chp 5 receiving, storing, inventory. ethics
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
what are the elements for receiving activity (8)
-Competent personal
-Facilities and equipment
-Specification
-Critical control in receiving
-Sanitation
-Adequate supervision
-Scheduled hours
-security
define receiving
Activity for ensuring that products delivered by suppliers are those that were ordered
receiving involved what besides acceptance and signing of delivery
-verifying that quality, size, and quantity meet specifications
-the price on the invoice agrees with the purchase order
-perishable goods are tagged or marked with the date received
what & or revenue is spent on food purchasing in foodservice establishment
30-50%
competent personell
Responsibility for receiving should be assigned to a specific member of the foodservice staff and person assigned needs to be well trained to it correctly
facilities and equipment
want there to the enough space and equipment to perform receiving correctly
-like thermometer, lifting equipment, storage area
specifications
-the employee who is receiving should know the standards the supplier must meet
-delivery should be checked against the specifications
- and copy of all purchase orders should be provided to the receiving personnel
critical control in receiving
receiving is MAJOR critical control point for many foods so need use HACCP
sanitation for receiving
receiving area should be designed for easy cleaning and have cleaning supplies conveniently located
adequate supervision
The management of a foodservice operation should monitor the receiving area at irregular intervals to check security and ensure that established procedures are being followed
scheduled hours
-Suppliers should be directed to make deliveries at specified times.
-Reduces confusion and wasting of tim
security
should have security to prevent internal theft of supplies
(security can help reduce 60% internal theft)
what are the 5 steps of the receiving process
1. Inspection against the purchase order
2. Instructions against the invoice
3. Acceptance and rejection of orders
4. Completion of receiving records
5. Removal of storage
how do we inspect the purchase order
received order needs to be checked against purchase order and all established specifications
-if too many are below tolerance levels it should be rejected
after product have been checked against the purchase order and specifications, what should be done
delivery should be compared to the invoice prepared by the supplier
what are the 3 main receiving methods
invoice received, blind receiving, electronic receiving
what is invoice receiving
The receiving clerk checks the quantity of each product against the purchase order. Any discrepancies are noted on both the purchase order and the invoice
-method is quick but can be unreliable if the receiving clerk does not compare the two records and only looks at the delivery invoice
blind receiving is what
The receiving clerk uses an invoice or purchase order with the quantity column blanked out and records on it the quantity of each product received. This method requires that each product be checked because the amount ordered is unknown
-time consuming for both receiver and deliverer
what is electronic receiving
Technology is speeding up the receiving process, although it is still too expensive for small foodservice operations.
-UPC (universal product code) makes this easy — is the barcode
if quantites and prices are correct and quality is correct, what should be done
invoice should be signed
what is completion of receiving records
The receiving record provides an accurate list of all deliveries of food and supplies, date of delivery, supplier’s name, quantity, and price data
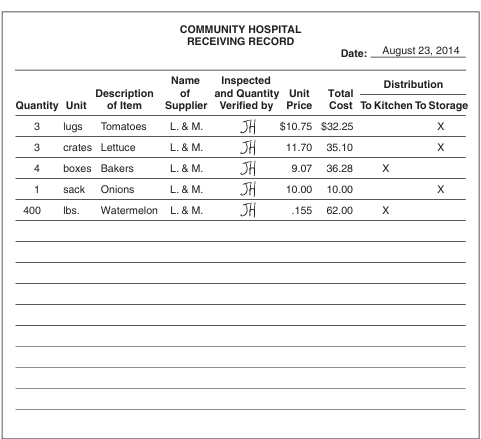
removal to storage
Products should be transferred immediately from receiving to the secure storage area
spoilage and deterioration may occur if refrigerated and frozen products are held at room temperature for any period of time
after food has been received properly, we move onto what
storage
define storage
Holding of products under proper conditions to ensure quality until time of use
what are major considerations in ensuring quality of stored food (3)
Proper storage maintenance, temperature control, and cleaning and sanitation
what is a major concern when storing
prevention of theft and pilferage
define theft
premeditated burglary
define pilferage
inventory shrinkage caused by employees stealing food
when should food be stored
ll foods should be placed in storage as soon as possible after delivery, unless they are to be processed immediately. Dry groceries, canned foods, and staples should be placed in dry stores. Perishable foods must be placed in refrigerated or frozen storage promptly
storage facilities should be: (floors, cleanability, doors, windows, ventilation, temp, humidity)
-Slip resistant floors
-Easy to clean
-Light colored walls and smooth surface
-Doors should be limited
-Windows opaque
-Good ventilation
-50-70F
-Humidity not above 60% (50-60% is fine)
low temp storage units can be categorized into what 3 types
refrigerators, tempering boxes, storage freezers
define refrigerators
Storage units designed to hold the internal temperature of food products below 41°F
define tempering boxes
Separate units for thawing frozen foods, specially designed to maintain a steady temperature of 40°F regardless of room temperature or product load.
define storage freezers
Separate units for thawing frozen foods, specially designed to maintain a steady temperature of 40°F regardless of room temperature or product load.
what are the 3 types of thermometers needed
remote reading thermometer, recording thermometer, and refrigerator/freezer thermometer
what humidity for most foods, for perishable foods
between 75-95% for most foods
-85-95% for perishable foods
what is remote reading thermometer
Placed outside the unit to permit reading the temperature without opening the door
what is recording thermometer
Mounted inside or outside the unit, continuously records temperatures in the unit or transmits temperatures to computer for tracking.
what is refrigerator/freezer temp
Mounted or hung on a shelf in the warmest area inside the unit.
temps should be checked how many times a day
2
what foods absorb odors? give off odors?

critical control in storage
Storage can be a critical control point for food items. The microbiological safety of raw food products while in storage before production is critical. The HACCP flowchart should identify storage procedures.
INVENTORY NOW
what are a significant investment of the orgs assets?
materials held in storage
for inventory to control to be effective what should be done (4)
access to storage should be limited, authorized people to remove goods from storage, and inventory levels monitores, as well as recordkeeping
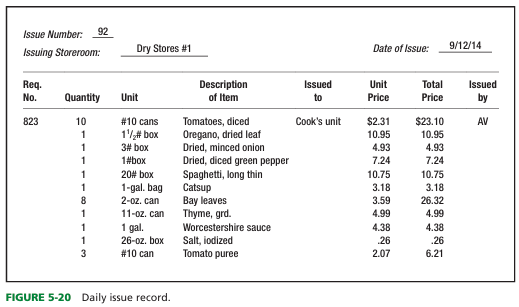
what do we mean by issuing products
Issuing is the process used to supply food to production units after it has been received
WHAT IS IT: entails control of food and supplies removed from storage
what are direct issues/purchases?
Products sent directly from receiving to production without going through storage
-For foods that will be used the day they are delivered
what are storeroom issues?
products are issued from a storage area when needed for production or service
-for food received but not used that same day
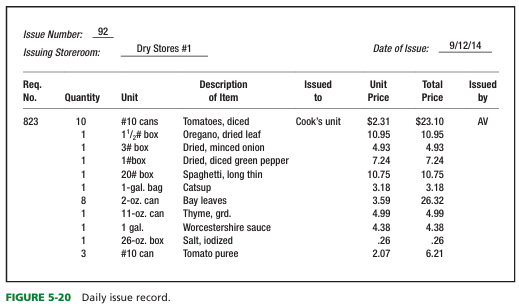
control of issuing from storage has what 2 important aspects:
-First, goods should not be removed from the storeroom without proper authorization
-Second, only the required quantity for production and service should be issued
inventory records contain what 4 basic objectives
-Provision of accurate information of food and supplies in stock
-Determination of purchasing needs
-Provision of data for food cost control
-Prevention of theft and pilferage
define physical inventory
Periodic actual counting and recording of products in stock in all storage areas
-usually done at end of each month

what is the simplest way to do food cost

For inventories conducted as infrequently as 2 or 3 months, daily food cost is determined
computing the cost or direct and requisition issues
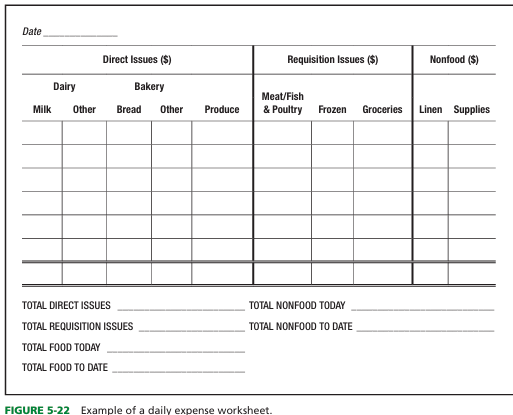
requisition issues are made only when
on requisitions from using units and are taken from inventory
define perpetual inventory
Purchases and issues continuously are recorded for each product in storage, making the balance in stock available at all times.
perpetual inventory is usually restricted to only what products
those in dry and frozen storage
define Just-in-time (JIT) purchasing
Purchasing of products for immediate production and consumption by the customer without having to record it in inventory records.
what is the technique of maintaining assets at desired quantity levels
inventory control
what permits managers to conduct physical inventory and calculate the value of stock faster than manual operation
bar codes and scanning technology
define universal product code (UPC)
System for uniquely identifying products that consists of a rectangular box with vertical lines of various widths
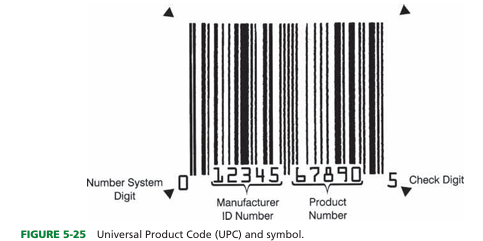
what are the 4 inventory control methods
-ABC method
-mini-max method
-economic order quantity method
-inventory valuation method
what is a indicator that can be used to monitor the effectiveness of inventory control
inventory turnover
define inventory turnover
Estimate of how rapidly product is being brought in and used.
formula for inventory turnover
food cost/average food inventory
define the ABC method
Tool for classifying products as A, B, or C according to value, with A being the highest value
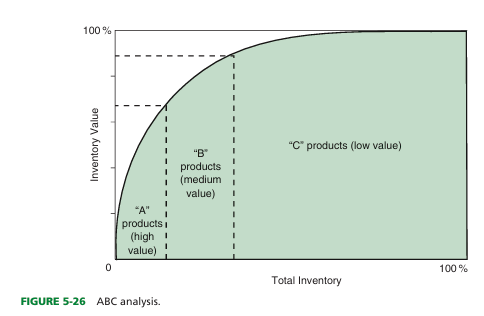
what is the principle for ABC method
that effort, time, and money for inventory control should be allocated among products according to their value
high, medium, and low value (what letter assigned, what % of inventory they represent, and % of total inventory they account for
-The high-value A products represent only 15 to 20% of the inventory but typically account for 75 to 80% of the value of total inventory.
-The medium-value B products represent between 10 and 15% of total inventory value and 20 to 25% of the products in inventory.
-C products are those whose dollar value accounts for 5 to 10% of the inventory value but make up 60 to 65% of the inventory
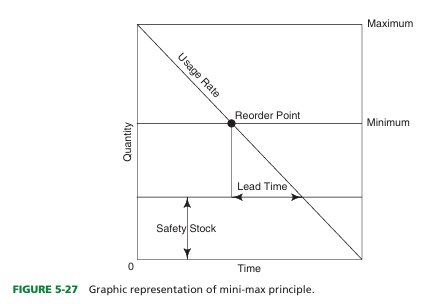
define mini-max method
Tool for controlling inventory by establishing lower and upper levels for each product in storage.
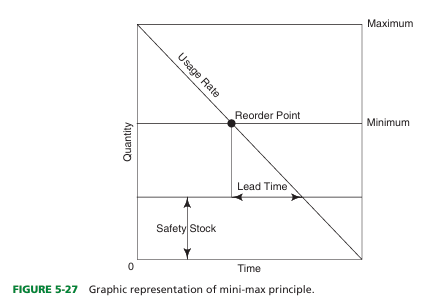
what is the safety stock in min-max method
Backup supply to ensure against sudden increases in product usage rate.
-There instead of minimum being 0
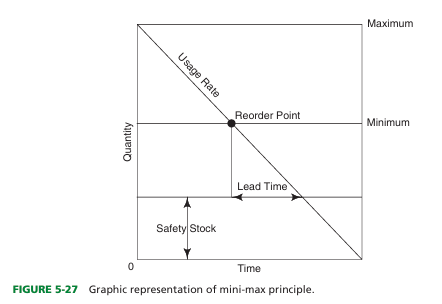
define lead time
Interval between the time that a requisition is initiated and receipt of the product.
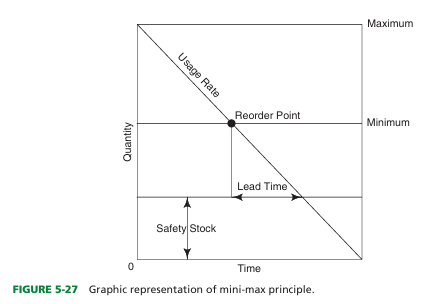
define usage rate
How rapidly a product is used
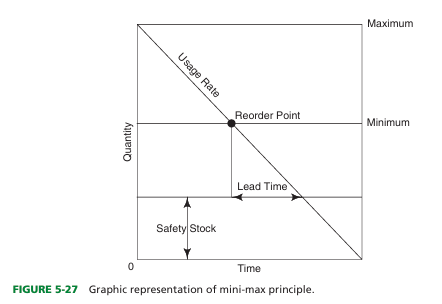
define reorder point
Lowest stock level that safely can be maintained to avoid emergency purchasing.
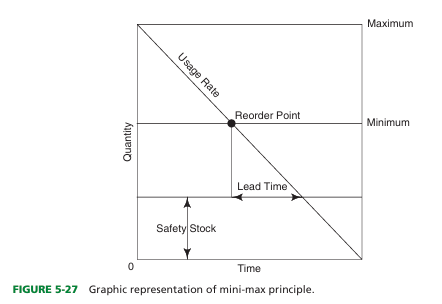
reorder minimum inventory
Lowest quantity that safely can be maintained in inventory to avoid a stock-out or emergency purchasing
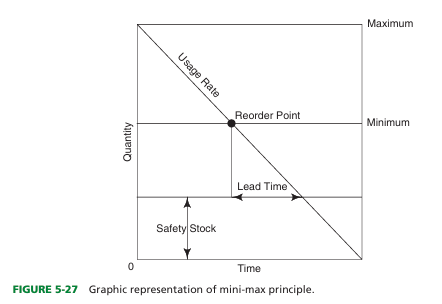
The difference in the safety stock amount and the minimum inventory amount occurs because
of impact of time and usage
what is impact of time
he impact of time occurs because a product will not be delivered immediately after it is ordered, and it will take time (sometimes days) to get product into the organization once it is ordered.
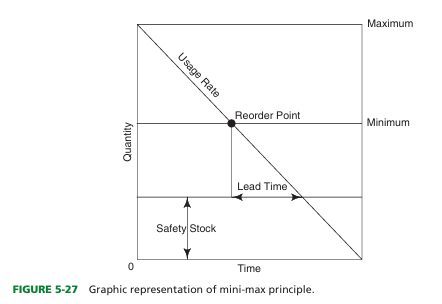
what is impact of usage
he impact of usage is that products continue to be used after that product is reordered, so the amount of ordered product on hand when a delivery arrives is less than what it was when the order was placed
what is economic order quantity (EOQ) method
Inventory concept based on a sensible balance of ordering cost and holding cost
-the ordering cost is a curve diminishing in ordinates as the abscissae, the order quantities, increase
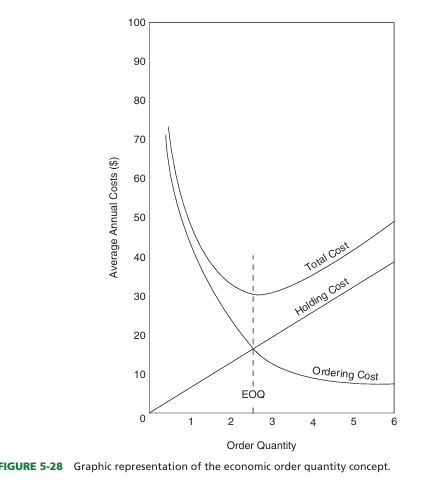
Ordering cost diminishes rapidly as the size of the orders is ______, and holding cost of the inventory ______directly with the size of the order.
increased; increases
objective of EOQ method
to determine the relationship between the ordering cost and the holding cost that yields the minimum total cost
what is the ordering cost is EOQ
includes the total operating expenses of the purchasing and receiving departments, expenses of purchase orders and invoice payment, and data processing costs pertinent to purchasing and inventory
what is the holding cost in EOQ
the total of all expenses in maintaining an inventory and includes the cost of capital tied up in inventory, obsolescence of products, storage, insurance, handling, taxes, depreciation, deterioration, and breakage.
assumptions made with EOQ (7)
-total annual usage is known and constant.
-Withdrawals are continuous at a constant rate.
-Quantity purchases are available instantly.
-Shortages are not tolerated.
-Unit cost is constant.
-Ordering cost is constant.
-Unit cost of inventory products is constant.
EOQ not suitable for most food servive orgs because
because of a variable demand for certain food products, seasonal menu changes, and indefinite lead times.
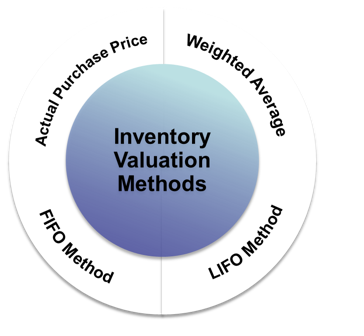
what are the 5 types of valuation methods
actual purchase price, weighted average, FIFO, (first in, first out), LIFO (last in, first out), and latest purchase price
every accounting period of generally 1 year, an accounting cycle usually begins and ends each month. Hence, inventories are taken monthly and the dol lar value is included as an asset, or a debit, on the monthly balance sheet. A beginning and ending inventory occurs each month; the ending inventory becomes what?
the beginning inventory for the next month.
define actual purchase price
Inventory valuation method involving pricing the inventory at the exact price of each product
define weighted average
Inventory valuation method in which a weighted unit cost is used and is based on both the unit purchase price and the number of units in each purchase.
define FIFO
first in, first out
-The oldest products in the storeroom are used before the newest ones.
-The ending inventory reflects the current cost of products because inventory is valued at the prices for the most recent purchases
define LIFO
Last in, first out
-based on the assumption that current purchases are largely, if not completely, made for the purpose of meeting current demands of production.
-The purchase price of the oldest stock, therefore, should be charged out first
define latest purchase price
Inventory valuation method in which the last price paid for a product is used
ETHICS
define ethics
Principles of conduct governing an individual or business.
define personal ethics
Person’s principles derived from religion, values, morals, or philosophy of life that govern conduct.
define business ethics
- Self-generating principles of moral standards to which a substantial majority of business executives in a firm gives voluntary assent.
define code of ethics
Set of rules for standards of professional practice or behavior established by a group.
what is institute for supply management (ISM)
uses Principles and Standards of Ethical Supply Management Conduct as a guide for ethical behavior by members
- touch on many areas in which the buyer might err ethically

3 main categories of ethical issues
1.Efforts to gain inside information about competitors that will benefit competition (e.g., receiving information about competitors through shared suppliers)
2. Activities that allow buyers to gain personal benefits from suppliers (free lunches, dinners, entertainment, trips, and gifts)
3. Activities that manipulate suppliers to benefit the purchasing organization (overstating the seriousness of a problem to obtain concessions from the supplier, threatening the use of a second source, using the organization’s economic clout, and permitting information on bids from other suppliers)