exam 4 shit i dont know
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
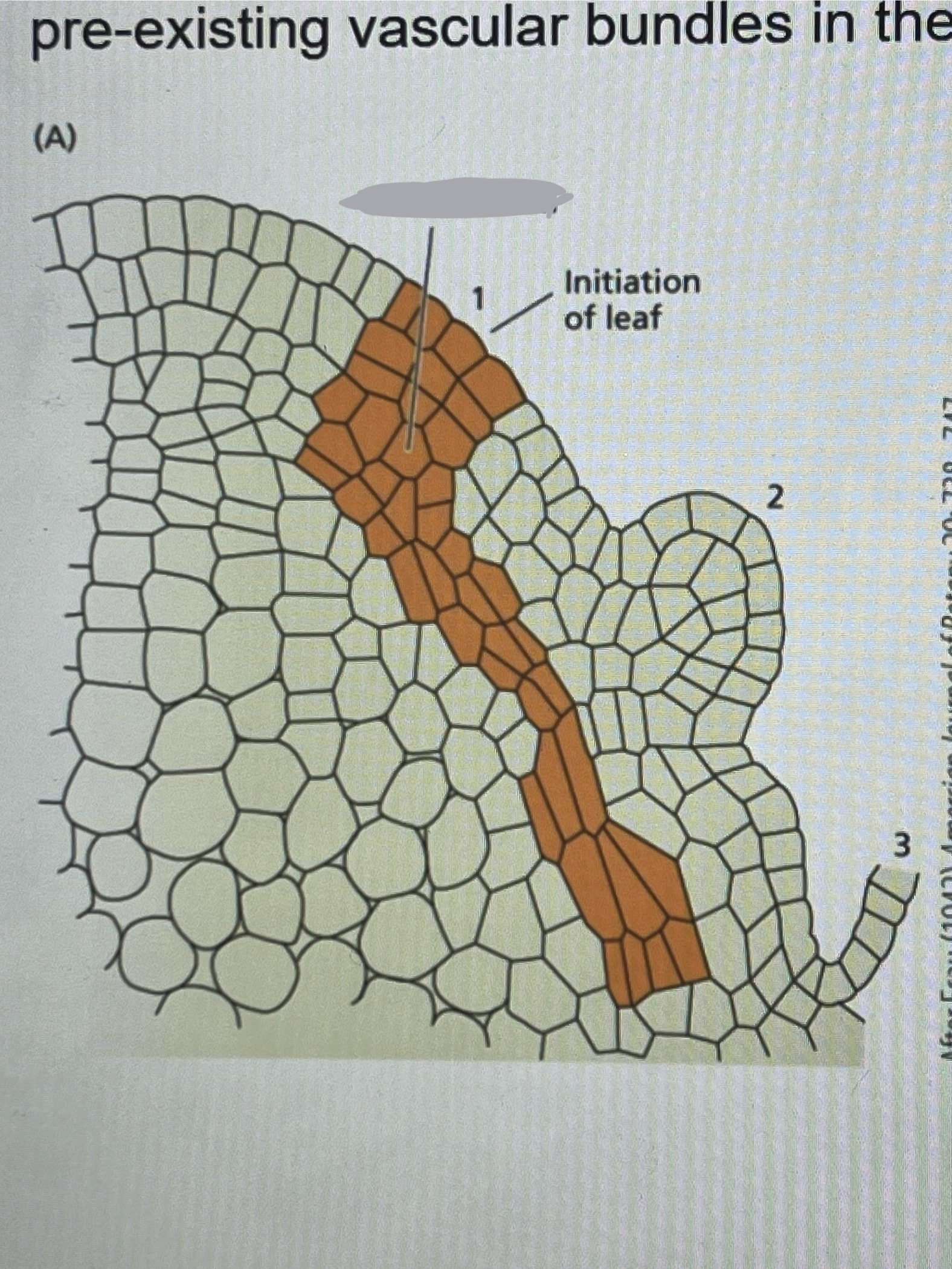
Procambium
Initiate where the new leaf will form
Stages of leaf senescence
Initiation: from nitrogen sink to source. Photosynthesis declines
Degenerative: cells break down
Terminal: cell death and leaf abscission
Monocarpic
Plant puts all its resources into one reproductive event and then dies. Usually annual or biennial plants.
Polycarpic
Perennials that reproduce many times in a life time
Evocation
When the plant is committed to flowering. Could still require secondary signal
Phase change
Meristem changes it fate from veg to flower
Plant phases
juvenile
Vegetative adult
Reproductive
ARP genes
Encode myB transcription factors and antagonize KNOX genes functions in leaf polarity and structure
aysemetric leaf 1
Roughsheath2
Phantastica
Totipotent
Versatile cells that can differentiate into any cell type
Pluripotent
Further into development, more restricted in differentiation potential
Coincidence model
Signal within circadian rhythms (CO) must coincide with daylight oscillations in 24hr period.
Constans (CO)
Long day - activator
Short day - inhibitor
Stable in the light and degrades with dark. Activates FT
Floral identity genes
Leafy
APATELLA1
Organ identity genes
ABC model
A - APATELLA2
B - APATELLA3/PISTILLA
C - AGAMOUS
Central zone (SAM)
slowly, dividing stem cells at top of the shoot
Maintain stem cell pop
Peripheral zone (SAM)
Cells on the edges
Divide quickly
Differentiate
Rib zone (SAM)
cells in the middle
Divide quickly
Ground tissues and support
L1 layer (SAM)
Epiderm layer
L2 layer(SAM)
Ground tissue layer
L3 layer(SAM)
Internal tissues
Genes that control adaxial fate
ARP
Genes that control abacial fate
KANADI
Statoliths
Starch grains/amyloplast. Settle to bottom of cell in root cap to provide directional info
Expansions
Enzyme with acidic pH optimum that loosens cell wall polymers for expansion
3 phases of germination
Imbibition
Prep
Post germ ( radical free )
Monocot seed
Nutrients in starchy endosperm
Dicot seed
Nutrients in cotlyedon at maturity
Aleroune layer
Embryo produces GA and transfers to
the endosperm to convert starch to glucose
Alurone with GA stim amylase prod to