E7- DIsorders of the gonads
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the function of gonads
hormone production
gomete production
Define hypogonadism
Decresed functional activity of the gonads
What are the classifications of hypogonadism
onset time
fetal, prepubertal, post pubertal
genetic alterations
congenital, acquired
HPG axis
organic, functaional
location of disruption of HPG axis
primary, secondary
What is the difference in primary and secondary hypogonadism
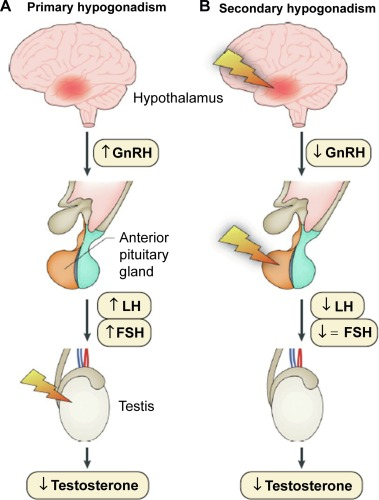
What is the difference between hypergonadotropic and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
hypergonadotropic- primary= high LH, FSH
hypogonadotropic- secondary= low LH, FSH
Define female hypogonadism
during the age range from normal puberty to normal menopause= amenorrhea
with
deficiency ovarian folliculogenesis
impaired sex hormone secreteion
anovulation
sexual or vasomotor symptoms
What are the types of amenorrhoea
primary
no cycles at age of 16
secondary
> 3 cycles lacking- if cycles were regular previously
>6 months lacking- if cycles were irregular before
What is the biochemical cause of amenorrhoea
Persistently low circulating serum 17 beta estraadiol concentration
What is it when there is amenorrhea and elevated LH/FSH
Premature ovarian insufficiency
What is it when there is amenorrhea and low/ normal LH. FSH
Central hypogonadism
What are the types of premature ovarian insufficiency
Turner syn
Autoimmune
Iatrogenic
Single gene defect
What are the types of central hypogonadism
Congenital hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
hypothalamic amenorrhea
hypopituitarism
other- opioids, diabetes, obesity
What is the diagnostic workup inn premature ovarian insufficiency
personal and family history
karyotype
FMR1 gene screening for fragile X syndrome
mental retardation, tremor/ ataxia, ovarian failure
TSH
thyroid peroxidase antibody
What are the autoimmune causes of premature ovarian insufficiency
Autoimmune oophoriti- Selective theca cell destruction
What are the iatrogenic causes of premature ovarian insufficiency
irradiation
chemotherapy
ovarian surgery
What are the single gene defect causes of premature ovarian insufficiency
FRMC gene mutation
What is turner syn
Chromosomal disorder that affects phenotypic females who have 1 intact X chromosome and complete or partial absence of the second sex chromosome in association with one or more clinical manifestations
45 X
What are the features of Turner syn
short stature
low hairline
early sensorineural hearing loss
shield shaped thorax
constriction of aorta
coarction of aorta, bicuspid aortic valve
elbow deformity
underdeveloped gonadal structures
What are the indications for chromosomal analysis in Turner syn
only clinical feature
fetal cystic hyfroma, hydrops
idiopathic short stature
obstructive left sided congenital heart defect
unexplained delayed puberty
couple with infertility
at least 2 of the following
renal anomaly- horseshoe, absence, hypoplasia
neuropsychologic problems
dysplastic or hyperconvex nails
hearing impairment
What are the most common abnormalities assiciated with Turner syn
Endocrine
growth failure
glucose intolereance
type 2 DM
hypothyroiditis
decreased bone mineral content
GI, hepatic
increased hepatic enzymes
celiac
IBD
Neurocognitive, psychosocial
emotional immaturity
specific learning disorder
psychological and behavioural problems
CV
bicuspid aortic valve
coarction of aorta
aortic dilation/ aneurysm
hypertension
What is the treatment of h=Tyrner syndrome
Growth hormone- recombinant hGH
initiation- 4-6yo, before 11-12yo
GH dose (4.0–4.5 IU/m2/day)
Hormone replacement therapy
What are the types of congenital isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Asosmic- Kallmann syn
Normosmic CHH
What is Kallmann syndrome
Problem with development and migration of GnRH neurons
low LH, FSH
What is normosmic CHH
Genes that affect synthesis and secretion of GnRH
What are the associated abnormalities of CIHH
renal agenesis
hearing loss
midline defects- cleft lip/ palate
dental and skeletal anomalies
What are the causes of hypothalamic amenorrhoea
genetic disorders- Prader Wili
functional causes- inhibited hypothalamus
structural causes
What is Prader Wili syndrome
genetic neurodevelopmental syndrome
absence of expression of paternally active genes on the long arm of chromosome 15
hypothalamic pituitary dysfunction with severe hypotonia and feeding deficits during neonatal perio
followed by an excessive weight gain period with hyperphagia + risk of severe obesity during childhood and adulthood
What is the clinical manifestation of PWS
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
behavioural issues
learning difficulties
symptoms of hyperphagia with progressive development of obesity
What is functional causes of hypothalamic amenorrhoea
Suppressed hypothalamus
surgery, brain injuries, myocardial infarctionm, stroke, sepsis
hyperprolactinemia
restricted nutritional intake
low fat mass- restricted nutritional intake exercise
What are the goals of female HRT
treatment to restore normal menstrual cycle
possible fertility
enhancement of secondary sexuality
increase bone mineral content
What is the femalr HRT
estrogen monotherapy- if there is no uterus
Estrogen/ progestin regime- if intact uterus
progestin to prevent estrogen induced endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma
Estrogen- transdermal, vaginal. oral estradiol
progestin- micronised progesterone daily for a month or medroxyprogesterone acetate daily for a month
What are the side effects of female HRT
impaired liver function tests
hypertension
DVT- pulmonary embolism
What are the absolute contraindications of female HRT
endometrial and breast carcinoma
active DVT, PE
active liver disease
What are the other causes of prolonged amenorrhoea
hyperandrogenism in female
What is hyperandrogenism in females
Medical condition characterised by high levels of androgens
PCOS, androgen secreting adrenal/ ovarian tumours
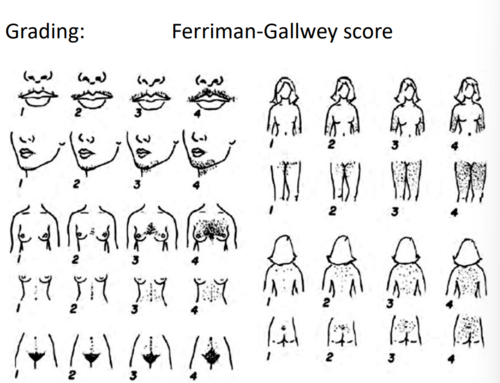
What is the grading of hyperandrogenism in females
Ferriman Gallway score
9 different areas of the body are scored for presence of hair
score of 9+ is considered diagnostic of hirsutism
Describe PCOS
most common disease in women
5-15% affected in reproductive age
most common cause of anovulation, infertility
clinical symptoms start in adolescence + seen at later stages in life
What are the components of PCOS
hyperandrogenism
irregular menstrual cycles
bilateral ovaries with enlarged, immature follicles
What is the course of PCOS

What is the pathophysiology of PCOS
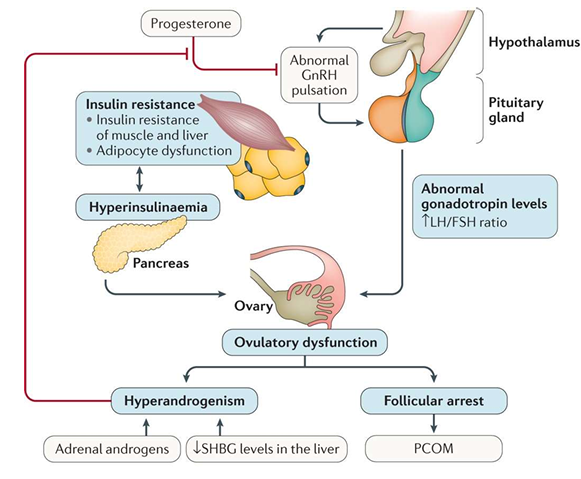
How do you diagnose PCOS
Rotterdam criteria 2/3
irregular menstrual cycles
clinical and/or biochemical hyperandrogenism → LH/ FSH ratio >2
polycistic ovaries on ultrasound
or AMH determination may be used instead of ultrasound
follicle number per ovarium, per secretion and ovarian volume
How do you use AMH to diagnose PCOS
AMH is secreted by granulosa cells of immature follicles
AMH determination can be used to confirm PCOS but only in adults
What is the treatment goals of PCOS
Amelioration of hyperandrogenic features
hirsutism, acne, scalp hair loss
management of metabolic abnormalities + reduce risk of T2DM an CV disease
prevent endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma
as a result of chronic anovulation
contraception- oligomenorrhoea ovulate intermittently and unwanted pregnancy prevention
ovulation induction for those wanted kids
What are the treatment approaches for PCOS
lifestyle changes- diet, weight reduction
androgen treatment for irregular cycles
oral contraception
metformin
low dose spironolactone
ovulation induction medication- clomiphen citrate
treatment of infertility
letrozol
gonadotropins with US monitoring
ovarian drilling
IVF
What are other potential causes of prolonged amenorrhoea
Androgen secreting adrenal/ ovarian tumours
rare
severe hyperandrogenism- virilisation
significant increase in serum T >200ng/dl
imaging- TVS, pelvic MRI
Leydig, sertoli, hilus cell tumours
usually benign
treatment- surgical removal
What are symptoms of male hypogonadism
melancholy
loss of libido
visceral adiposity
insulin resistance
osteoporosis
infertility
erectile dysfunction
loss of muscle mass
anemia
Describe the eunochoid body
lack of closure of epiphyseal plates
limbs disproportionate to trunk
gynecomastia, female pubic hair pattern
insufficient testicular and penile growth
osteoporosis, lack of masculine muscle mass
What is the classification of male hypogonadism
Primary
testicular
secondary
hypothalamic causes
pituitary causes
target organ resistance
androgen receptor resistance
5 alpha reductase deficiency
age related hypogonadism
late onset
What are the testicualr causes of male hypogonadism
Klinefelter syn
orchitis
testicular maldescent
testicular tumours
What are the hypothalamic causes of secondary male hypogonadism
congenital HH
normosmic, anosmic- Kallmann syn
constitutional delay of growth and development
What is Klinefelter syndrome
most common cause of primary hypogonadism-gonadal dysgenesis
only 25-50% of patients are diagnosed
47 XXY (XXXY, XXXXY, XXYY)
phenotype of Klinefelter is affected by androgen responsivenes
Total T and free T decrease/ FSH increased
What is the clinical presentation of Klinefelter syndrome
Neonatal- micropenis, hyopspadias or cryptorchidism
teen- delayed puberty
adults- small testes and androgen deficiency or infertility
gynecomastia, ED, osteoporosis
oligo azoospermia
very small, firm testes
What are the common morbidities of Klinefelter syn
emphysema
COPD
T2DM
risk of breast cancer
autoimmune disease
What is the treatment of Klinefelter syndrome
Lifelong T replacement
prevent osteoporosis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes
treat reduced fertility
surgical extreaction of sperm from testes
life long care- due to comorbidities
What are rare causes of testicular primary/ hypergonadootrop hypogonadism
Del Castillo syndrome/ Sertoli cell only syndrome
Noonan syndrome
Myotonic dystrophy
Kartagener syndrome
What is Del Castillo syndrome/ Sertoli cell only syndrome
microdeletions in the long arm of the Y chromosome
Testicular biopsies : germinal cell maturation arrest or Sertoli cell-only syndrome
FSH↑, LH, testosteronenormal
What is Noonan syndrome
bothgendercanbe affected
autosomaldominant, cryptorchidism, testicular hypogonadism
likeTurner systigmas( without renal disease and aortic stenosis)
Atrial septumdefect, valvular pulmonal stenosis
46XY, 6-12 chromosomeparcial deletion
What is myotonic dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal disorder with delayed onset (age 30 to 40 years) of impaired motor function
testicular hypogonadism, cataracts, premature frontal balding, mild mental retardation, and infertility
What is Kartagener syndrome
dynein defect- immobilised sperm
situs inversus, bronchial disease
What is androgen insensitivity syndrome
synonym- testicular feminisation/ androgen receptor dysfunction
genetic origin- mutations that cause impairment of androgen receptor
X linked recessive
46 XY
phenotype depends on residual androgen receptor activity
complete, partial, mild androgen insensitivity syndrome
What is the treatment of male hypogonadism
androgen substitution if patient wants children
testosterone supplementation
GnRH supplementation in HG
dopamine agonists in hyperprolactinaemia
What is the treatment for primary male hypogonadism
T replacement
ROA- depot IM injection, transdermal gel
SE- acne, oily skin, breast tenderness, HDL chol decrease, increased RBC, azoospermia
contraindication- prostate cancer, elevated liver function or liver neoplasm
What do you need to monitor during HRT in male primary hypogonadism
Testosterone levels (initially every 3 months then 6-12m)
Hematocrit levels (every 6-12 months)
Liver function tests (every 6-12 months)
PSA (annually) Abdominal (liver) ultrasound (annually)
What is the treatment of hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
androgen substitution and/or LH-FSH (to have childbearing potencial)
LH analogs: HCG treatment → Leydig cell T secretion
long-term testosterone treatment if the patient has no active intention to have children
dopamine agonists: in cases of hyperprolactinemia:
clompihen-citrate: in mild HH