Lecture 5: Consumers, Prodcuers, and Efficiency of the Market
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does the allocaton of resources mean?
The allocation of resources refers to:
How much of each good is produced
What producers consume it
Which producers consume it
What does welefare economies study?
Welefare economics studies how the allocation of resources affects economic well being
Willingness to pay (WTP)
The maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good
Measures how much the buyer values the good
Will a buyer purchase a good if it’s Price is greater than the WTP?
Since WTP is the maximum price a buyer is willing to spend on a good, a buyer will not purchase a good if it’s price is greater than their WTP
Marginal Buyer
The buyer who would leave the market if P (Price) were any higher
Consumer Surplus
The amount a buyer is willing to pay minus the amount the buyer actually pays
CS= WTP- Price
What is the total CS equal to area wise?
The toal CS is equal to the area under the demand curve above the price from 0 to Q
What is the CS value?
Consumer surplus is the area between the Price and Demand curve from 0 to Q
Above the price value
Can use the area of a triangle to find it
How does a higher price reduce Consumer surplus?
If price is increased, there is a fall in the CS:
The remaining buyers pay a higher price
Some buyers leave the market, since the price is higher
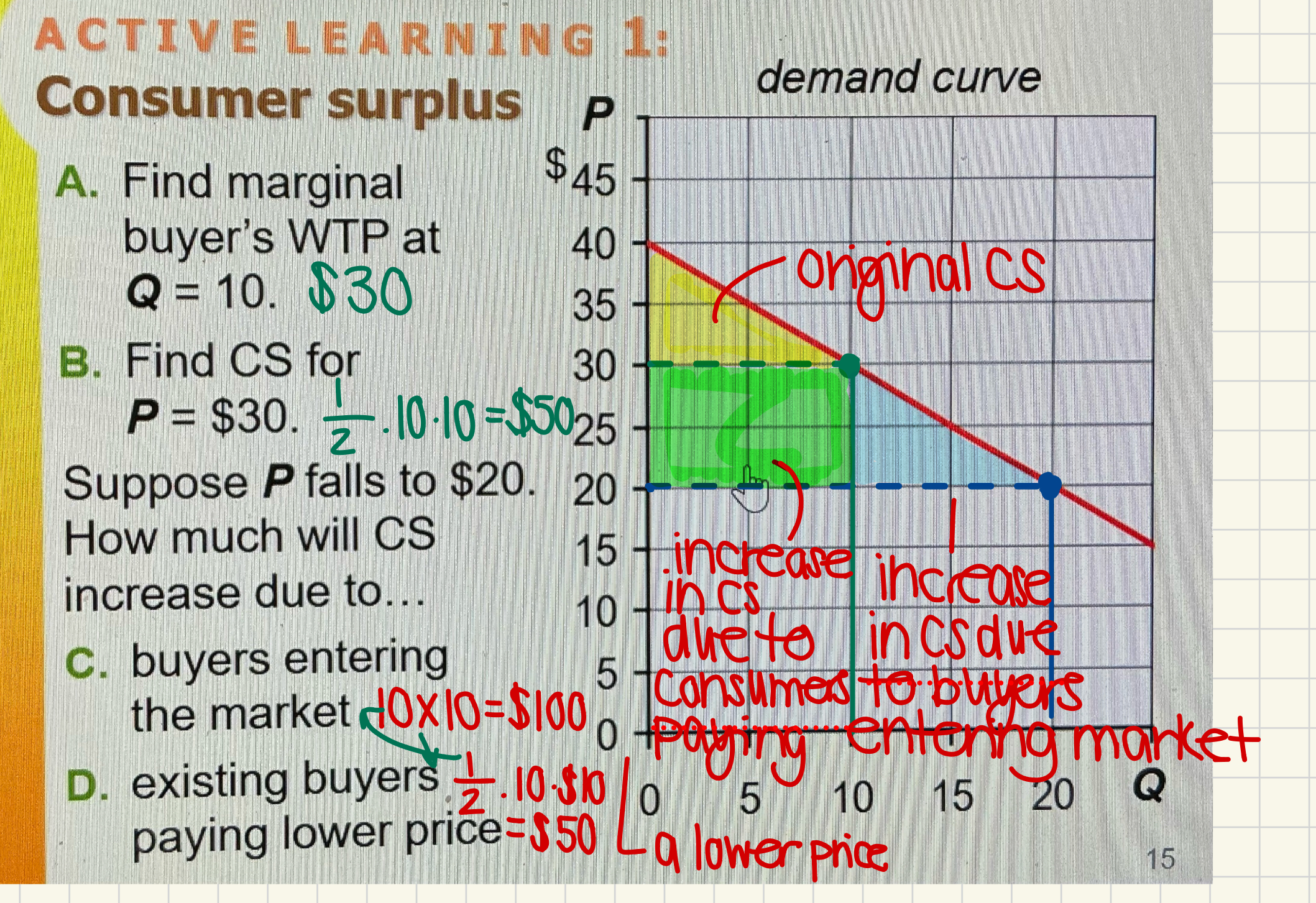
Consumer Surplus Word Problem
Cost
Value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good, for example the opportunity cost
Includes the value of all of the resources used to produce a good, including the value of the seller’s time
When will a seller produce and sell a good?
A producer will produce and sell a good only if the price is greater than their cost
Cost is a measure of willingness to sell
Marginal Seller
The seller who would leave the market if the price were any lower
Producer Surplus (PS)
The amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s cost
PS= Price - cost
What is total PS equal to in terms of the area?
Total PS is equal to the area above the supply curve under the price, from 0 to Q
What is the area of the Producer Surplus (PS)?
PS is the area between the Price and the Supply curve from 0 to Q
How does a lower price influence PS?
When there is a lower price, this influences PS:
Decrease in PS, from seller receving a lower price
Decrease in PS from sellers leaving the market
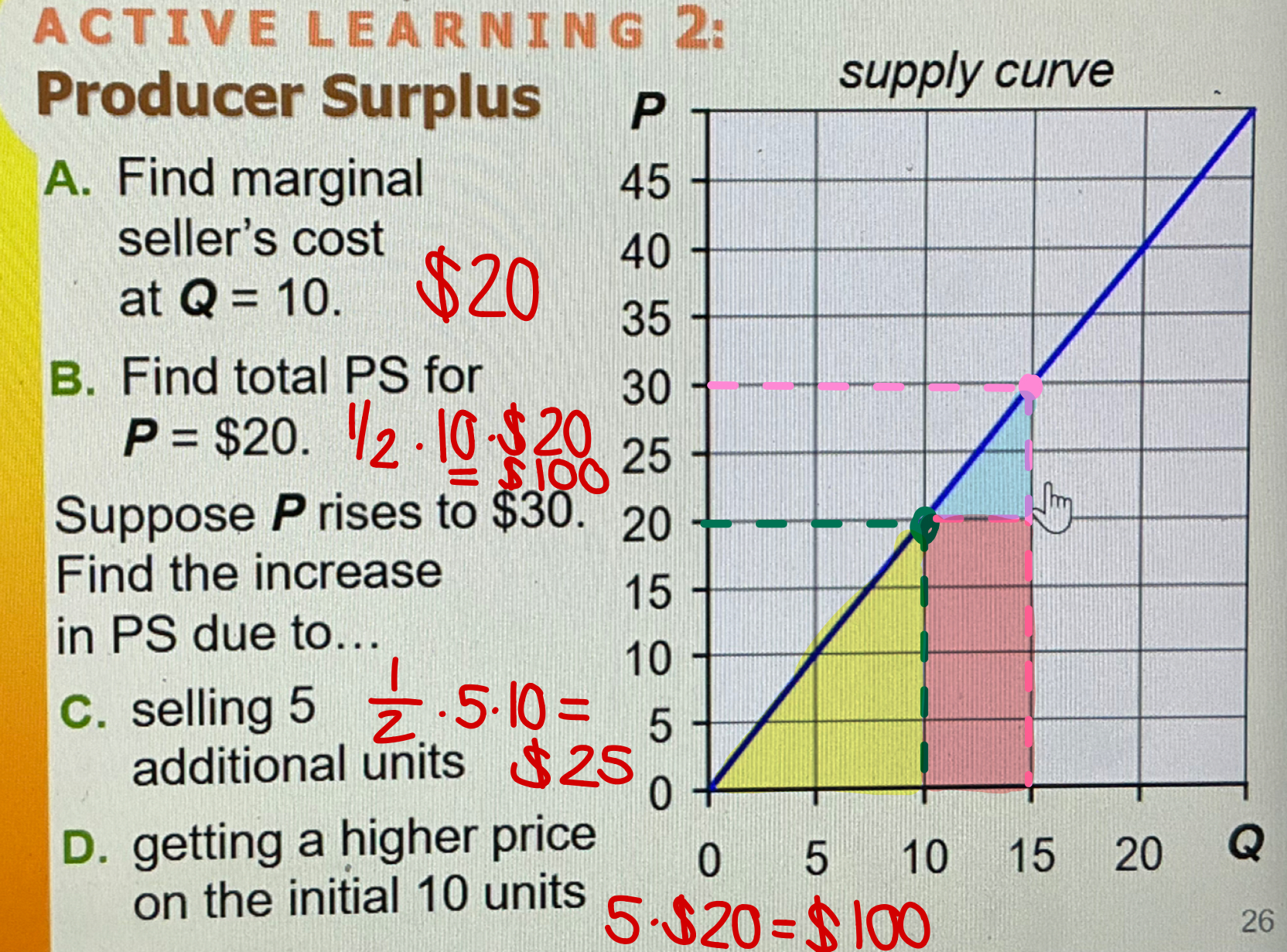
Producer Surplus Example
What do CS and PS measure?
The CS measures the buyer’s benefits from participating in the market, while the PS measures the seller’s benefit from participating in the market
What is total surplus?
Total surplus= CS + PS
Total gains from trade in a market
Total Surplus (broken down)
TS= CS + PS
TS= (Value to buyers)- (amount paid by buyers) + (amount received by sellers)- (Cost to sellers)
TS= Value to buyers- cost to sellers
When is the allocation of resources efficient?
The allocations of resources is efficient if it maximizes total surplus
Efficient when changing the quantity of a good wouldn’t increase total surplus
Goods are made by producers with the lowest cost
Goods are consumed by buyers who value them the most