Topic 12- Reproduction I (Male)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is asexual reproduction?
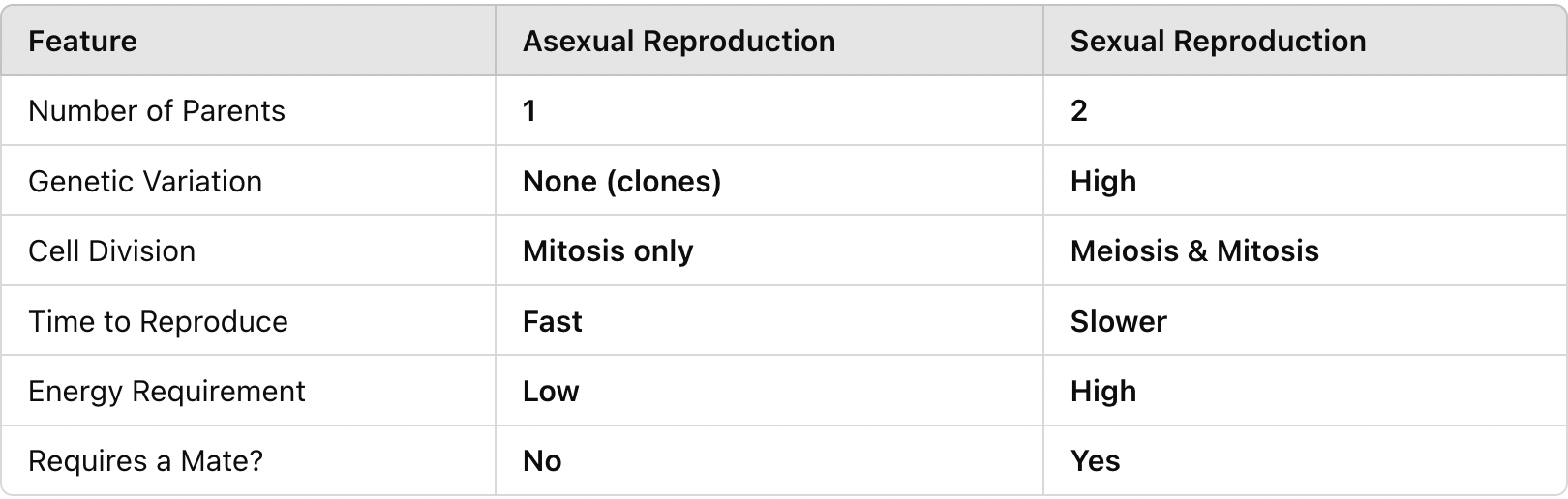
A single parent produces offspring using mitosis, passing on 100% of its genes without gametes.
What are the types of asexual reproduction?
Parthenogenesis (unfertilized diploid eggs develop), budding, fission, and fragmentation (offspring via mitosis).
Why do organisms reproduce asexually?
It is fast, does not require a mate, and passes on 100% of genes.
What is sexual reproduction?
Meiosis produces gametes (n). Sperm (n) fertilizes egg (n) → zygote (2n) forms and develops into an embryo.
Why do organisms reproduce sexually?
Genetic variation among offspring increases adaptability and survival.
What is the function of the male reproductive system?
To produce and deliver sperm for fertilization.
What is the pathway of sperm? (SEVEn UP)
Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Penis.
What are the functions of the testes?
Spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules, and Leydig cells produce testosterone.
What are the three types of cells in seminiferous tubules?
Spermatocytes → Undergo meiosis. Sertoli cells → Support sperm, secrete inhibin & ABP. Leydig cells → Produce testosterone.
What is the function of the epididymis?
Sperm transport, maturation (3 weeks), and storage.
Why is the scrotum important?
It keeps testes 1-2°C cooler, increasing sperm longevity.
What does the penis do?
Delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract.
How does an erection occur?
Nitric oxide (NO) relaxes smooth muscles → arteries dilate → veins compress → blood engorges erectile tissue.
What are the three male accessory glands?
Seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands.
What do the seminal vesicles produce?
60% of semen volume, fructose (energy), and prostaglandins (stimulate uterine contractions).
What does the prostate gland produce?
Anticoagulant enzyme & citrate to keep semen fluid for sperm mobility.
What do the bulbourethral glands secrete?
Mucus to neutralize vaginal acidity and lubricate sperm movement.
What is spermatogenesis?
The process of sperm production in the testes via meiosis.
What is the sequence of spermatogenesis?
Spermatogonial stem cells (2n) divide → Spermatogonia (2n). Spermatogonia mitosis → 1 primary spermatocyte (2n). Meiosis I → 2 secondary spermatocytes (n). Meiosis II → 4 spermatids (n). Spermatids mature into sperm cells (spermatozoa).
How long does spermatogenesis take?
About 7 weeks.
What are the parts of a sperm cell?
Head: DNA & acrosome (enzymes). Midpiece: Mitochondria (ATP for movement). Tail: Flagellum for motility.
What is the main male sex hormone?
Testosterone, which supports spermatogenesis and puberty.
What happens if testosterone is too low?
Sperm production decreases (< 15 million sperm/ml), leading to infertility.
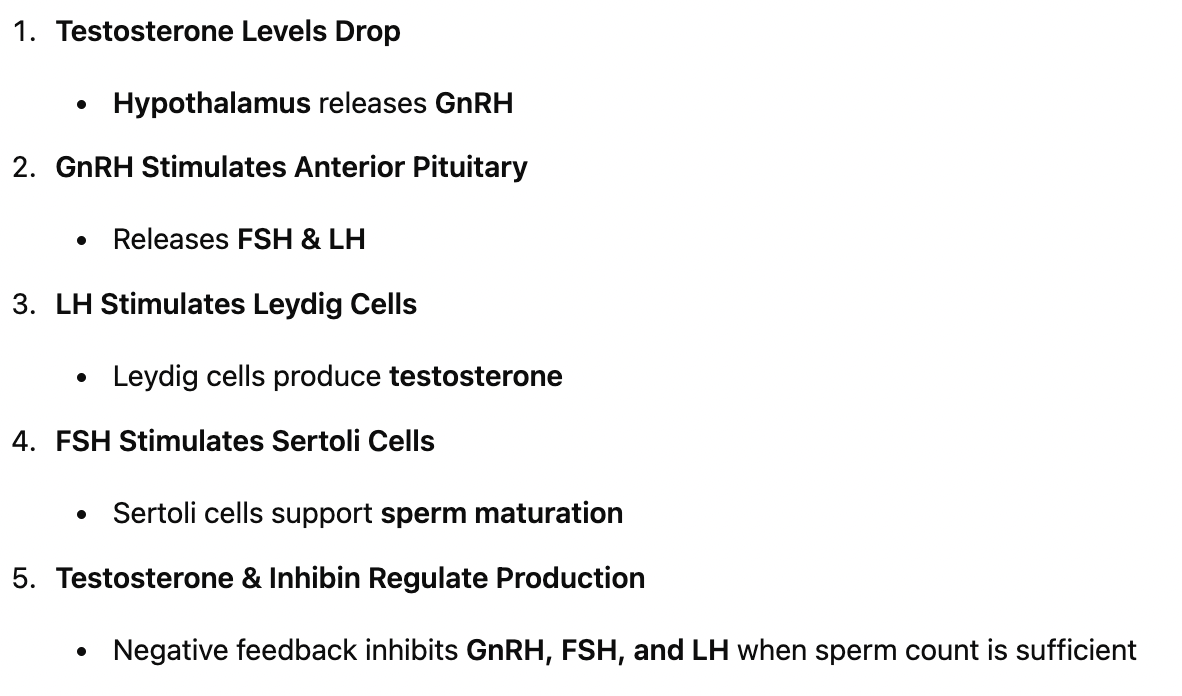
What are the steps in male reproductive hormonal regulation?
Hypothalamus releases GnRH. Anterior pituitary releases FSH & LH. LH → Stimulates Leydig cells → Produces testosterone. FSH → Stimulates Sertoli cells → Supports sperm production.
What are the two key hormones released by the anterior pituitary?
FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) & LH (Luteinizing Hormone).
What is the role of inhibin?
Sertoli cells release inhibin, which inhibits FSH to regulate sperm production.
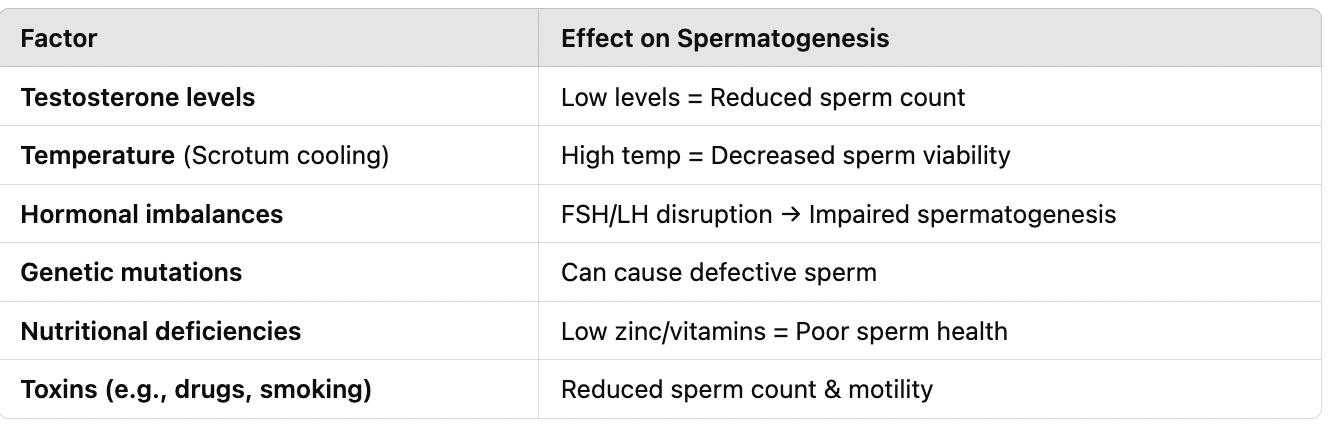
What factors can impact spermatogenesis?
High temperature = reduced sperm viability. Low testosterone = low sperm count. Toxins/drugs = abnormal sperm production. Nutritional deficiencies = poor sperm health.
What factors can impact male reproductive endocrinology?
Steroid use = suppresses natural testosterone. Pituitary disorders = reduce FSH & LH levels. Chronic stress = disrupts GnRH secretion. Obesity = increases estrogen, lowering testosterone.
Sequence animal reproduction in terms of asexual and sexual reproduction.

Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction in terms of the number of parents, genetic variation, cell division, time to reproduce, energy requirement, and mate requirement.
Compare and contrast male reproductive systems with their functions.

Sequence spermatogenesis

Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on spermatogenesis.
Sequence male reproductive endocrinology
Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on male reproductive endocrinology with factors such as low testosterone levels, FSH/LH imbalance, Steroid Use, Pituitary Disorders, Chronic Stress, and obesity
