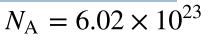heat and wave
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
acoustic impedance
property of medium that makes the propagation of sound waves more difficult
antinode
point of maximum displacement
bow wake
V-shaped disturbance created when the wave source moves faster than the wave propagation speed
Doppler effect
an alteration in the observed frequency of a sound due to motion of either the source or the observer
Doppler shift
the actual change in frequency due to relative motion of source and observer
Doppler-shifted ultrasound
a medical technique to detect motion and determine velocity through the Doppler shift of an echo
fundamental
the lowest-frequency resonance
harmonics
the term used to refer collectively to the fundamental and its overtones
hearing
the perception of sound
infrasound
sounds below 20 Hz
intensity
the power per unit area carried by a wave
intensity reflection coefficient
a measure of the ratio of the intensity of the wave reflected off a boundary between two media relative to the intensity of the incident wave
loudness
the perception of sound intensity
node
point of zero displacement
note
basic unit of music with specific names, combined to generate tunes
overtones
all resonant frequencies higher than the fundamental
phon
the numerical unit of loudness
pitch
the perception of the frequency of a sound
sonic boom
a constructive interference of sound created by an object moving faster than sound
sound
a disturbance of matter that is transmitted from its source outward
sound intensity level
a unitless quantity telling you the level of the sound relative to a fixed standard
sound pressure level
the ratio of the pressure amplitude to a reference pressure
timbre/tone
number and relative intensity of multiple sound frequencies
ultrasound
sounds above 20,000 Hz
amplitude
the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position of an object oscillating around the equilibrium position
antinode
the location of maximum amplitude in standing waves
beat frequency
the frequency of the amplitude fluctuations of a wave
constructive interference
when two waves arrive at the same point exactly in phase; that is, the crests of the two waves are precisely aligned, as are the troughs
critical damping
the condition in which the damping of an oscillator causes it to return as quickly as possible to its equilibrium position without oscillating back and forth about this position
deformation
displacement from equilibrium
destructive interference
when two identical waves arrive at the same point exactly out of phase; that is, precisely aligned crest to trough
elastic potential energy
potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring
force constant
a constant related to the rigidity of a system: the larger the force constant, the more rigid the system; the force constant is represented by k
frequency
number of events per unit of time
fundamental frequency
the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform
intensity
power per unit area
longitudinal wave
a wave in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation
natural frequency
the frequency at which a system would oscillate if there were no driving and no damping forces
nodes
the points where the string does not move; more generally are where the wave disturbance is zero in a standing wave
oscillate
moving back and forth regularly between two points
over damping
the condition in which damping of an oscillator causes it to return to equilibrium without oscillating; oscillator moves more slowly toward equilibrium than in the critically damped system
overtones
multiples of the fundamental frequency of a sound
period
time it takes to complete one oscillation
periodic motion
motion that repeats itself at regular time intervals
resonance
the phenomenon of driving a system with a frequency equal to the system's natural frequency
resonate
a system being driven at its natural frequency
restoring force
force acting in opposition to the force caused by a deformation
simple harmonic motion
the oscillatory motion in a system where the net force can be described by Hooke’s law
simple harmonic oscillator
a device that implements Hooke’s law, such as a mass that is attached to a spring, with the other end of the spring being connected to a rigid support such as a wall
simple pendulum
an object with a small mass suspended from a light wire or string
superposition
the phenomenon that occurs when two or more waves arrive at the same point
transverse wave
a wave in which the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation
under damping
the condition in which damping of an oscillator causes it to return to equilibrium with the amplitude gradually decreasing to zero; system returns to equilibrium faster but overshoots and crosses the equilibrium position one or more times
wave
a disturbance that moves from its source and carries energy
wave velocity
the speed at which the disturbance moves. Also called the propagation velocity or propagation speed
wavelength
the distance between adjacent identical parts of a wave
adiabatic process
a process in which no heat transfer takes place
Carnot cycle
a cyclical process that uses only reversible processes, the adiabatic and isothermal processes
Carnot efficiency
the maximum theoretical efficiency for a heat engine
Carnot engine
a heat engine that uses a Carnot cycle
change in entropy
the ratio of heat transfer to temperature Q/T
coefficient of performance
for a heat pump, it is the ratio of heat transfer at the output (the hot reservoir) to the work supplied; for a refrigerator or air conditioner, it is the ratio of heat transfer from the cold reservoir to the work supplied
cyclical process
a process in which the path returns to its original state at the end of every cycle
Entropy
a measurement of a system's disorder and its inability to do work in a system
first law of thermodynamics
states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system
heat engine
a machine that uses heat transfer to do work
heat pump
a machine that generates heat transfer from cold to hot
human metabolism
conversion of food into heat transfer, work, and stored fat
internal energy
the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of a system’s atoms and molecules
irreversible process
any process that depends on path direction
isobaric process
constant-pressure process in which a gas does work
isochoric process
a constant-volume process
isothermal process
a constant-temperature process
macrostate
an overall property of a system
microstate
each sequence within a larger macrostate
Otto cycle
a thermodynamic cycle, consisting of a pair of adiabatic processes and a pair of isochoric processes, that converts heat into work, e.g., the four-stroke engine cycle of intake, compression, ignition, and exhaust
reversible process
a process in which both the heat engine system and the external environment theoretically can be returned to their original states
second law of thermodynamics
heat transfer flows from a hotter to a cooler object, never the reverse, and some heat energy in any process is lost to available work in a cyclical process
second law of thermodynamics stated in terms of entropy
the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant; it never decreases
statistical analysis
using statistics to examine data, such as counting microstates and macrostates
conduction
heat transfer through stationary matter by physical contact
convection
heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of fluid
emissivity
measure of how well an object radiates
greenhouse effect
warming of the Earth that is due to gases such as carbon dioxide and methane that absorb infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface and reradiate it in all directions, thus sending a fraction of it back toward the surface of the Earth
heat
the spontaneous transfer of energy due to a temperature difference
heat of sublimation
the energy required to change a substance from the solid phase to the vapor phase
kilocalorie
1 kilocalorie = 1000 calories
latent heat coefficient
a physical constant equal to the amount of heat transferred for every 1 kg of a substance during the change in phase of the substance
mechanical equivalent of heat
the work needed to produce the same effects as heat transfer
net rate of heat transfer by radiation
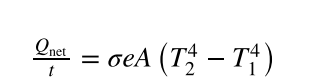
R factor
the ratio of thickness to the conductivity of a material
Radiation
heat transfer which occurs when microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, or other electromagnetic radiation is emitted or absorbed; energy transferred by electromagnetic waves directly as a result of a temperature difference
rate of conductive heat transfer
rate of heat transfer from one material to another
specific heat
the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of a substance by 1.00 ºC
Stefan-Boltzmann law of radiation
where sigma is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, A is the surface area of the object, T is the absolute temperature, and e is the emissivity
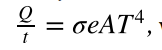
sublimation
the transition from the solid phase to the vapor phase
thermal conductivity
the property of a material’s ability to conduct heat
absolute zero
the lowest possible temperature; the temperature at which all molecular motion ceases
Avogadro’s number
the number of molecules or atoms in one mole of a substance (units are particles/mole)