proteins
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
amino acid
building block of protein
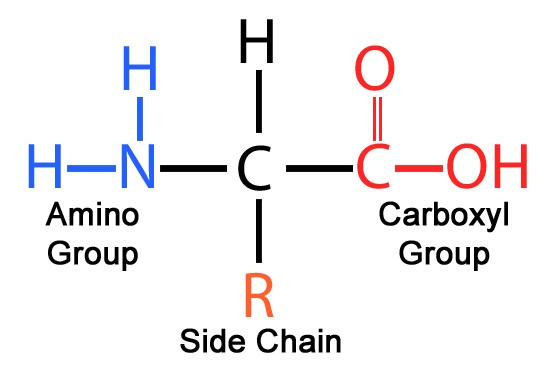
amino acid structure
a-carbon
h atom
carboxyl group (COO-)
amino group (NH3)
R group
amino acid forms
exist as 2 stereoisomers
d- and l- amino acids
l amino acids used in protein synthesis
amino acid function
depends on the r groups of the aa
polar, uncharged
non polar, uncharged
charged amino acids
polar, uncharged amino acids
R groups contain NH2 ( amide) , SH (sulfhyde ) , OH (hydroxyl)
r groups would be on the inside, hiding away from water
nonpolar, uncharged amino acids
hydrocarbon chains may have N or S atoms
r groups would be on the inside, hiding away from water
charged amino acids
contain a literal charge
contain negatively charged acids (eg COO-)
contain positively charged bases (eg NH3+)
proteins structure ( simple description)
made of amino acids + peptide bonds
2 proteins = dimer
3 = trimer
4 =tetramer
primary structure
linear sequence of amino acids joined by covalent peptide bonds
secondary structure
a- helix, beta sheet or random coik
with peptide bonds + hydrogen bonds
tertiary structure
3d folding of a single polypetide chain
with peptide bonds, disulphide, bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, vanderwaals interactions, hydrophobic interactions
stablises the overall shape
quaternary structure
the formation of more than just one polypeptide
all the bonds = tertiary structure
peptide bonds
formed by condensation reaction
2 H FROM NH3+
O from carboxyl
covalent bond
hydrogen bonds
donors ( eg amine or hydroxyl of aa)
have H atom linked to a more electronegative atom of an acceptor ( eg COO or SH)
weak bond w -5kcal energy
disulphide bonds
formed between an oxidation reaction of cysteine molecules
S-S
very strong, form of covalent bonding
ionic bonds
weak in (aq)
NH3+COO-
low/ high ph affects ionic bonds
vanderwaals forces
exist between non polar
typically weak
hydrophobic interactions
exist between hydrophobic molecules far from water
stronger bonds
ph effect on proteins
ph affects proteins by chnaging the protonation state of the charged residues
neutral state of protein
uncharged
isoelectric point or pI
acid
low pH
increase in H+
NH3+ part gets more H+
base
high pH
decrease H+
NH2, negative part
which bonds would be effected by ph
ionic bonds
hydrogen bonds
isoelectric point
ph at which proteins r at zero charge
positive and negative charges are balances
dependent on the r groups
what does the pi also affect
it affects the solubility
proteins interact w each other rather than water
might pecipitate
where solubility is lowest
oblique
angled - external oblique