HIV
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
1
New cards
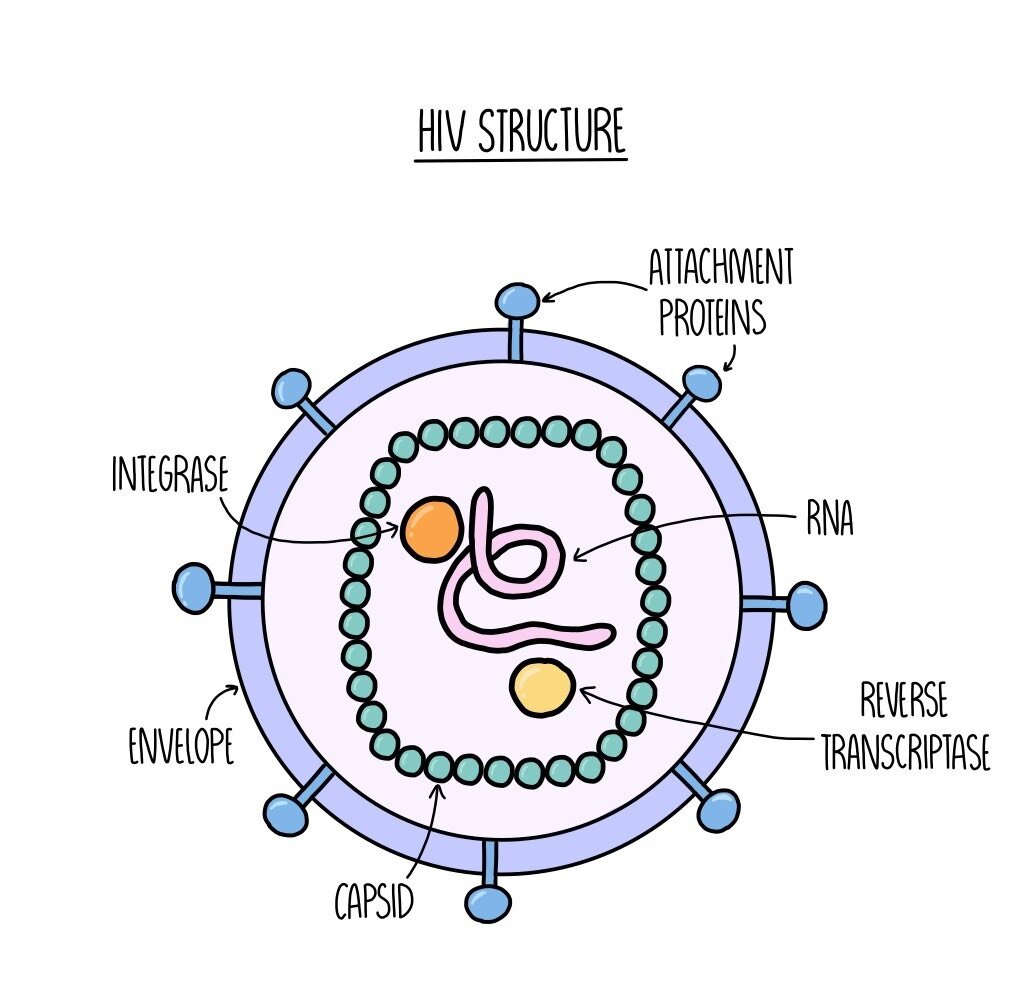
5.7 - Describe the structure of HIV
* Lipid envelope + attachment proteins embedded
* inside the envelope, Capsid encloses two single RNA strands + enzymes including reverse transcriptase(it is called this because it catalyses the production of DNA from rna )
\
* It's a retrovirus as it contains RNA
* inside the envelope, Capsid encloses two single RNA strands + enzymes including reverse transcriptase(it is called this because it catalyses the production of DNA from rna )
\
* It's a retrovirus as it contains RNA
2
New cards
Explain the process by which HIV replicates (7)
1. HIV Enters bloodstream + circulates
2. Protein on HIV binds to CD4 protein receptors (normally on T-Helper cells)
3. The protein capsid fuses with cell surface membrane. RNA + enzymes of HIV enter the helper t cell.
4. HIV Reverse transcriptase converts RNA → DNA
5. DNA is moved into helper t cells nucleus and inserted into host DNA.
6. DNA transcribed into mRNA, which uses ribosomes to make viral proteins.
\
7)mRNA passes out of the nucleus through a nuclear pore and uses the cells’ protein synthesis mechanisms to make HIV particles.
\
8) HIV particles leaves helper t cell , using part of cell’s CSM to from lipid envelope.
3
New cards
How does HIV infect a host?
Infects and kills helper T-cells (the host cells)
Their role in the immune response is stopped
AIDS occurs when the number of helper T-cells in the body reaches a low level
Their role in the immune response is stopped
AIDS occurs when the number of helper T-cells in the body reaches a low level
4
New cards
What organelles does the HIV require form the host T-helper cell and why?
Needs the enzymes and ribosomes to enable it to reproduce
5
New cards
How does HIV lead to the development of AID’s?
Attacks helper T cells
\
\-t cells are important in cell mediated immunity.without a sufficient number of t cells, the immune system cannot stimulate the b cells to produce antibodies or the cytotoxic t cell.
Memory cells may also become infected and destroyed
\
infects immune system, so sufferers cannot respond effectively to other pathogens secondary diseases ultimately cause deaths.
\
\
\-t cells are important in cell mediated immunity.without a sufficient number of t cells, the immune system cannot stimulate the b cells to produce antibodies or the cytotoxic t cell.
Memory cells may also become infected and destroyed
\
infects immune system, so sufferers cannot respond effectively to other pathogens secondary diseases ultimately cause deaths.
\
6
New cards
Recall 2 ways to diagnose AIDs. MS [2]
check for AIDs-related symptoms
Number of Th cells
Number of Th cells
7
New cards
5.7 - Explain why antibiotics are ineffective against viral disease
Antibiotics work by preventing bacteria making normal cell walls; causing them to burst when water enters via osmosis
Viruses rely on host cells for metabolic activities; no metabolic pathways for antibodies to disrupt
Viruses have a protein coat so do not have sites where antibiotics can work
Viruses rely on host cells for metabolic activities; no metabolic pathways for antibodies to disrupt
Viruses have a protein coat so do not have sites where antibiotics can work
8
New cards
What does AIDs stand for?
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
9
New cards
What is AIDS?
The immune system deteriorates and eventually fails
Those with AIDS are vulnerable to other infections such as pneumonia
Those with AIDS are vulnerable to other infections such as pneumonia