Stuff need know
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Spanish verb tense(when to use)
idk yet
Math 4 main t-series
idk yet
Math all the convergence checking rules
idk yet
ap physics c mechanics memorization stuff
Derivation of Conservation of momentum
Change of energy in a system equation(base of all dynamics)
Change in energy in a system = sum of all energy transfered in or out of the system
Net Work(some kind of energy eq)
Net Work = net change in kinetic energy
Work by friction = change in mech energy → true when?
no work removed or added to a system by a force
conversation of mech energy valid when?
Work by force applied = 0. No work by nonconservative force(friction)
Conservative force = ?
conservative force = - dU/dx
derivation of angular momentum
center of mass of rigid object with shape
r_cm = 1/m_total \int {r dm}
Parallel Axis theorem
inertia of object rotatin not around center of mass
I = I_(center of mass) + ML² (L is distance axis to cm)
object in SHP equation
d²x/dt² + w²x = 0 (x = pos of object, w = angular frequency, x can also be theta)
v_max and a_max of SHP
v_max = Aw | a_max = aw² (w = angular frequency, A = amplitude of motion.)
v_cm and a_cm from x_cm
derive once for v and twice for a over time
derivation of terminal velocity of object falling near surface of a planet.
v_terminal = sqrt(2mg/DpA) (p = density of fluid object is going through, the area the flow of the object motion goes through, drag coefficient)
Derivation Binding energy of an object to a planet(or any 2 objects to each other)
W_(F_a) = GMm/R
Derivatioin Escape velocity of an object from a planet
sqrt(2Gm/R)
Derivation Total Mechanical Energy of Orbital Object:
ME_total = − GM*m/2r
Derivation Kepler’s third law
T² = r³ (4pi²)/(Gm) (T = period, m = mass of planet, r = orbit of planet)
the equation of x in SHP to differentiate to get v and a
x = Acos(ωt + φ)
Derivation of Moment of Inertia
uniform ring or cylinder shell on cylinder axis
uniform rod at center
uniform cylinder or disk at cylinder axis
I = mR²
1/12 mL²
½ mR²
Quantization of charge
Q = ne (n = charge carriers, e = elementary charge)This principle states that electric charge is quantized, meaning it exists in discrete amounts represented by integer multiples of the elementary charge.
electric field around a point charge(derivation too)
E = F/q & F = kq1q2/r² → E = kq/r²
Electric field around a continuous charge distribution(derivation)
E(point charge) = kq/r² → dE = k dq/r² →(int both sides) E(condchdis) = k ∫(dq/r²)
Equation for electric flux for a flat surface in a uniform electric field
E * A → EAcos\theta
The electric potential difference across a uniform electric field. Remember d is the straight-line distance parallel to the electric field.
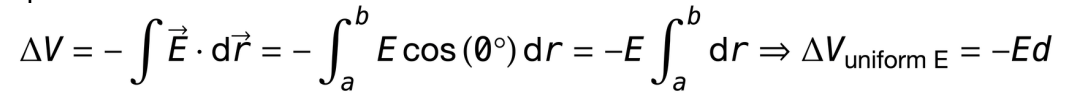
3 energy stored in capacitor equations
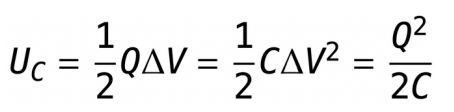
3 Electric Power equations
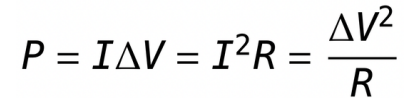
Motional emf(how to derive and what the eq assumes)
emf = vBL (L = length of conductor)
inductance of ideal solenoid(derivation and what its determined by)

The angular frequency of LC circuits, and therefore, all the simple harmonic motion equations for LC circuits.
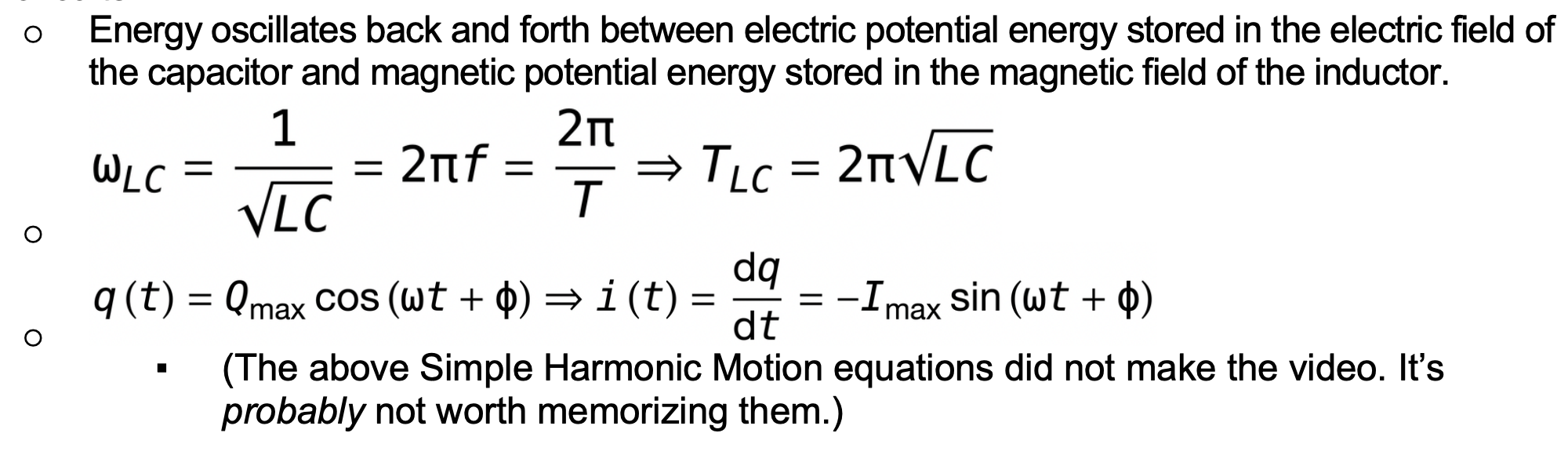
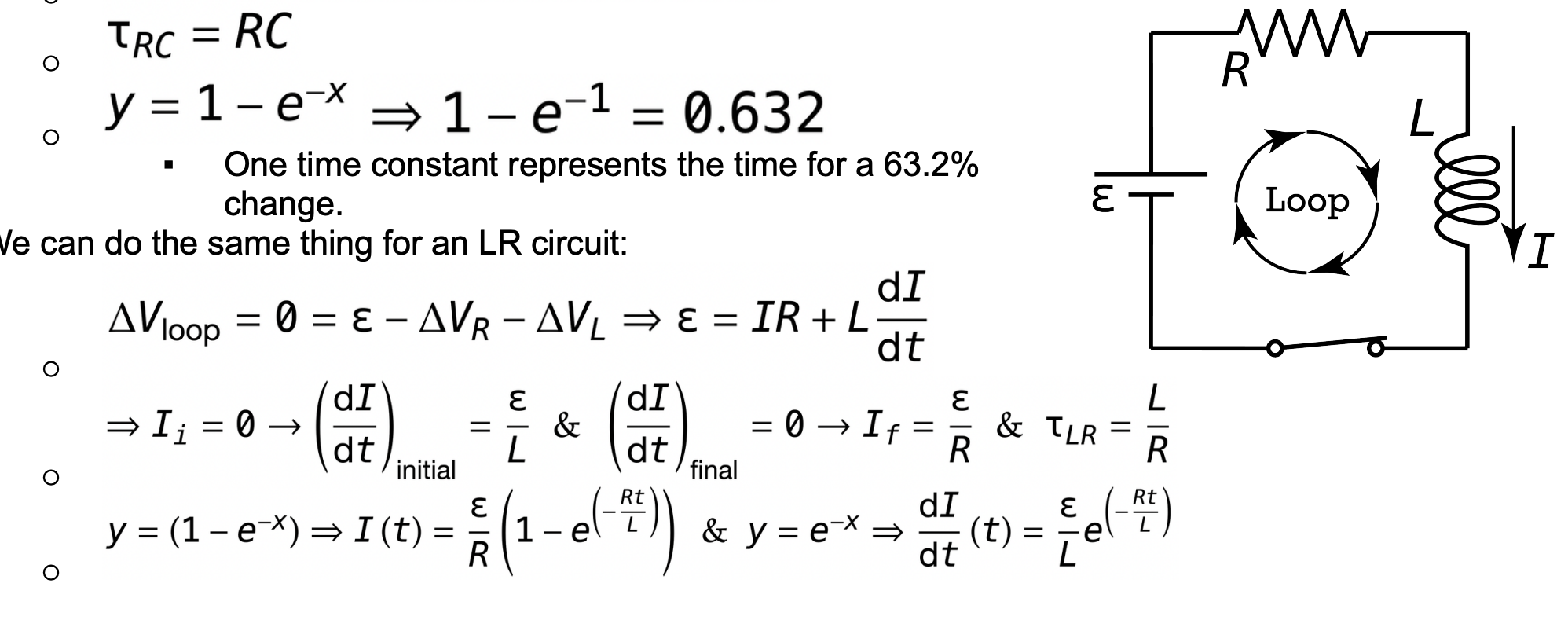
One time constant represents
time for 63.2% change
RC circuit (shape and max of graphs of currentvst, chargevst, how to find the max of these graphs, time constant expression)
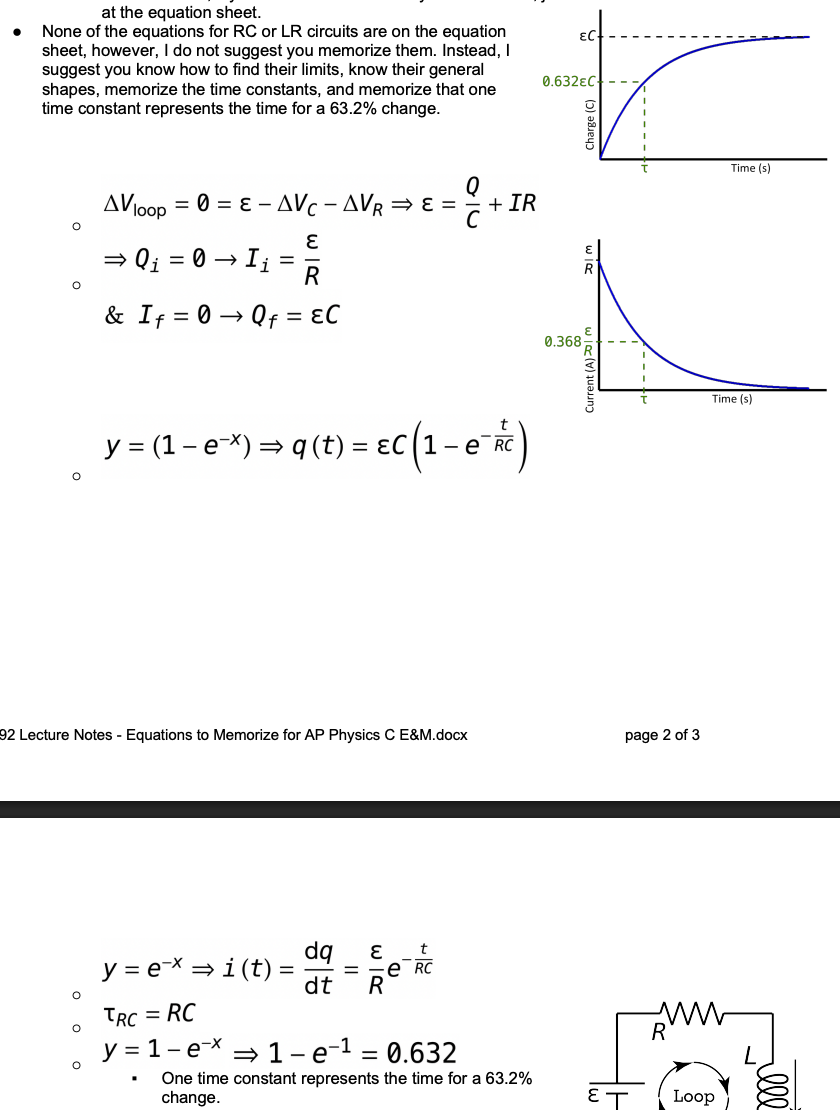
LR circuit (shape and max of graphs of currentvst, chargevst, how to find the max of these graphs, time constant expression)