Topic 5- Light and the EM Spectrum (copy)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
reflection
a wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but stays in the original medium
where is the angle of a wave measured?
between the wave and the normal
angle of incidence (i) / angle of reflection (r)
angle of a wave approaching/leaving the boundary
law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
refraction
the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, caused by a change in its speed
when light rays pass from less dense to more dense media, the light bends…
towards the normal (slows down)
when light passes from a more dense medium to a less dense medium, it bends…
away from the normal (speeds up)
which wave properties change during refraction?
speed and wavelength
NOT frequency (frequency determines colour)
Critical Angle
the minimum angle of incidence for TIR to occur at a boundary
Total Internal Reflection (TIR)
ray is reflected back into the medium instead of being refracted at the boundary. occurs when angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle and the incident medium is denser than the second.
specular reflection
reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction, so i=r (reflection can be seen clearly)
Diffuse reflection
reflection from a rough surface that causes scattering (light leaves surface in all directions) (gives objects dull appearance)
absorption
energy is transferred from the wave into the particles of a substance
light will be absorbed (and later reemitted as heat) if…
the frequency of light matches the energy levels of the electrons in the substance
how do colour filters work?
they absorb certain frequencies of light and transmit other frequencies
lens power definition
how strongly it focuses the light
lens power (equation + units)
power = 1 / focal length
measured in dioptres
How does shape & focal length affect lens power?
the more curved the lens, the shorter the focal length
The shorter the focal length, the greater the power
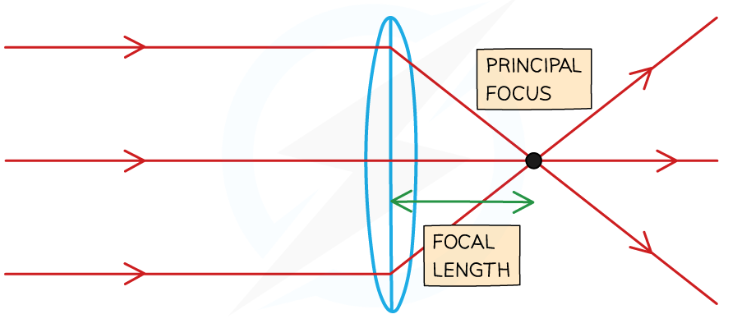
convex lens (other name + what it does)
converging lens
rays of light brought to a focal point/principal focus
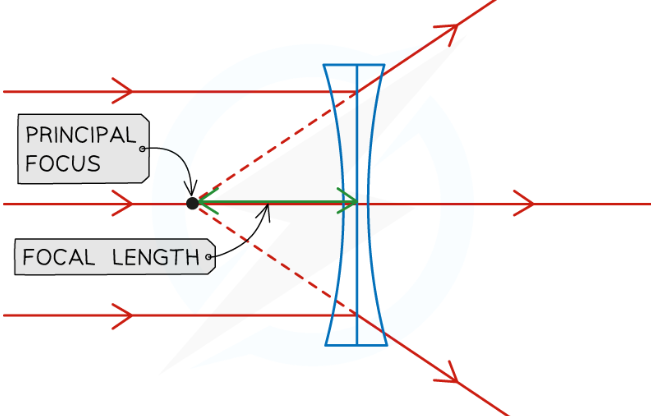
concave lens (other name + what it does)
diverging lens
rays of light diverge from a point
focal point is the point from which rays appear to diverge from (focal length is negative)
real image
formed when the light rays from an object converge and meet each other and can be projected onto a screen
always inverted
virtual image
image formed when the light rays from an object do not meet but appear to meet behind the lens
cannot be projected onto a screen
always upright
3 things to consider when describing an image
real or virtual
magnified or diminished
upright or inverted
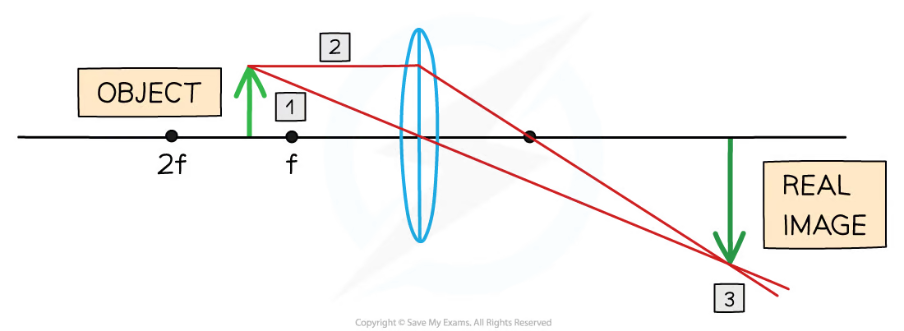
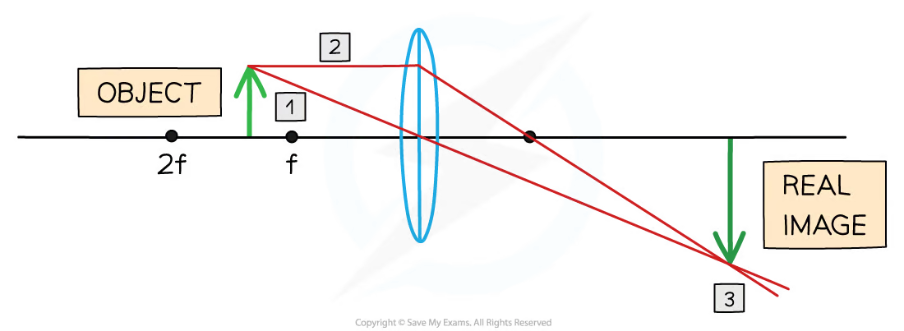
if an object is placed further than the focal length from converging lens, the image will be…
real
inverted
magnified
if an object is placed closer than the focal length from a converging lens, the image will be…
Virtual
upright
magnified
if an object is placed further than the focal length from a diverging lens, the image will be…
virtual
diminished
upright
electromagnetic waves are…
transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
that can travel through a vacuum, all at the same speed
examples of energy transfer by EM waves
microwaves in a microwaves oven transfer energy from the electronics to heat the food inside
all hot objects emit infrared radiation, which can be absorbed by other objects, heating them
the sun emits visible light (so we can see), infrared radiation (heat the earth) and ultraviolet radiation (provides plants with energy)
type of electromagnetic waves (longest wavelength to shortest)
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible light
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
patterns in EM spectrum from radio to gamma waves
Increasing
wave energy, frequency
Decreasing
wavelength
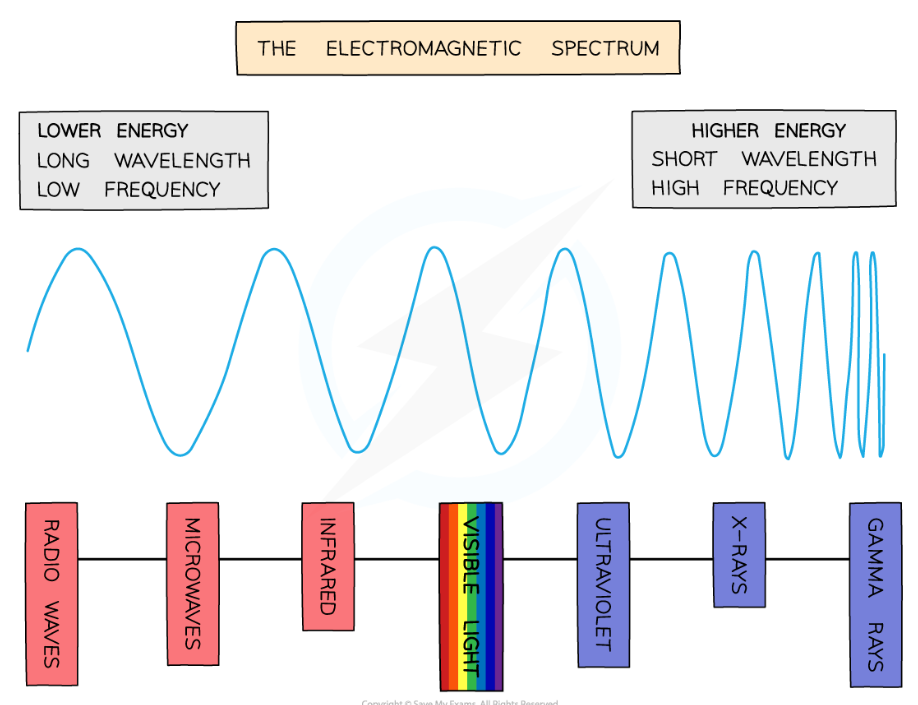
in the visible light spectrum, ____ has the longest wavelength (and lowest frequency), and ___ has the shortest wavelength (and highest frequency)
Red
violet
wavelength and frequency are…
inversely proportional
dispersion
different wavelengths of light change speed (and therefore are refracted) by different amounts.
In visible light, white is split up into all its colours.
EM waves travel ___ in denser substances
slower
when EM waves pass from one medium to another, they can be:
transmitted
absorbed
reflected
refracted
what affects how an EM wave will interact with different substances?
the wavelength of the waves and the substance itself
as frequency of waves increases, energy…
also increases
which types of EM waves are ionising?
higher frequency than visible light (UV, X-rays, Gamma rays)
ionisation
removing electrons from an atom leaving a charged ion
what affects the danger of EM waves?
frequency (higher frequency = highly ionising = high danger)
intensity of radiation (how ‘concentrated’)
potential dangers of excessive exposure to EM radiation
microwaves: internal heat damage to body cells
infrared: skin burns
UV: eye damage, sunburn, skin cancer
X-rays/Gamma rays: damage/kills cells, leading to mutations and cancer
uses of radio waves
broadcasting/communications (radio + tv)
uses of microwaves
heating food
communication (wifi, mobile phones, satellites)
uses of infrared
heating and cooking
thermal imaging
remote controls
optical fibres
security systems
uses of visible light
vision (duh!)
photography
illumination
uses of UV
security marking (on bank notes)
fluorescent lamps
disinfecting water
sunbeds
uses of x-rays
x-ray imaging for medicine, airport security and industry
uses of gamma rays
sterilising food + medical instruments
detecting + treating cancer
interaction of a EM wave with an atom
when it collides, it can be absorbed by an e-
this e- gains energy and jumps up an energy level
it then moves back down to a lower energy level and emits this energy as another EM wave
EM waves can be absorbed and emitted by atoms over a wide range of frequencies, but the energies that tend to be emitted by electron transition are:
visible and UV (sometimes X-rays)
higher energy waves can only be emitted when an EM wave interacts with…
the nucleus
how are radio waves produced + received
by connecting antenna to a high frequency a.c. power source
oscillation of charge produces radio waves of same frequency
radio waves absorbed by an aerial at a distance,
inducing an alternating current with the same frequency as the transmitted wave
all bodies emit…
(a spectrum of) thermal radiation (in the form of EM waves) e.g. infrared/visible
temperature of the body affects the _______ of any emitted waves
intensity and wavelength distribution
the hotter an object, the more ____ it radiates in a given time
infrared radiation
as the energy and therefore heat of an object increases, the wavelength…
decreases
Thermal equilibrium
when an object reaches a point of constant temperature when it absorbs radiation at the same rate it emits radiation.
if a body absorbs radiation at a higher rate than it emits, it…
heats up (and vice versa)
Greenhouse Effect and its effect on Earth’s teperature
majority of Earth’s heat received from thermal radiation from Sun
Earth emits its own thermal radiation (of a longer wavelength, so the Earth is significantly cooler than the Sun)
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb and emit back some of this radiation in all directions, trapping some in the atmosphere
some emitted heat passes through atmosphere into space
this process makes the Earth warmer
the temp of the Earth depends on a number of factors, e.g….
the rate that light and infrared radiation from the sun are:
reflected back into space
absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere/surface
emitted from earth’s atmosphere/surface into space