Mark 4322 Final - Wallman
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
First principles of Marketing Strategy
Listen to your customer, win with strength, do your duty, change the rules, weigh the pros and cons
Strategic Transaction
Change the rules for transacting
Rooted in unexpected success
Change the way transactions are constructed
Six questions for marketing yourself:
What are my strengths?
What are my values?
How do I perform?
Where do I belong?
What do I contribute?
What relationship am I responsible for?
What are my strengths? (Example)
Feedback analysis
Duty List
What are my values? (Example)
Decision analysis model
How do I perform? (Example)
Context analysis
What relationships am I responsible for? (Example)
Trust and communication
Feedback analysis
Write down your expectations when you make a decision, compare it to the actual results.
Context analysis
Discovering how you perform, what type of environment you do well in (alone, in a group, observing others).
Value analysis
Discovering your values based on decision modeling
"pros and cons"
Drucker's Five Managerial Questions for Making a Strategy
What is my mission?
Who is my customer?
What does my customer value?
What are the results we seek?
What is my plan?
Components of a Mission Statement
Why do you do what you do?:
What is your purpose?
Who do you serve?
How do you serve them?
Components of a Mission Statement - What is your purpose?
Needs
Components of a Mission Statement - Who do you serve?
Markets
Components of a Mission Statement - How do you serve them?
Technologies
First Three Rules of Marketing Strategy
Niche
Position
Narrow
Segmentation
A group that responds homogeneously to marketing strategy variables. "Who is my customer"?
Positioning
"Why should they transact with me?"
Dimensions of strategy
Creating value, handling imitation and shaping a perimeter.
This is a complicated way of saying that every market or niche of a product has it's own "dimension" involving the value of the product, the competition, and the perimeter of the market itself.
Executives define markets using...
dimensions of strategy (essentially, a niche or market). These dimensions are often in conflict, due to competitors also creating dimensions (competition between niches/markets).
Top two criteria for positioning a dimension
1. Benefits the customer and is relative to consumer decision-making
2. Beats or differs from the competitor.
Two questions on gap analysis
1. Is the gap real?
2. Is there a demand for action?
What is gap analysis?
The difference between the current state and the desired future state. Identifies what needs to be done in a project.
Three policies for making the future:
1. Preventative Care
2. Continuous Improvement
3. Exploiting Success
Preventative Care
Continuously analyze and evaluate assets to only keep what is beneficial for future success (trim the fat).
Must abandon yesterday to free up tomorrow.
Continuous Improvement
Most dependable means for driving change.
Improvement for the customers.
Exploiting Success
Low risk -- Starve the problem, feed the success
Seven Sources of Innovation
1. Unexpected success
2. Incongruity
3. Acquire new knowledge
4. Changing moods/meaning
5. Note unexpected market changes
6. Identify process opportunities
7. Take advantage of demographics
Incongruity
When the way things are differ from the way things ought to be.
Note unexpected market changes
Exploit rapid market expansion.
Take advantage of demographics
Easiest to predict, we have lots of data.
Conditions for valid linear decision model:
Satisfaction
Attributes
Independence
Linearity
Scale
(SAILS)
Satisfaction
Is the decision maker satisfied with the decision suggested by the model?
Attributes
Can you decide without any attribute (points listed)?
Independence
Is there any "double counting"? If so, eliminate it.
Linearity
Is "more" better for a pro? Is "less" better for a con?
Scale
Do all attribute scores add up to 100 (or is there scale invariance)?
Peter Drucker Strategy
Create customers
Drucker's four ways to grow
1) Market Penetration
2) Market Development
3) Product Development
4) Diversification
Market Penetration
existing product, existing market
Market development
existing product, new market
Product development
new product, existing market
Diversification
new product, new market
Brad Gale's Strategy
Create customer value
Drucker's ways to create customers:
a. "Four ways to grow"
b. Strategies that create customers
c. Marketing - today and tomorrow
Gale's ways to create customer value:
a. Create and develop strategies that create customer value
b. Limitations - Causality - Value is hard to measure
Michael Porter's Strategy
Industrial Organization Approach
Porter's Approach to Industrial Organization
Develop and implement strategies that position the firm economically in its environment. E.g. how to reduce costs or add value.
Limitation to Porter's Approach to Industrial Organization
Top down view from industry down to the customer; therefore, not customer focused at all.
Alfred Rappaport's Strategy
Shareholder Value Approach
Rappaport's Shareholder Value Approach
Develop shareholder value
Rappaport's Develop Shareholder Value Approach Limitations
Not customer focused.
Everything is based on cash.
MPQ
Market-perceived quality
Market perceived quality
How does the market rate the quality of your goods or firm?
Which strategy does MPQ go with?
Goes with Gale's Customer Value approach that the customer is sovereign. Companies succeed when they provide superior customer value over their competitors. E.g. Chick-fil-A
PIMS model
Profit Impact of Market Strategies
Profit Impact of Market Strategies
Research that discovered a strong positive relationship between a firm's market share and product quality with its return on investment.
MPP
Market Perceived Price
Market Perceived Price
Generally accepted strategic principle.
Customer Value approach, both financial and customer data are used in evaluating performance.
Five Forces Model
1. Threat of new entrants
2. Threat of substitutes
3. Bargaining power of buyers
4. Bargaining power of suppliers
5. Current rivalry
Threat of new entrants
A measure of the degree to which barriers to entry make it easy or difficult for new companies to get started in an industry.
Threat of New Entrants examples
Undifferentiated products
Government policies not an issue
Brand not well known
Threat of Substitutes
The threat posed to a company when buyers can choose alternatives that provide the same item or service, often at attractive savings.
Threat of Substitutes Examples
Substitute is cheaper than current industry product
Substitute is better or equal in quality to existing product
Low switching costs
Bargaining power of suppliers
A measure of the influence that suppliers of parts, materials, and services to firms in an industry have on the prices of these inputs.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers Example
High supplier switching costs
Few suppliers and many buyers
Few or no substitutes
Bargaining power of buyers
The measure of the influence that customers have on a firm's prices.
Bargaining power of buyers examples
Substitutes are available or plentiful.
Buyer switching costs are low
Buyer is well-educated regarding the product
Competitive Rivalry
The ongoing set of competitive actions and competitive responses that occur among firms as they maneuver for an advantageous market position.
Competitive rivalry examples
The industry's fixed costs are high
If brand loyalty is insignificant
The products within the industry have little to no differentiation
Pmin
Minimum operating profit required to generate value for shareholders.
Shareholder value is the difference between...
after tax operating cash flow and the investment.
Triggers to sales growth
-Changes in volume
-Selling Price
-Sales mix
Sales Mix
The combination of products that make up total sales.
Selling Price
The price paid by the customer for the product.
Sales Volume
The number of items or products or services sold by a business over a period of time.
Triggers to operating profit growth
-Selling Price
-Sales mix
-Scales of economies
-Cost of efficiencies
Economy of Scale
As output increases, long-run average cost decreases.
Cost efficiency
The act of saving money by making a product or performing an activity in a better way.
How to create cash:
1. Change in cash
2. Times the operating spread
3. Times what you keep
4. On a risk-adjusted basis
Strategies to manage change
1. Use technology to advance education
2. Start the conversation about change management early in projects
3. Create and maintain a culture of embracing change
positioning map
Tool that helps marketers place products in a market by graphically illustrating consumers' perceptions of competing products within an industry.
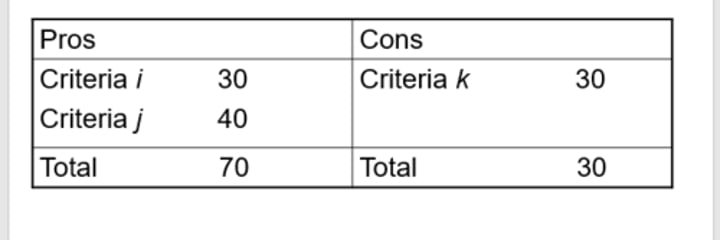
Linear Additive Decision Model Steps:
1) List the pros and cons
2) Assign weights (must add to 100)
3) Add weights
4) Compare pros and cons
5) Evaluate
How is shareholder value created using Rapapport's shareholder value model?
1. Anticipated cash flow of strategy
2. Discounted by the cost of capital
Value Leadership Model Steps and Example
-Product
-Actor A (Consumer)
-Actor A's Value Offered (i.e., $ or loyalty)
-Actor B
-Actor B's value offered (i.e., the utility of transacting with them)
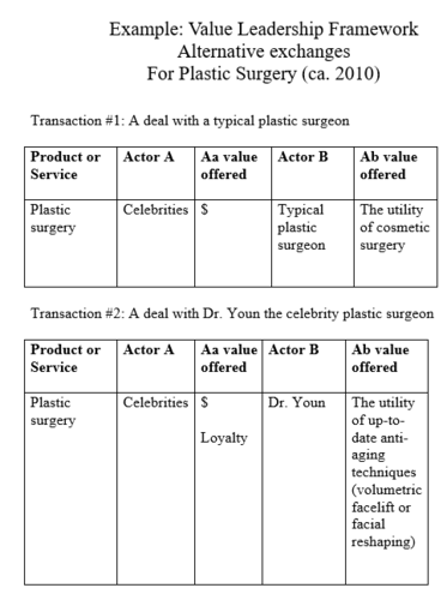
What does the first chart in the value leadership analysis show?
The typical transaction
What does the second chart in the value leadership analysis show?
The transaction innovation that changed the market (or will change the market in the future).
The key to the Eli Lily case in the lecture was...
Partnerships
Switching costs
Fixed costs buyers face when they change suppliers.
What is the Pixar film that stars a Cowboy action figure and a Spaceman action figure getting over their differences?
Toy Story
Which Pixar film stars a clown fish looking for his lost son?
Finding Nemo