Unit 1 AP Test Review
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic Perspective
Focusing on the unconscious mind and how it directs behavior. PAST
Biological Perspective
How the brain & body make thought connections, emotions, and memory. BRAIN (chemicals, genes)
Humanistic Perspective
Human growth, potential, and self concept. Being a better person.
Cognitive Perspective
How we take in, store, and retrieve information, and how our perceptions influence our actions. (thinking, memory)
Sociocultural Perspective
Human behavior and how its interpreted in a social and cultural context
Evolutionary Perspective
How natural selection has caused behavior to adapt.
Behaviorist Perspective
How our behavior is shaped by our learning process. (How we learned to fear things, etc.)
Structialist/Introspective Perspective
Study consciousness, how mind was organized and related. Looking inward and considering decisions, thoughts, and feelings.
Ivan Pavlov
Studied conditioning, most famously training a dog to salivate at the sound of a bell.
Behavior
Sigmund Freud
Focused on abnormal behavior, believed all behavior & mental processes are directed by unconscious forces. problems arise from conflict in unconscious mind. Known for free association- saying wtv comes to mind. Ideas were controversial
John B. Watson
Known for behaviorism. Disagreed w/ EVERYONE. Believed psychology should only study what’s observable. Worked with B.F. Skinner
Conditioning
Wilhelm Wundt
Father of psychology. established 1st psychological laboratory in 1879 in Leipzig, Germany. Studied consciousness and how different parts of the mind were related - STRUCTURALISM. Lots of introspection (looking in and considering one’s actions.)
B.F. Skinner
Thought only external factors influenced behavior. Agreed with a lot of the points of John B. Watson
Operational Definition
PRECISE definition of variable being observed so it’s measurable and manageable.
Independent Variable
“Cause” - factor manipulated by experimenter (group 1 gets X, control group doesnt.)
Dependent Variable
“Effect” - factor that may change in response to independent variable.
Placebo
Fake Treatment
Confounding Variable
Anything else that could change the outcome of the experiment (other than independent variable)
Single Blind Study
Participants don’t know what group they’re in (Control or experiment)
Double Blind Study
Nobody knows what group they’re in, participant or person gathering data
Experimental Group
Group that receives treatment
Control Group
Group that doesn’t receive treatment
Representative Sample
Small group that represents bigger population
Stratified Sample
Makes a Representative Sample. Population is divided into relevant subcategories and random sample is taken from each subcategory
Weak Correlation
Less predictive variables, less able to be seen, less correlation
Strong Correlation
More predictive variables- more correlation
Positive Correlation
Two variables increase and decrease TOGETHER. One goes up, other goes up. One goes down, other goes down.
Negative Correlation
Two variables that move in opposite directions. One goes up, other goes down, vice versa.
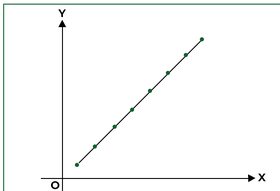
Perfect Positive Correlation
+1.00
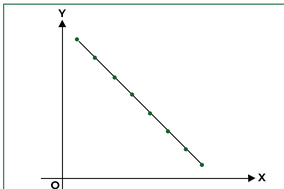
Perfect Negative Correlation
-1.00
What relationship does this correlation have?
-.78
Strong Negative
What relationship does this correlation have?
+.05
Weak Positive
What relationship does this correlation have?
-.43
Weak-ish Negative
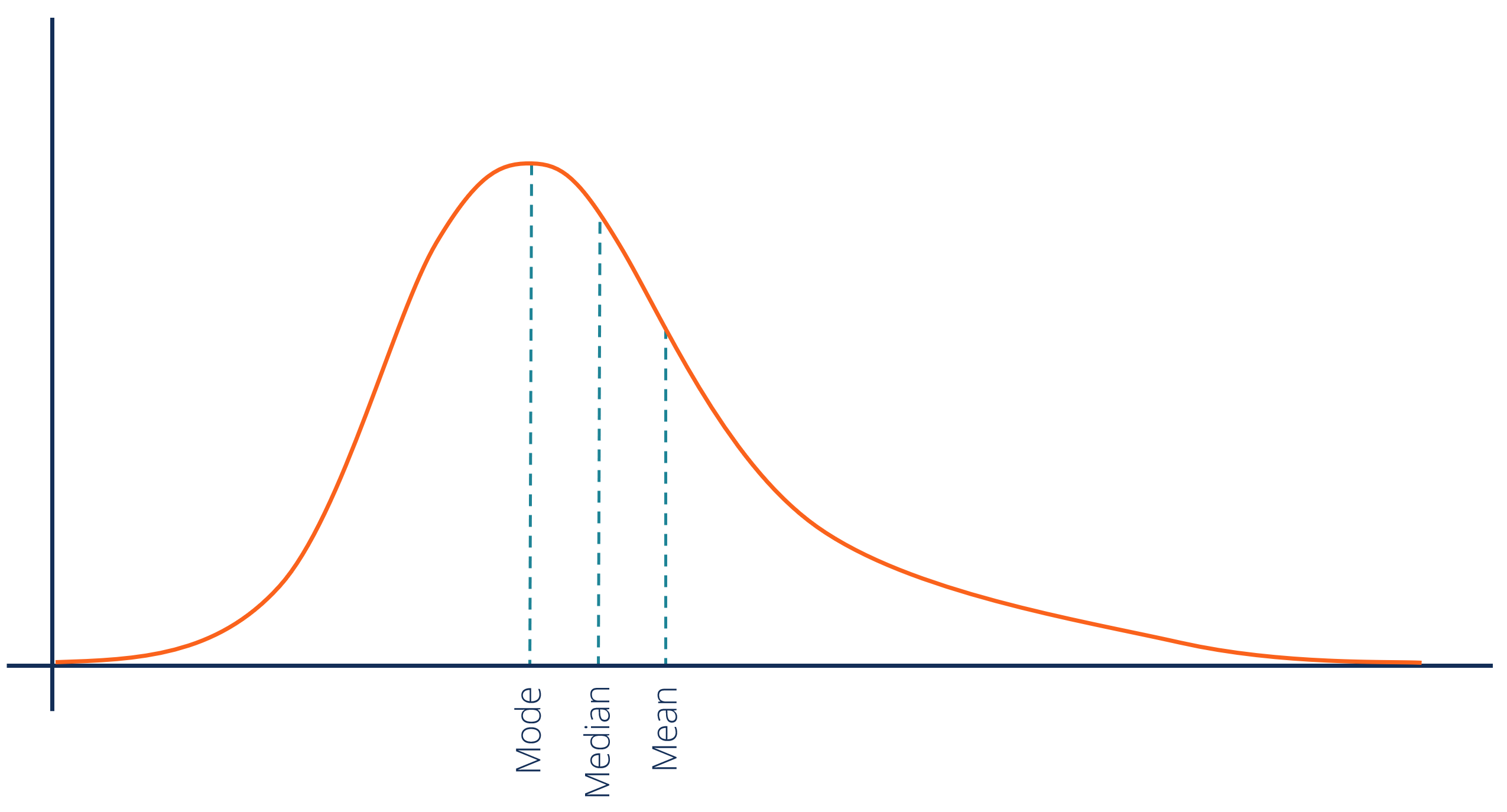
Mean
Average of scores made by adding scores and dividing by how many there were.
Median
Middle score in rank distribution
Mode
Most frequently occurring score.
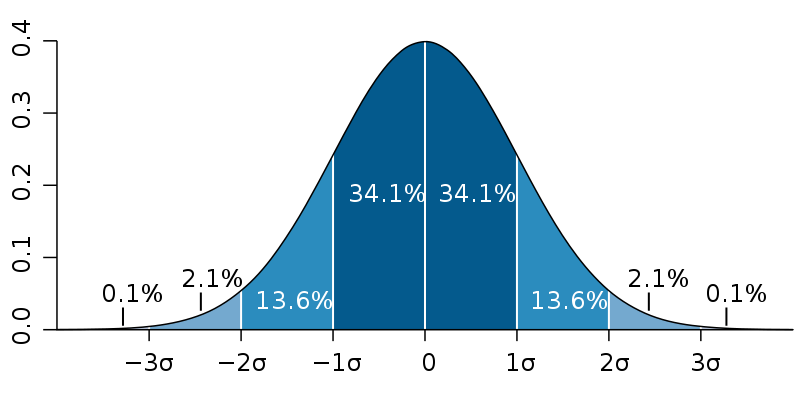
Standard Deviation
Average difference between each score and the mean
Negative skewed distribution
One/few extremely low scores
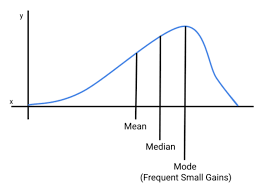
Postively skewed distribution
One/few extremely high scores
Statistical Significance
Whether or not something is due to just chance or if due to experimental influences. “Did the experiment matter?”
What is most affected by skewness? (Mean, Mode, or Median)
The mean.