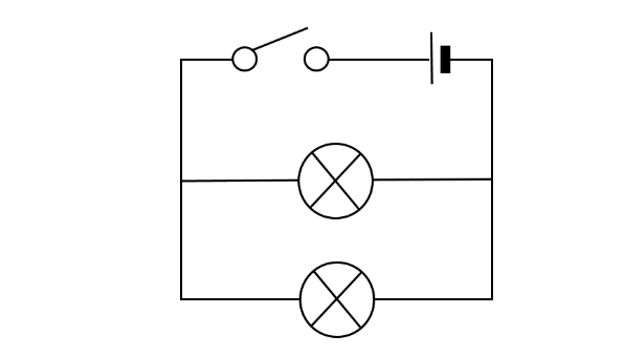
Parallel Circuit
A circuit in which the current is split to power two or more electrical components.
* The voltage of each branch is the same, but the currents may vary
* IT = I₁ + I₂ + I₃ + I₄
* The voltage of each branch is the same, but the currents may vary
* IT = I₁ + I₂ + I₃ + I₄
14
New cards
When more bulbs are added in a series circuit, the brightness_____.
Dims
* The current is split across each bulb and grows weaker.
* The current is split across each bulb and grows weaker.
15
New cards
When more bulbs are added in a parallel circuit, the brightness ______.
Stays the same
* The current is split evenly across each bulb.
* The current is split evenly across each bulb.
16
New cards
Electric Resistance (R)
When a current experiences opposition as it passes through a material cue to collisions of the electrons.
* Measured in ohms (Ω)
* Measured in ohms (Ω)
17
New cards
Resistors
Materials that oppose/resist the flow of electric currents.
18
New cards
Insulators have _______ resistance.
Infinite
19
New cards
Conductors have _______ resistance.
Near-zero
20
New cards
Semi-conductors have _______ resistance.
Some
21
New cards
Resistors have _______ resistance.
Finite