Coenzymes & metabolic reactions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are coenzymes and the classifications?
Coenzymes are …
thermo-labile , organic compounds loosely attached to enzyme.
Mainly water soluble Vit B and Vit C derivatives
Co enzymes can be classified into:
Co-dehydrogenase co enzymes (H carriers)
Group transferring co enzymes (Other groups than H)**
** Eg:methyl/acyl/Co2/aldehyde
Co -dehydrogenase are used in what reactions and include?
Co hydrogenase are hydrogen carriers used in Redox reactions
They include:
Nicotinamide derived coenzymes (derived from Vit B3)
Flavin derived coenzymes (derived from Vit B2)
Gluathione
L-ascorbic acid (Vit C)
Coenzyme Q
Lipoic acid
Types of Nicotinamide derived coenzymes (Derived from Vit B3)
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate)
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (Co III) NMN
Niacin or Nicotinic acid (Name. Contains. what is converted into niacin)
Name: Vit B3 (Niacin or Nicotinic acid)
Contains: Pyridine ring
In body:
Tryptophan convert to Niacin.
Tryptophan 60mg = Niacin 1mg
Niacin or Nicotinic acid - bioactive coenzymes names functions and reduced form
Bio active coenzyme forms = NAD+ , NADP+
Functions:
NAD+ and NADP+ coenzymes in redox reaction.
Coenzyme undergoes reduction of pyridine ring by accepting hydride ion (H atom + electron)
Reduced forms:
NAD+ —> NADH + H+
NADP+ —> NADPH + H+
Flavin derived coenzymes (Derived from Vit B2) : Name, Bio active forms of Vit B2, How is FAD formed?
Name : Riboflavin (Vit B2)
Bio active forms: FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide), FMN (Flavin mononucleotide)
ATP— P—> FMN = FAD + …
Vit B2: FAD and FMN reduced forms and binding (with example)
FMN & FAD can reversible accept 2 H atoms forming FMNH2 or FADH2
FMN and FAD bound tightly to flavoenzymes that catalyse oxidation/reduction of substrate. (Eg: Succinate hydrogenase [FAD])
Gluathione - What is it
Gluathione is tripeptide formed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine amino acid (y glutamyl cysteine glycine) G-SH
Acts as hydrogen doner (2 G-SH ←→ G-S-SG)
L- absorbic acid (Name , and deficiency is called)
Name: Vit C (L- absorbic acid)
Deficiency disease = Scurvy
L-ascorbic acid ( functions + examples)
Main function: Reducing agent
Functions:
Coenzyme in hydroxylation reactions
Example: hydroxylation of proline and lysine residues of collagen maintaining normal connective tissue and wound healing (Reduce easy bleeding)
Reduces ferric iron to ferrous form
Absorption of dietary iron from intestine
Coenzyme Q
Co enzyme Q (Ubiquone)
Structurally similar to Vit K
Plays a role in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation in respiratory chain
Lipoic acid
Member of Vit B group
Important for oxidative decarboxylation (eg:forms acetyl-coa from pyruvic acid or aKG→ S.CoA)
Group transferring coenzymes
Coenzymes transfer chemical groups other than hydrogen
Coenzyme A (CoA-SH) [contain pantothenic acid (Vit B5)]
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) [Vit B1]
Pyridoxal phosphate [Vit B6]
Biotin [Vit B7]
Folic acid [Vit B9]
Cobalamine [Vit B12]
Pantothenic acid (Name , Functions, structures it is a component of)
Name: Vit B5 (Pantothenic acid)
Functions:
coA contains thiol group (coA-SH) that carries acyl compounds
Pantothenic acid component of acyl carrier protein of fatty acid synthase .
Structures it is a component of: Succinyl coA, fatty acyl CoA, acetyl CoA
Pantothenic acid distribution and deficiency
Distribution : widely distributed but eggs, liver, and yeast most important sources
Deficiency: not well characterised in humans and no recommended daily allowance (RDA) established.
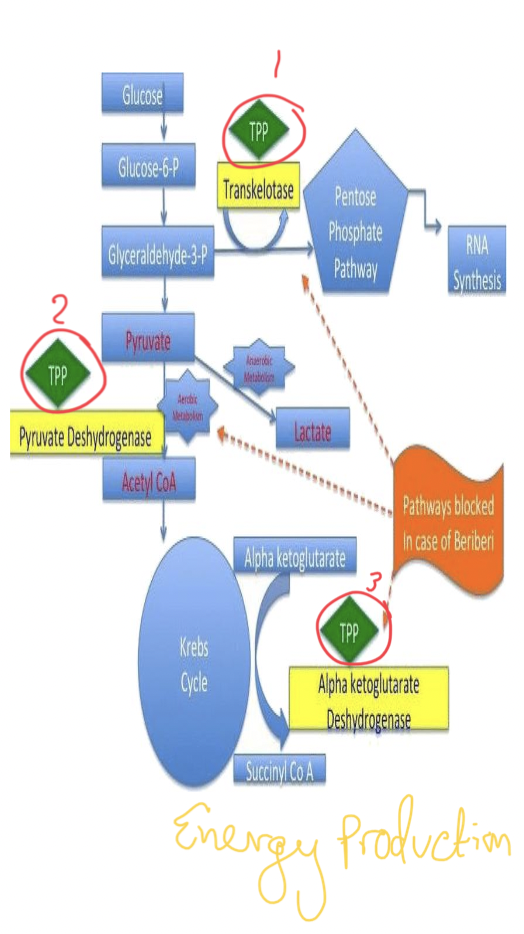
Thiamine (Name, Bio active form coenzyme function)
Name : Vit B1 (Thiamine)
Bio active form : TPP ( Thiamine + Pyrophosphate group from ATP)
Functions:
Transketolase reaction (imp for pentose synthesis from glucose)
Oxidative decarboxylation of a-keto acid
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate & a-ketoglutarate which plays key role in energy metabolism of most cells & imp in CNS tissues
Pyridoxine (Name, Similarities of types, difference of types and types )
Name: Vit B6 (collective term of Pyridoxine, Pyridoxal, and Pyridoxamine)
Similarities: All Vit B6 types derived from pyridine and are precursors of PLP.
Diff: Types differ in nature of functional groups attached to rings
Types:
Pyridoxine = Plants
Pyridoxal = Food from animals
Pyridoxamine = Food from animals
PLP definition and functions
PLP is biologically active coenzyme called pyridoxal phosphate.
Functions (for enzymes catalyse reactions could involve amino acids):
Transamination (non essental amino acid)
Deamination
Decarboxylation (Histidine → Histamine + CO2)
Condensation (glycine + Succinyl CoA → δ aminolevulinic acid acid A (haem synthesis))
Glycogen phosphorylase (glycogenesis)
Biotin (Name, bond, found where and symptoms)
Name : Vit B7 (Biotin)
Bonded : Covalently bonded to ε-amino group of lysine residues in biotin-dependent enzymes
Found: large % requirement is supplied by intestinal bacteria
Biotin Deficiency incl symptoms and explanation
Antibiotic may cause deficiency in B7 → Hair loss/ depression/ dermatitis
Explanation : This is because large % of biotin supplied by intestinal bacteria
(Normal diet up to 20 eggs/day) Excess raw egg white as protein source → dermatitis glossitis, loss of appetite and nausea
Explanation: Raw egg white has glycoprotein avidin which tightly binds biotin and prevents absorption from intestine
Raw egg may cause Salmonella infection
Folic Acid (Name, Key roles, Source)
Name: Vit B9
Key roles :
1C metabolism which is essential for biosynthesis of several compounds
Folate (as N5-methyl-THF) acts as the methyl donor for converting homocysteine → methionine.
Sources: Leafy, dark green vegetables
Folic acid (Deficiency subtypes, primary result with explanation)
Deficiency:
Most common in US (especially among preg woman and alcoholics)
Primary result is Megablastic anemia
Caused by diminished synthesis of purines and TMP → Inability of cells (incl RBC precursor) to make DNA & inability to divide.
Cobalamin (Name, Enzyme reactions with explanation)
Name: Vit B12 (Cobalamin)
2 essential enzymatic reaction
Deoxy adenosyl cobalamin - methylmalanoyl CoA isomerization to → Succinyl CoA
Explanation: important for glucogenesis from some amino acid & odd number fatty acids
Methyl cobalamine: for homocysteine (Hcy) → methionine
Explanation: methylation reaction & myeline sheath formation
Cobalamin Absorption
B12 released from food in acidic environment of stomach
Free B12 binds to R protein (glycoprotein)
The complex moves into the duodenum (intestine)
B12 released from R protein by pancreatic enzymes and binds to IF (intrinsic factor) glycoprotein.
The cobalamin-IF complex travels through intestine then binds to specific receptor on surface of mucosal cells in ileum (last part small intestine)
Cobalamin transported into mucosal cell → into general circulation where carried by transcobalamin (its binding protein)
B12 taken up and stored in liver (primarily) → released into bile and efficiently reabsorbed in ileum
Cobalamin Deficiency due to (rare and common)
Rarely due to lack of Vit in diet
More common in patients who fail to absorb vit from intestine eg:
Lack of intrinsic factor
Gastectomy (No IF production)
Atrophic gastritis (Cell damage so no IF production)
Grastic malignancy (Cell damage so no IF production)
Achlorhydia (reduced gastric acid secretion) in elderly → most often cause of cobalamin malabsorption
Cobalamin deficiency leads to, its characterised by + explanation
Pernicious anemia
Megablastic anemia -
Folic acid acid (N5- methyl THF) also needed for Hcy remethylation so B12 deficiency → folate trap → megoblastic anemia + ↑Hcy levels.
Neurological disorder
Used for myelin sheath formation
Group transferring coenzymes (ATP , UDP, CDP,Active Sulphate, Active methionine)
ATP = Phosphate donor
UDP = Sugar carrier (eg: UDP-glucose , UDP galactose, UDP-glucoronic
CDP = Nitrogenous bases carrier (eg: CDP choline)
Active Sulphate: Phosphoadenosyl phosphorysulphate (PAPS) = Sulphate donor
Active methionine: SAM (S-adenosyl methionine = Universal Methyl donor (Melatonin, Epinephrine, Creatinine)