Biomechanics Exam V: Mechanics of Articular Cartilage
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Where is the most amount of cartilage found in the body?
the hips, knees, and shoulders
_____ joints have articular cartilage at the end of bones.
Diarthrodial
Diarthrodial Joint
a freely moveable synovial joint
What is articular cartilage?
a type of connective tissue that is thin, but densely packed and relatively transparent in appearance
Articular cartilage lacks what three things?
blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic connection
What are the two primary functions of articular cartilage?
to cushion / absorb impacts at joints
reduce friction
Articular cartilage is the ____ abundant cartilage in the body.
MOST
Chondrocytes
cartilage cells
What does articular cartilage contain?
chondrocytes
matrix
collagen
Collagen provides ___ & __ in articular cartilage.
strength and structure
What are the three layers of articular cartilage from the surface downward?
Superficial Zone
Intermediate Zone
Deep Zone
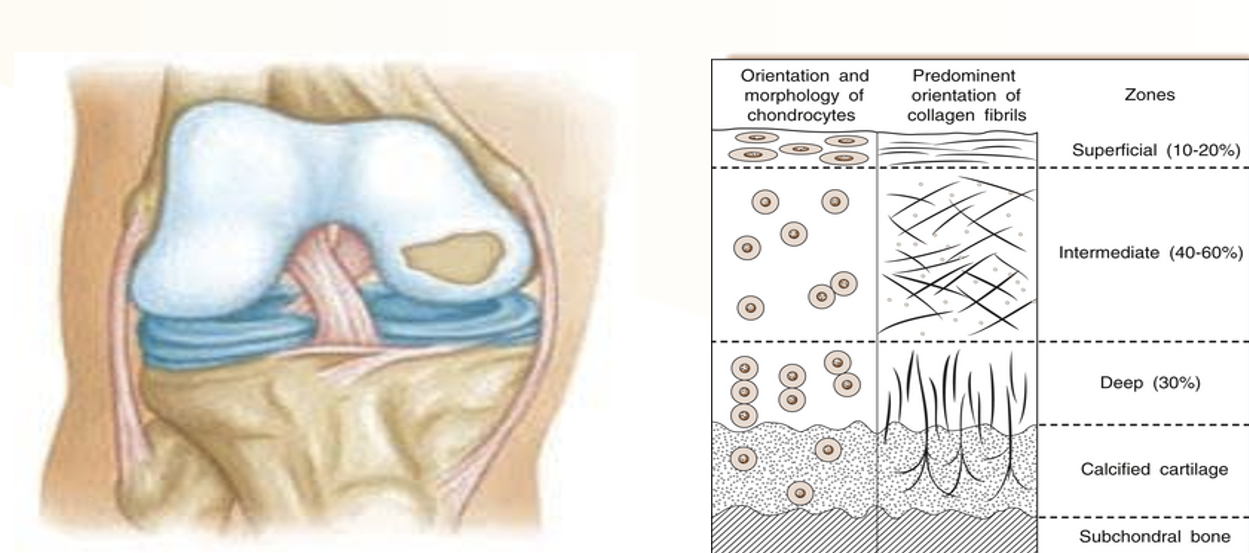
Superficial Zone
The outermost layer of articular cartilage, where chondrocytes are flattened and compact
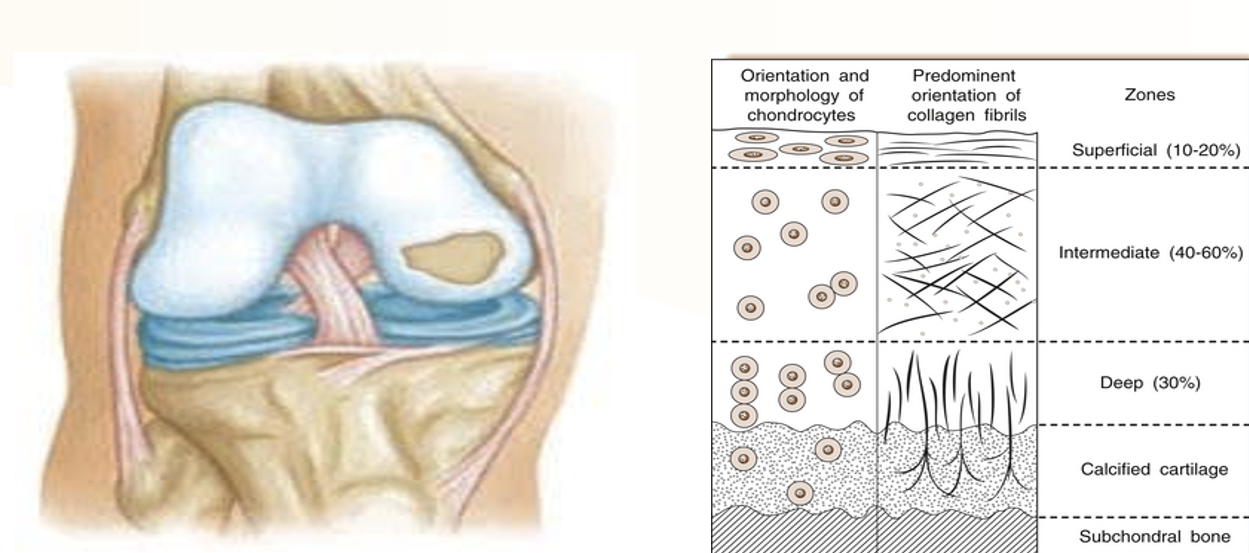
The Superficial Zone accounts for ___ percent of the thickness in articular cartilage.
10-20%
Intermediate Zone
the middle layer of articular cartilage composed of round chondrocytes that are randomly arranged and lots of matrix
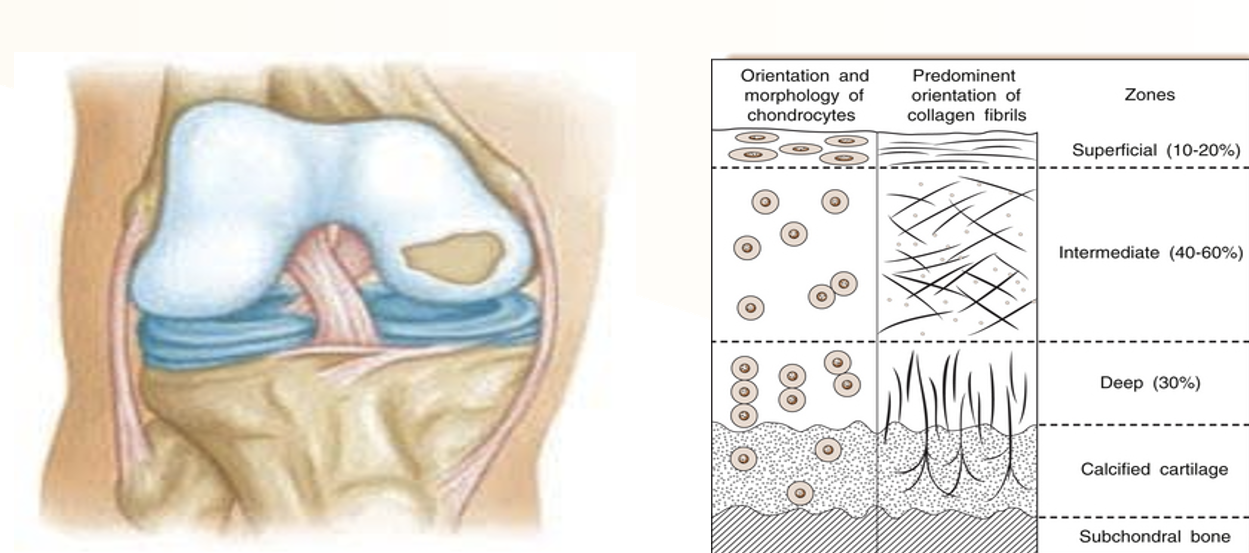
The Intermediate Zone accounts for ___ percent of the thickness in articular cartilage.
40-60%
Deep Zone
the innermost layer of articular cartilage characterized by chondrocytes arranged in columns and a dense extracellular matrix
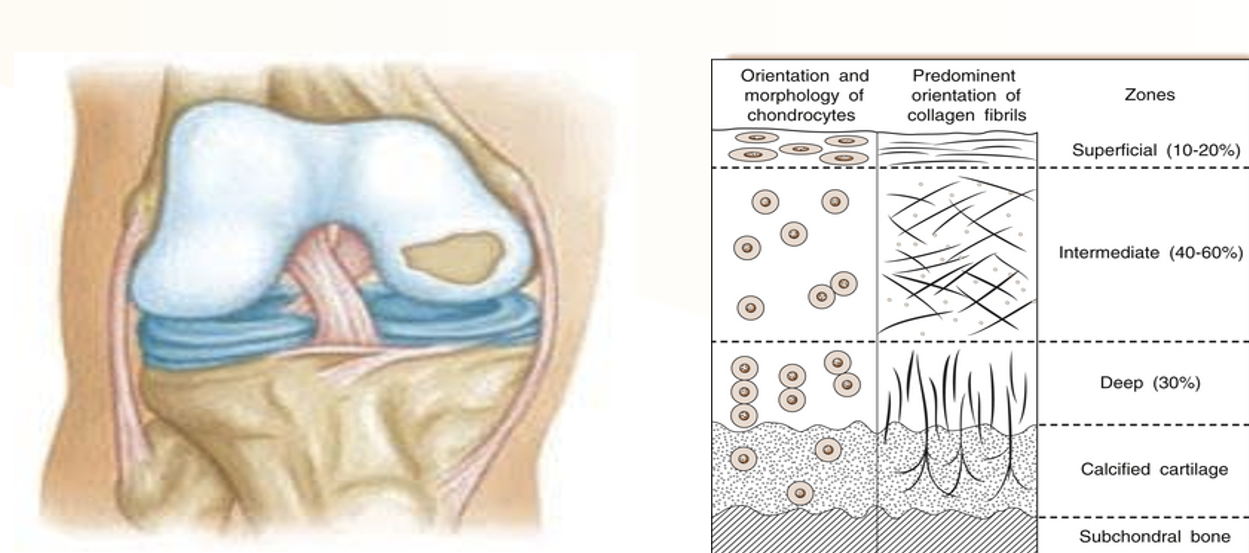
The Deep Zone accounts for ___ percent of the thickness in articular cartilage.
30%
How do the collagen fibers change from superficial to deep in articular cartilage?
they become more like bone and are organized in a more perpendicular arrangement to the surface, providing additional support and resistance to compressive forces
Articular cartilage has a high ____ content.
water
What are the important roles articular cartilage plays?
shock absorption
creates lubrication between joints
brings nutrients in and pushes waste out
How would you describe articular cartilage?
strong, yet flexible
Rank the layers of articular cartilage by water content.
Intermediate zone
Deep zone
Superficial zone
What zone has the most deformation and why?
the intermediate zone has the most deformation due to its high water content and space to move
Describe the orientation of collagen in articular cartilage.
collagen is arranged parallel to the surface in the superficial zone
collagen has a more random orientation in the intermediate zone
collagen is arranged perpendicular to the surface in the deep zone
collagen fibers tend to intersect with one another when they rise to the surface
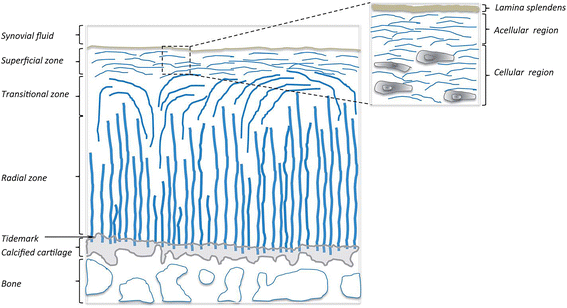
How are collagen fibers and proteoglycans oriented on a microscopic level and what is their collective function?
collagen fibers are crossed with proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid, giving articular cartilage its structural integrity.
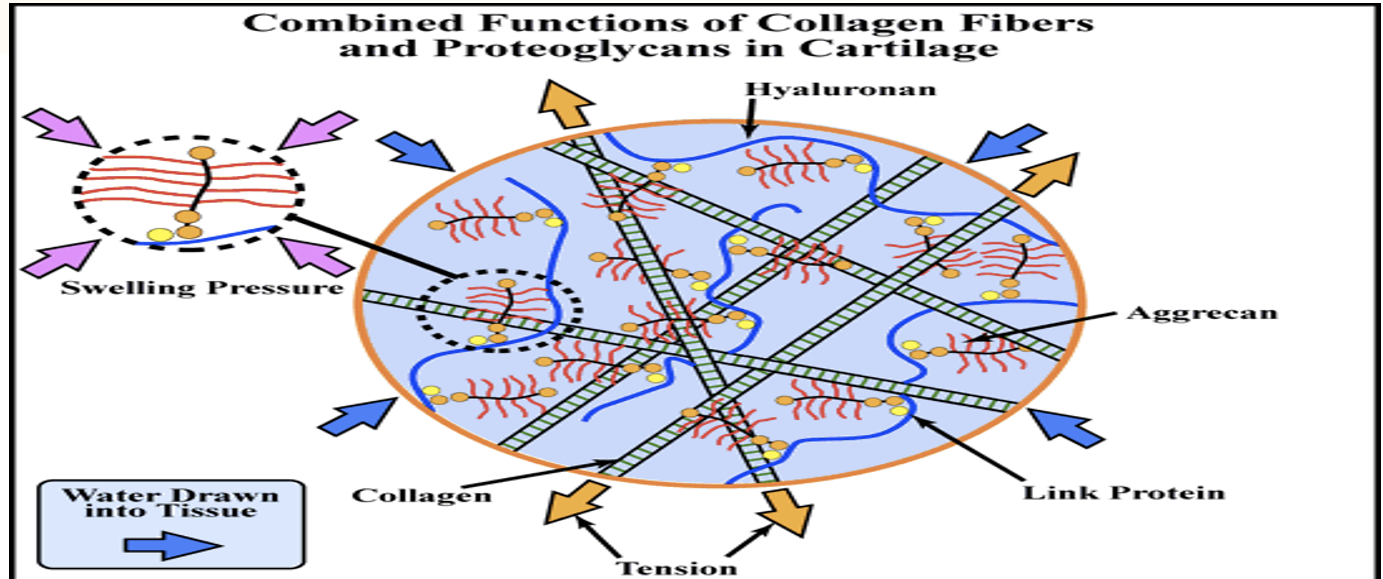
As water is drawn into articular cartilage…
nutrients comes in
articular cartilage swells and its pressure increases
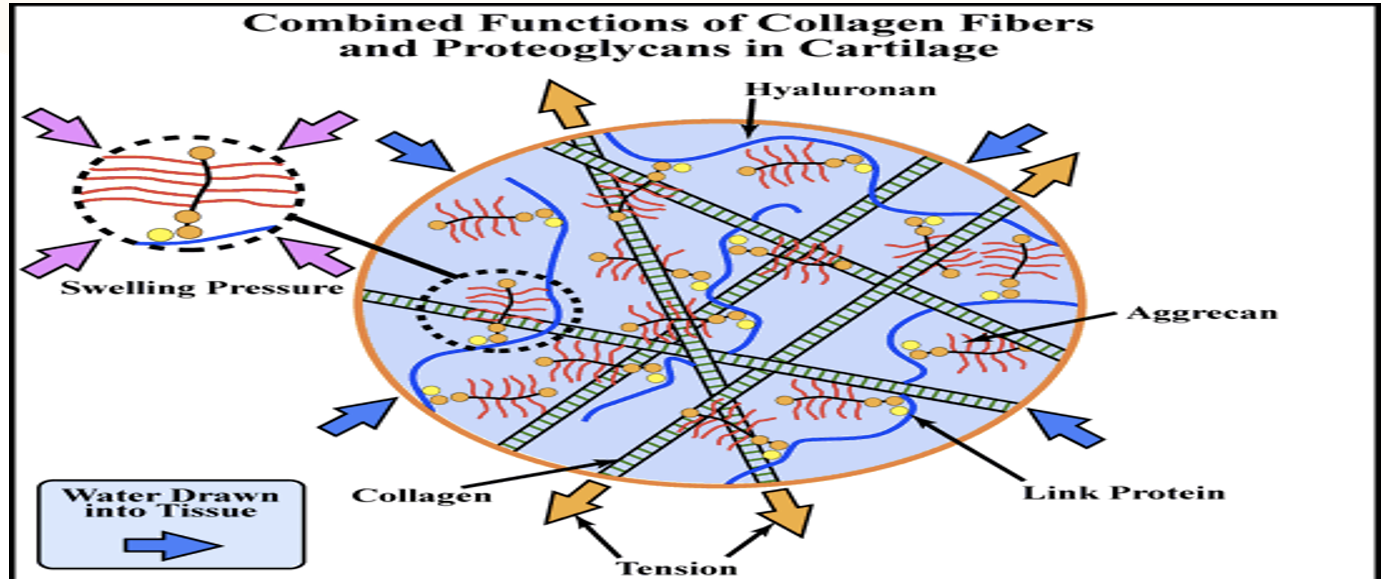
As water is drawn out of articular cartilage…
waste is pushed out
cartilage becomes compressed
volume and pressure decrease
What is essential to cartilage function?
appropriate loading of muscles and joints
What is the mechanical behavior of articular cartilage?
multiphasic response to loading: the solid matrix, water, and ions all respond to a load
compression
interstitial fluid phase: the fluid leaves the cartilage, leading to decreased volume and increased solid phase stress
porous-permeable solid phase: the solid matrix allows fluid movement under load.
How do the different layers of articular cartilage respond to a load?
the superficial layer tries to take the bite out of the initial force
the intermediate layer absorbs shock by shifting its water weight
the deep layer acts as an anchor and holds the other two layers in place so they can perform their function
When do problems arise with articular cartilage?
when compression is combined with sliding / sheering forces, which can cause cartilage to tear