m.12 Lipid Modifying Drugs *
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
statin
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What three things does a blood lipid panel test for
total cholesterol, LDL, and HDL
lovastatin is the ________ name
what is the other name
generic name of lovastatin name
mevacor trade name
generic name pravastatin brand name
pravachol
brand name zocor whats generic
generic name simvastatin
lipitor id brand what is generic
atorvastatin is generic
rosuvastatin is generic what is brand name
crestor
what three impacts do lipid modifying drugs have
lipid levels in the bloodstream, primarily to reduce cardiovascular risk.
reduce ldl
increase hdl levels
manage triglycerides.
HDL stands for what and is known for what
High Density Lipoprotein, known as 'good cholesterol' that helps remove cholesterol from the blood.
LDL stands for what and is known as what
Low Density Lipoprotein, known as 'bad cholesterol', which can build up in arteries.
what is the ideal LDL levels in blood lipid panels
<100 mg/dL
What is borderline to too high LDL in blood lipid panels
130-159, 160-»190 mg/dL
What is ideal HDL levels in blood lipid panel
>60 mg/dL
what are borderline and too low levels of HDL
borderline 40(w)-59 mg/dL
too low
<40men mg/dL
<50 women mg/dL
What are the ideal levels of triglycerides
<150 mg/dL
What are the border to too high levels of triglycerides
borderline high 150-199 mg/dL,
high 200-499 mg/dL,
above that is considered V high 500+
What is protein is considered an early indicator for atherogenesis and is a marker of systemic inflammation and elevated in response to inflammatory process that occur in blood vessels during early stages of atherosclerosis
CRP
C reactive proteinis a substance produced by the liver in response to inflammation, and its levels can indicate an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases.
what is the function of HDL
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) helps transport cholesterol from the arteries to the liver for excretion or re-utilization,
reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
What is the first line of drug for reducing LDL
Statins, which lower LDL cholesterol levels and help reduce cardiovascular risk.
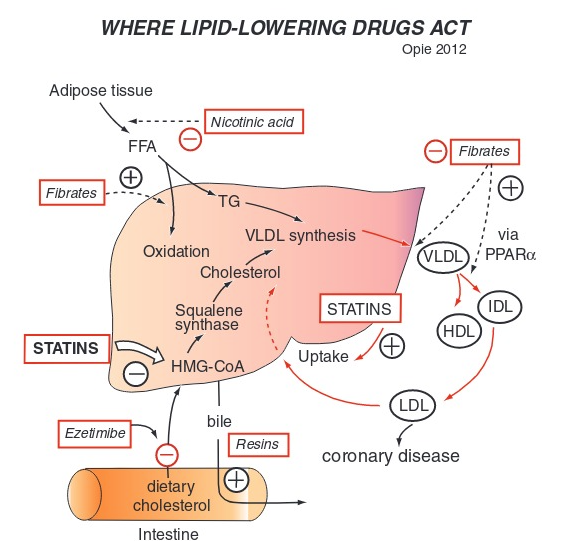
What is the mechanism of statins
inhibit HMG-CoA reductase which is an enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis in the liver
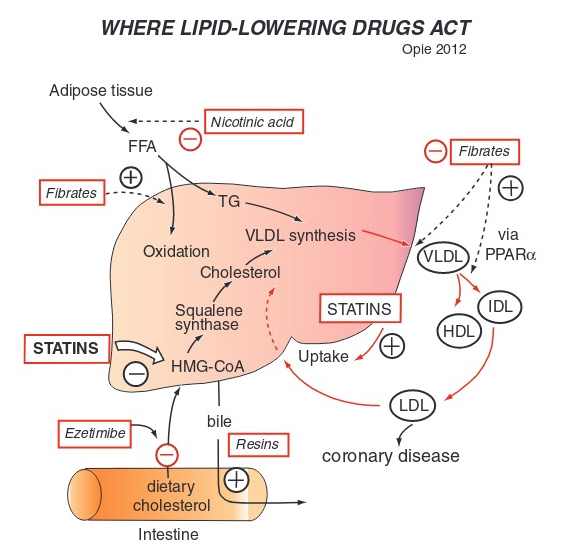
the two effect of statins
decreased cholesterol production HMG CoA reductase
increased LDL receptor expression on hepatocytes enhancing LDL clearance from the blood
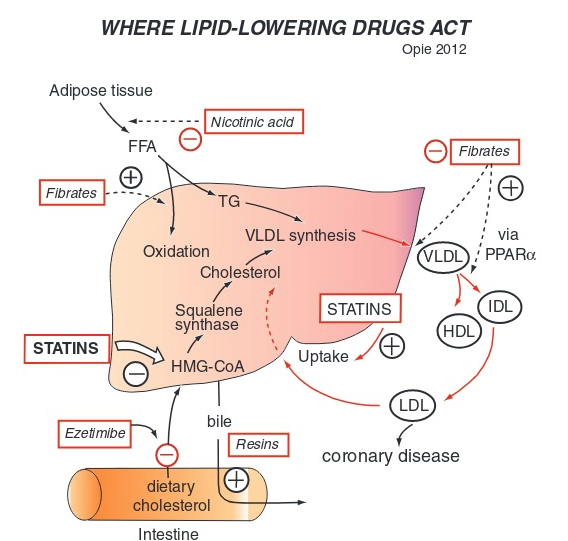
What do statin medications end in
statinsuffixes such as -statin, like atorvastatin or simvastatin.
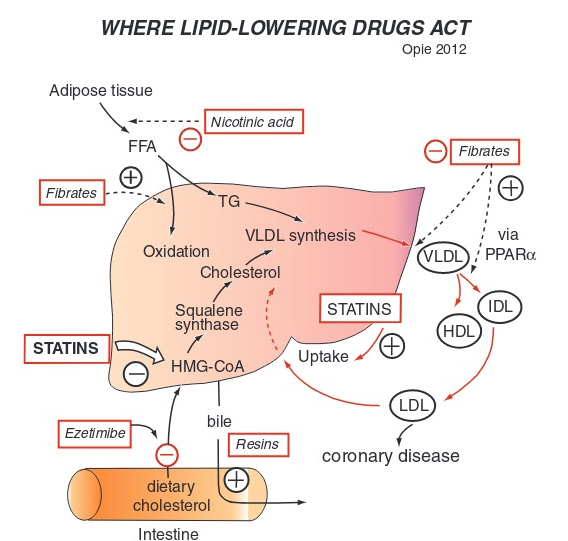
What LDL level indicates need for statin
LDL >130 m/dl is generally needed for statin therapy
What do Fibrates do
Reduces LDL by increasing HDL
What is an example of a fibrates 3 options
Lopid
Bezafibrate
Tricor
What do Resins do
Bind bile acids to lower cholesterol levels by promoting bile secretion into the intestine
Bile acid seuestrants are also known as
Resins
What is the function of Niacin 3 things
Decreases mobalization of free fatty acids from adipose tissue which lead to a
reduction in both LDL and triglycerides while
increasing HDL cholesterol levels.
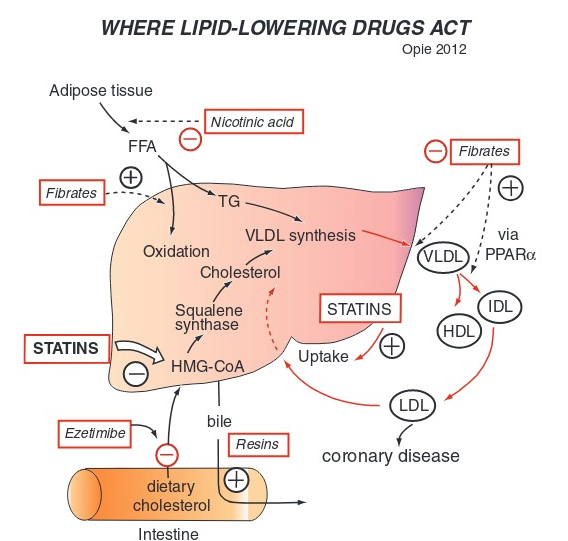
What was the first statin developed and introduced to the market
Lovastatin (mevacor)
Name an example of Resins or bile acid sequestrants 3 total 8
Welcohol
Questran
Colestid
name an example of a niacin
Niaspanis an extended-release form of niacin used to improve cholesterol levels.
Atherogenesis is the process fatty plaques develop leading to what?
Atherosclerosis and smooth muscle activation
Smooth muscle activation in the context of atherogenesis refers to the process in which smooth muscle cells (SMCs), which are normally present in the walls of blood vessels, are activated and migrate into the inner layers of the blood vessel (the intima)
what is atherogenesis
the development of fatty plaques in the arteries, contributing to atherosclerosis.
What are the 5 actions of atherogenisis (5 key point summaries)
Endothelial damage - oxidative stress, nicot, inflammation
LDL penetration and oxidation-accross endothelial cell layer
immune cell recruitment- ldl signal. neutrophils adhere to E.C. layer. then VACM(attaches margophages)
formation of foam cells- both end up across but macrophg turn in to foam cells.
smooth muscle cell activation-smooth muscle proliferation and migration, leading to plaque formation.
Just read this
Endothelial damage caused by oxidative stress, nicotine, and inflammation triggers the process of atherogenesis. This damage allows LDL to penetrate the endothelium and become oxidized (oxLDL), signaling immune cells like neutrophils and monocytes to adhere to the endothelial surface. VCAM-1 facilitates the binding and migration of monocytes into the intima, where they differentiate into macrophages. The macrophages engulf oxLDL, becoming foam cells. These foam cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines and ROS, perpetuating damage and creating a chronic inflammatory cycle. Over time, smooth muscle cells are activated, leading to plaque growth and potential complications like rupture.
A type of fat found in the blood, used for energy but high levels can increase heart disease risk.
Triglycerides
Total Cholesterol Level
The overall amount of cholesterol in the blood, composed of both LDL and HDL.
Ideal Cholesterol Level
Borderline Cholesterol Level
Total cholesterol 200-239 mg/dL, LDL 130-159 mg/dL.
High Cholesterol Level
Total cholesterol >240 mg/dL, LDL 160-189 mg/dL.
Very High Cholesterol Level
Total cholesterol >500 mg/dL, LDL >190 mg/dL.
A type of immune cell that can ingest LDL and become foam cells.
Macrophage
Macrophages filled with oxidized LDL, contributing to plaque buildup.
Foam Cells
LDL that has undergone oxidation, increasing its atherogenic potential.
Oxidized LDL
a marker of inflammation in the body. C*****
CRP
A1C Test is A ********
A test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
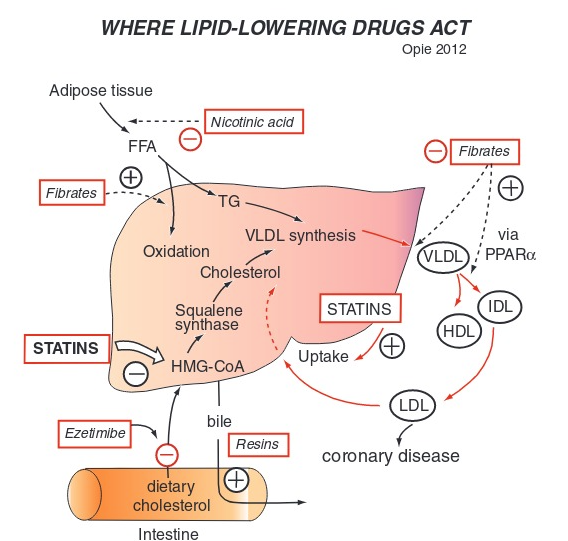
Statins affect what 2 proteins that result in what
Lower LDL
Increased HDL
reducing vascular inflammation and lowering risk of heart attacks
A statin drug used for lowering cholesterol, sold under the brand Mevacor.
Lovastatin
A statin that helps manage cholesterol; marketed as Pravachol.
Pravastatin
A statin medication, known commercially as Zocor.
Simvastatin
A highly prescribed statin, sold as Lipitor@
Atorvastatin
Drugs that bind bile acids to reduce cholesterol levels.
Bile Acid Sequestrants
A class of drugs that increase HDL and lower LDL levels.
Fibrates
The absorption of low-density lipoprotein by cells.
LDL Uptake
A protein that initiates blood coagulation and influences atherogenesis.
Tissue Factor
Platelet Activation
The process that leads to clotting in damaged blood vessels.
The process of breaking down fibrin in blood clots.
Fibrinolysis
What statin is safest for HIV patients
Pitavastatinis considered the safest statin for HIV patients due to its minimal drug interactions.
Contraindications for Statins
name1
Conditions under which statins should not be used, like liver disease.