Psychology In Your Life (chapter 9)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Achievement motivation
The need, or desire, to attain a certain standard of excellence.

Affect-as-information theory
People use their current moods to make decisions, judgements, and appraisals, even if they do not know the sources of the moods.

Androgens
A class of hormones that are associated with sexual behavior and are more prevalent in males: testosterone is one example.

Arousal
Physiological activation (such as increased brain activity) or increased autonomic responses (such as increased heart rate, sweating, or muscle tension.)
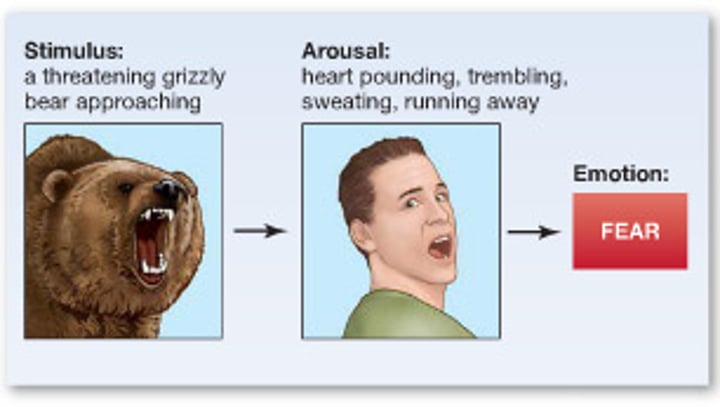
Cannon-Bard theory
Emotions and bodily responses both occur simultaneously due to how parts of the brain process information.
Display rules
Rules that are learned through socialization and that dictate what emotions are suitable in certain situations.

Drive
A psychological state that, by creating arousal, motivates an organism to engage in a behavior to satisfy a need.
Incentives
External objects or external goals, rather than internal drives, that motivate behaviors.

Motivation
Factors of differing strength that energize, direct, and sustain behavior.

Primary emotions
Evolutionarily adaptive emotions that are shared across cultures and associated with specific physical states; they include anger, fear, sadness, disgust, happiness, and possibly surprise and contempt.

Secondary emotions
Blends of primary emotions; they include remorse, guilt, shame, submission, and anticipation.
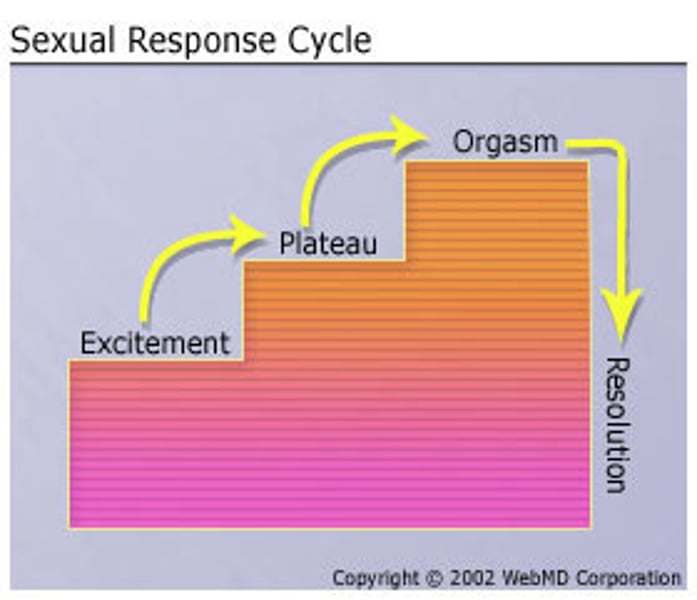
Sexual response cycle
A four-stage pattern of physiological and psychological responses during sexual activity.
Sexual strategies theory
Women and men have evolved distinct mating strategies because they have faced different adaptive problems over the course of human history. The strategies used by each sex maximize the probability of passing along their genes to future generations.

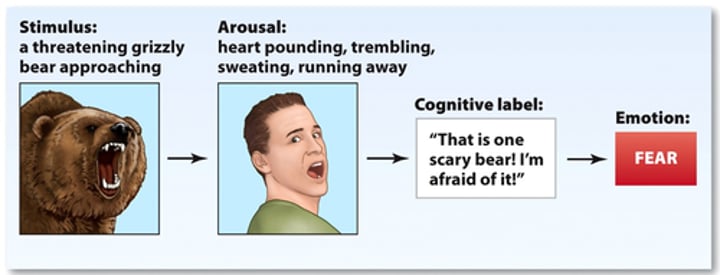
Two-factor theory
How we experience on emotion is influenced by the cognitive label we apply to explain the physiological changes we have experienced.
Emotion
Feelings that involve subjective evaluation, physiological processes, and cognitive beliefs.

Estrogens
A class of hormones that are associated with sexual behavior and are more prevalent in females: estradiol is one example.

Extrinsic motivation
A desire to perform an activity because of the external goals that activity is directed toward.

Ghrelin
A hormone that is associated with increasing eating behavior based on short-term signals in the bloodstream.

Guilt
A negative emotional state associated with anxiety, tension, and agitation.

Intrinsic motivation
A desire to perform an activity because of the value or pleasure associated with that activity, rather than for an apparent external goal or purpose.

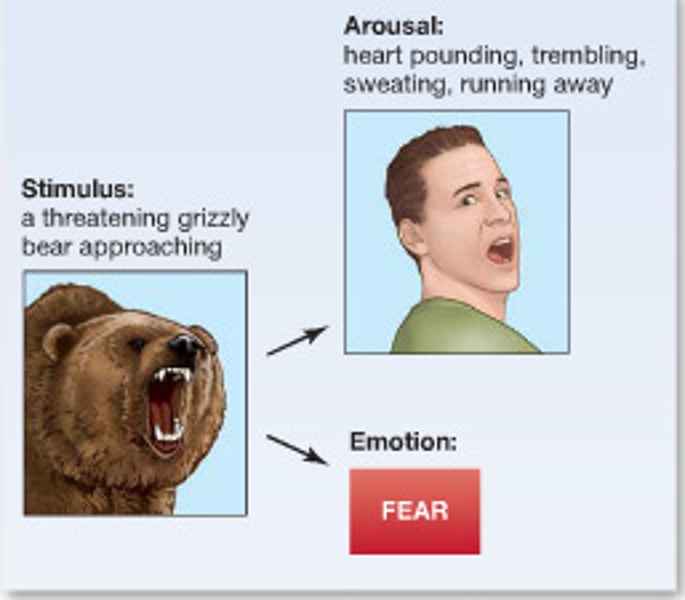
James-Lange theory
Emotions result from the experience of physiological reactions in the body.
Leptin
A hormone that is associated with decreasing eating behavior based on long-term body fat regulation.
Need
A state of biological or social deficiency.

Need hierarchy
An arrangement of needs, in which basic survival needs must be met before people can satisfy higher needs.
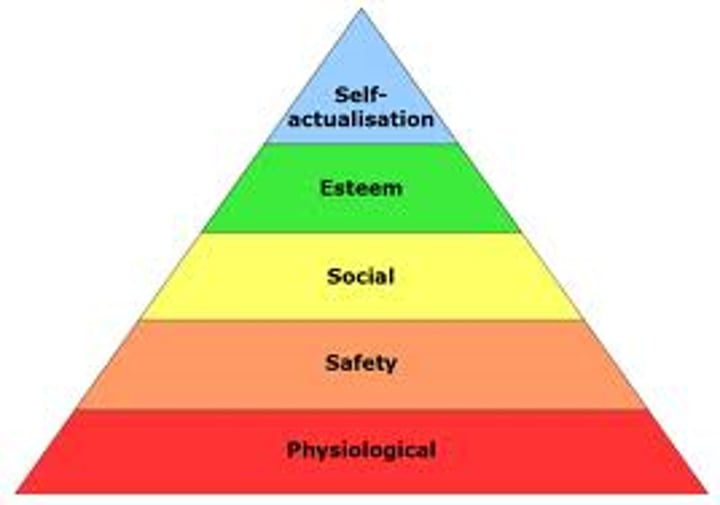
Need to belong theory
The need for interpersonal attachments is a fundamental motive that has evolved for adaptive purposes.
