biology 2.1 - eukaryotic cells and organelles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the the function and structure of the cells surface membrane?
Made of lipid and proteins. Has receptor molecules that respond to chemicals. Regulates the movement of substances in and out the cell.
What is the function and structure of the nucleolus?
It is in the nucleus and makes ribosomes.
What is the function and structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
It is a system of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space. Surface is covered in ribosomes. Folds and processes proteins made in the ribosomes.
What is the function and structure of the nucleus?
Contains chromatin (DNA + proteins). Controls the activity by controlling DNA transcription. DNA contains instructions to make proteins.
What is the function and structure of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
There are no ribosomes. Synthesises and processes lipids.
What is the function and structure of the mitrochindrion?
Double membrane with the inner folded to form cristae. Inside is the matrix which contains enzymes involved in respiration. Site of aerobic respiration where ATP is produced.
What is the function and structure of the lysome?
Membrane bound organelle. No clear internal structure. Contains digestive enzymes that that digest invading cells and breakdown worn out organelles.
What is the function and structure of the ribosomes?
Made of proteins and RNA. Has a small and large subunit. No membrane bound. Site of protein synthesis.
What is the function and structure of the nuclear envelope?
Double membrane. Has nuclear pores so substances can move between nucleus and cytoplasm.
What is the function and structure of the Golgi apparatus?
Group of membrane bound flattened sacs. Vesicles often around. Processes and packages new proteins and lipids. Makes lysosomes.
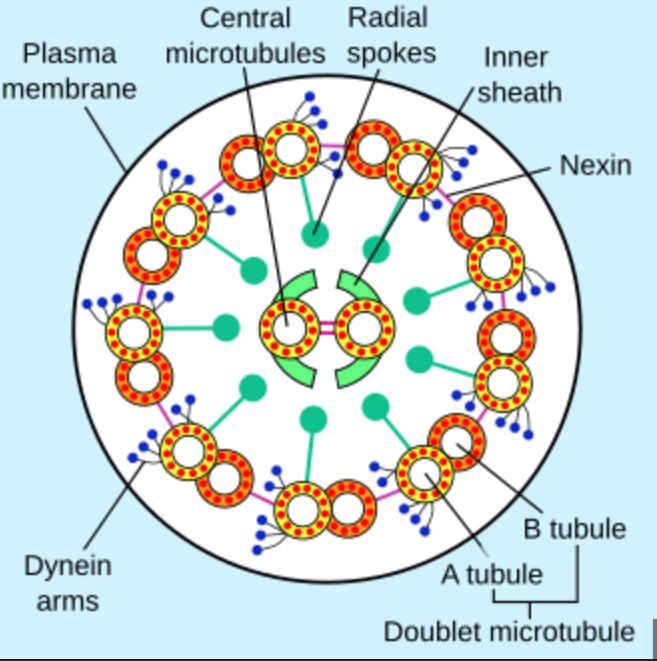
What is the function and structure of the cilla?
Has microtubules in a 9 + 2 formation that allows it to move so it can move substances on the cell surface.
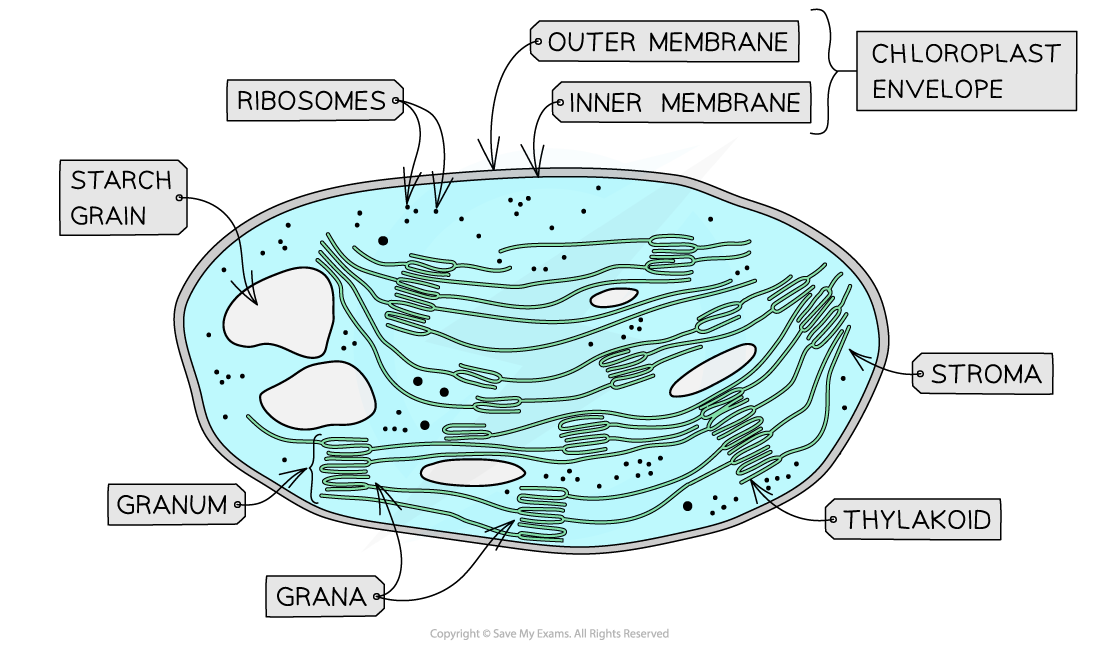
What is the function and structure of the chloroplasts?
Light independent stage of photosynthesis happens in the storms. Flat pieces thylakoid membrane joins grana together. Stacked thylakoid membranes form grana which is where light dependent stage of photosynthesis occurs.
What is the function and structure of the plasmidesma?
Chanel’s for exchanges substances in adjacent plant cells.
What is the function and structure of the vacuole?
Compartment containing cell sap.
What is the function and structure of the cell wall?
Made mostly of the carbohydrate cellulose. Supports plant cells.
What is the function and structure of the centrioles?
Small, hollow cylinders made of microtubules. In animal and some plant cells. Involved in separation of chromosomes during cell division.
What is the function and structure of the flagellum?
Surrounded by plasma membrane. 9 + 2 formation of microtubules. Propels cell forwards.