Unit 4: Cell Communication & the Cell Cycle
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
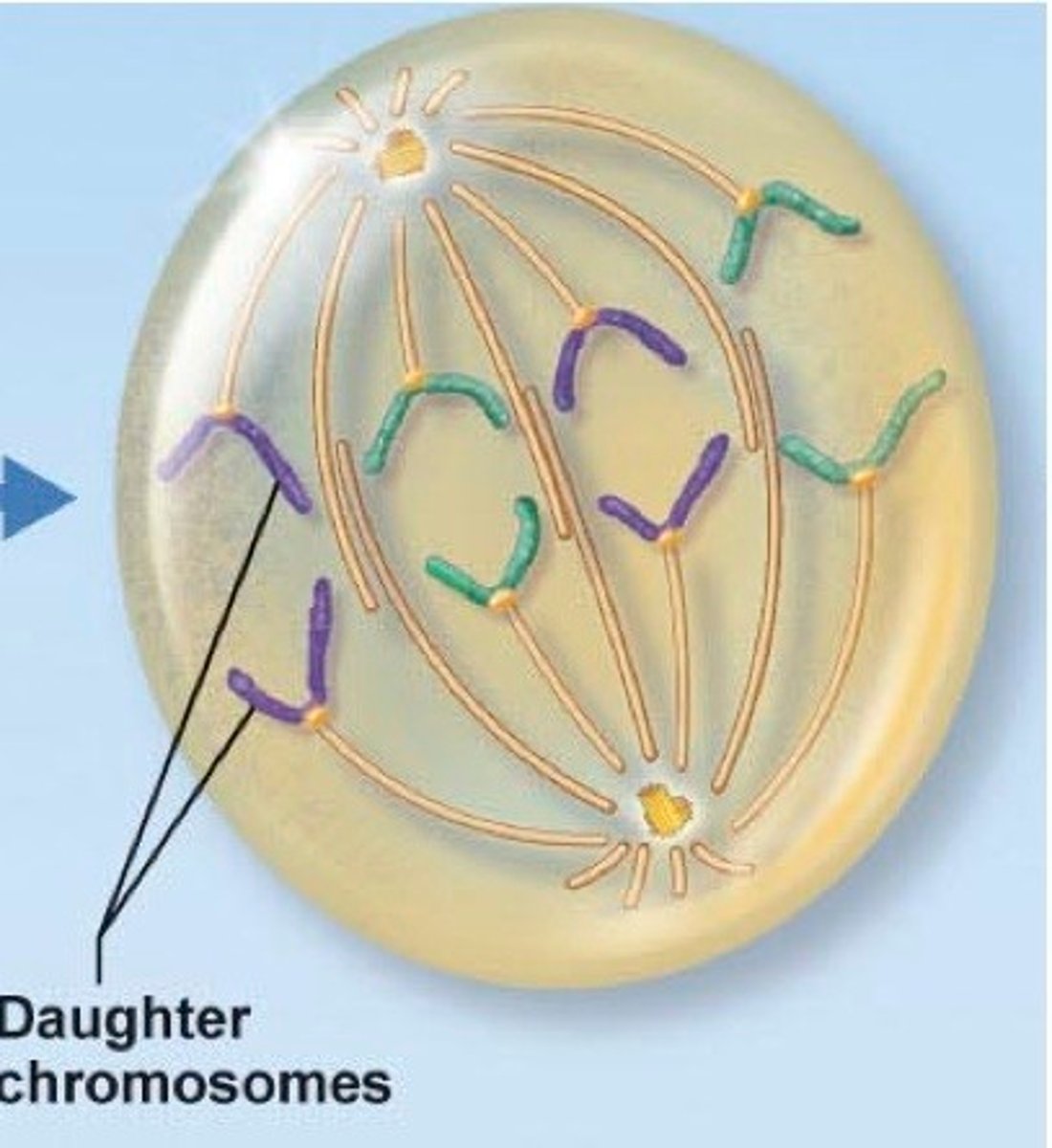
Anaphase
A stage of mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death used to remove damaged or unnecessary cells.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction involving one parent that produces genetically identical offspring.
Autocrine
A type of cell signaling where a cell targets itself.
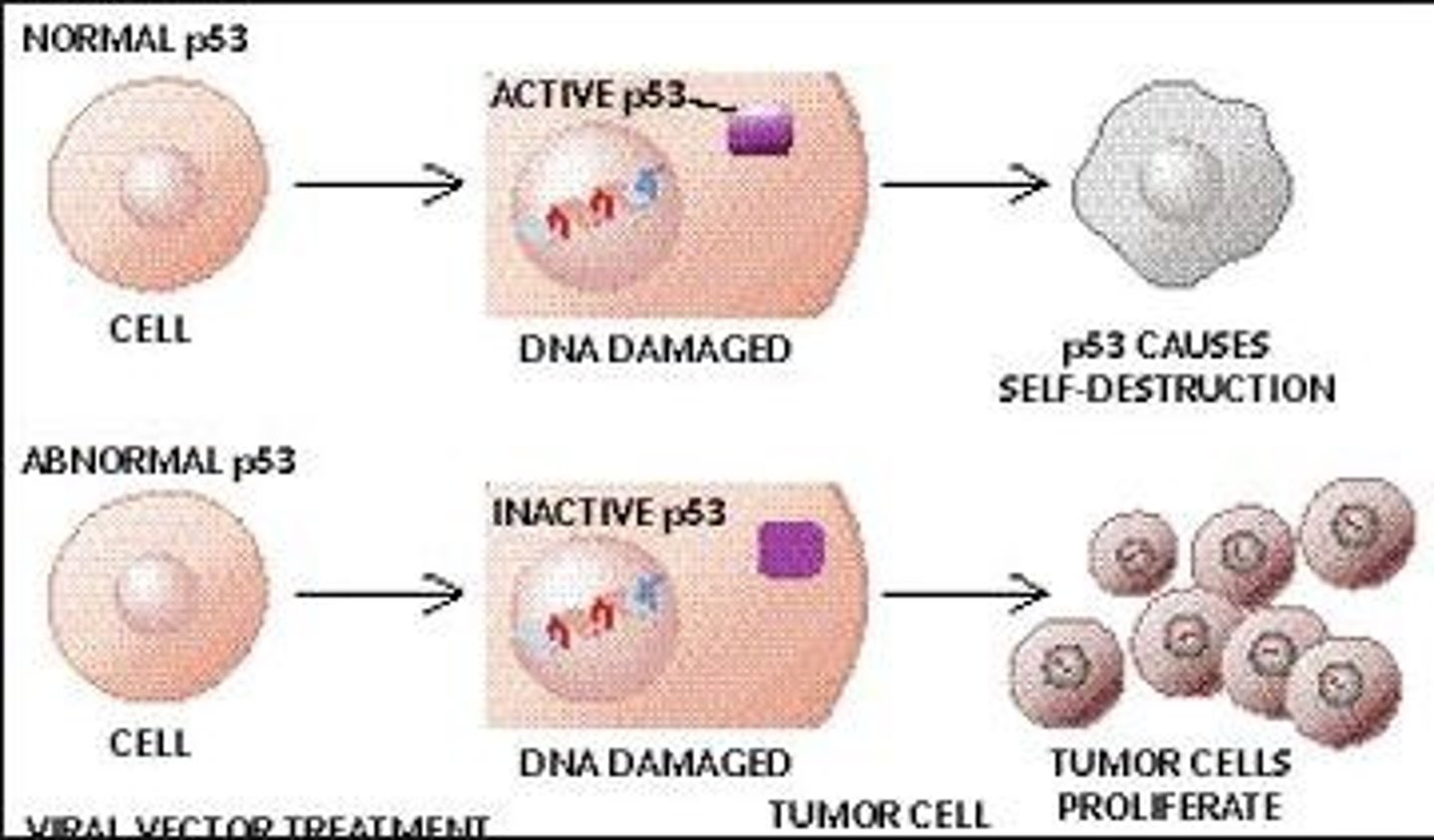
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell growth due to failures in cell cycle regulation.
Cell cycle
The series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide.
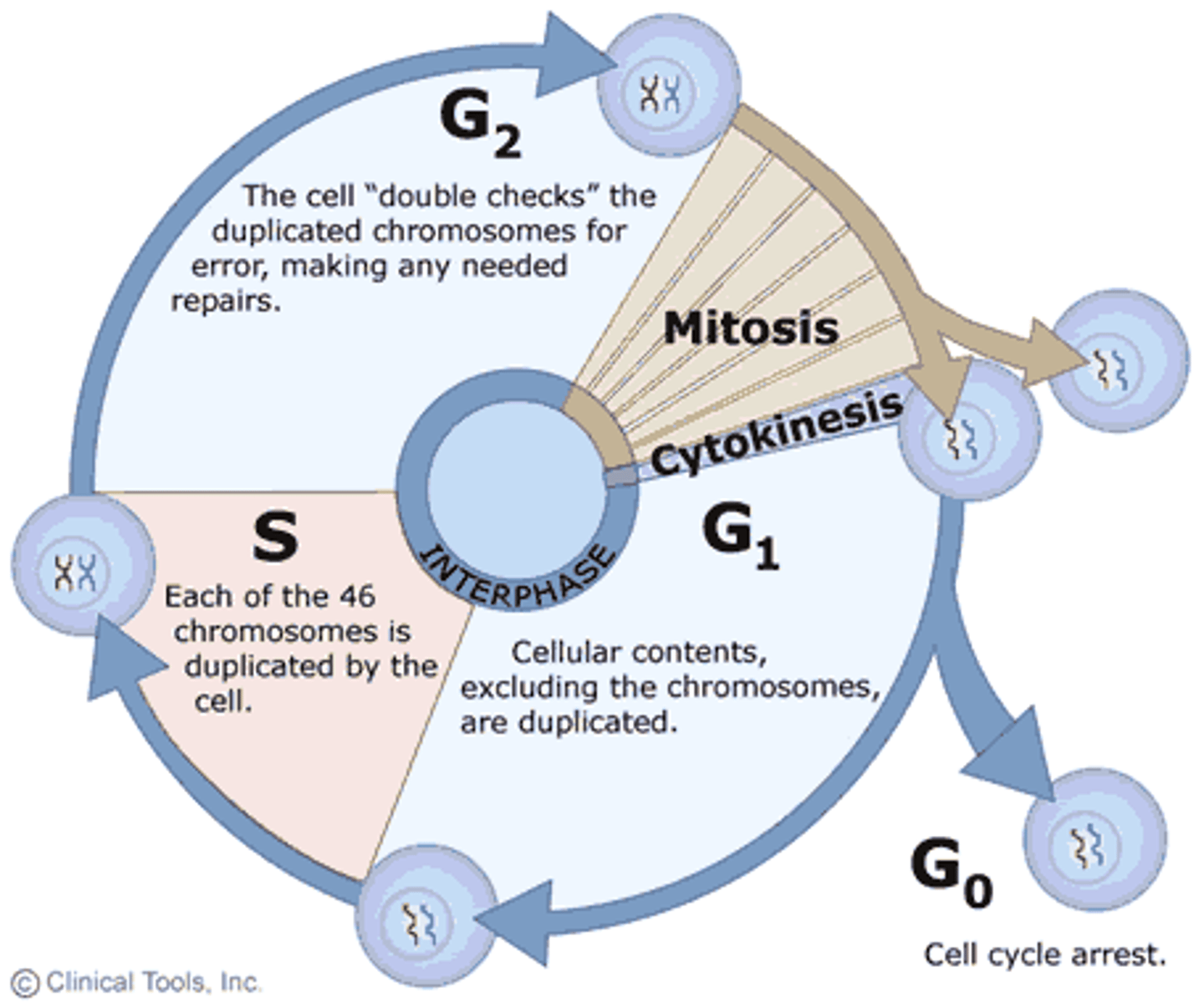
Cell cycle checkpoints
Control mechanisms that ensure the cell is ready for the next phase.
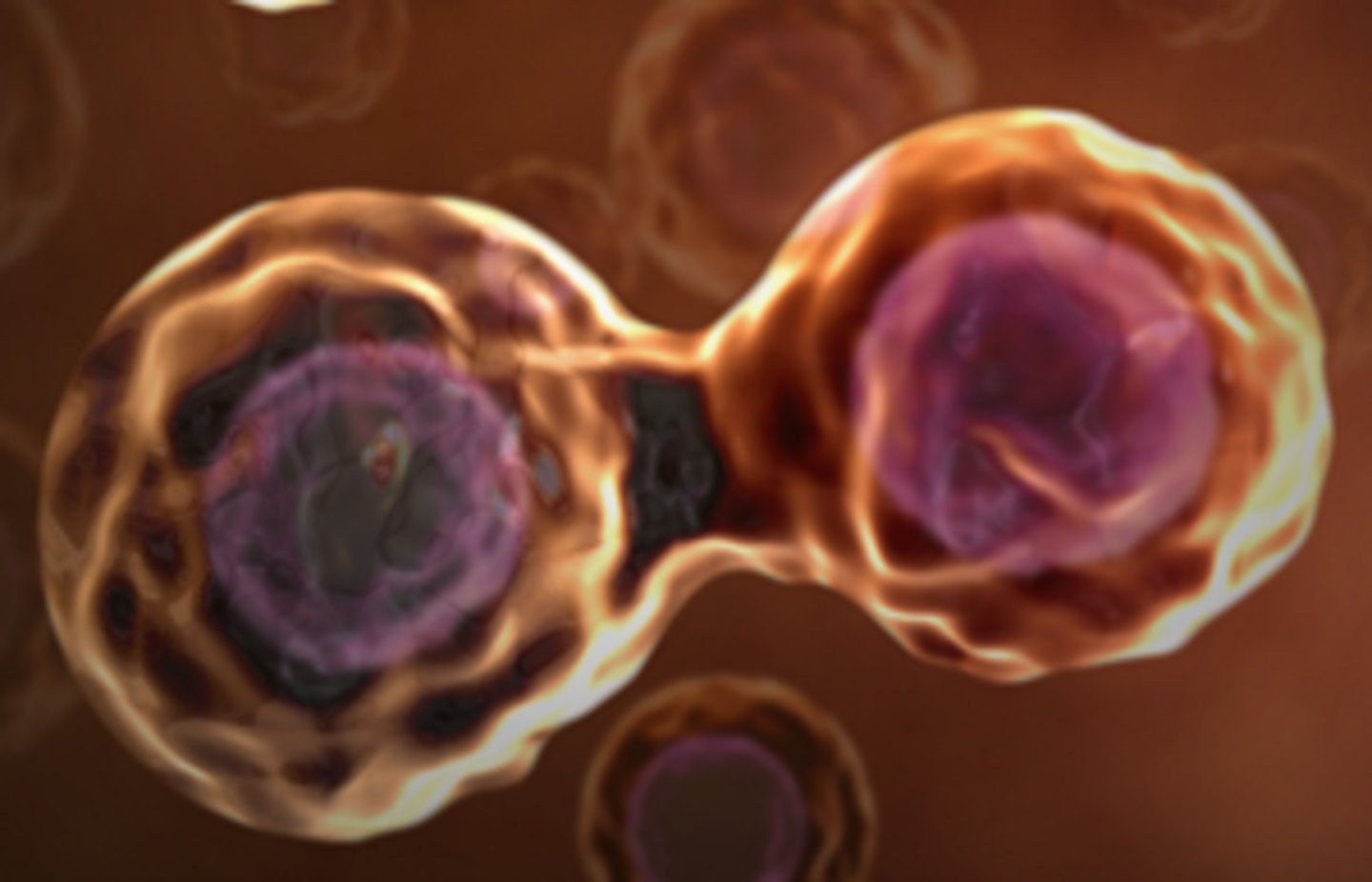
Cell division
The process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells.
Cell signaling
The process by which cells communicate using chemical signals.
Cellular differentiation
The process by which a cell becomes specialized for a specific function.
Centrioles
Structures that help organize the mitotic spindle during cell division in animal cells.
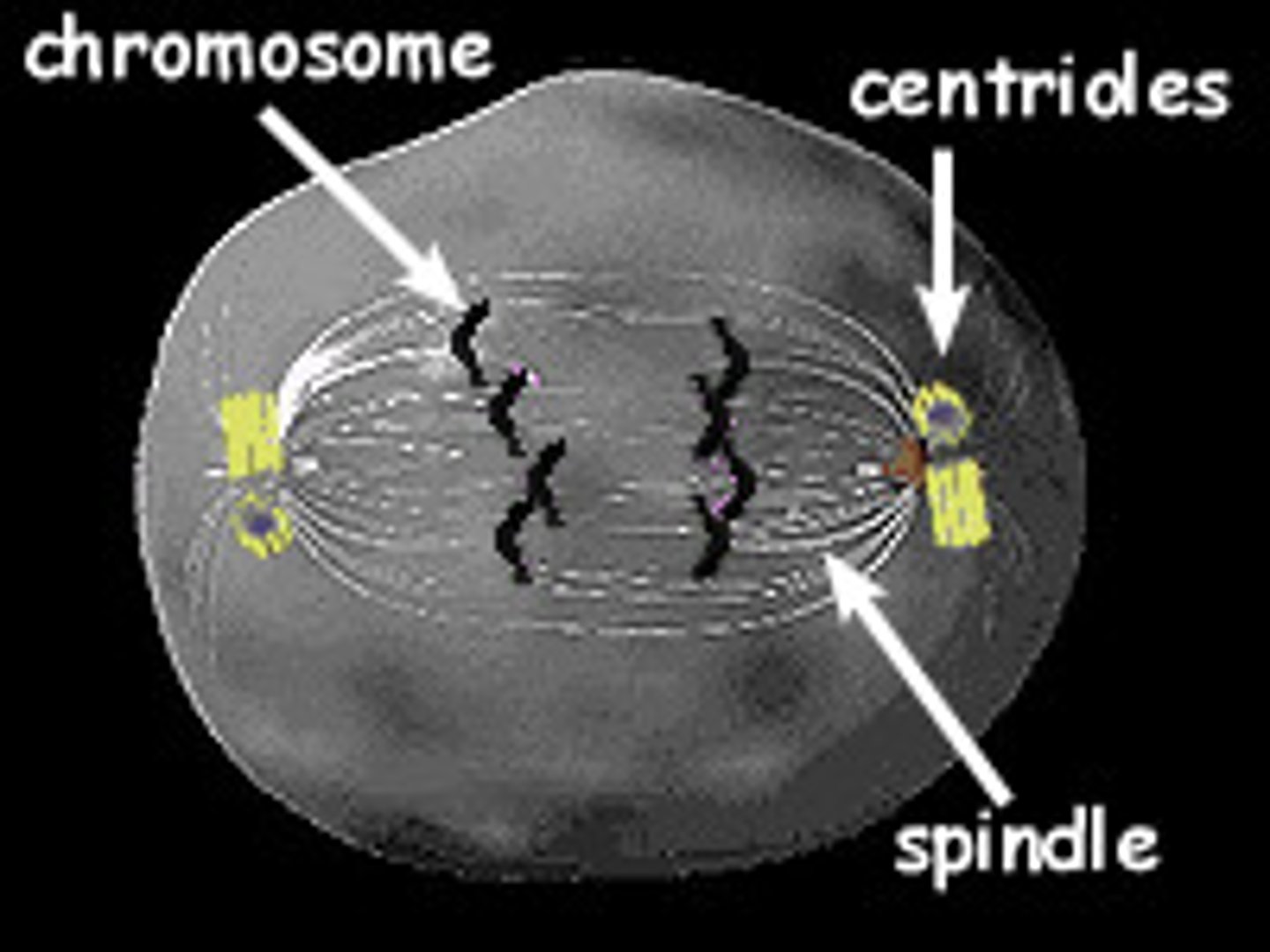
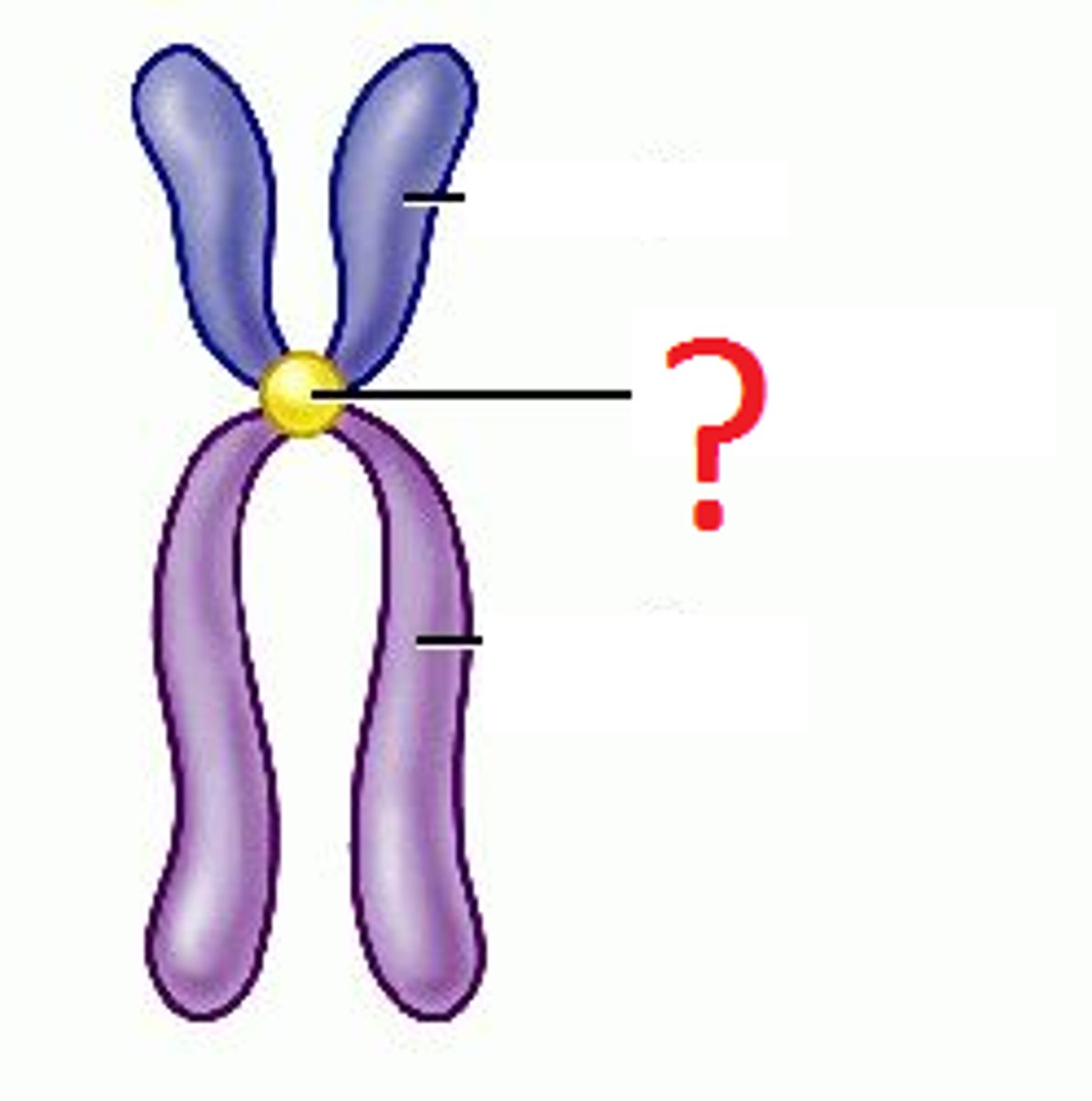
Centromeres
The region of a chromosome where the sister chromatids are joined.
Chromatin
The uncondensed form of DNA found in the nucleus during interphase.
Chromosome
A condensed form of DNA visible during cell division.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
A second messenger involved in signal transduction pathways.
Cyclin
dependent kinase - Enzymes that regulate the cell cycle when activated by cyclins.
Cyclins
Proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle.
Cytokine
Signaling molecules that mediate communication between cells, especially in the immune system.
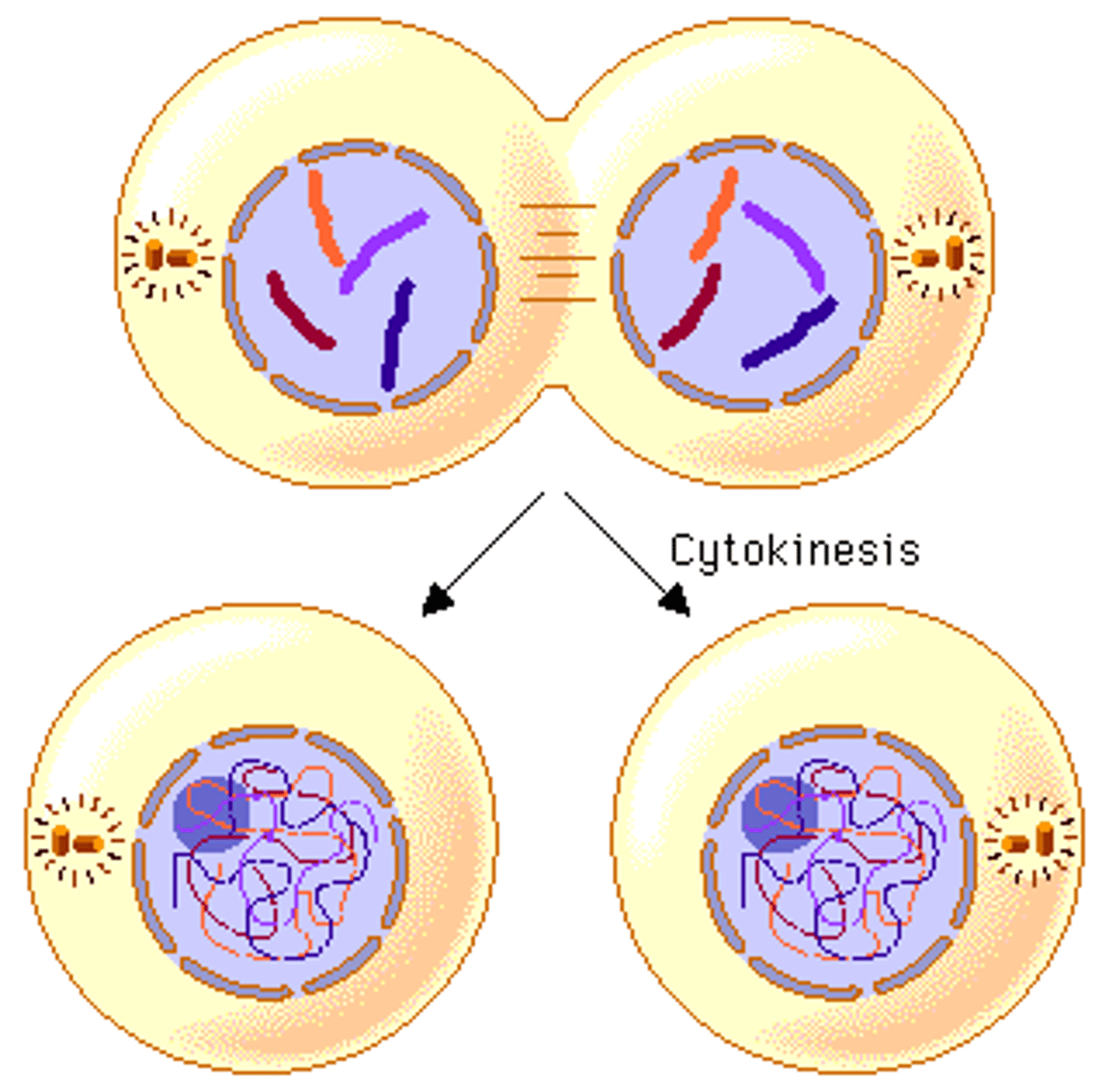
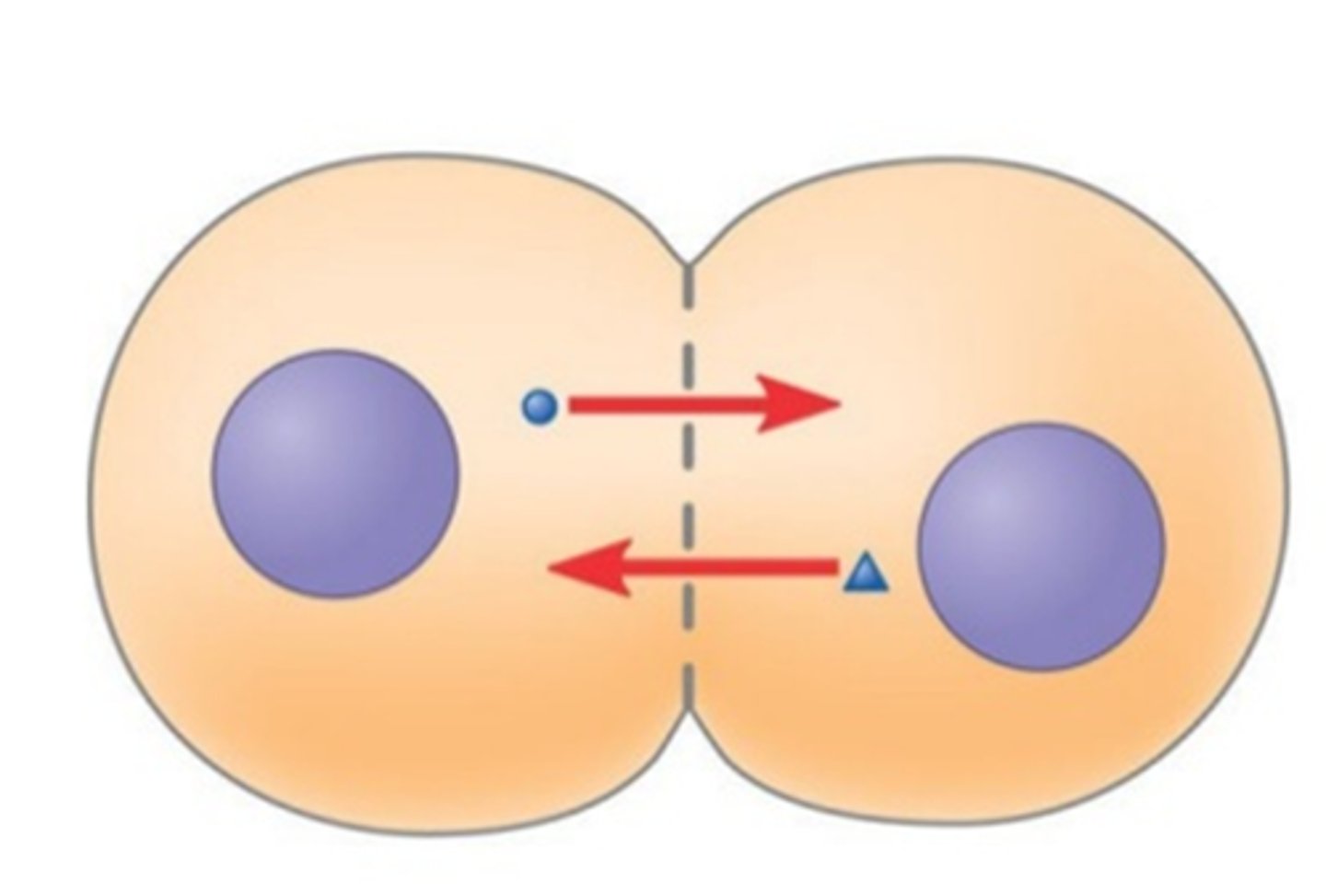
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm at the end of cell division.
Diploid
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Direct communication
Signaling between cells that are physically connected, such as through gap junctions.
DNA Replication
The process of making an identical copy of DNA before cell division.
Endocrine system
The body system that produces hormones for long-distance signaling.
G
protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) - A membrane receptor involved in signal transduction using G-proteins.
G0 Phase
A resting or non-dividing phase of the cell cycle.
Gap junctions
Channels between animal cells that allow direct communication.
Gene expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to make a functional product like a protein.
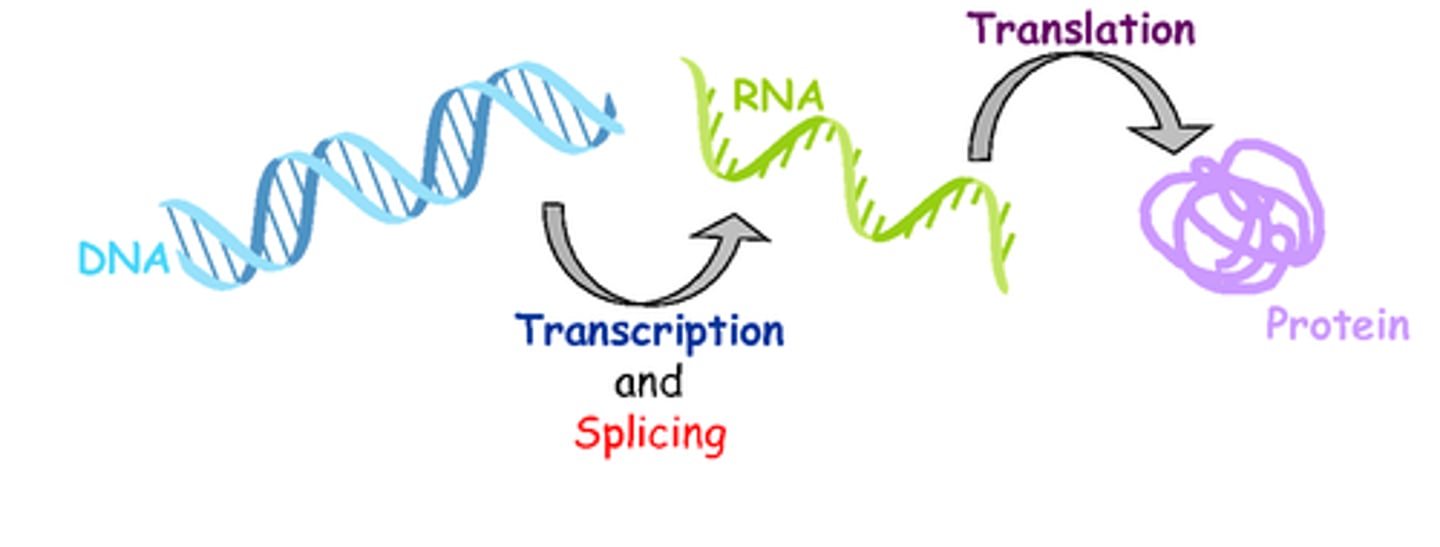
Genome
The complete set of genes or genetic material in an organism.
Growth
An increase in cell size or number.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal environment.
Homologous chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes with the same genes but possibly different alleles.
Hormones
Chemical messengers used in long-distance signaling within the body.
Immune system
The body system that defends against infection and disease.
Insulin
A hormone that lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating cellular uptake.
Interphase (G1, S, & G2)
The phase of the cell cycle between divisions where the cell grows and replicates DNA.
Ligand
A molecule that binds to a receptor to initiate a signal.
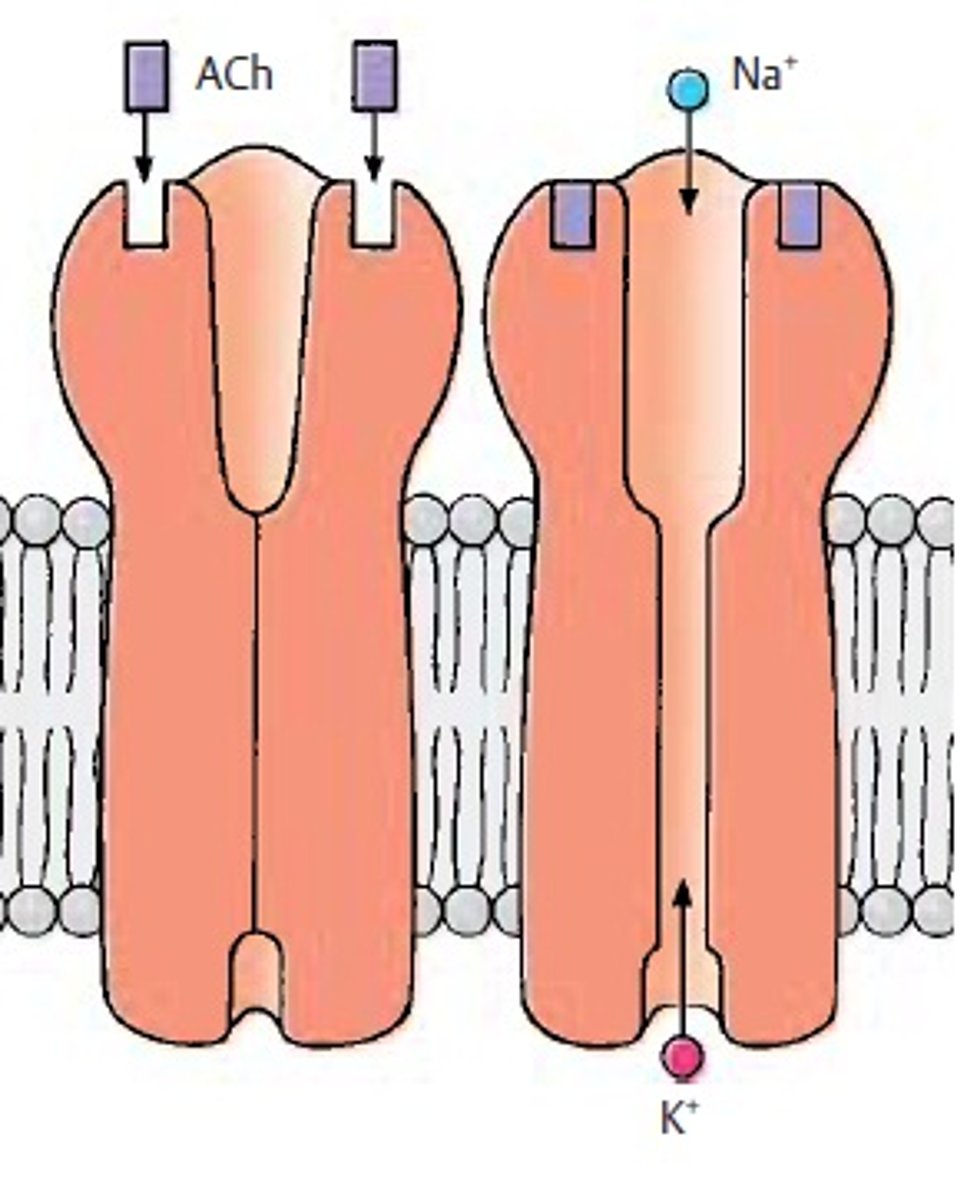
Ligand gated ion channel
A membrane protein that opens or closes in response to a ligand binding.
Local communication (paracrine)
Cell signaling over short distances to nearby cells.
Long distance communication (endocrine)
Signaling between cells in different parts of the body using hormones.
Metaphase
A stage of mitosis where chromosomes align at the cell's equator.
Mitosis
The process of nuclear division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Morphogens
Signaling molecules that govern tissue development and patterning.
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence.
Necrosis
Unplanned cell death due to injury or damage.
Negative feedback loop
A regulatory mechanism that reverses a change to maintain stability.
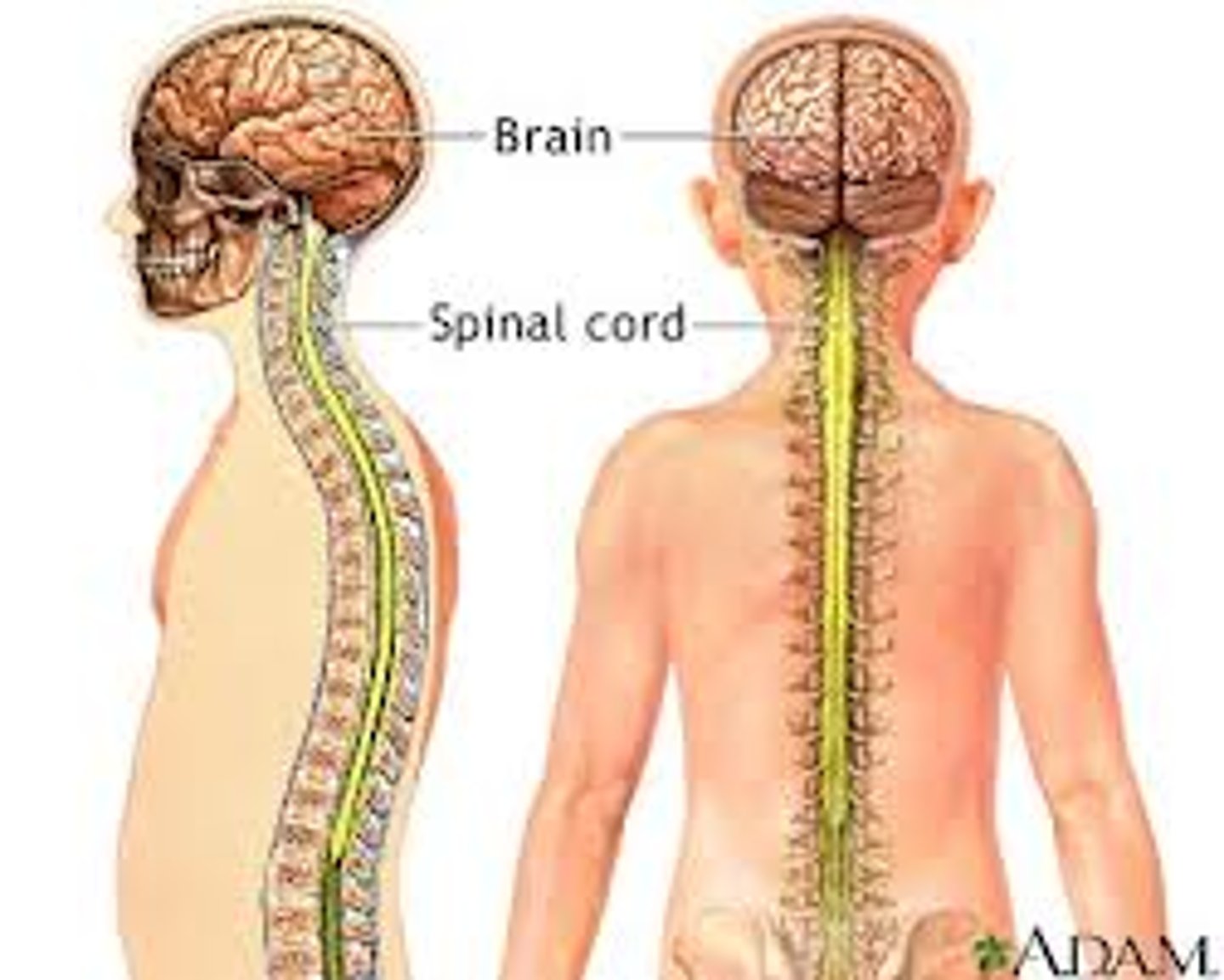
Nervous system
A body system that transmits signals rapidly using neurons.
Neurotransmitter
A chemical messenger that transmits signals across a synapse between neurons.
Nuclear division
The process of dividing the nucleus during mitosis or meiosis.
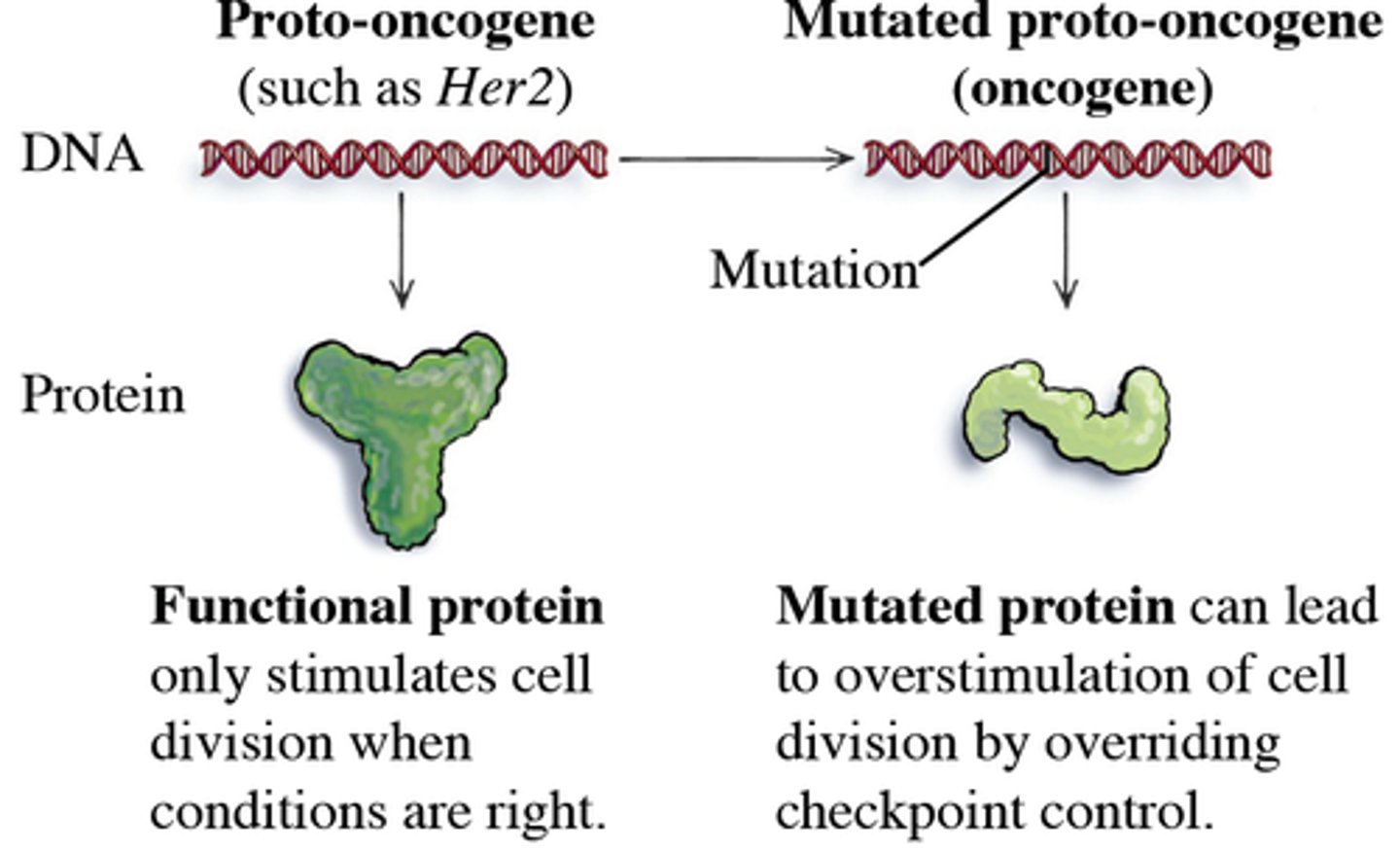
Oncogenes
Mutated genes that promote uncontrolled cell division and can lead to cancer.
p53
A tumor suppressor protein that regulates the cell cycle and prevents cancer.
Paracrine
A type of signaling where cells communicate with nearby target cells.
Phosphorylation cascade
A series of events where one enzyme activates another through phosphorylation.
Positive feedback loop
A regulatory mechanism that amplifies a change or response.
Prophase
The first stage of mitosis where chromatin condenses and spindle fibers form.
Protein hormone
A hormone made of amino acids that binds to receptors on cell surfaces.
Protein kinase
An enzyme that adds phosphate groups to other proteins.
Protein modification
The process of altering protein structure or function after translation.
Quorum sensing
A form of communication among bacteria to coordinate group behavior based on population density.
Reception
The first step in cell signaling where a cell detects a signaling molecule.
Receptor
A protein that binds to a specific ligand and initiates a response.
Response
The final step in cell signaling that leads to a cellular change or activity.
Second messenger
A small molecule that amplifies and relays the signal within a cell.
Secretion
The release of substances from a cell.
Self signaling (autocrine)
A type of signaling where a cell sends a signal to itself.
Set point
The target value for a physiological condition maintained by homeostasis.
Shmooing
A morphological change in yeast cells in response to mating signals.
Signal transduction pathway
A sequence of molecular events triggered by a signal that leads to a response.
Sister chromatids
Two identical copies of a chromosome connected by a centromere.
Somatic cell
Any body cell that is not a sperm or egg cell.
Steroid hormone
A lipid-based hormone that can pass through membranes and bind to intracellular receptors.
Synapse
The junction between two neurons where neurotransmitters are released.
Target cell
A cell that has receptors for a specific signal or hormone.
Telophase
The final stage of mitosis where chromosomes uncoil and nuclear membranes reform.
Transduction
The process of converting a signal into a cellular response.
Tumor suppressor genes
Genes that prevent uncontrolled cell division and tumor growth.