Chapter 11 - Carbohydrates and Glycoproteins
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
carbohydrate
carbon based molecule high in hydroxyl groups. also known as polyhydroxyl aldehydes or ketones
carbohydrate empirical formula
(CH2O)n
monosaccharides
"simple sugar" aldehydes or ketones that contain two or more hydroxyl groups
3-7 carbons in length
have many isomers
monosaccharide nomenclature
chain length (3 C chain = trioses, 7 C chain = heptoses)
most oxidized group (if it's the keto group = molecule is a ketose)
constitutional isomers
molecules with identical molecular formulas that differ in how the atoms are ordered
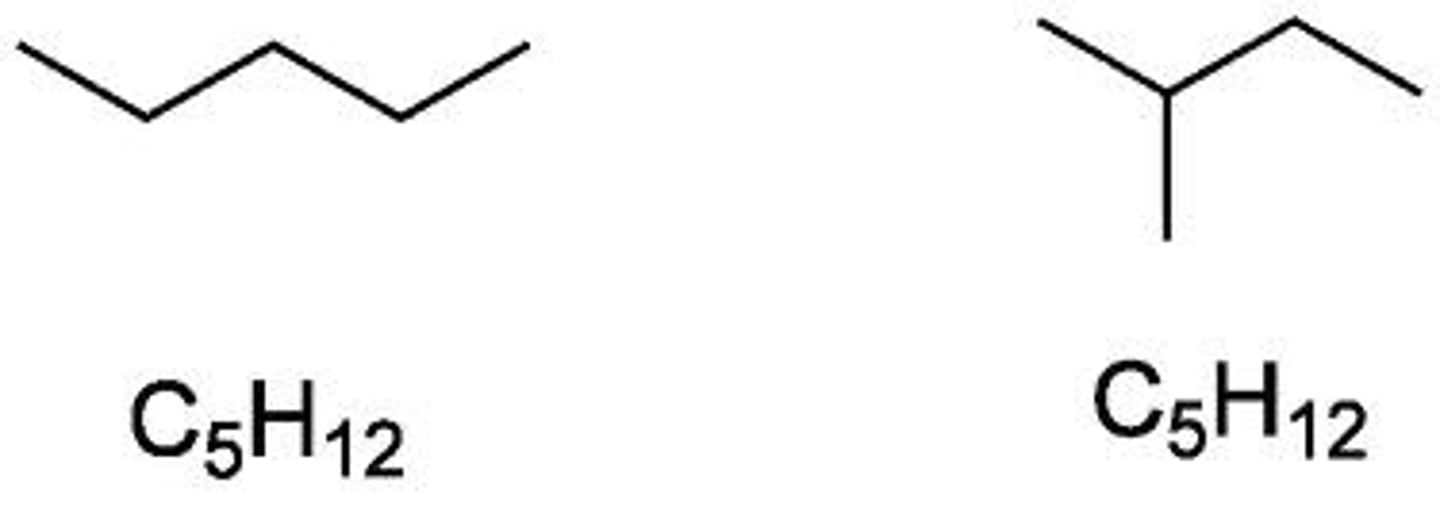
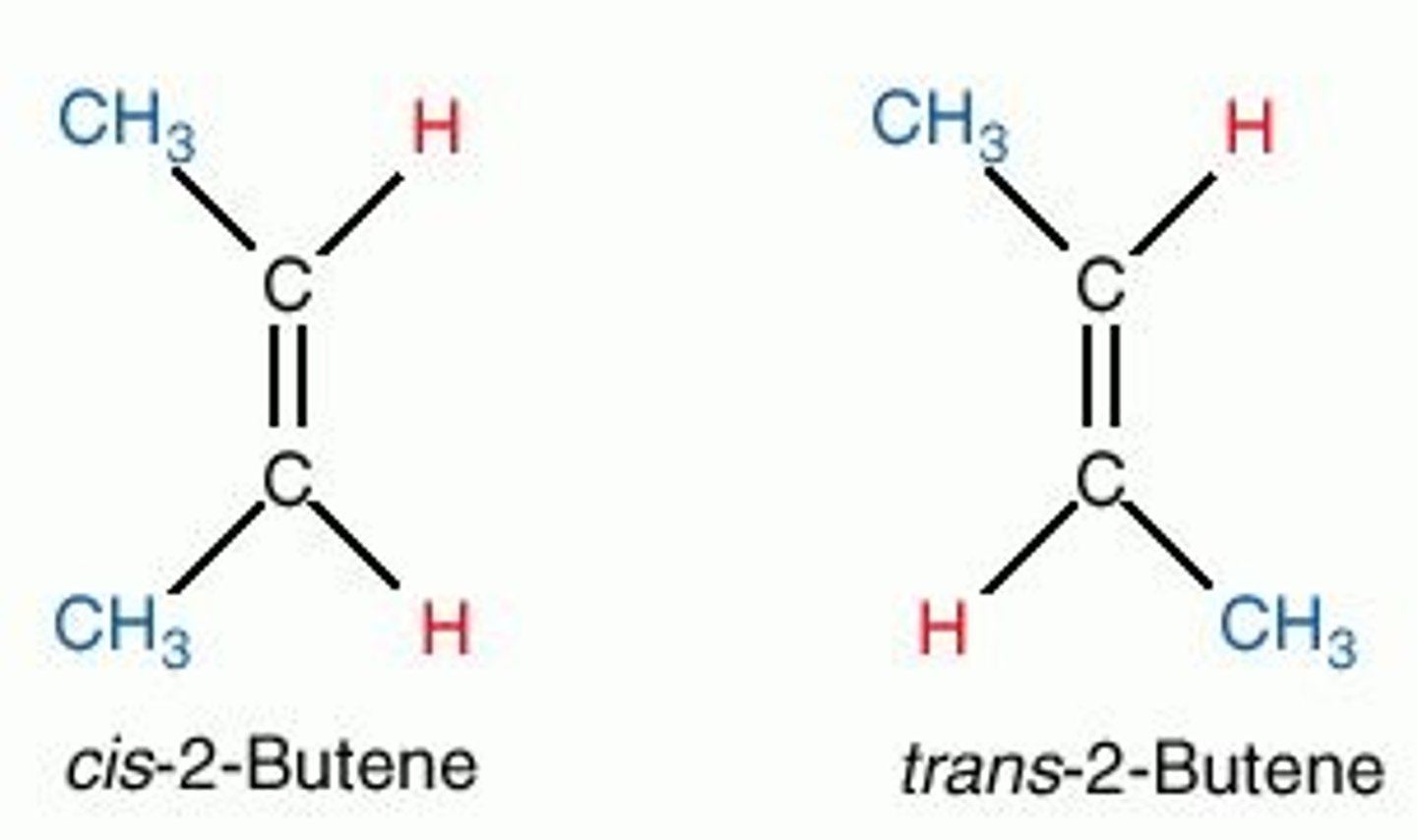
stereoisomers
molecules that differ in spatial arragement but not bonding order
- L or D
- enantiomers or diastereoisomers
determining the number of possible stereoisomers
2^n where n is the number of asymmetric carbon atoms
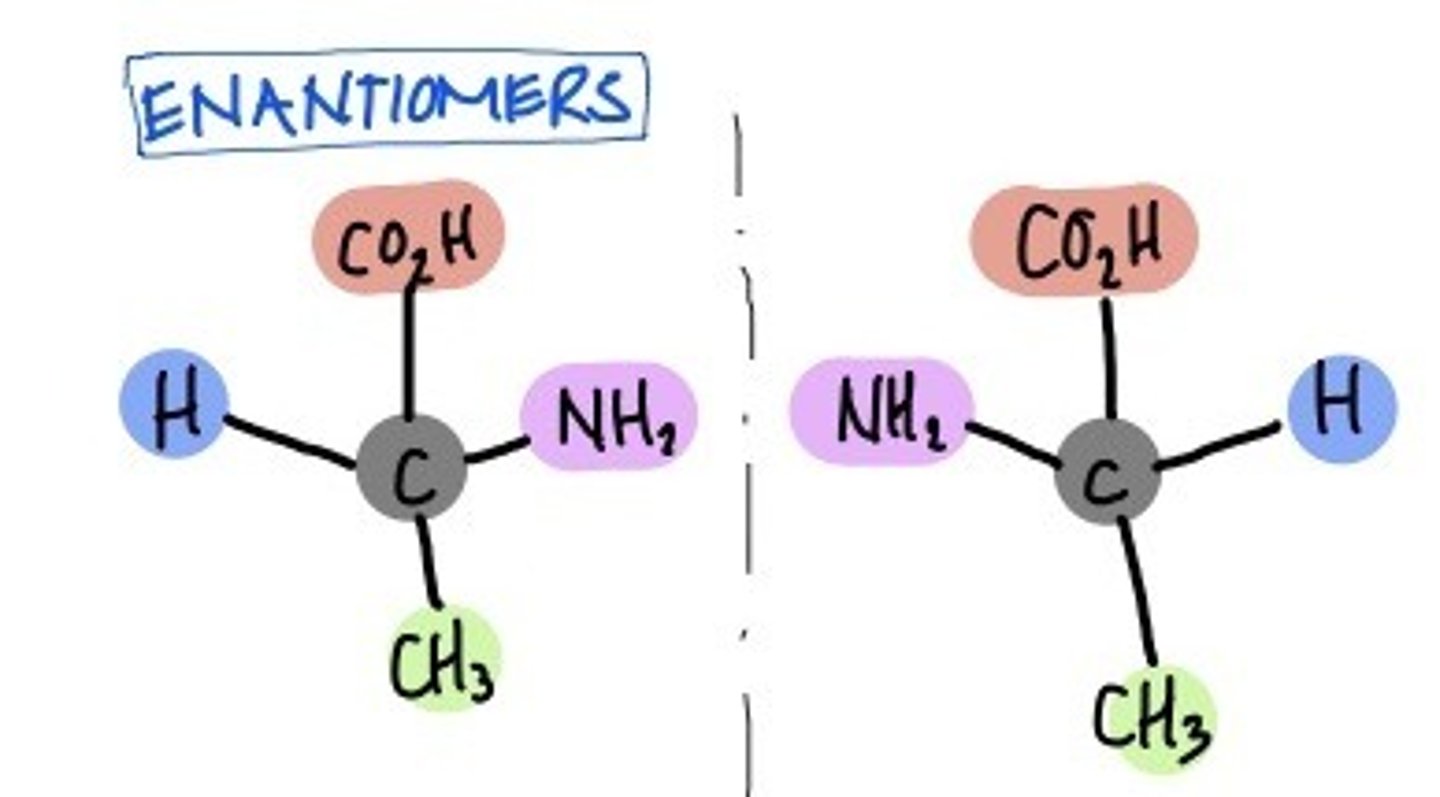
enantiomers
mirror images of each other
diastereoisomers
not mirror images of each other
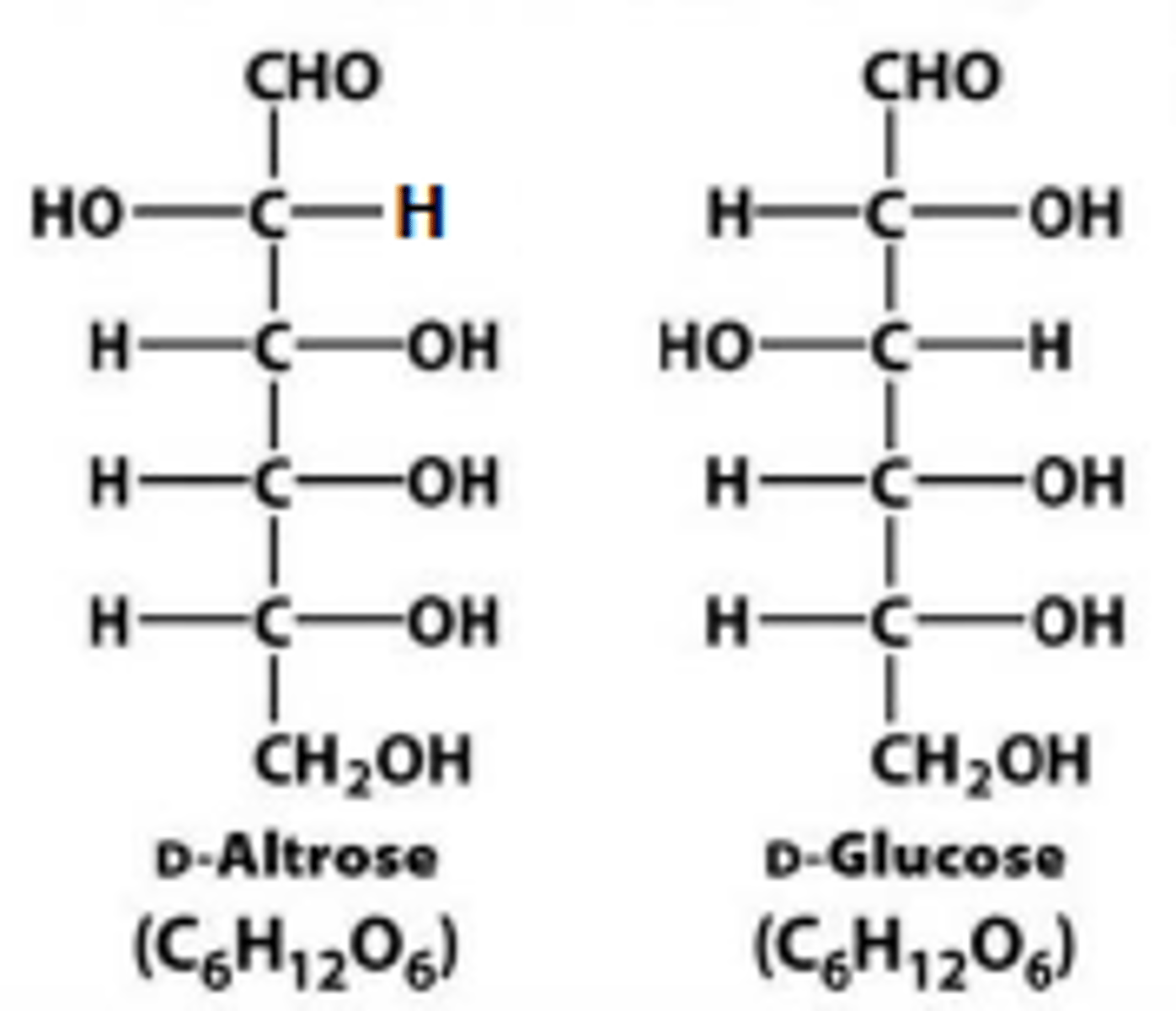
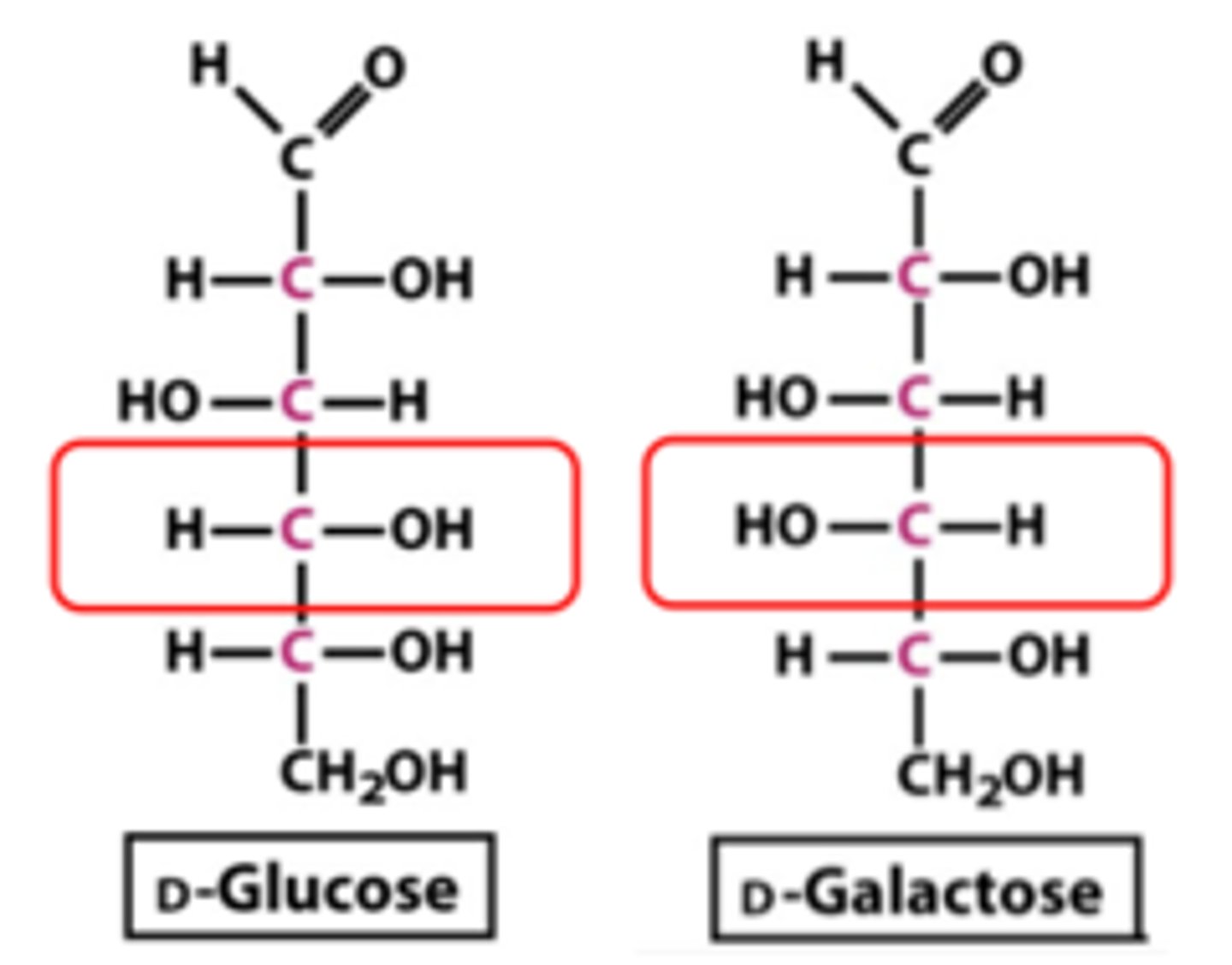
epimers
sugars that are diastereoisomers differing in configuration only at a single asymmetric center
monosaccharides in vivo
exist as interchanging cyclic forms, mostly found in cyclic forms
aldehyde + alcohol = hemiacetal
ketone + alcohol = hemiketal
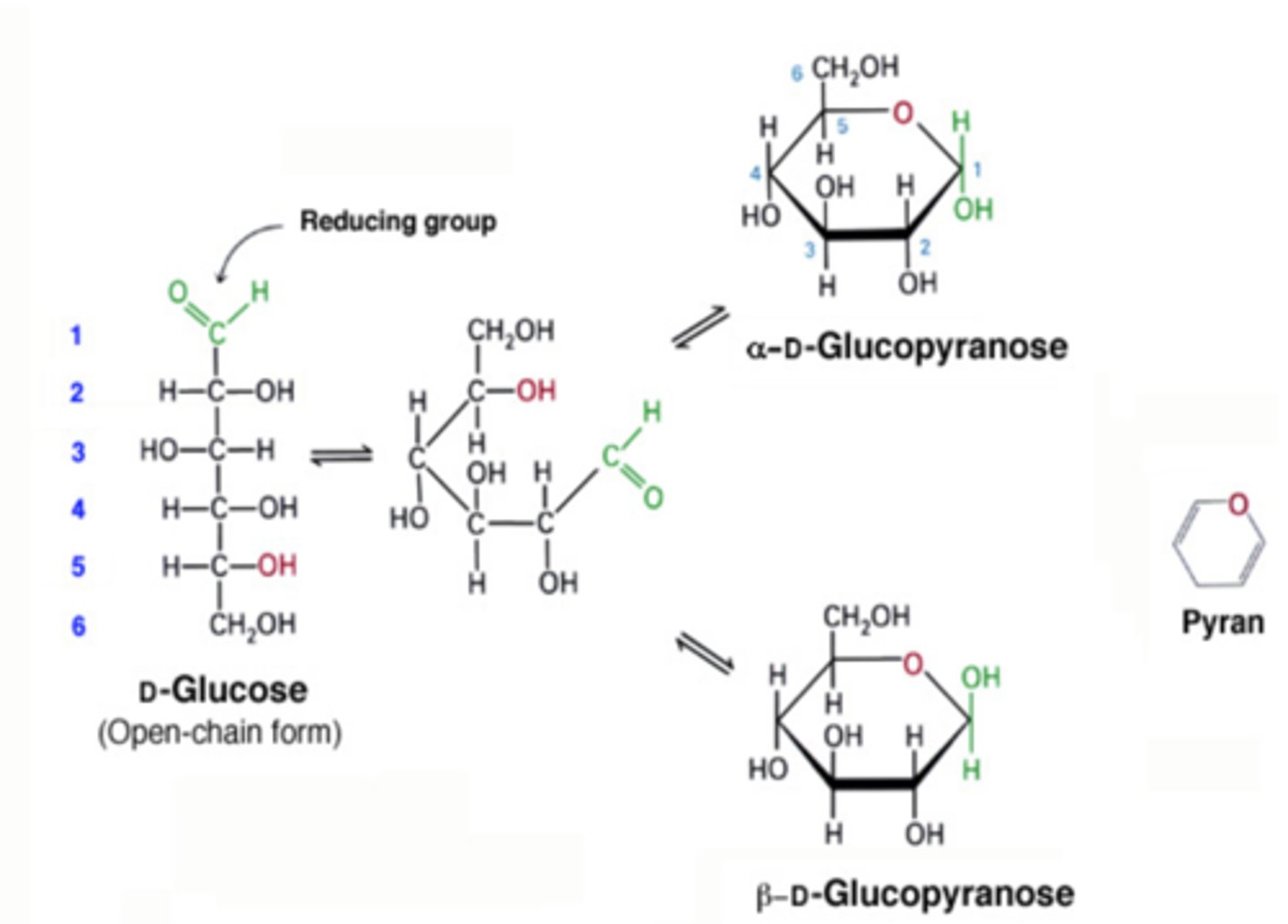
pyranose formation
when a glucose-based molecule in strand formation folds into a ring formation resembling pyran (6 carbon ring)
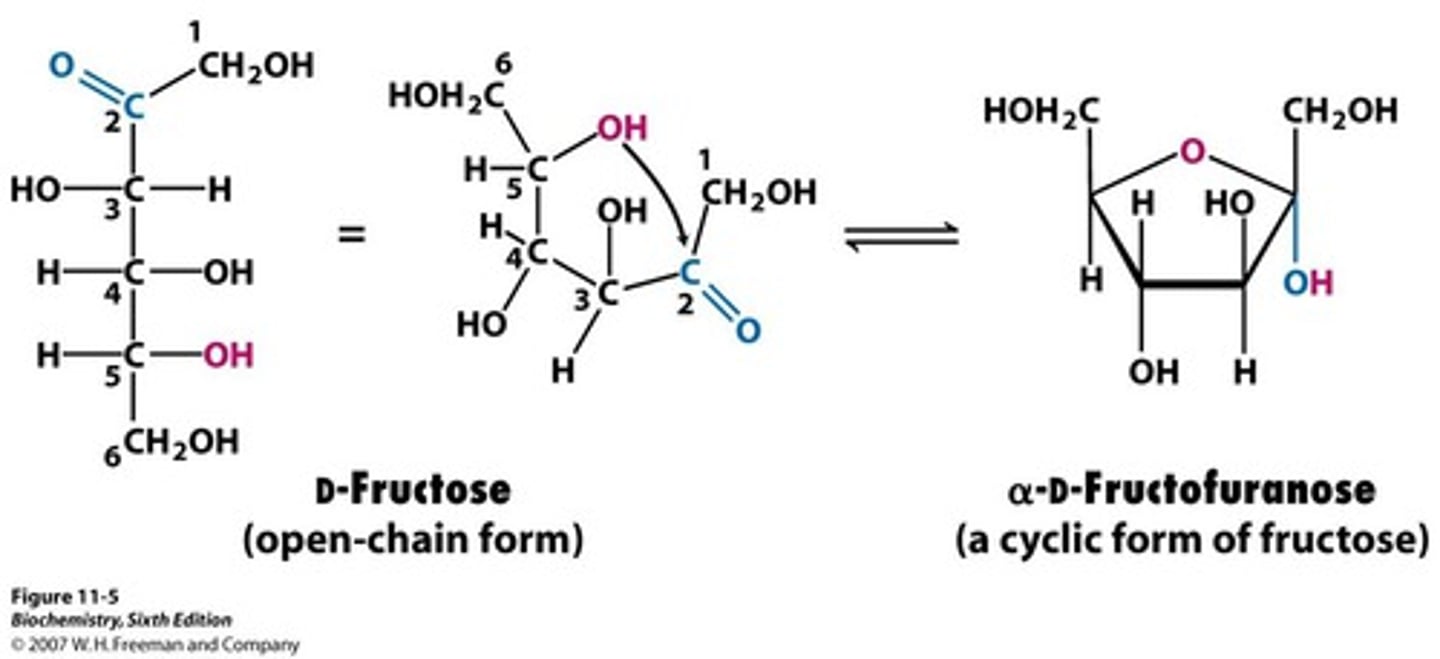
furanose formation
when a glucose-based molecule in strand formation folds into a ring formation resembling furan (5 carbon ring)
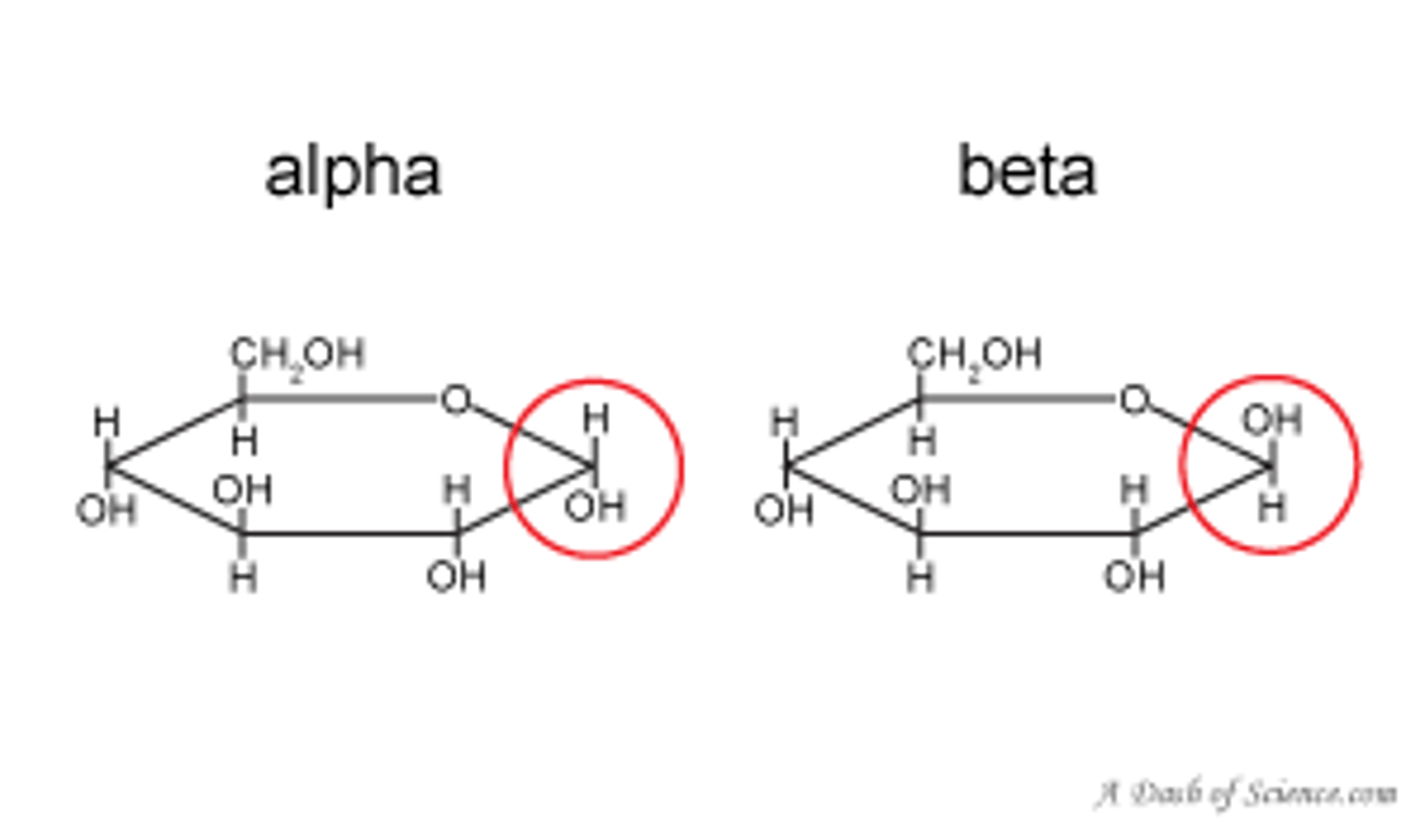
anomer
diastereoisomeric form of sugars that forms when a cyclic hemiacetal is formed and an additional asymmetric center is created upon ring closure
D-fructose anomers
C2 is the anomeric carbon
pyranose form (2 anomers) most abundant in solution
furanose form (2 anomers) most abundant in fructose derivatives
pyranose ring conformation
chair and boat confirmations
chair confirmations
substituents are either axial or equitorial. axial subs will hinder each other if on the same side of the ring
conformations of B-D-Glucose
a pyranose molecule. chair is most abundant bc hydrogens take the axial positions and boat is very sterically hindered
what is blood sugar
the D-glucose that circulates in the blood
- only fuel used by brain and RBCs in non-starving conditions
why is D-glucose an important fuel
- glucose can be formed from formaldehyde under prebiotic conditions, suggesting availability as food source for primitive biochemical systems
- glucose is relatively inert
- most stable structure is B-D-glucopyranose
glycation
nonenzymatic addition of a carbohydrate to another molecule
example of glycation
reducing sugars will nonspecifically react with free amino groups on proteins (Lys or Arg) to form a stable covalent bond
D-glucose glycation
D-glucose has a low tendency to glycate proteins unless concentrations of sugar and protein are very high for long periods of time
advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
products resulting from cross-linking following the primary modifications
implicated in aging, arteriosclerosis, diabetes, and other pathological conditions
A1C levels
D-glucose reacts with hemoglobin to form glycated hemoglobin, which is what A1C's track. eliminated when RBCs die (120 days)
<6% glycated hemoglobin = nondiabetic
~10% glycated hemoglobin = uncontrolled diabetes
modifications to monosaccharides
increase biochemical versatility by allowing monosaccharides to act as signal molecules or facilitate metabolism
need to be reacted with an alcohol, amine, or phosphate
O-glycosidic linkage
covalent linkage formed between the anomeric carbon atom of a carbohydrate and the oxygen atom of an alcohol
N-glycosidic linkage
covalent linkage formed between the anomeric carbon atom of a carbohydrate and the nitrogen atom of an amine
phosphyrylation
a common modification of sugars in metabolism reactions, phosphorylates sugars can be seen as intermediates
purpose of phosphorylating sugars
- make them anionic to prevent crossing the cell membrane and interacting with other transport proteins
- blocks the formation of alternative ring conformation
- creates reaction intermediates that more readily undergo metabolism
oligosaccharides
sugars that contain 2 or more monosaccharides linked by O-glycosidic bonds
oligosaccharide directionality
defined by their reducing and nonreducing ends
reducing end
has a free anomeric carbon atom that can form the open-chain form
nonreducing end
has an anomeric carbon in a glycosidic linkage that cannot convert to the open-chain form
a-1,4-glycosidic linkage
glycosidic linkage between the a-anomeric form of C-1 on one sugar and the hydroxyl oxygen atom on the C-4 of the adjacent sugar
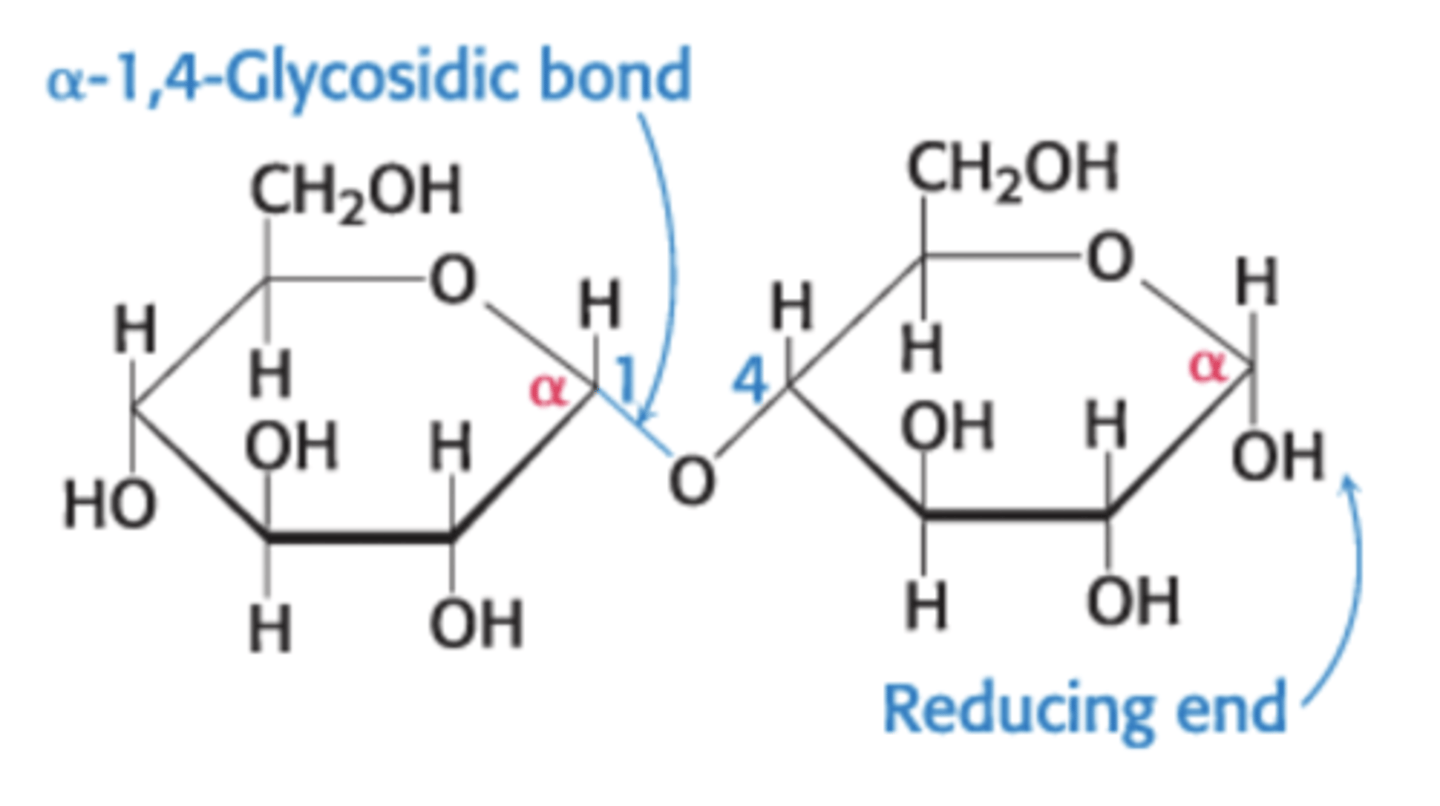
disaccharide
two sugars joined by an O-glycosidic linkage
role of disaccharides
cleavage products can be processed to provide ATP energy
common disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
sucrose
disaccharide of sugar cane or sugar beets consisting of glucose linked to fructose at anomeric carbons
- alpha glucose and beta fructose
- not a reducing sugar
- cleaved by sucrase
lactose
disaccharide of milk consisting of a glucose linked to a galactose at anomeric carbons via B-1,4-glycosidic linkage
- can be hydrolyzed via lactase or B-galactosidase (in bacteria)
- lack of lactase = lactose intolerance
maltose
beer
disaccharide resulting from hydrolysis of large oligosaccharides, consisting of two linked glucose molecules via a-1,4-glycosidic linkage
- hydrolyzed via maltase
human milk
>150 oligosaccharides in human milk protect newborn infants from infection bc they can't digest it
oligosaccharides serve as a fuel source for beneficial bacteria and prevent attachment of microbial pathogens to newborn's intestinal wall
storage of glucose
free glucose cannot be stored bc high concentrations will disturb the cell's osmatic balance. instead they have to be converted to glycogen and starch (polysaccharides)
polysaccharides (glycans and startch)
large polymeric oligosaccharides formed by the linkage of multiple monosaccharides. helps with energy storage and structural integrity
homopolymer
polymer in which all the monosaccharide units are the same
glycogen
large, branched homopolymer of glucose residues.
- most common homopolymer in animals
- storage form of glucose
- linked and branched via a-1,4-glycosidic linkage
- hydrolyzed via a-amylase
glycogen branching
increases SA to allow better access for enymes to rapidly breakdown glycogen
startch
homopolymer that serves as the nutritional resevoir in plants, hydrolyzed by a-amylase
two forms: amylose and amylopectin
amylose
unbranched (!) type of starch composed of glucose residues in a a-1,4-glycosidic linkage
amylopectin
branched (!) type of starch with ~1 a-1,6-linkage per 30 a-1,4-linkages
cellulose
unbranched polymer of glucose residues joined by B-1,4 linked
structural support, not nutritional
cellulose configuration benefits
the beta config allows cellulose to form long, straight chains that interact with one another through H bonding to yield a rigid, supportive structure
a linkages of glycogen and starch
form compact hollow cylinders suitable for accessible storage
can we digest cellulose
nope bc we don't have cellulase
insoluble fibers
increase the rate of absorption of digestion products and the speed at which products pass through the large intestine. bulks and soften stools
soluble fibers
slow the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract and facilitates absoprtion of nutrients from the diet
chitin
homopolymer of B-1,4 linked N-acetylglucosamine
- found in fungal cell walls and arthropod exoskeletons
- crosslinked fibers composited with minerals and proteins to increase strength
uses of chitin
- carrier to assist drug delivery
- component of cosmetic and food products
- surgical dressing
glycoprotein
a carbohydrate group covalently attached to a protein
they make up 50% of the human proteome
important for cell adhesion
glycosylation
enzymatically adding sugar groups onto proteins. increases the complexity of the human proteome
proteoglycans
a carbohydrate with a protein component attached to it via glycosaminoglycan
important for structure and joint lubrication
mucins (mucoproteins)
central carbohydrate molecule with protein compotents that are heavily glycosylated by N-acetylgalactosamien at Ser and Thr residues
- mucus and lubricants
N-linkage of glycoproteins
links the sugars in glycoproteins to the amide nitrogen atom in the side chain of Asn
specific form of Asn needed for N-linkage
must be a part of an Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr sequences, where X is any residue EXCEPT Pro
O-linkage of glycoproteins
links the sugars in glycoproteins to the oxygen atom in the side chain of Ser or Thr
erythopoietin (EPO)
a glycoprotein secreted by the kidneys into the blood serum to stimulate production of RBCs
EPO fun facts
- cloned recombinant has helped anemia, but has also been abused by athletes
- glycosylation enhances the stability of the protein in blood
oligosaccharides on EPO
N-glycosylated at three Asn residues
O-glycosylated at a Ser residue
40% carbohydrate by weight
GlcNAcylation
the post translational, covalent attachment of a single N-acetylglucosamine to Ser or Thr residues
- reversible
- occurs when nutrients are abundant
- catalyzed via O-GlcNAc transferase
O-GlcNAc transferase
its GlcNAcylation sites are potential phosphorylation sites. could be involved in cross talk with protein kinases
improper regulation of O-GlcNAc transferase
insulin resistance
diabetes
cancer
neurological pathologies
proteoglycan composition
up to 95% glycosaminoglycans by weight, resembling polysaccharides more than proteins
glycosaminoglycans
long, unbranched polysaccharides composed of repeating units of disaccharides containing a derivative of an amino sugar
glycosaminoglycans sugars
the sugar derivative is either glucosamine or galactosamine
at least one of two sugars has a negative carboxylate or sulfate group
proteoglycan functions
- lubricants and structure in connective tissue
- mediate cell adhesion to ECM
- bind factors that regulate cell proliferation
inability to degrade glycosaminoglycans
causes diseases marked by skeletal deformities and reduced life expectancies
cartilage
contains the protein collagen and the proteoglycan aggrecan
aggrecan
large molecule with three globular domains
- glycosaminoglycans attach between G2 and G3
- G1 noncovalently binds to a central polymer of hyaluronate
water cushioning
water bound to glycosaminoglycans cushions compressive forces by being squeezed out when under pressure and rebinding when pressure is released
osteoarthritis
form of arthritis that results when water is lost from proteoglycan with aging
tandem repeats (VNTR) region
region of the protein backbone of mucins that is rich in O-glycosylated Ser and Thr residues
mucin functions
- adheres to epithelial cells and acts as a protective barrier
- hydrates the underlying cells
- plays a role in fertilization, immune response, and cell adhesion
overexpression of mucin
occurs in bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, and adenocarcinomas
ER and Golgi Complex
organelles that play central roles in protein trafficking
protein glycosylation location
N-linked glycosylation beings in the ER and continues in the Golgi
O-linked glycosylation occurs only in the Golgi
golgi complex
a stack of flattened membranous sacs. sends proteins to either lysosomes, secretory granules, or the plasma membrane, based on signals within their amino acid sequences and 3d structures
glycosyltransferases
catalyzes the formation of glycosidic linkages. most common carbohydrate donor is activated sugar nucleotides
blood groups
based on protein glycosylation pattterns (A, B, or O),
- all have a core O antigen
- A/B have one extra monosaccharide through an a-1,3 linkage to a galactose moiety of the O antigen
A antigen
type A transferase adds N-acetylgalactosamine to form the A antigen
B antigen
type B transferase adds galactose to form the B antigen
blood by enzymes present
O blood lacks both enzymes
AB has both
A has type A transferase
B has type B transferase
lysosomes
organelles that degrade and recycle cellular components or endocytosed material
i-cell disease
a lysosomal storage disease that causes severe psychomotor impairment and skeletal deformities.
- affected lysosomes contain undigested glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids
- active enzymes responsible for degredation are synthesizes but they lack appropriate glycosylation and are exported instead of delivered to lysosomes
biochemistry of i-cell disease
normally a mannose 6-phospahte residue of N-oligosaccharide will direct enzymes from golgi to lysosome, but in i-cell the mannose is missing a phosphate due to a deficiency of N-acetylglucosamine phosphotransferase
glycan-binding proteins
bind to specific carbohydrate structures on neighboring cell surfaces
lectins
class of glycan-binding proteins
ex. the mannose 6-phosphate receptor that binds and directs lysosomal enzymes to lysosomes
lectin functions
- facilitate cell to cell contact
- usually contain 2+ carbohydrate binding sites
- linked to carbohydrates by a number of weak noncovalent interactions
C-type lections
calcium requiring, found in animals
function in receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell-cell recognition
L-type lectins
rich in the seeds of legumes
serve as toxins for herbivores and acts as chaperones in the eukaryotic ER
C-type lection biochemistry
Ca2+ acts as a bridge between lectin and sugar, bound by two Glu residues. H bonds both between lectin side chains and carbohydrate