AP Psych Unit 3 Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Last updated 6:30 PM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
sensation
Stimulus in the environment activates sensory receptors and passes on the information to the brain
2
New cards
perception
How our brain organizes and interprets the sensory input
3
New cards
bottom-up processing
Processing the sensory stimulation at the most basic level as it hits your brain
4
New cards
top-down processing
Your brain takes your previous experiences, schemas, etc., and makes the stimulus into what it wants
5
New cards
absolute threshold
the minimum energy needed to produce a sensation
6
New cards
difference threshold
Is the point at which you can discriminate between two stimulus
7
New cards
webers law
quantifying the perception of change in a given stimulus
8
New cards
selective attention
that we can focus on one sensation at a time
9
New cards
cocktail part effect
the ability to focus one's attention a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli
10
New cards
stroop effect
Trying to read “color” words when they are actually colored in a different color
11
New cards
signal detection theory
that we will pick up on “weak” stimulus earlier if you are alert and are expecting it, or if it’s important to you
12
New cards
in-attentional blindness
we only take in a small amount of what we see
13
New cards
change blindness
where people don’t notice major changes in the environment occur
14
New cards
perceptual adaptation
our brain adapts to the way it perceives stimuli
15
New cards
perceptual set
that our assumptions and influences often change our perception
16
New cards
figure/ground
We organize stimuli into figures seen against the background
17
New cards
proximity
Grouping nearby figures together
18
New cards
similarity
Grouping similar items together
19
New cards
continuity
We view smooth patterns
20
New cards
connectedness
Connected stimuli are seen as one unit
21
New cards
closure
We fill in the gaps, close items
22
New cards
depth perception
the ability to perceive the relative distance of objects in one's visual field
23
New cards
Gibson and Walk visual cliff
Mothers tried to coax 6-14-month-olds to cross a Plexiglas plane that appeared to be a drop-off
24
New cards
transduction
the action or process of converting something and especially energy or a message into another form
25
New cards
rods
Black and White
26
New cards
cones
Color
27
New cards
blind spot
the part of the optic nerve leaves the eye
28
New cards
opponent process theory
some receptors are turned on to certain colors and turned off by others
29
New cards
color blindness
we have 3 types of color receptors (red, green, and blue)
30
New cards
cochlea
the spiral cavity of the inner ear, which produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations
31
New cards
basilar membrane
separates incoming sound into its component frequencies
32
New cards
types of taste buds
salt, sweet, sour, bitter, and umami
33
New cards
gate-control theory
in which pain signals can be sent up to the brain to be processed to accentuate the possible perceived pain, or attenuate it at the spinal cord itself
34
New cards
binocular cues
Cues that need both eyes to work in concert (together)
35
New cards
retinal disparity
that our eyes receive slightly different images
36
New cards
convergence of the eyes
the concept that explains that our eyes work at a more inward angle as an object gets closer
37
New cards
monocular cues
many other cues that our brain uses that only rely on one eye
38
New cards
interposition
When an object is placed in front of another, we see the object in front as closer
39
New cards
relative size
If we think we are seeing two similar-sized stimuli, we perceive the smaller image as farther away
40
New cards
texture gradient
The finer texture appears to be farther away
41
New cards
relative height
The higher item in our visual field appears farther away
42
New cards
linear perspective
Parallel lines appear to converge; therefore the closer they are the farther away (and bigger) you perceive an object between them
43
New cards
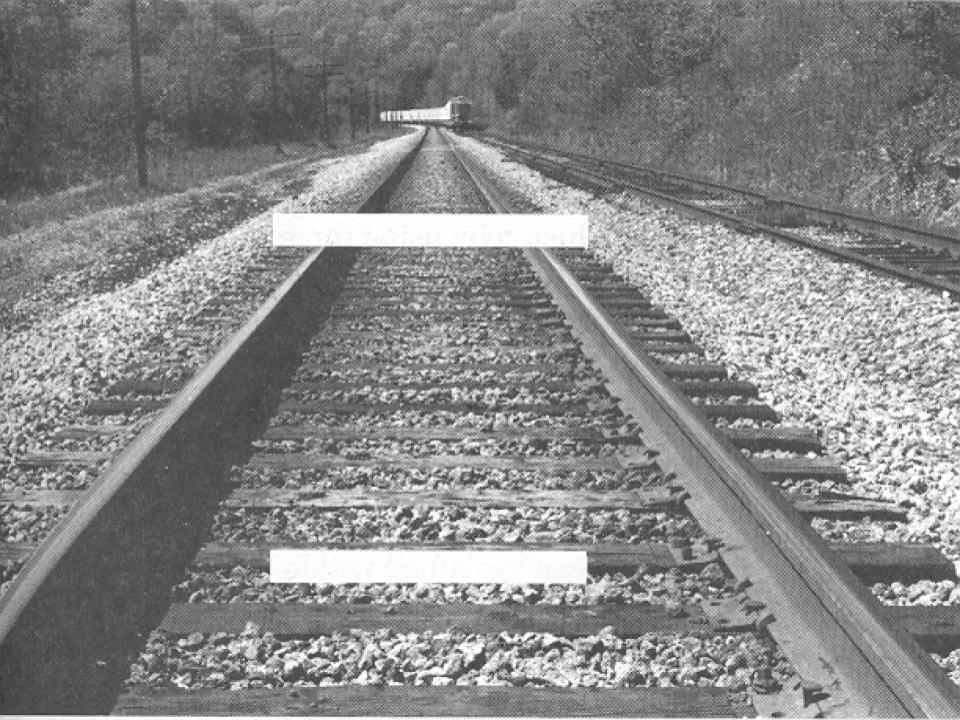
ponzo illusion
a visual illusion in which the upper of two parallel horizontal lines of equal length appears to be longer than the bottom
44
New cards
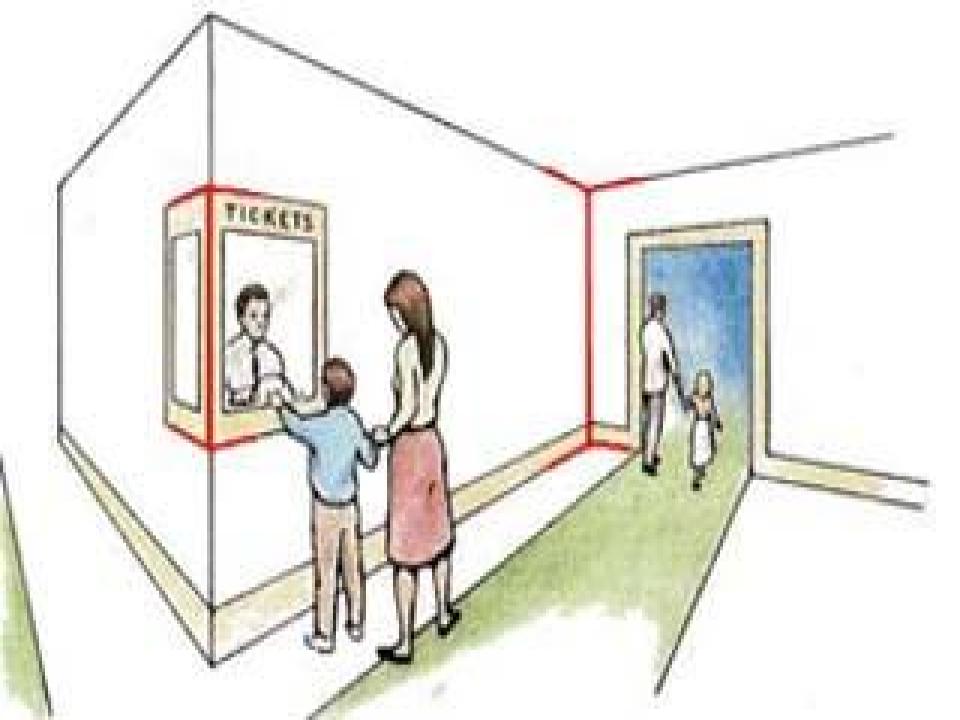
muller-lyer illusion
When a line is connected to inward arrows, we perceive it as smaller, yet the same-sized line with a connected outward arrow will appear bigger
45
New cards
Olfactory Bulb
receives information from the olfactory membrane and sends it to the brain