Blood Cell Identification Quiz
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Matured in the thymus, under the direction of thymocins
Lymphocyte
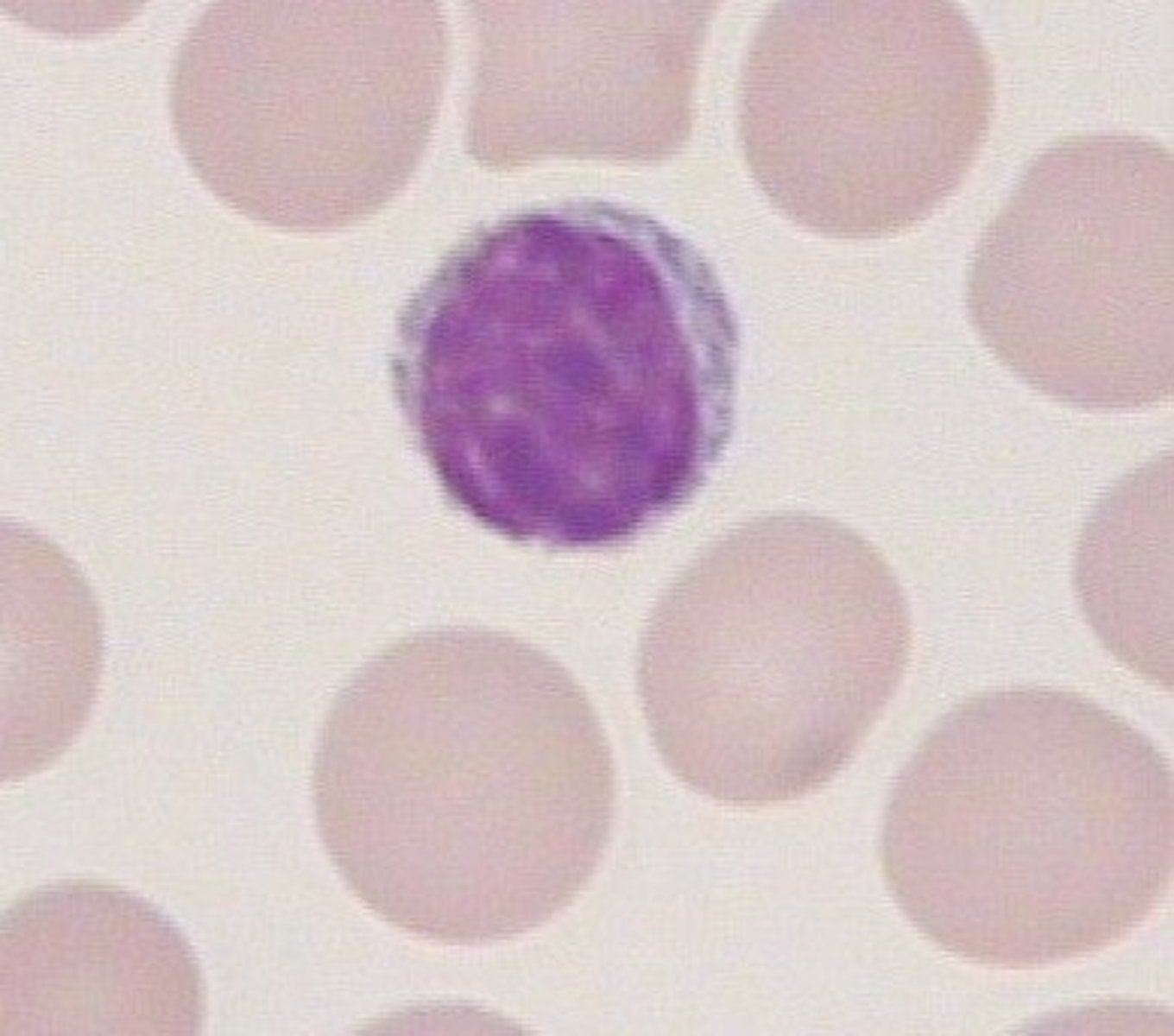
Produced from megakaryocytes in the red bone marrow
Basophils
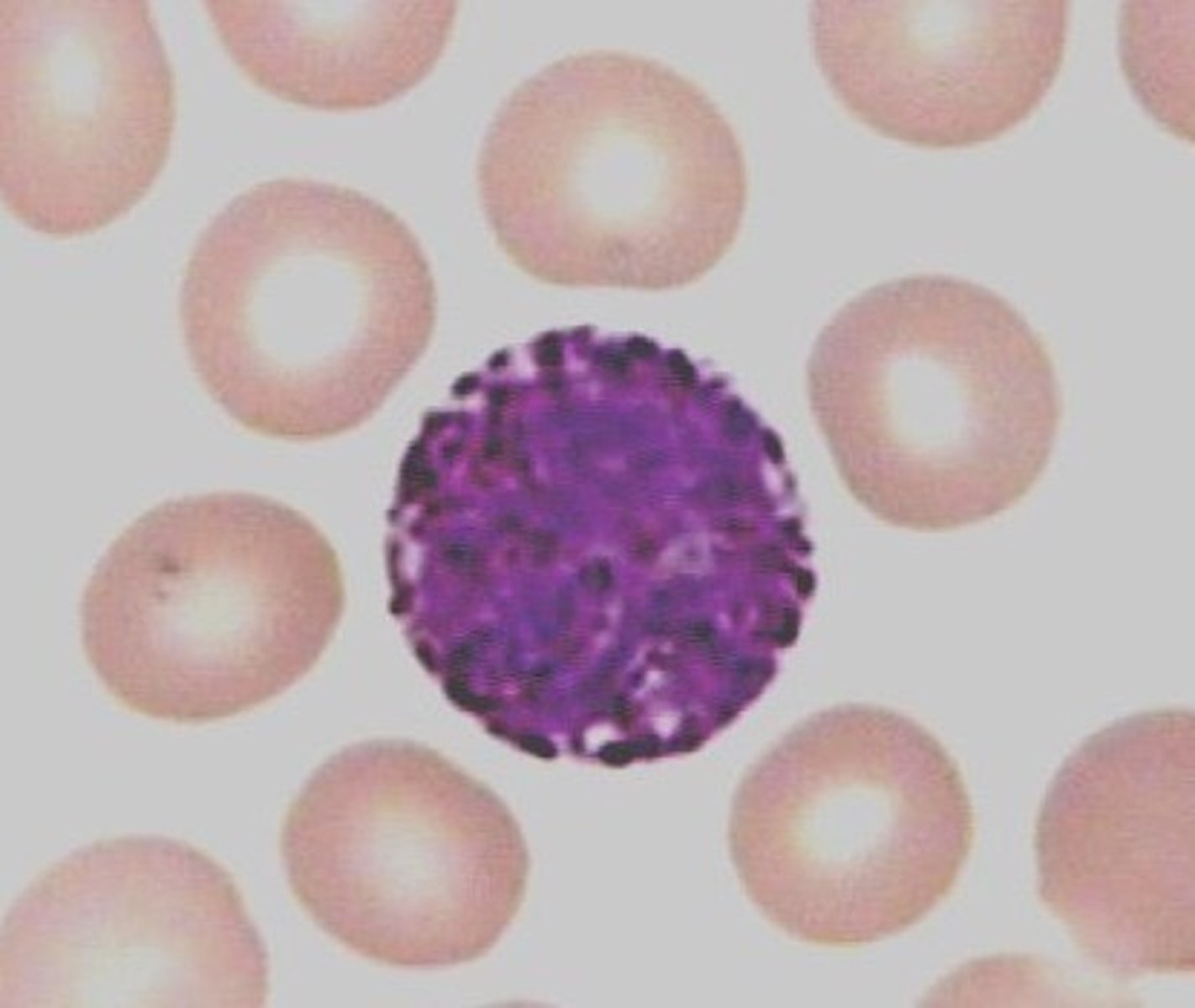
First responders
Neutrophils
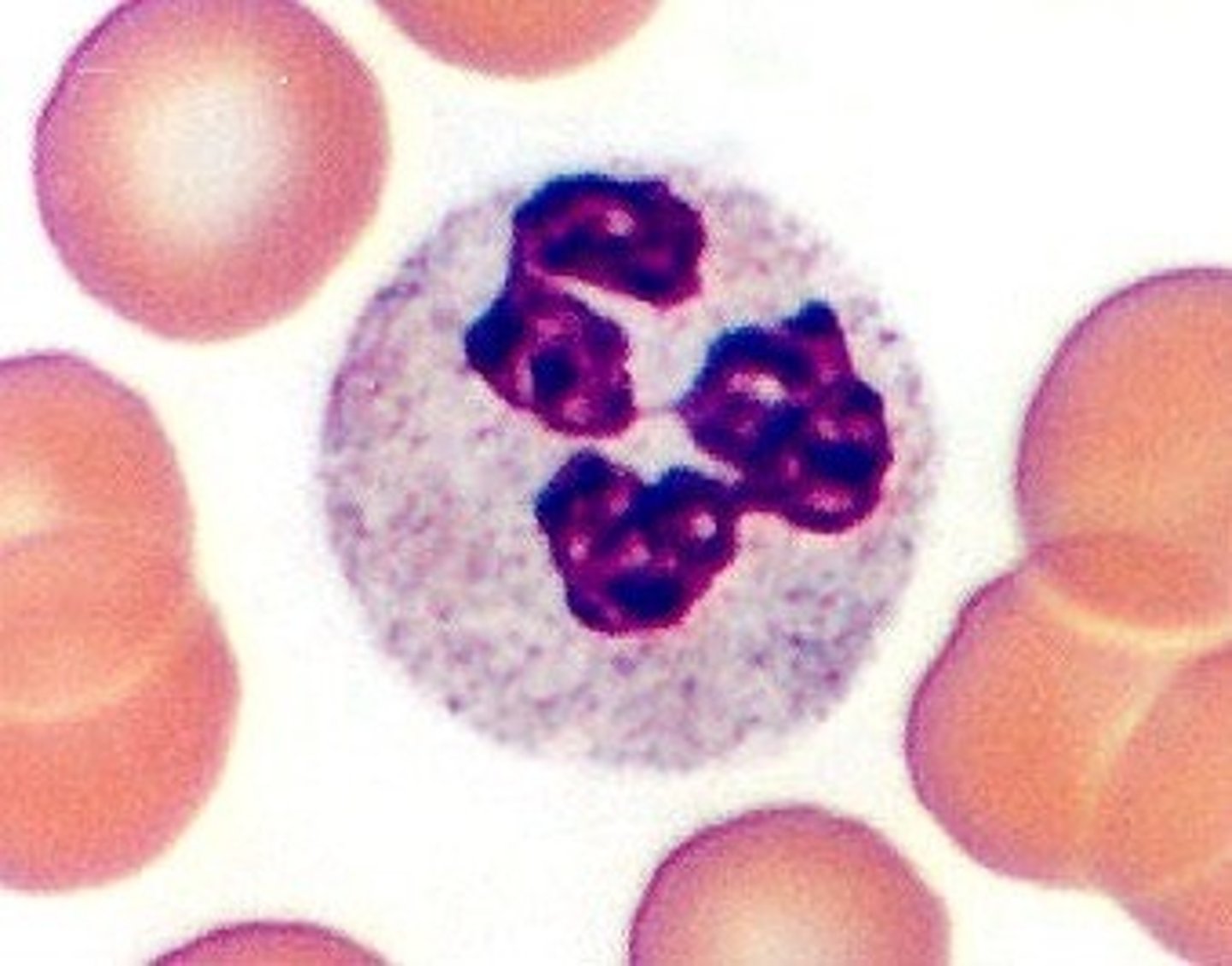
Considered macrophages when in the tissue
Monocyte
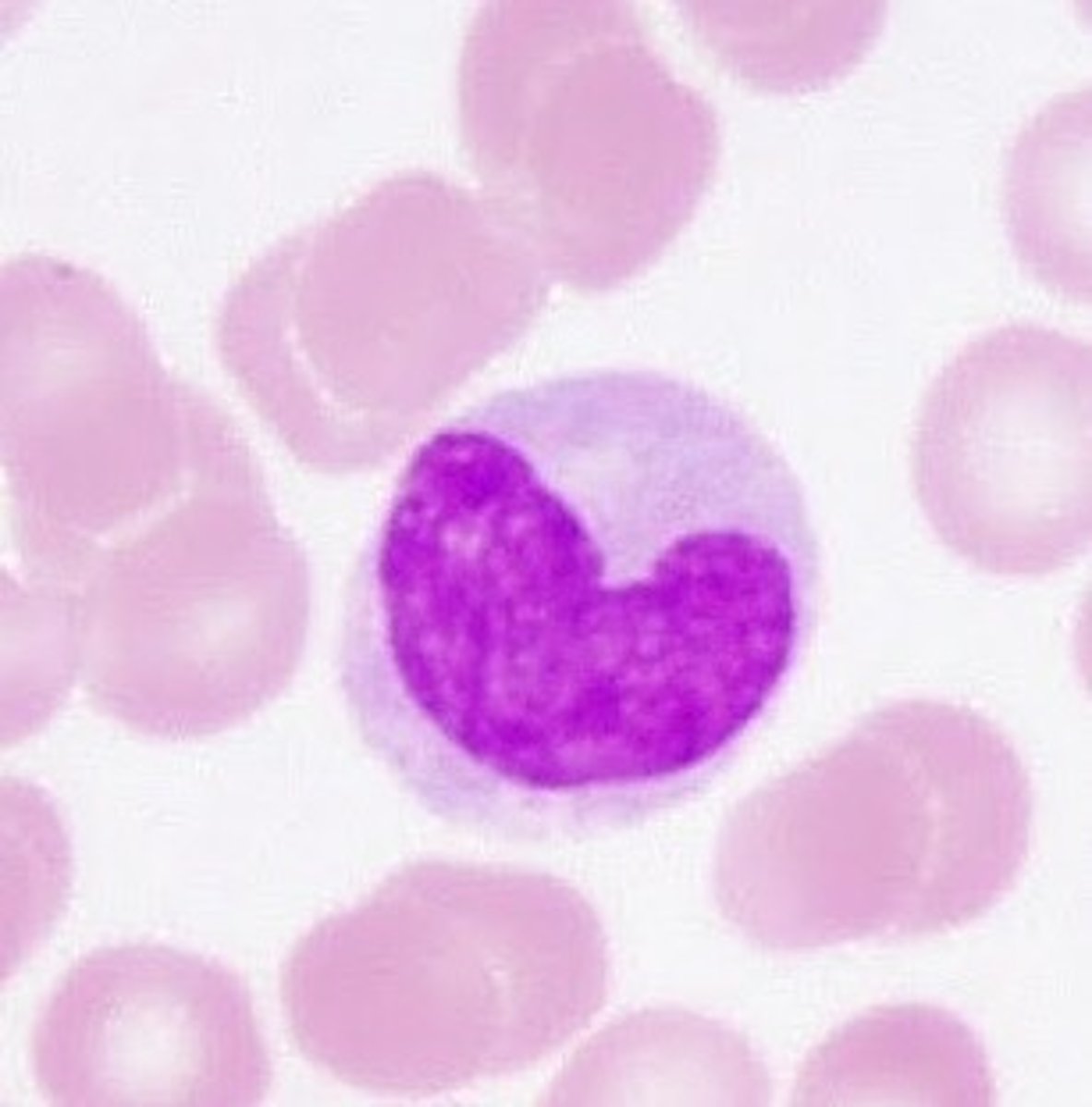
Hct formula
(RBC x MVC) / 10
MCH (Mean Cell Hemoglobin) Formula
(Hgb x 10) / RBC
MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration) Formula
(Hgb x 10) / RBC
MCV (Mean Cell Volume) Formula
(Hct x 10) / RBC
Microcytic MCV
< 80
Normocytic MCV
80 - 100
Macrocytic MCV
>100
Hypochromic MCHC
<32
3 part counts…
lymphocytes, monocytes, granulocytes
5 part counts..
neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
Absolute Lymphocyte Count Formula
(WBC x % of lymphocytes) / 100
WBC = 5 × 109 / L; lymphocytes = 30%
5.0 × 0.30 = 1.5 × 109 / L
Retic % Formula
(# retics / 1000 RBCs) x 100
Corrected Retic % Formula
Retic % x (Patient Hct / 45%)
Retic 3.5; Hct = 26
3.5 x (26/45) = 2.0%
RPI Formula
Retic count in % x (Hct / 45%) / Maturation Time
Retic = 7.8; Hct = 30%; Maturation Time for 30% is 2 days
RPI = 7.8 x (30/45) / 2 → 2.6
Adequate bone marrow reponse: RPI > 3
1 day maturation time
40-45
1.5 day maturation time
35-39
2 day maturation time
25-34
2.5 day maturation time
15-24
3 day maturation time
<15
Abosolute Retic Count
(Retic % x RBC count) / 100
Actives site of bone marrow
vertebrase, sternum, pelvis, ribs, skill, proximal femur/humerus
Asplenia
absence or non-functioning spleen → increased infection risk, presence of abnormal RBCs (Howell-Jolly bodies)
Primary Lymphoid organs
Bone marrow (B cell), Thymus (T cells)
Secondary lymphoid organs
Lymph nodes, spleen, MALT
Wright stain
general morphology, differential count
Prussian blue stain
iron
Normal M:E ratio
Myeloid to erythroid ratio
2:1 to 4:1
Erythropoiesis steps
Pronormoblast, Basophilic normoblast, Polychromatic normoblast, Orthocrhomic normoblast, Reticulocyte, Mature RBC (erythrocyte)
Please Bring Purple Oranges Right Eway
Myelopoiesis steps
Myeloblast, Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Metamyelocyte, Band, Segmented neutrophil
My Poor Mother Made Bad Soup
Where is EPI produced?
Kidneys
Function: stimulates erythroid progenitor cell proliferation.differentiation in bone marrow in reponse to hypoxia
Lipids precent
40% - maintains fluiditiy/flexibility
phospholipids, cholesterol
Proteins precent
50 % - structual integrity and transport-
Spectrin, ankyrin, band 3, glycophorins
Carbohydrates precent
10% - blood group antigens, surface charge
glycoprotiens
Embden-Meyerhof (glycolysis)
ATP production
Hexose monophophate shunt (H6PD)
procudes NADPH, reduces glutathione (GSH) to prevent oxidative damage
Rapaport-Luebering Shunt
produces 2,3-BPG, regluates oxygen release
Methemoglobin reducatase pathway
Kepps iron in Fe2+ state
Burr cells (Echinocytes)
Even projections
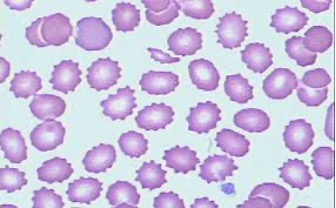
Stomatocytes
slit-like central pallor
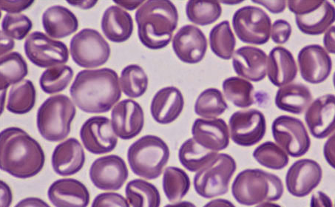
Target Cells (Condocytes)
bullseye
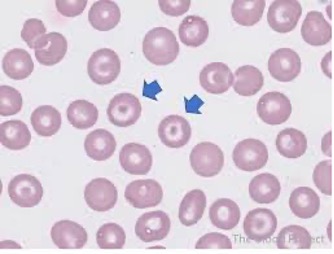
Acanthocytes
Irregular projections
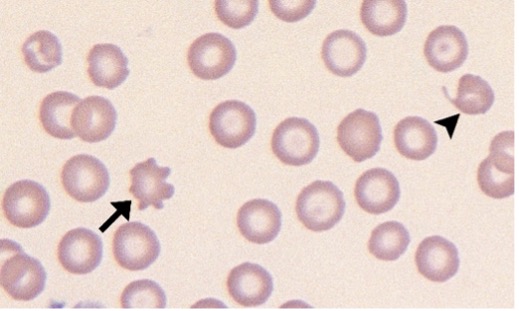
Spherocytes
No central pallor (suppose to have dark membrane and pale inside)
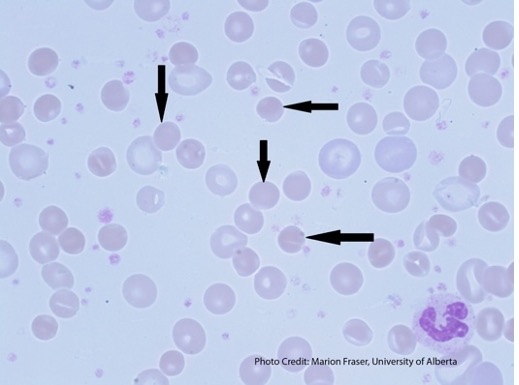
Elliptocytes
Oval
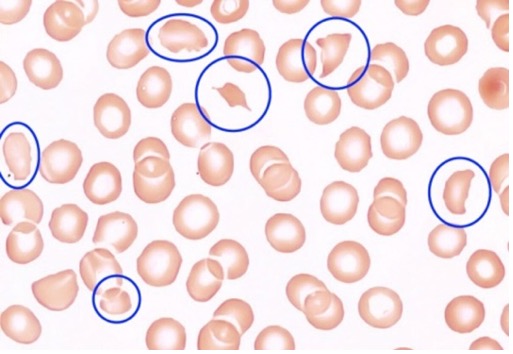
Schistocytes
fragments
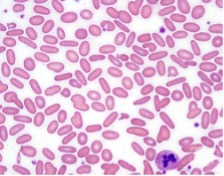
Sickle Cell
crescent
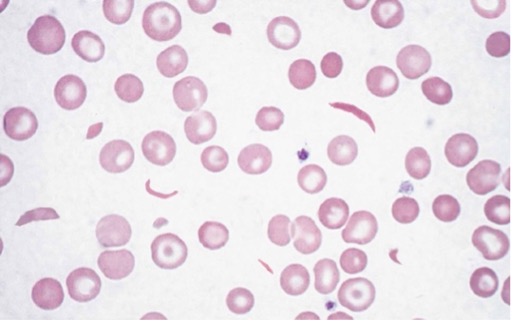
Teardrop Cells
Teardrop
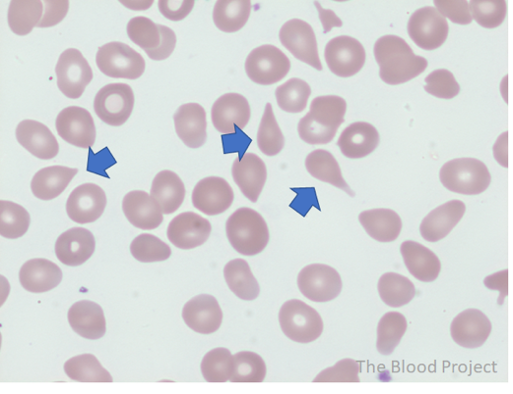
Anisocytosis
Size variation
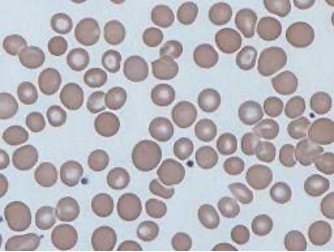
Poikilocytosis
Shape variation
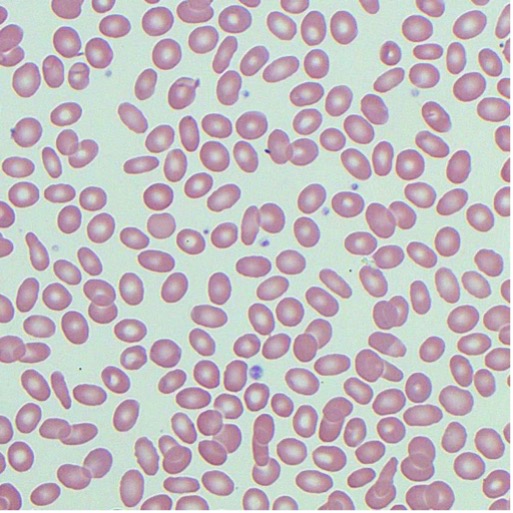
Hypochromic Cells
pale centers of >3um
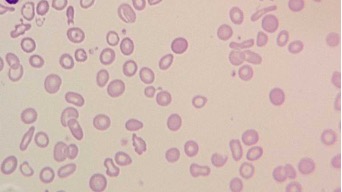
Hypochromic grading
1+ area of central pallor is ½ of the cell diameter
2+ area of pallor is 2/3 of cell diameter
3+ area of pallor is ¾ of cell diamter
4+ Thin thin of hemoglobin (most cell is pale)
Microcytes
Small RBCs (<6)
Macrocytes
Large RBCs (> 8,5)
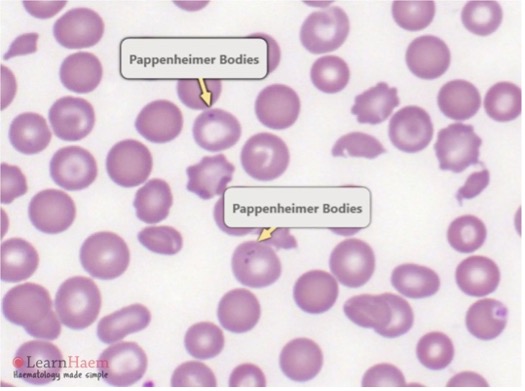
Pappenheimer Bodies
Iron granules
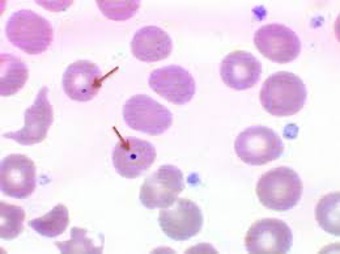
Howell-Jolly Bodies
DNA remants
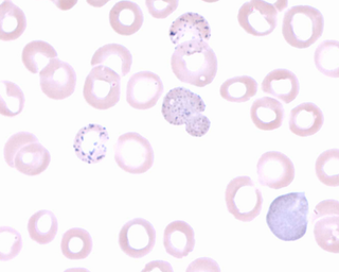
Basophilic stippling
RNA remnants
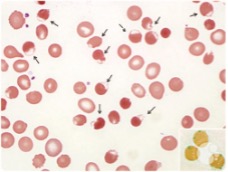
Heinz Bodies
Denatured Hgb (only viisble with supravital stain)
Polychromatic Cells
Blusish tint
First reaction and last reaction of heme synthesis
First: Succinyl-Coa + Glycine → ALA
Last: Insertion of Fe2+ into protoporphyrin IX → heme
Grower 1
2 zeta, 2 epsilon
embryo
Grower 2
2 alpha, 2 epsilon
embryo
Portland
2 zeta, 2 gamma
Embryo
HbF
2 alpha, 2 gamma
Fetal
HbA
2 alpha, 2 beta
Adult (96-98%)
HbA2
2 alpha, 2 delta
Adult (2-3%)
HbA normal
96-98%
HbA2 normal
2-3%
HbF normal
<1%
P50
Partial pressure of O2 where Hb is 50% saturated
Normal: 26-27 mmHg
Increased P50 leads to
↓ affinity (right shift)
Right shift
(↓ affinity): ↑ CO₂, ↓ pH, ↑ 2,3-BPG, ↑ temp
Left shift
(↑ affinity): ↓ CO₂, ↑ pH, ↓ 2,3-BPG, ↓ temp
Carboxyhemoglobin
CO bound to Hb → cherry red color
Methemoglobin
Fe3+ → cannot bind to O2
Sulfhemoglobin
irreversible sulfur binding → cyanosis
Normal hemoglobin for Male
13.5 - 17.5 g/dL
Normal Hemoglobin females
12 - 16 g/dL
Fragmentation
intravascular
Mechanical trauma
↑ LDH, ↓ haptoglobin, hemoglobinemia, schistocytes
Macrophage-mediated
Extravascular
Splenic/liver macrophages
Sphereocytes, inc bilirubin, splenomegaly
Condocytes
Target cells
Drepanocytes
Sickle cell
Dacryocytes
Tear drop cells