Chemistry: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Preparation of RX from ROH
ROH + HCl ——> RCl + H2O
Reagent: Anhydrous ZnCl2
ZnC
Preparation of RX from Phosphorus Halides with Alcohols
ROH + PCl5 ——> RCl + H3PO3
ROH + PCl3 ——> RCl + POCl3 + HCl
Preparation of RX from ROH using Thionyl Chloride
ROH + SOCl2 ——> RCl + HCl + SO2
Reagent: pyridine
Why is this preferred?
A: Byproducts are gasses, so pure component is obtained
Preparation of RX from alkane
RCH3 + X2 ——> RCH2X (and isomers) (presence of sunlight)
Why disadvantageous → formation of isomers, difficult to seperate
Iodination is reversible so addition of HIO3 (ox agent) to shift eqbln to right
Preparation of RX from alkene
RCH=CH2 + HX —> RCHX-CH3 (markonikov)
RCH=CH2 + HX —> RCH2-CH2X (anti markonikov, if benzoyl peroxide)
CH2=CH2 + X2 —> CH2X-CH2X (vicinal dihalide)
Finkelstein’s Reaction (obtaining Iodoalkanes)
R-X + NaI —> R-I + NaX
Reagent: Acetone
Swartz Reaction (obtaining Fluoroalkanes)
R-X + AgF —> R-F + AgX
(Freons - CFCs)
3CCl4 + 2SbF3 —> 3CCl2F2 + 2SbCl3
Preparation of Haloarenes from Arenes
Electrophilic Substitution
Aryl Fluorides can’t be made due to the high reactivity

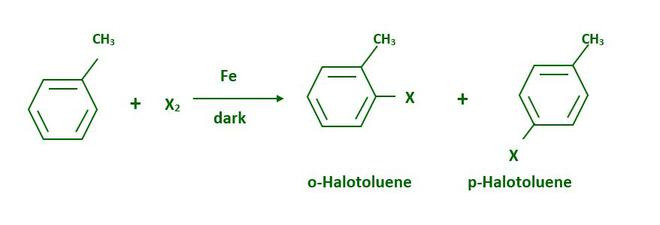
Preparation of Haloarenes from Toluene
Large difference in MP of products so its easy to seperate
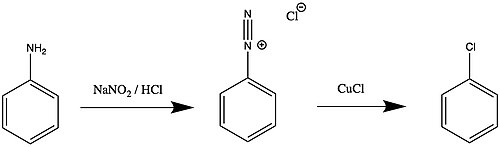
Sandmayer’s Reaction
Aniline has fishy odour