Chapter 13: Gauss's Law
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
area vector
a vector with magnitude equal to the surface’s area and direction perpendicular to the area.
2
New cards
flux
the volume rate of flow of the liquid through the wire frame.
3
New cards
Electric flux
is more difficult to conceptualize because the electric field is more abstract than fluid velocity; furthermore, we generally deal with electric flux through imaginary surfaces.
4
New cards
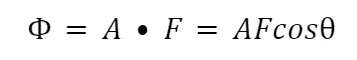
Definition of Flux
5
New cards
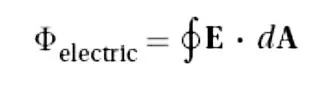
Definition of Electric Flux
6
New cards
Gauss’s law
States that the electric flux out of a closed surface equals 1/ε0 times the charge enclosed within the surface.
7
New cards
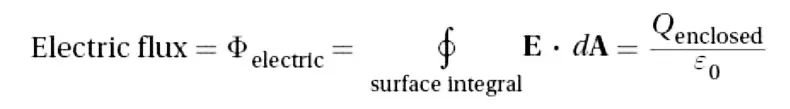
Gauss's Law
8
New cards
Electric field lines
These begin or end only on positive and negative point charges, respectively.
9
New cards
Insulators
are materials that have no “free” electrons, so the charge is not free to move within them.
10
New cards
nonconductors
Consequently, all sorts of charge distributions are possible on \________; You can put charge wherever you want to and it stays there.
11
New cards
Conductors
have free electrons, so the charge is free to move within them.
12
New cards
V \= πr²L
volume of a cylinder